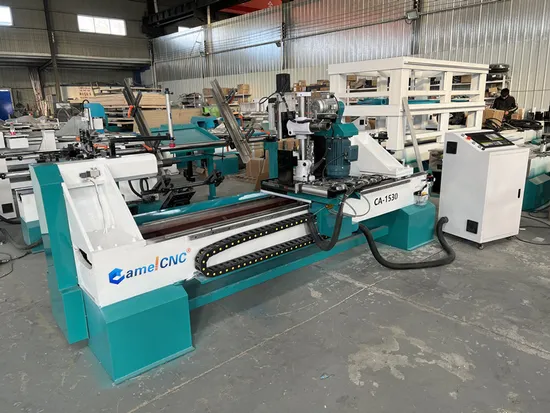
The global wood spinning machine market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for precision-turned wooden components in furniture, construction, and decorative industries. According to Grand View Research, the global woodturning machinery market size was valued at USD 2.1 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in CNC technology, increasing automation in woodworking processes, and a surge in sustainable timber usage. As manufacturers prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and reduced labor costs, the demand for high-performance wood spinning machines continues to rise. In this competitive landscape, several global leaders have emerged, combining innovation, reliability, and technical expertise to dominate market share. Based on industry performance, technological capabilities, and global reach, here are the top 10 wood spinning machine manufacturers shaping the future of modern woodworking.
Top 10 Wood Spinning Machine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Robert Sorby Ltd
Domain Est. 1996
Website: robert-sorby.co.uk
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of the highest quality woodturning tools and accessories. Proudly made in Sheffield, England UK….
#2 Wells Wood Turning
Domain Est. 2003
Website: wellswoodturning.com
Key Highlights: We are an original manufacturer of custom wood products made in the USA. We make wood rolling pins, wood handles and wood craft parts….
#3 EMCO lathes & milling machines manufacturer, CNC training …
Domain Est. 2007
Website: emco-world.com
Key Highlights: EMCO has been a leading manufacturer of lathes and milling machines for over 75 years and offers a wide range of development opportunities….
#4 to Mazak Corporation
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mazak.com
Key Highlights: Mazak provides products and solutions that can support a wide range of parts machining processes, such as high-speed and high-accuracy machines, various ……
#5 Charnwood Machinery Ltd
Domain Est. 1999
Website: charnwood.net
Key Highlights: Charnwood has supplied woodworking machinery and tooling – suitable for everyone from hobby enthusiasts, to professional trade users….
#6 Easy Wood Tools
Domain Est. 2008
Website: easywoodtools.com
Key Highlights: Easy Wood Tools makes high quality, easy to use, hand-crafted turning tools and accessories so people will have more time to relax, create, and enjoy ……
#7 CNC Wood Turning Lathe Machine
Domain Est. 2011
#8 The Woodturning Store Homepage
Domain Est. 2012
Website: thewoodturningstore.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $200 · 30-day returns…
#9 Wood Mill Turn CNC Machine
Domain Est. 2018
Website: boarke-tw.com
Key Highlights: It is a precision tool designed for shaping and crafting wood into various cylindrical or curved profiles. It has a dust-free enclosure design can be easily ……
#10 Schnitzer Machine CNC Wood Turning
Website: schnitzer.com.tr
Key Highlights: Schnitzer produces the fasteststrongesttop quality CNC Wood Lathe Machines. Schnitzer with its rapidly growing team provide 24/7 support and ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Wood Spinning Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Wood Spinning Machines
The global market for wood spinning machines is poised for notable transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, rising demand for sustainable wood products, and evolving manufacturing practices. These machines, used primarily in the production of wooden components such as spindles, balusters, and furniture legs through automated turning processes, are witnessing increased adoption across woodworking industries. The following key trends are expected to shape the wood spinning machine market in 2026:
-
Increased Automation and Smart Manufacturing Integration
By 2026, wood spinning machines are anticipated to feature advanced automation, including CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems and IoT-enabled monitoring tools. Manufacturers are investing in smart factories, where wood spinning machines communicate with other production units in real time to optimize output, reduce waste, and enhance precision. This integration supports Industry 4.0 principles and improves operational efficiency. -
Growing Demand from Furniture and Construction Sectors
The furniture and residential construction industries continue to be primary end-users of wood spinning machines. With a resurgence in handcrafted and custom wood furniture, especially in North America and Europe, demand for high-precision spinning machines is rising. Additionally, architectural woodwork in commercial and luxury residential projects is fueling the need for consistent, high-volume production capabilities. -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Production
As environmental regulations tighten and consumer preferences shift toward sustainable materials, wood spinning machine manufacturers are prioritizing energy-efficient designs and compatibility with reclaimed or FSC-certified wood. Machines that minimize material waste through optimized cutting algorithms and dust collection systems are gaining market preference. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Regions such as Southeast Asia, India, and Latin America are expected to see increased investments in woodworking infrastructure by 2026. Rising urbanization and growth in the middle class are driving demand for wooden furniture and interiors, creating new opportunities for wood spinning machine suppliers. Local production hubs are emerging, reducing reliance on imported machinery and encouraging regional customization. -
Technological Advancements in Multi-Axis and Hybrid Machines
Next-generation wood spinning machines are evolving to include multi-axis turning, laser measurement, and hybrid functionalities that combine spinning with milling or sanding. These advancements allow for the production of complex, sculpted wood components without manual intervention, appealing to high-end design and bespoke manufacturing segments. -
Rise of Customization and On-Demand Manufacturing
The trend toward personalized home décor and made-to-order furniture is pushing manufacturers to adopt flexible wood spinning systems. Machines capable of rapid reconfiguration and short production runs are becoming essential, enabling businesses to meet niche market demands efficiently. -
Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
By 2026, the wood spinning machine market is expected to experience consolidation, with key players acquiring niche technology firms to enhance their digital and automation capabilities. Companies such as SCM Group, Homag, and Biesse are likely to lead innovation, while smaller manufacturers focus on specialized applications and regional markets.
In conclusion, the 2026 outlook for wood spinning machines reflects a shift toward smarter, greener, and more adaptable manufacturing solutions. As industries continue to balance craftsmanship with industrial efficiency, wood spinning technology will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of wood product manufacturing.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Wood Spinning Machines: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing wood spinning machines from international suppliers, particularly in regions with less stringent regulatory oversight, exposes buyers to significant risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Being aware of these pitfalls is crucial for protecting your investment and business reputation.
Poor Build Quality and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent issues is receiving machines constructed with inferior materials and poor workmanship. Suppliers may use low-grade steel, undersized components, or inadequate welding techniques to cut costs. This results in reduced durability, higher maintenance needs, and shorter machine lifespans. Always request material certifications and conduct factory audits to verify manufacturing standards.
Inaccurate or Overstated Machine Specifications
Some suppliers exaggerate performance metrics such as spindle speed, power output, or precision tolerances. Machines that fail to meet advertised specifications can disrupt production workflows and compromise product consistency. Insist on third-party testing reports and live demonstrations before finalizing orders.
Lack of Quality Control Processes
Suppliers without robust quality assurance systems may deliver inconsistent units, even within the same batch. Absence of ISO certifications or documented QC procedures increases the risk of defects going undetected. Ask for detailed information about their quality control protocols and consider hiring an independent inspection agency prior to shipment.
Counterfeit or Copycat Machines
Many wood spinning machines available in the market are unauthorized replicas of patented designs from reputable manufacturers. These clones often mimic the appearance of original equipment but lack engineering integrity and performance reliability. Purchasing such machines can expose your business to legal liability.
Intellectual Property Infringement Exposure
Using or importing a machine that violates existing patents or design rights can lead to cease-and-desist orders, customs seizures, or litigation. Buyers may be held accountable even if unaware of the infringement. Conduct due diligence by verifying the original manufacturer’s IP status and requiring suppliers to provide IP compliance documentation.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Spare Parts
Low-cost suppliers often lack reliable technical support and spare parts inventories. When machines break down, extended downtimes occur due to delayed repairs or unavailability of components. Confirm the supplier’s service network, warranty terms, and spare parts availability before committing.
Hidden Costs from Repairs and Downtime
While initial purchase prices may seem attractive, poor-quality machines incur higher long-term costs through frequent repairs, production delays, and reduced output efficiency. Factor in total cost of ownership—not just the upfront price—when evaluating sourcing options.
No Traceability or Documentation
Reputable machines come with detailed technical manuals, CE or other compliance certifications, and traceable component sourcing. Lack of proper documentation not only raises safety concerns but also complicates customs clearance and insurance claims. Ensure all required paperwork is provided and authentic.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough supplier vetting, independent inspections, and legal review of IP rights. Investing time and resources upfront can prevent costly setbacks and protect your business from avoidable risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Wood Spinning Machine
Product Classification and HS Code
Identify the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for the wood spinning machine to ensure accurate customs classification. Typically, wood turning or spinning machines fall under HS Code 8465.95 (Machines for working wood, whether or not numerical controlled). Confirm with local customs authorities or a licensed customs broker to avoid misclassification and potential delays or penalties.
Export Controls and Licensing
Check if the wood spinning machine or its components are subject to export controls. While most standard wood spinning machines are not restricted, models with advanced automation, CNC systems, or dual-use technology may require an export license depending on the destination country. Consult national export regulations (e.g., U.S. Commerce Control List, EU Dual-Use Regulation) and obtain necessary permits before shipment.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Ensure the machine is securely packaged to withstand international transit. Use wooden crates or heavy-duty steel-reinforced packaging with moisture barriers. Clearly label packages with handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Do Not Stack”) and include the machine’s model number, serial number, and weight. Anchor the machine inside the crate to prevent movement during transport.
Transportation Modes and Route Planning
Choose the appropriate transportation method—typically ocean freight for heavy machinery due to cost efficiency. For urgent deliveries, consider air freight with prior coordination for oversized cargo. Plan the route to avoid regions with political instability or logistical bottlenecks. Confirm port or airport accessibility for oversized loads and arrange for specialized lifting equipment at both origin and destination.
Import Regulations and Duties
Research import requirements for the destination country, including applicable tariffs, value-added tax (VAT), and import permits. Some countries may require conformity assessments or certifications (e.g., CE, UKCA, EAC) before allowing entry. Provide a complete commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading/air waybill, and certificate of origin to facilitate customs clearance.
Safety and Technical Compliance
Verify that the wood spinning machine meets the safety standards of the destination market. This may include electrical safety (e.g., IEC, UL, CE), noise emission levels, and mechanical guarding requirements. Include user manuals in the local language and ensure all safety labels are affixed and legible.
Documentation Checklist
Prepare and retain the following documents:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Export License (if applicable)
– Technical Specifications and User Manual
– Safety and Compliance Certifications
Insurance and Risk Management
Obtain comprehensive marine cargo insurance covering damage, theft, and delays during transit. Clearly define Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) in the sales contract to allocate responsibilities between buyer and seller. Conduct a risk assessment for high-value shipments and consider contingency plans for rerouting or storage.
End-of-Life and Environmental Compliance
Ensure compliance with environmental regulations regarding packaging materials (e.g., ISPM 15 for wooden crates requiring heat treatment). Inform customers of proper disposal or recycling procedures for machine components, especially electrical and electronic parts, in accordance with local WEEE or equivalent directives.
Ongoing Compliance Monitoring
Stay updated on changes in international trade policies, sanctions, and technical standards. Regularly review logistics partners and compliance procedures to maintain efficient and lawful operations. Maintain records of all shipments and compliance documentation for a minimum of five years.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Wood Spinning Machine
Sourcing a wood spinning machine requires a careful evaluation of production needs, machine specifications, budget, and long-term operational goals. Whether for small-scale artisanal projects or large industrial production, selecting the right machine involves balancing precision, durability, automation features, and cost-effectiveness. Thorough research into reputable suppliers, comparative analysis of technical capabilities, and consideration of after-sales support are essential to ensure reliability and efficiency.
Additionally, factors such as energy consumption, ease of maintenance, and compatibility with different wood types should not be overlooked. Sourcing from suppliers offering warranties, training, and technical assistance can significantly reduce downtime and improve productivity. Ultimately, investing in a high-quality wood spinning machine tailored to specific manufacturing requirements will enhance product consistency, reduce waste, and provide a strong return on investment over time. A strategic sourcing approach ensures both immediate functionality and sustainable growth in woodturning operations.