The global laser cutting machines market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision manufacturing across industries such as furniture, construction, automotive, and consumer goods. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% through 2029. This expansion is mirrored in the rising adoption of laser-cut wood sheets, where accuracy, repeatability, and design flexibility are paramount. As manufacturers seek cost-effective and sustainable materials suitable for intricate fabrication, the demand for high-quality wood sheets optimized for laser processing has surged. From plywood to MDF and hardwood veneers, the right material significantly impacts cut quality, edge finish, and production efficiency. In this data-driven landscape, identifying the top-performing wood sheet manufacturers has become critical for fabricators aiming to maintain competitive advantage and ensure consistent output. The following overview highlights the eight leading suppliers whose materials consistently deliver superior laser compatibility, dimensional stability, and industry compliance.
Top 8 Wood Sheets For Laser Cutting Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 CNC & Laser Cutting Sheet Goods
Domain Est. 1997
#2 Wood For Laser Engraving & Cutting
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ocoochhardwoods.com
Key Highlights: Thin wood in 1/16″, 1/8″, 1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″ and 3/4″ that works great for laser cutting or engraving. Try thin Alder, Basswood, Walnut, Cherry or Hard Maple….
#3 Wood Sheet
Domain Est. 2005
#4 Custom Online Laser Cutting Services
Domain Est. 2015
Website: xometry.com
Key Highlights: Xometry offers an online custom laser cutting service in metal, plastic, rubber, foam, and wood. Xometry’s laser cutting offers a cost-effective, on-demand ……
#5 Materials for Laser Engraving, Laser Cutting …
Domain Est. 2019
Website: us.store.bambulab.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryDiscover premium materials for laser engraving, laser cutting, and blade cutting—plywood, acrylic, cork, bamboo, and more—to craft unique, detailed designs ……
#6 Laser Engraving & Cutting Materials on Creatorally.com
Domain Est. 2022
Website: creatorally.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $35 30-day returnsCreatorally 8pc mixed color plywood sheets Premium laser-safe colored plywood – 3mm UV-coated, durable & kid-. Sold Sale -29% · EU Exclusive Cr…
#7 Craft Wood and Sheets for Laser Engraving Projects
Domain Est. 2023
Website: crealityfalcon.com
Key Highlights: Discover top-quality craft wood and sheets for laser engraving and cutting. Choose from various sizes and designs to spark your creativity….
#8 TruFlat® Walnut Laser Plywood
Domain Est. 2024
Website: truflatplywood.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 4.8 (41) Official distributer of TruFlat® Laser & CNC Plywood. Looking to save on shipping … Pre-finished panels perfect for Laser Cutters, Scroll Saws & CNCs!…
Expert Sourcing Insights for Wood Sheets For Laser Cutting

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Wood Sheets for Laser Cutting
The global market for wood sheets designed specifically for laser cutting is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies, growing demand for personalized products, and the expansion of maker culture and small-scale production. This analysis explores key trends shaping the industry under the H2 classification, providing insights into material innovation, market demand, regional dynamics, and sustainability.
1. Rising Demand in DIY and Maker Communities
By 2026, the do-it-yourself (DIY) and maker movements are expected to continue fueling demand for laser-cuttable wood sheets. The accessibility of affordable desktop laser cutters, especially CO2 models, has empowered hobbyists, educators, and small entrepreneurs. As a result, there is increasing demand for precision-cut plywood, birch, and MDF sheets optimized for clean engraving and cutting. Suppliers are responding with pre-sized, ready-to-use sheets tailored for popular laser cutter bed dimensions (e.g., 12″ x 24″, 24″ x 36″).
2. Material Innovation and Quality Standardization
Manufacturers are investing in higher-grade wood composites engineered specifically for laser applications. In 2026, expect broader availability of ultra-low formaldehyde (ULEF) and formaldehyde-free engineered woods, as well as veneer-core plywood with consistent density to reduce charring and improve cut accuracy. Brands are beginning to offer “laser-grade” certifications, ensuring uniform thickness, minimal glue pockets, and smooth finishes—key factors in achieving professional results.
3. Growth in Custom Furniture and Architectural Models
Architects, interior designers, and custom furniture makers are increasingly adopting laser-cut wood sheets for prototyping and production. The ability to create intricate joints, tessellated patterns, and modular designs with precision is driving commercial adoption. By 2026, the integration of CAD/CAM software with laser systems will streamline workflows, increasing demand for compatible wood sheet formats with optimized grain orientation and thickness tolerances.
4. Sustainability and Eco-Certification Trends
Environmental concerns are reshaping sourcing preferences. By 2026, buyers—especially in Europe and North America—are prioritizing FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and PEFC-certified wood sheets. Recycled wood composites and fast-growing species like bamboo are gaining traction as sustainable alternatives. Manufacturers are also minimizing waste through optimized sheet packaging and offering scrap bundles for upcycling, aligning with circular economy principles.
5. E-Commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Expansion
Online platforms are becoming the primary distribution channel for wood sheets for laser cutting. By 2026, B2C and B2B e-commerce sites will dominate, offering subscription models, bulk discounts, and global shipping. Marketplaces like Amazon, Etsy, and specialized suppliers (e.g., SendCutSend, Xometry) are integrating real-time laser compatibility filters, enabling users to select materials validated for specific laser wattages and cut types.
6. Regional Market Diversification
While North America and Western Europe remain dominant markets, Asia-Pacific—particularly China, Japan, and South Korea—is experiencing rapid growth due to rising adoption in education, small manufacturing, and tech startups. Local production of laser-compatible wood sheets is increasing in Southeast Asia, reducing shipping costs and lead times. Meanwhile, government initiatives supporting vocational training in digital fabrication are boosting institutional procurement.
7. Integration with Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
Advanced workshops and micro-factories are integrating laser cutting into automated production lines. By 2026, wood sheet suppliers may offer RFID-tagged or QR-coded materials that communicate optimal laser settings (speed, power, frequency) directly to smart machines, minimizing setup errors and enhancing repeatability.
In conclusion, the 2026 landscape for wood sheets for laser cutting will be defined by smarter materials, eco-conscious sourcing, digital distribution, and deeper integration with design and manufacturing ecosystems. Businesses that align with these H2-level trends—particularly in quality control, sustainability, and digital enablement—are likely to gain competitive advantage in this evolving niche market.
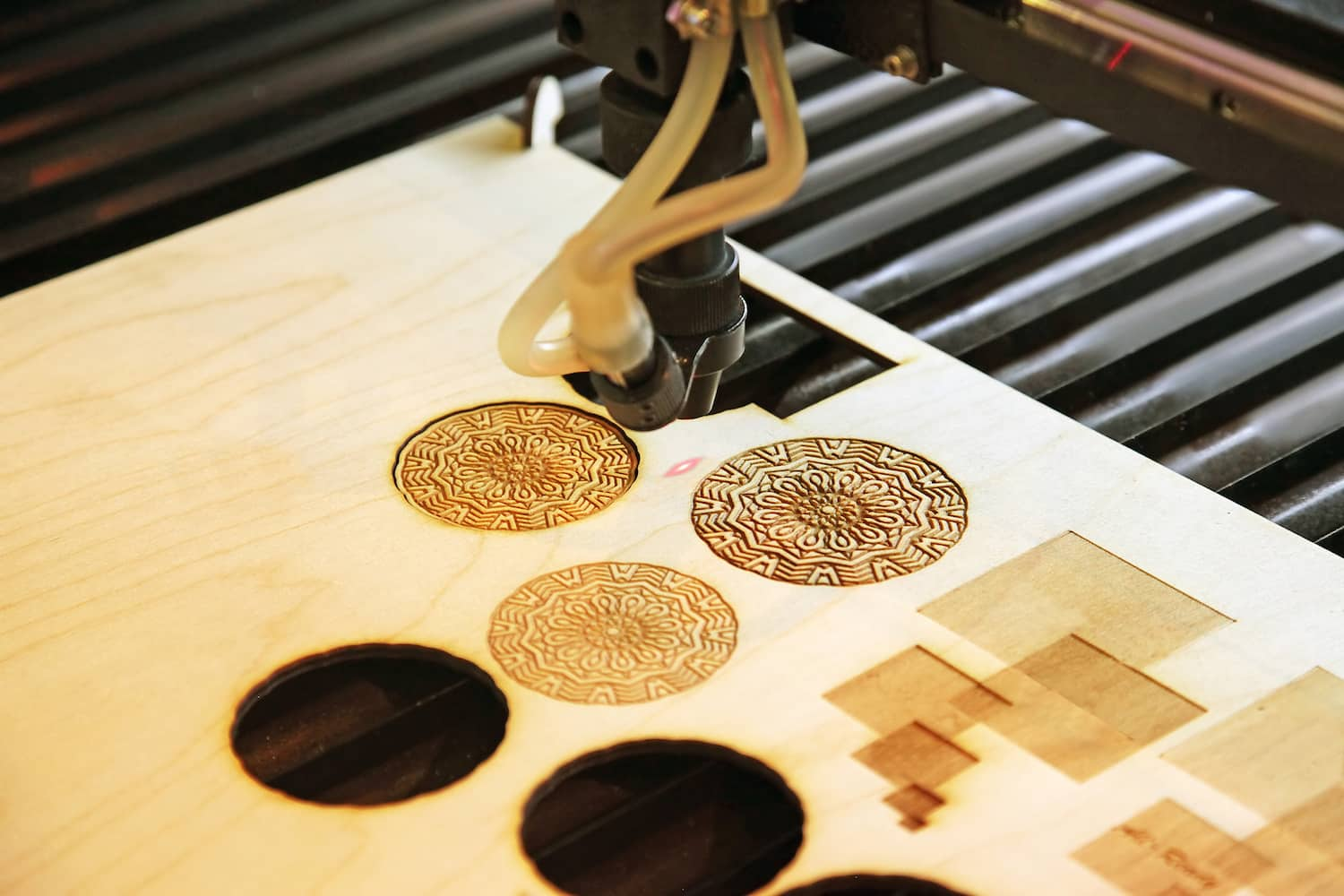

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Wood Sheets for Laser Cutting (Quality, IP)
Sourcing wood sheets for laser cutting requires careful consideration to ensure both the quality of the final product and compliance with intellectual property (IP) rights. Overlooking key factors can lead to production delays, safety hazards, legal issues, or subpar results. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Wood Quality and Inconsistency
Low-quality or inconsistent wood sheets can cause significant problems during laser cutting. Issues such as warping, uneven thickness, knots, or voids may lead to incomplete cuts, charring, or even machine damage. Plywood with inconsistent glue layers or delamination risks can fail under laser heat.
Tip: Source from reputable suppliers who provide specifications (e.g., thickness tolerance, ply count, core material). Request samples before bulk orders and verify flatness and edge quality.
Use of Treated or Coated Woods
Some wood sheets are treated with fire retardants, finishes, or adhesives that release toxic fumes (e.g., formaldehyde, chlorine gas) when laser-cut. These emissions are not only hazardous to health but can also corrode laser optics and violate workplace safety regulations.
Tip: Only use untreated, natural wood such as Baltic birch, poplar, or maple. Confirm with the supplier that the wood is free from harmful coatings or additives.
Hidden Intellectual Property (IP) Restrictions
Designs intended for laser cutting may inadvertently infringe on copyrighted, trademarked, or patented material—especially when sourcing pre-designed templates or licensed artwork. Additionally, some wood suppliers or distributors may impose restrictions on commercial use of their branded materials.
Tip: Always verify the licensing terms of any design files you use. When in doubt, create original designs or obtain written permission from the IP holder. Avoid using brand logos or character-based designs without proper authorization.
Inaccurate Material Specifications
Misrepresentation of wood type, thickness, or grain direction can lead to incorrect machine settings. For example, assuming all 3mm wood behaves the same can result in under- or over-cutting. Some suppliers may list approximate thicknesses that vary beyond acceptable tolerances.
Tip: Double-check material specs with physical measurements upon delivery. Use calibrated calipers and document batch variations to refine laser settings accordingly.
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Without proper documentation, it’s difficult to verify the wood’s origin, sustainability (e.g., FSC certification), or compliance with environmental regulations. This can be critical for commercial products, especially in eco-conscious markets.
Tip: Prioritize suppliers who provide batch traceability and certifications. This supports responsible sourcing and strengthens your product’s market credibility.
Overlooking Moisture Content
Wood with high moisture content can warp during or after laser cutting, leading to poor fit in assemblies. It may also require higher laser power, increasing the risk of fire or excessive charring.
Tip: Store wood in a climate-controlled environment and allow it to acclimate before cutting. Ideal moisture content for laser cutting is typically between 6–8%.
By addressing these common pitfalls—focusing on both material quality and IP compliance—you can ensure safer, more reliable, and legally sound laser cutting projects.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Wood Sheets for Laser Cutting
Product Overview
Wood sheets intended for laser cutting are typically thin, flat panels made from materials such as plywood, MDF (medium-density fiberboard), Baltic birch, or solid hardwood veneers. These sheets are pre-cut to standard sizes (e.g., 12”x12”, 18”x24”, or 24”x48”) and are used in crafting, prototyping, signage, and industrial design. Safe handling, transport, and compliance with regulations are essential due to flammability, material sourcing, and chemical treatment concerns.
Material Classification & Harmonized System (HS) Codes
Proper classification is critical for international shipping and customs clearance. Common HS codes for wood sheets used in laser cutting include:
– 4412.31 – Plywood consisting solely of sheets of wood each ply not exceeding 6 mm thickness, for non-structural use.
– 4412.94 – Other plywood, including decorative or specialty plywood.
– 4410.11 – Particle board (e.g., MDF) of wood or other ligneous materials.
– 4408.39 – Veneer sheets, other than those for plywood.
Note: Final HS code assignment depends on composition, thickness, adhesive type, and country-specific tariff schedules. Always confirm with a customs broker.
Regulatory Compliance
International Trade Regulations
- Lacey Act (USA): Requires declaration of the species and origin of wood products. Importers must certify that the wood was harvested in compliance with applicable laws in the country of origin.
- EUTR (EU Timber Regulation): Prohibits placing illegally harvested timber on the EU market. Due diligence, including risk assessment and mitigation, is required.
- CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species): Applies if the wood species is listed (e.g., certain tropical hardwoods). Export/import permits are mandatory.
Chemical & Safety Standards
- CARB & EPA Phase II (USA): Regulates formaldehyde emissions from composite wood products like MDF and plywood. Ensure compliance with formaldehyde emission limits (≤ 0.05 ppm for MDF).
- REACH & SVHC (EU): Restricts the use of Substances of Very High Concern. Verify that adhesives and treatments do not contain banned chemicals.
- Flammability: Wood sheets are combustible. Shipping and storage must comply with local fire safety codes. Clearly label as flammable if applicable.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
- Protective Packaging: Use edge protectors, shrink wrap, or corrugated cardboard to prevent chipping, warping, and moisture damage.
- Stacking & Palletization: Stack sheets flat and secure them on wooden or plastic pallets. Weight limits per pallet should not exceed 1,500 lbs (680 kg) for safe handling.
- Moisture Control: Include desiccants and moisture barriers in packaging if shipping through humid environments. Relative humidity should be maintained between 35–50% during storage.
- Labeling: Clearly mark each package with:
- Product description and dimensions
- Lot number or batch code
- Country of origin
- Handling instructions (e.g., “Keep Dry”, “Do Not Stack”, “Fragile”)
Transportation & Shipping
Domestic Shipping (USA & Canada)
- Freight Options: LTL (Less-Than-Truckload) or full truckload depending on volume. Use flatbed or dry van trailers.
- Hazardous Materials: Most wood sheets are non-hazardous unless treated with flammable finishes. Verify with SDS (Safety Data Sheet) if coatings are used.
- Insurance: Declare full value to protect against damage or loss during transit.
International Shipping
- Incoterms: Use appropriate terms such as FOB (Free On Board), CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight), or DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) to clarify responsibilities.
- Documentation: Provide commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificates of origin. Include Lacey Act declaration or Due Diligence Statement for EUTR if required.
- Customs Clearance: Ensure all documentation matches physical goods. Delays may occur due to wood inspections or missing compliance paperwork.
Storage & Inventory Management
- Environment: Store indoors in a dry, temperature-controlled facility. Ideal conditions: 60–80°F (15–27°C), 35–50% relative humidity.
- Shelving: Keep sheets flat on level racks. Avoid leaning or vertical storage to prevent warping.
- Rotation: Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) to reduce aging and moisture exposure risks.
End-Use & Laser Safety Considerations
- Ventilation: Laser cutting produces flammable fumes and particulates. Use industrial-grade fume extractors with HEPA and carbon filtration.
- Fire Prevention: Install fire suppression systems (e.g., laser fire stops, CO2 extinguishers) in laser work areas.
- Material Suitability: Avoid pressure-treated, painted, or PVC-coated wood sheets, as they release toxic gases when lasered.
Sustainability & Certification
- FSC® or PEFC Certification: Preferred for environmentally responsible sourcing. Include certification codes on packaging and invoices if applicable.
- Recycling & Waste: Encourage customers to recycle wood offcuts. Provide guidance on proper disposal of laser residue (char, dust).
Conclusion
Successfully managing the logistics and compliance of wood sheets for laser cutting requires attention to material sourcing, international regulations, safe handling, and environmental conditions. By adhering to this guide, businesses can minimize delays, ensure regulatory compliance, and support safe, sustainable product use. Always consult local authorities and legal experts for region-specific requirements.
Conclusion: Sourcing Wood Sheets for Laser Cutting
Sourcing the right wood sheets for laser cutting is a critical step in ensuring high-quality results, efficient production, and project success. After evaluating various wood types, suppliers, and material specifications, it is clear that factors such as wood species (e.g., plywood, balsa, birch, MDF), thickness consistency, adhesive quality (in plywood), and formaldehyde content significantly impact laser cutting performance and safety.
Laser cutting demands materials that are uniform in density and free from defects such as warping, voids, or inconsistent glue layers. Baltic birch plywood often emerges as a top choice due to its clean layers, minimal voids, and excellent machinability. However, cost, availability, and project requirements may favor alternatives like hardboard (MDF) for smooth finishes or balsa for lightweight applications.
When sourcing, prioritizing reputable suppliers who provide consistent, laser-grade materials—preferably with certifications for low emissions and environmental safety—is essential. Local suppliers can offer faster turnaround and reduced shipping costs, while online specialty vendors may provide a broader selection of pre-cut, ready-to-laser sheets.
In conclusion, the ideal wood sheet for laser cutting combines material quality, dimensional accuracy, and compatibility with laser systems. Careful sourcing based on project needs, budget, and safety considerations ensures clean cuts, reduced machine maintenance, and professional end results. Establishing reliable supply channels and testing materials beforehand will lead to greater efficiency and consistency in any laser cutting workflow.