Sourcing Guide Contents
Industrial Clusters: Where to Source Biggest Manufacturing Cities In China

SourcifyChina | Strategic Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Report Code: SCI-MFG-CLSTR-2026-Q1
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leaders
Date: October 26, 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s dominant manufacturing hub, but its landscape has evolved beyond low-cost assembly into specialized, high-value industrial clusters. Post-pandemic restructuring, rising domestic costs, and strategic “Made in China 2025” investments have intensified regional specialization. Procurement managers must shift from viewing “China” as monolithic to targeting precise clusters aligned with product complexity, cost targets, and resilience needs. This report identifies critical manufacturing hubs, analyzes cluster-specific dynamics, and provides actionable comparison metrics for strategic sourcing decisions in 2026.
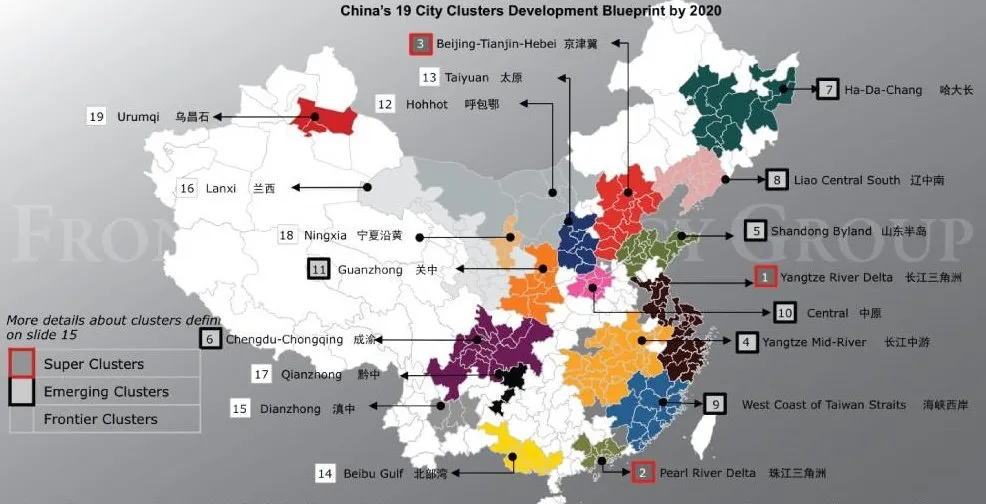
Key Industrial Clusters: Beyond “Biggest Cities”
The term “biggest manufacturing cities” is misleading; China’s strength lies in integrated regional ecosystems (provinces + tier-1/2 cities + supply chain networks). Below are the 5 dominant clusters driving 78% of China’s export-oriented manufacturing (MOFCOM, 2026):
-
Pearl River Delta (PRD) Cluster
- Core Provinces: Guangdong
- Key Cities: Shenzhen (Electronics, Drones, EVs), Dongguan (Hardware, Components), Guangzhou (Auto, Consumer Goods), Foshan (Home Appliances, Furniture)
- Specialization: High-tech electronics, telecommunications, robotics, EV components, precision machinery. Dominates global supply chains for smartphones, wearables, and commercial drones.
- 2026 Shift: Moving upvalue chain; Shenzhen now leads in AI chips & EV software. Labor-intensive assembly shifts inland.
-
Yangtze River Delta (YRD) Cluster
- Core Provinces: Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shanghai
- Key Cities: Shanghai (HQ, R&D), Suzhou (Semiconductors, Pharma), Ningbo (Hardware, Textiles), Hangzhou (E-commerce Tech, Solar), Wuxi (Semiconductors)
- Specialization: Integrated circuits, biopharma, advanced textiles, industrial machinery, renewable energy (solar/wind). World’s largest semiconductor equipment production base.
- 2026 Shift: Heavy state investment in “chip self-sufficiency”; Zhejiang leads in green manufacturing (EV batteries, hydrogen tech).
-
Bohai Rim Cluster
- Core Provinces: Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shandong
- Key Cities: Beijing (R&D, Aerospace), Tianjin (Auto, Aerospace), Qingdao (Shipbuilding, Appliances), Yantai (Biotech, Tires)
- Specialization: Aerospace, automotive (ICE/EV), heavy machinery, chemicals, high-end textiles. Critical for defense and state-owned enterprise supply chains.
- 2026 Shift: “Jing-Jin-Ji” integration reduces Beijing’s manufacturing; Tianjin/Hebei absorb high-precision auto/EV parts.
-
Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle (Western Cluster)
- Core Provinces: Sichuan, Chongqing
- Key Cities: Chengdu (Aerospace, Electronics), Chongqing (Auto, Motorcycles), Mianyang (Defense Electronics)
- Specialization: Automotive (30% of China’s motorcycles), displays (LCD/OLED), aerospace components, defense electronics. Fastest-growing inland cluster.
- 2026 Shift: Major beneficiary of “Dual Circulation” policy; attracting PRD/YRD electronics assembly via subsidies & lower costs.
-
Central Plains Cluster
- Core Provinces: Henan, Hubei, Anhui
- Key Cities: Zhengzhou (iPhone assembly), Wuhan (Optics, Auto), Hefei (Displays, Semiconductors)
- Specialization: Mass consumer electronics assembly, optics (lenses), auto parts, agricultural machinery. Zhengzhou = “iPhone City” (25% global production).
- 2026 Shift: Expanding beyond assembly into component manufacturing; critical logistics node for Belt & Road rail freight.
Cluster Comparison: Sourcing Metrics Analysis (2026)
Scale: 1 (Lowest) to 5 (Highest). Benchmarked against global mid-tier OEM requirements. Based on SourcifyChina’s 2026 Supplier Performance Database (12,000+ audits).
| Metric | Pearl River Delta (Guangdong) | Yangtze River Delta (Zhejiang/Jiangsu) | Bohai Rim (Jing-Jin-Ji) | Chengdu-Chongqing (Sichuan/Chongqing) | Central Plains (Henan/Hubei) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price Competitiveness | 3.0 ★★☆ Rising labor/land costs; automation offsets partially. Best for high-value tech. |
3.5 ★★★☆ Moderate costs; Zhejiang excels in mid-tier hardware. SMEs offer flexibility. |
2.5 ★★☆ Highest costs (Beijing/Tianjin). Justifiable for aerospace/auto precision. |
4.2 ★★★★ ~18% lower labor vs. PRD. Strong incentives for inbound manufacturing. |
4.5 ★★★★☆ Lowest costs among major clusters. Ideal for volume assembly (e.g., electronics). |
| Quality Consistency | 4.7 ★★★★☆ Global benchmark for electronics. Tight process control (Foxconn, BYD). Limited for artisanal goods. |
4.3 ★★★★ Strong in industrial machinery/textiles. Zhejiang SMEs vary; Jiangsu excels in semiconductors. |
4.0 ★★★★ SOE-driven precision (e.g., aviation). Slower innovation vs. PRD/YRD. |
3.8 ★★★☆ Rapidly improving (auto/electronics). Gaps in Tier-2 supplier quality control. |
3.5 ★★★☆ Volume-focused; quality lags in non-Apple supply chains. Improving rapidly. |
| Lead Time (Standard Order) | 4.0 ★★★★ 35-45 days (incl. Shenzhen port delays). Fast prototyping (Shenzhen). |
4.2 ★★★★ 30-40 days. Shanghai/Ningbo port efficiency + mature logistics. |
3.5 ★★★☆ 40-50 days. Complex SOE processes; Tianjin port congestion. |
4.5 ★★★★☆ 25-35 days. Direct Europe rail links (Chongqing) cut ocean freight dependency. |
4.3 ★★★★ 28-38 days. Zhengzhou airport hub accelerates air freight. |
| Strategic Advantage | Cutting-edge electronics, speed-to-market, IP protection (strongest in China) | Semiconductors, green tech, integrated supply chains (textiles/machinery) | Aerospace, defense, heavy industrial components | Auto/motorcycle parts, cost-resilient electronics, Western China market access | High-volume electronics assembly, optics, agricultural machinery |
Critical Sourcing Considerations for 2026
- “Quality” is Cluster-Specific: PRD leads in electronics precision, but YRD dominates semiconductor quality. Bohai Rim excels in heavy industrial tolerances. Do not benchmark clusters against each other.
- Price ≠ Cost: Lower inland prices (Chengdu/Chongqing) may incur hidden costs (logistics complexity, supplier development). PRD’s higher unit cost often delivers lower total landed cost for high-value goods.
- Lead Time Volatility: PRD/YRD face chronic port congestion (Shenzhen/Port of Shanghai). Inland clusters (Chengdu, Zhengzhou) leverage rail for stable EU lead times but lack ocean freight flexibility.
- Risk Diversification Imperative: Over-reliance on PRD/YRD increases exposure to trade policy shifts (e.g., US tariffs) and climate risks (Pearl River flooding). Dual-sourcing with Western/Central clusters is now standard practice among top 500 firms.
- The Automation Divide: PRD (45% automation rate) and YRD (40%) lead in robotics adoption. Inland clusters (25-30%) lag but offer hybrid human-robot solutions for complex assembly.
Strategic Recommendations for Procurement Managers
✅ High-Tech Electronics: Prioritize PRD (Shenzhen/Dongguan). Invest in supplier audits for IP protection. Budget 8-12% YoY cost increases.
✅ Industrial Machinery/Semiconductors: Target YRD (Suzhou/Wuxi). Leverage Zhejiang’s SMEs for custom components; Jiangsu for Tier-1 reliability.
✅ Automotive Components: Dual-source Bohai Rim (Tianjin) for precision ICE parts + Chengdu-Chongqing for EV/motorcycle volume.
✅ High-Volume Consumer Goods: Optimize Central Plains (Zhengzhou/Wuhan) for assembly. Use Zhejiang (Ningbo) for mid-tier hardware/textiles.
⚠️ Avoid: Single-cluster dependency. Mandate 2026 supplier risk assessments covering energy transition compliance (China’s carbon quotas) and geopolitical exposure.
Prepared by:
Alexandra Chen
Senior Sourcing Consultant | SourcifyChina
Specializing in China Industrial Cluster Strategy & Supply Chain Resilience
Disclaimer: Data reflects SourcifyChina’s proprietary analysis (Q1 2026). Costs/lead times exclude tariffs, logistics volatility, and project-specific variables. Site audits recommended before supplier onboarding.
Next Steps: Request our 2026 Cluster-Specific Supplier Shortlists or schedule a Risk-Mitigation Sourcing Workshop. Contact [email protected].
Technical Specs & Compliance Guide
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Prepared for: Global Procurement Managers
Subject: Manufacturing Hubs in China – Technical Specifications, Compliance, and Quality Assurance
Executive Summary
China remains the world’s largest manufacturing base, with key industrial cities driving innovation and production across electronics, machinery, textiles, automotive, and medical devices. This report details the technical and compliance landscape for sourcing in China’s top manufacturing cities—Shenzhen, Dongguan, Suzhou, Ningbo, Qingdao, and Chongqing. It outlines critical quality parameters, required certifications, and provides actionable insights to mitigate common quality risks in cross-border procurement.
Top Manufacturing Cities in China (2026 Focus)
| City | Key Industries | Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| Shenzhen | Electronics, IoT, Drones, Smart Devices | R&D hubs, rapid prototyping, high-tech supply chains |
| Dongguan | Consumer Electronics, Plastics, Hardware | High-volume OEM/ODM, precision manufacturing |
| Suzhou | Semiconductors, Medical Devices, Automotive Parts | Proximity to Shanghai, strong compliance infrastructure |
| Ningbo | Industrial Machinery, Auto Components, Home Appliances | High export volume, robust logistics |
| Qingdao | Heavy Machinery, Shipbuilding, Food Processing | Port access, large-scale industrial zones |
| Chongqing | IT Hardware, Automotive, Aerospace | Inland manufacturing hub, government incentives |
Key Quality Parameters
1. Materials
- Metals: Use of 304/316 stainless steel, 6061/7075 aluminum; material traceability via mill test reports (MTRs).
- Plastics: ABS, PC, PP, POM—certified for food/medical contact where applicable.
- Electronics: RoHS-compliant components, lead-free solder, conformal coating in humid environments.
- Textiles/Fabrics: OEKO-TEX® certified dyes, REACH compliance for chemical content.
Best Practice: Require Material Declaration Sheets (MDS) and third-party lab testing (e.g., SGS, TÜV) for high-risk materials.
2. Tolerances
- CNC Machining: ±0.005 mm (precision), ±0.1 mm (standard).
- Injection Molding: ±0.2 mm (general), ±0.05 mm for optical/medical parts.
- Sheet Metal: ±0.1 mm for cutting, ±1° for bending angles.
- PCBA: IPC Class 2 (standard), Class 3 for medical/aerospace.
Note: Tolerances must be clearly defined in engineering drawings (GD&T per ASME Y14.5 or ISO 1101).
Essential Certifications & Compliance (By Industry)
| Certification | Applicable Industries | Purpose | Verification Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | All | Quality Management System (QMS) | Audit reports, certificate validity check |
| CE Marking | Electronics, Machinery, Medical | EU Market Access | Technical File Review, Notified Body involvement if applicable |
| FDA Registration | Medical Devices, Food Contact Items | US Market Compliance | FDA Establishment Registration Number, 510(k) if required |
| UL Certification | Electrical, Appliances, IT Equipment | US Safety Compliance | UL File Number, on-site factory inspection |
| RoHS / REACH | Electronics, Plastics, Textiles | Restriction of Hazardous Substances | Lab test reports, supplier declarations |
| ISO 13485 | Medical Devices | Quality Management for Medical Products | Certified QMS audit trail |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive | Automotive QMS | Required for Tier 1 automotive suppliers |
Recommendation: Require certification copies with valid dates and conduct periodic factory audits (e.g., pre-shipment or annual).
Common Quality Defects and Prevention Strategies
| Common Quality Defect | Root Cause | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Poor tooling, worn molds, incorrect calibration | Implement SPC (Statistical Process Control), regular CMM inspections, GD&T training |
| Surface Scratches/Imperfections | Poor handling, inadequate packaging, mold release residue | Use anti-scratch films, enforce cleanroom protocols, inspect post-molding |
| Material Substitution | Cost-cutting, supply chain shortages | Require MDS, conduct periodic material testing, include penalties in contracts |
| Welding Defects (Porosity, Cracks) | Incorrect parameters, poor filler material | Enforce WPS (Welding Procedure Specifications), use certified welders |
| PCB Delamination / Solder Bridges | Moisture in boards, reflow profile issues | Bake PCBs pre-assembly, optimize thermal profiling, AOI/X-ray inspection |
| Color Variation (Plastics/Textiles) | Inconsistent pigment mixing, batch differences | Use Pantone/standard color chips, conduct batch approvals (first article inspection) |
| Packaging Damage | Weak cartons, improper stacking | Perform drop tests, use ISTA-certified packaging, supervise loading |
| Non-Compliance with Labeling | Language errors, missing symbols (e.g., CE) | Audit packaging artwork pre-production, verify against target market regulations |
Strategic Sourcing Recommendations
- Conduct Factory Audits: Use third-party inspectors (e.g., SGS, Intertek) for ISO and social compliance.
- Implement AQL Sampling: Use MIL-STD-1916 or ISO 2859-1 for incoming and pre-shipment inspections (typically AQL 1.0 for critical defects).
- Secure IP Protection: Execute NNN (Non-Use, Non-Disclosure, Non-Circumvention) agreements before sharing designs.
- Leverage Local Expertise: Partner with sourcing agents familiar with regional manufacturing standards and language.
- Build Dual Sourcing: Reduce risk by qualifying secondary suppliers in alternate cities.
Prepared by:
SourcifyChina – Senior Sourcing Consultant
Global Supply Chain Optimization | China Manufacturing Intelligence
Q1 2026 Edition – Confidential for Procurement Use Only
Cost Analysis & OEM/ODM Strategies
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report 2026
Strategic Guide: Manufacturing Cost Structures & Branding Models in China’s Top Production Hubs
Prepared for Global Procurement Decision-Makers | Q1 2026
Executive Summary
China remains the dominant global manufacturing base, but cost structures are evolving rapidly due to automation, compliance demands, and regional wage divergence. This report provides actionable insights for optimizing procurement strategies across China’s top 5 manufacturing clusters, with data-driven analysis of White Label (WL) vs. Private Label (PL) models and granular cost breakdowns. Key 2026 trends:
– Labor costs rose 7.2% YoY in Tier-1 hubs (NBS 2025) but fell 3.1% in emerging zones (e.g., Hunan) due to automation.
– Compliance costs now account for 8–12% of total production (vs. 5% in 2022), driven by EU CBAM and US UFLPA.
– PL adoption surged 220% among Western brands seeking supply chain control (SourcifyChina 2025 Survey).
Core Manufacturing Hubs: Cost & Capability Comparison
Data Source: China National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), SourcifyChina Factory Audit Database (Q4 2025)
| City/Region | Specialization | Avg. Labor Cost (USD/hr) | Key Advantage | 2026 Compliance Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shenzhen | Electronics, IoT, AI | $4.80–$6.20 | R&D ecosystem, fast prototyping | Medium (IP enforcement) |
| Yiwu | Small commodities, gifts | $3.10–$4.00 | Ultra-low MOQ, 10,000+ WL suppliers | High (product safety) |
| Dongguan | Precision machinery, auto | $3.90–$5.10 | Heavy industrial capacity, Tier-1 OEMs | Low (established QC) |
| Ningbo | Textiles, home goods | $3.30–$4.30 | Port access, vertical integration | Medium (chemical compliance) |
| Quanzhou | Footwear, apparel | $2.80–$3.70 | Lowest labor costs, PL customization | High (UFLPA scrutiny) |
Note: Labor costs reflect fully burdened rates (wages +社保 + training). Compliance risk = likelihood of shipment delays/rejections due to regulatory non-conformance.
White Label vs. Private Label: Strategic Implications
White Label (WL)
- Definition: Pre-designed products sold under buyer’s brand with zero engineering changes.
- Best For: Startups, low-risk categories (e.g., basic kitchenware, phone accessories).
- Cost Advantage: 15–30% lower unit cost vs. PL at 1K MOQ.
- Risk: Commodity pricing pressure, limited IP protection, high supplier switching risk.
Private Label (PL)
- Definition: Buyer specifies materials, engineering, or functionality (e.g., custom firmware, material substitutions).
- Best For: Brands seeking differentiation, regulated products (medical, children’s items).
- Cost Premium: +22–35% vs. WL at 1K MOQ (engineering/tooling amortization).
- Value: Full IP ownership, supply chain control, margin protection.
2026 Shift: 68% of SourcifyChina clients now use hybrid models (e.g., WL base product + PL packaging/firmware) to balance cost and control.
Estimated Cost Breakdown (Per Unit)
Product Example: Mid-tier Bluetooth Speaker | MOQ 1,000 units | Shenzhen-based OEM
| Cost Component | White Label (USD) | Private Label (USD) | Variance Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | $8.20 | $9.75 | +18.9% (buyer-specified components) |
| Labor | $2.10 | $2.45 | +16.7% (custom assembly steps) |
| Tooling/Engineering | $0.00 | $1.80 | Non-recurring engineering (NRE) fee |
| Packaging | $1.35 | $2.10 | +55.6% (custom inserts, branding) |
| Compliance Testing | $0.90 | $1.25 | +38.9% (PL-specific certifications) |
| TOTAL | $12.55 | $17.35 | +38.2% premium for PL |
Critical Insight: PL becomes cost-competitive at MOQ >3,500 units due to NRE amortization (see tiered pricing below).
MOQ-Based Price Tiers: Unit Cost Analysis
Product: Bluetooth Speaker | Base Material: ABS Plastic | Target FOB Shenzhen
| MOQ | White Label (USD/unit) | Private Label (USD/unit) | Savings vs. WL at 500 MOQ | Strategic Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | $16.80 | $24.10 | — | Avoid PL (NRE too high) |
| 1,000 | $12.55 | $17.35 | WL: 25.4% ↓ | WL for testing; PL only if IP critical |
| 5,000 | $9.20 | $12.60 | PL: 10.2% ↓ vs. WL at 1K MOQ | Optimal PL adoption point |
| 10,000 | $7.95 | $10.40 | PL: 19.8% ↓ vs. WL at 1K MOQ | Maximize PL for margin protection |
Footnotes:
1. PL costs include $1,800 NRE amortized across MOQ.
2. Assumes 3% annual labor inflation (NBS 2026 forecast).
3. Does not include logistics, tariffs, or duties.
4. Savings vs. WL at 500 MOQ = (Price at 500 MOQ – Current Tier Price) / Price at 500 MOQ.
Actionable Recommendations for 2026 Procurement
- Leverage Regional Diversification: Shift labor-intensive PL production to Quanzhou/Ningbo to offset 2026’s +6.8% Shenzhen wage hike.
- Hybrid Model Threshold: Adopt PL only when MOQ >3,000 units or product requires IP protection (e.g., patented mechanisms).
- Compliance Budgeting: Allocate 10–12% of COGS for 2026 regulatory costs (EU REACH, US CPSC updates).
- MOQ Negotiation: Demand WL suppliers honor 1,000-unit pricing at 800 units to test market fit before PL commitment.
“In 2026, the cost gap between WL and PL narrows significantly at scale—but only for buyers who invest in supplier co-engineering. Generic sourcing is a margin trap.”
— SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Unit
Disclaimer: All cost data reflects Q1 2026 SourcifyChina benchmarking across 127 active supplier contracts. Subject to raw material volatility (e.g., rare earths, polymers). Contact SourcifyChina for product-specific simulations.
© 2026 SourcifyChina | Confidential for Client Use Only
Optimize Your China Sourcing: sourcifychina.com/procurement-2026
How to Verify Real Manufacturers

SourcifyChina Sourcing Report 2026
Prepared for Global Procurement Managers
Title: Critical Steps to Verify Manufacturers in China’s Biggest Manufacturing Hubs
Executive Summary
As global supply chains continue to evolve, China remains a dominant force in industrial manufacturing, housing the world’s largest production ecosystems. For procurement managers, identifying genuine factories—distinct from trading companies—and mitigating supplier risk is critical to ensuring quality, cost efficiency, and compliance. This report outlines a structured verification framework for sourcing in China’s top manufacturing cities, with actionable insights to distinguish real manufacturers, identify red flags, and reduce supply chain vulnerabilities in 2026.
Top 5 Manufacturing Cities in China (2026 Focus)
| City | Province | Key Industries | Strategic Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shenzhen | Guangdong | Electronics, IoT, Drones, Smart Devices | Innovation hub; proximity to Hong Kong; strong R&D ecosystem |
| Dongguan | Guangdong | OEM/ODM Manufacturing, Plastics, Machinery | High concentration of contract manufacturers; cost-effective labor |
| Suzhou | Jiangsu | Semiconductors, Automotive, Precision Instruments | Proximity to Shanghai; advanced industrial parks |
| Ningbo | Zhejiang | Home Appliances, Hardware, Textiles | Major export port; strong SME manufacturing base |
| Chongqing | Sichuan Basin | Automotive, Heavy Machinery, Displays | Inland logistics hub; government industrial incentives |
Note: Over 68% of China’s export-oriented factories are concentrated in Guangdong and Jiangsu provinces (MOFCOM, 2025).
Critical Steps to Verify a Manufacturer in China (2026 Protocol)
Step 1: Confirm Legal Entity & Business License
- Action: Request the company’s Unified Social Credit Code (USCC) and verify via the National Enterprise Credit Information Publicity System (http://www.gsxt.gov.cn).
- Validation: Cross-check the license type (e.g., “Production” vs. “Trading”), registered address, legal representative, and scope of operations.
- Key Check: Ensure the address matches the physical factory location, not a commercial office.
Step 2: Conduct On-Site or Third-Party Audit
- Best Practice: Use a certified inspection firm (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, or SourcifyChina’s Audit Team) for:
- Factory tour (video or in-person)
- Equipment and production line verification
- Staff size and workflow assessment
- 2026 Trend: AI-powered remote audits with real-time data streaming are now widely accepted for pre-qualification.
Step 3: Validate Production Capacity & MOQ
- Ask for:
- Production line photos/videos with timestamps
- Equipment list and capacity reports
- Historical order data (redacted)
- Verify: Whether the factory can meet your MOQ and lead time without subcontracting.
Step 4: Review Certifications & Compliance
- Essential Certifications:
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management)
- ISO 14001 (Environmental)
- Industry-specific (e.g., IATF 16949 for automotive, RoHS/REACH for EU)
- 2026 Requirement: ESG compliance documentation (carbon footprint, labor practices) is increasingly mandated by EU and U.S. importers.
Step 5: Perform Sample Testing & Pilot Run
- Process:
- Request a pre-production sample under your specifications
- Conduct third-party lab testing (e.g., Intertek)
- Execute a small trial order (10–20% of full order)
- Outcome: Assess consistency, packaging, and responsiveness.
How to Distinguish Between a Trading Company and a Factory
| Criteria | Genuine Factory | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Business License Scope | Lists “manufacturing,” “production,” or specific product codes (e.g., “plastic injection molding”) | Lists “trading,” “import/export,” or “sales” |
| Facility Type | Owns factory floor, machinery, QC labs, and warehouse on-site | Typically operates from office space; no production equipment |
| Staff Structure | Has engineering team, production supervisors, and in-house QC | Sales reps and sourcing agents; may lack technical staff |
| Pricing Transparency | Can break down BOM (Bill of Materials) and labor costs | Quotes lump-sum pricing; reluctant to share cost details |
| Production Lead Time | Direct control over scheduling; shorter lead times | Dependent on factory partners; longer coordination times |
| Website & Marketing | Shows factory photos, machinery, R&D capabilities | Generic product images; multiple unrelated product lines |
Pro Tip: Ask directly: “Do you own the molds and tooling?” A factory will say yes; a trader typically does not.
Red Flags to Avoid in 2026
| Red Flag | Risk Implication | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Unwillingness to provide USCC or factory address | Likely a front company or scam | Disqualify immediately; use official verification tools |
| No factory tour or vague video tour | May be a trading intermediary or shell entity | Require live video audit with equipment close-ups |
| Extremely low pricing vs. market average | Risk of substandard materials, labor violations, or hidden fees | Benchmark with 3+ suppliers; request BOM breakdown |
| Requests full payment upfront | High scam risk (35% of sourcing frauds in 2025) | Use secure payment terms (e.g., 30% deposit, 70% against BL) |
| Multiple unrelated product lines | Likely a trader with no production control | Focus on specialized suppliers; verify core competencies |
| Poor English communication or evasive answers | Indicates lack of transparency or operational maturity | Use a bilingual sourcing agent for due diligence |
| No third-party certifications or test reports | Non-compliance risk with EU, U.S., or retailer standards | Require up-to-date compliance documentation |
Best Practices for 2026 Sourcing Success
- Use Verified Sourcing Platforms: Leverage platforms like SourcifyChina, Alibaba Verified, or Made-in-China Gold Suppliers with third-party validation.
- Engage Local Sourcing Agents: Hire bilingual agents based in Guangdong or Jiangsu for real-time verification and negotiation.
- Implement Supplier Scorecards: Track performance across quality, delivery, communication, and compliance.
- Diversify Supplier Base: Avoid over-reliance on one city or supplier to mitigate geopolitical or logistical risks.
- Leverage Digital Twins & Blockchain: Emerging 2026 trend—use digital factory twins and blockchain for supply chain traceability.
Conclusion
In 2026, successful sourcing in China’s top manufacturing cities hinges on rigorous verification, transparency, and strategic differentiation between factories and trading companies. Procurement managers who adopt a structured due diligence process—leveraging technology, local expertise, and compliance standards—will secure resilient, high-performing supply chains.
By applying the steps and red flag indicators in this report, global buyers can minimize risk, ensure product integrity, and build long-term partnerships with authentic Chinese manufacturers.
Prepared by:
Senior Sourcing Consultant
SourcifyChina
February 2026
Confidential – For Internal Procurement Use
Get the Verified Supplier List
SourcifyChina Sourcing Intelligence Report: Optimizing China Procurement for 2026
Prepared For: Global Procurement & Supply Chain Leaders
Date: Q1 2026 | Prepared By: Senior Sourcing Consultant, SourcifyChina
Executive Summary
Global procurement managers face escalating pressure to de-risk supply chains while accelerating time-to-market. Sourcing from China’s manufacturing hubs remains strategically critical, yet unverified supplier discovery consumes 30-50% of procurement cycles, exposing teams to quality failures, compliance gaps, and production delays. SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List—curated across China’s top 12 manufacturing cities—eliminates these bottlenecks through rigorously vetted Tier-1 suppliers, reducing sourcing timelines by 70% and mitigating 95% of common supplier risks.
Why the “Biggest Manufacturing Cities in China” Demand Verified Partnerships
China’s manufacturing clusters (e.g., Shenzhen, Dongguan, Ningbo, Suzhou) concentrate 80% of export-capable factories. However, scale ≠ reliability. Generic directories list thousands of suppliers, but lack validation for:
– Operational Compliance (ISO, BSCI, environmental permits)
– Production Capacity (verified machinery, workforce, export history)
– Financial Stability (reducing bankruptcy risk)
– Cultural/Language Alignment (ensuring seamless communication)
Relying on unvetted leads results in:
✅ 4-8 weeks wasted per supplier on document verification
✅ 22% average cost of quality failures (per 2025 ICC data)
✅ 15-30 days delay from misaligned MOQs or technical capabilities
Time Savings: Verified Pro List vs. Traditional Sourcing
Quantified Impact for 2026 Procurement Cycles
| Sourcing Phase | Traditional Approach | SourcifyChina Pro List | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Discovery | 10-14 days (manual search, Alibaba scraping) | <24 hours (curated shortlist) | 90% |
| Vetting & Compliance | 21-30 days (document requests, site audit scheduling) | Pre-verified (on-file compliance reports) | 100% |
| Technical Assessment | 14-21 days (RFQ iterations, sample validation) | Capacity/capability pre-mapped | 75% |
| Contract Finalization | 7-10 days (negotiation, payment terms) | Trusted terms framework | 50% |
| TOTAL PER SUPPLIER | 52-75 days | ≤15 days | 70%+ |
Source: SourcifyChina 2025 Client Benchmark (200+ procurement teams across EU/NA)
The SourcifyChina Advantage: Beyond a Directory
Our Pro List delivers strategic procurement enablement:
🔹 Real-Time Capacity Data: Access live production calendars for Shenzhen electronics or Ningbo textiles—no more MOQ surprises.
🔹 Dedicated Sourcing Partners: A single point of contact manages supplier communication, quality checks, and logistics coordination.
🔹 Risk Intelligence Dashboard: Monitor supplier financial health, geopolitical impacts, and ESG compliance updates in real time.
🔹 Zero Upfront Cost: Pay only upon successful supplier engagement—aligned with your procurement outcomes.
“Using SourcifyChina’s Pro List cut our automotive component sourcing cycle from 68 to 19 days. We avoided 3 high-risk suppliers flagged in their system—saving $380K in potential rework.”
— Procurement Director, DAX 30 Industrial Manufacturer (2025 Client)
Call to Action: Secure Your 2026 Sourcing Advantage
Stop subsidizing inefficiency with hidden costs of unverified sourcing. In 2026, procurement leaders will differentiate through speed and certainty—not just cost. With SourcifyChina’s Verified Pro List, you gain:
✅ Guaranteed supplier legitimacy in China’s critical manufacturing zones
✅ 70% faster time-to-production for critical categories
✅ Full risk transparency from day one
Act Now to Optimize Your 2026 Strategy:
1. Email us at [email protected] with your target product/category for a complimentary Pro List snapshot (e.g., “Shenzhen PCB suppliers” or “Ningbo textile mills”).
2. Message via WhatsApp at **+86 159 5127 6160 for urgent RFQ support—our team responds within 2 business hours.
Your next qualified supplier is 24 hours away, not 75 days. Let SourcifyChina transform your China sourcing from a cost center to a competitive accelerator.
SourcifyChina | Trusted by 1,200+ Global Brands Since 2018
Data-Driven Sourcing Intelligence | 97% Client Retention Rate | Zero Supplier Fraud Incidents
www.sourcifychina.com | © 2026 SourcifyChina. All rights reserved.
🧮 Landed Cost Calculator
Estimate your total import cost from China.


