The global wood pellets market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for renewable energy and increasing adoption in residential, commercial, and industrial heating applications. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 9.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.8% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated USD 13.7 billion by the end of the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by supportive government policies, carbon reduction targets, and the growing shift away from fossil fuels—particularly in North America and Europe. As sustainability becomes a strategic priority across energy sectors, leading wood pellet manufacturers are scaling production, enhancing supply chain efficiency, and investing in low-carbon technologies to capture market share. In this competitive landscape, the top 10 wood pellet manufacturers stand out through proven capacity, international reach, and consistent quality—positioning them at the forefront of the bioenergy revolution.
Top 10 Wood Pellets Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Greene Team Pellets
Domain Est. 2008
Website: greeneteampellets.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to GreeneTeamPellets.com, home of the manufacturers of Greene Team Pellets, Greene Team Platinum Pellets, and Green Gold Pellets….
#2 Enviva Biomass
Domain Est. 2010
Website: envivabiomass.com
Key Highlights: Our wood pellets provide biogenic carbon solutions for power and heat generation, industrial processes, chemicals, and advanced biofuels worldwide. A ……
#3 Highland Pellets
Domain Est. 2013
Website: highland-pellets.com
Key Highlights: Highland Pellets, LLC is a wood pellet manufacturer in Pine Bluff, Arkansas that can produce over 600,000 metric tonnes per year. Highland ……
#4 Pellet Fuels Institute
Domain Est. 1998
Website: pelletheat.org
Key Highlights: Wood pellets are produced in manufacturing sites across Canada and the United States and are available for purchase at the hearth and home retailers, farm and ……
#5 Somerset Pellet Fuel
Domain Est. 2007
Website: somersetpellets.com
Key Highlights: Somerset brand pellets are sold across the U.S. through major pellet distributors and retailers for use in pellet appliances. Learn More About Our Pellets….
#6 Y Pellets
Domain Est. 2010
Website: innasol.com
Key Highlights: Y Pellets is a premium supplier of EN Plus A1 grade biomass wood pellets. Discover how they are working with Innasol to decarbonise the UK….
#7 LumberJack BBQ: of the Real BBQ Wood Pellets
Domain Est. 2012
Website: bbqlumberjack.com
Key Highlights: BBQ Simply Unmatched · Competition grade grilling pellets with exceptional flavor and performance for the backyard BBQ to the professionals….
#8
Domain Est. 2016
Website: energypelletsamerica.com
Key Highlights: Energy Pellets of America offers products including wood fuel pellets and animal bedding pellets. Learn more about our products and our company….
#9 How we make our wood pellets with renewable energy.
Domain Est. 2019
Website: balcasenergy.com
Key Highlights: We source locally managed spruce and pine timber from sustainably managed forests. Scroll down to learn more about our detailed manufacturing process….
#10 Biomass / Wood Pellets
Domain Est. 2022
Website: patel-energy.com
Key Highlights: At Patel Energy, we make our pellets from sustainable biomass generated from the harvest and manufacturing of other wood products….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Wood Pellets
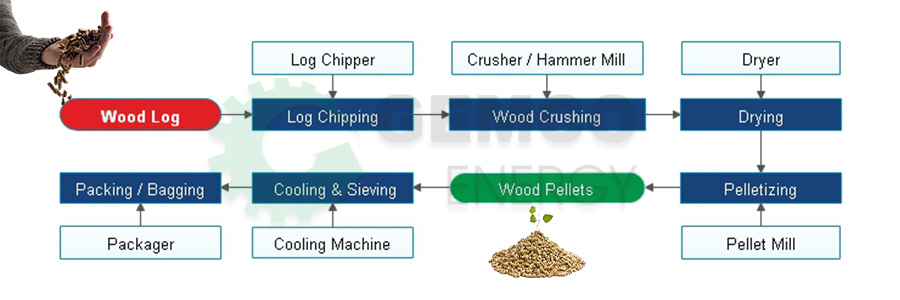
H2: Projected Wood Pellets Market Trends for 2026
Market Growth and Demand Outlook
The global wood pellets market is poised for significant expansion by 2026, driven by rising demand for renewable energy and decarbonization initiatives. According to market research, the wood pellets industry is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6–8% from 2022 to 2026, reaching a market value exceeding USD 15 billion by 2026. This growth is primarily fueled by increasing adoption in residential heating, industrial power generation, and co-firing in coal-based power plants.
Europe remains the largest consumer of wood pellets, accounting for over 50% of global demand. Countries such as the UK, Denmark, Italy, and Germany continue to rely on wood pellets to meet renewable energy targets under the European Green Deal. Meanwhile, emerging demand in Asia-Pacific—particularly in Japan and South Korea—is expected to accelerate due to government-backed biomass energy programs and the need to reduce dependency on fossil fuels.
Policy and Regulatory Drivers
Government policies and climate regulations are central to the 2026 outlook for wood pellets. The European Union’s Renewable Energy Directive (RED III), which sets a target of 42.5% renewable energy by 2030, is expected to sustain demand for certified sustainable wood pellets. Compliance with sustainability criteria—such as those from the Sustainable Biomass Program (SBP) and ENplus certification—will become increasingly mandatory, shaping supply chain practices and import standards.
In North America, particularly the United States and Canada, wood pellet exports are expected to rise to meet European and Asian demand. The U.S. Department of Energy and USDA support biomass energy through grants and sustainability initiatives, reinforcing the role of wood pellets in the clean energy transition.
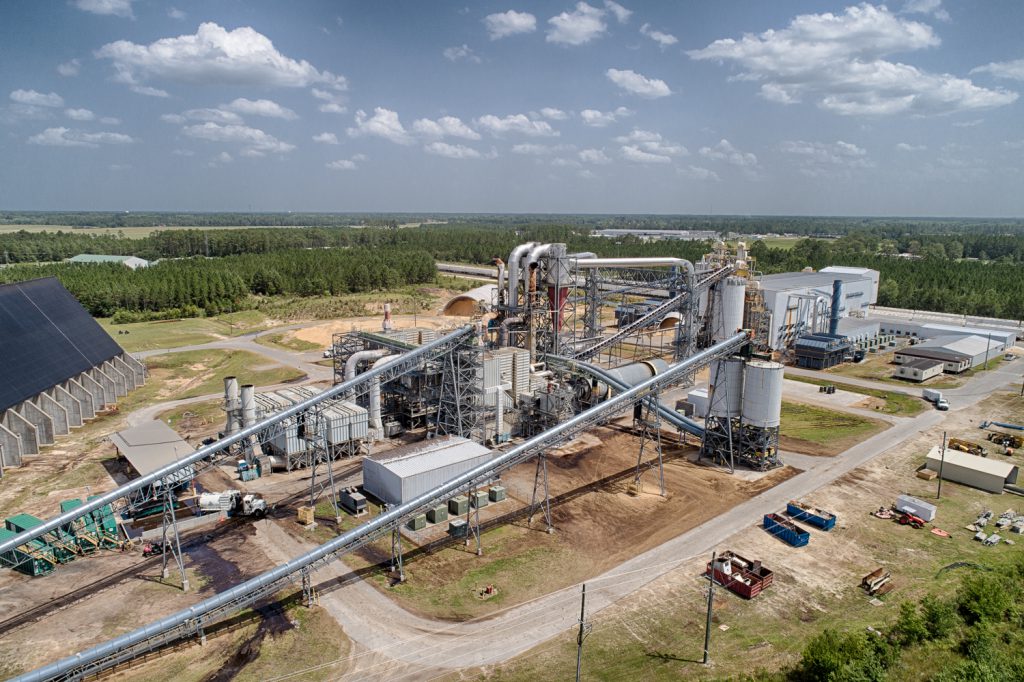
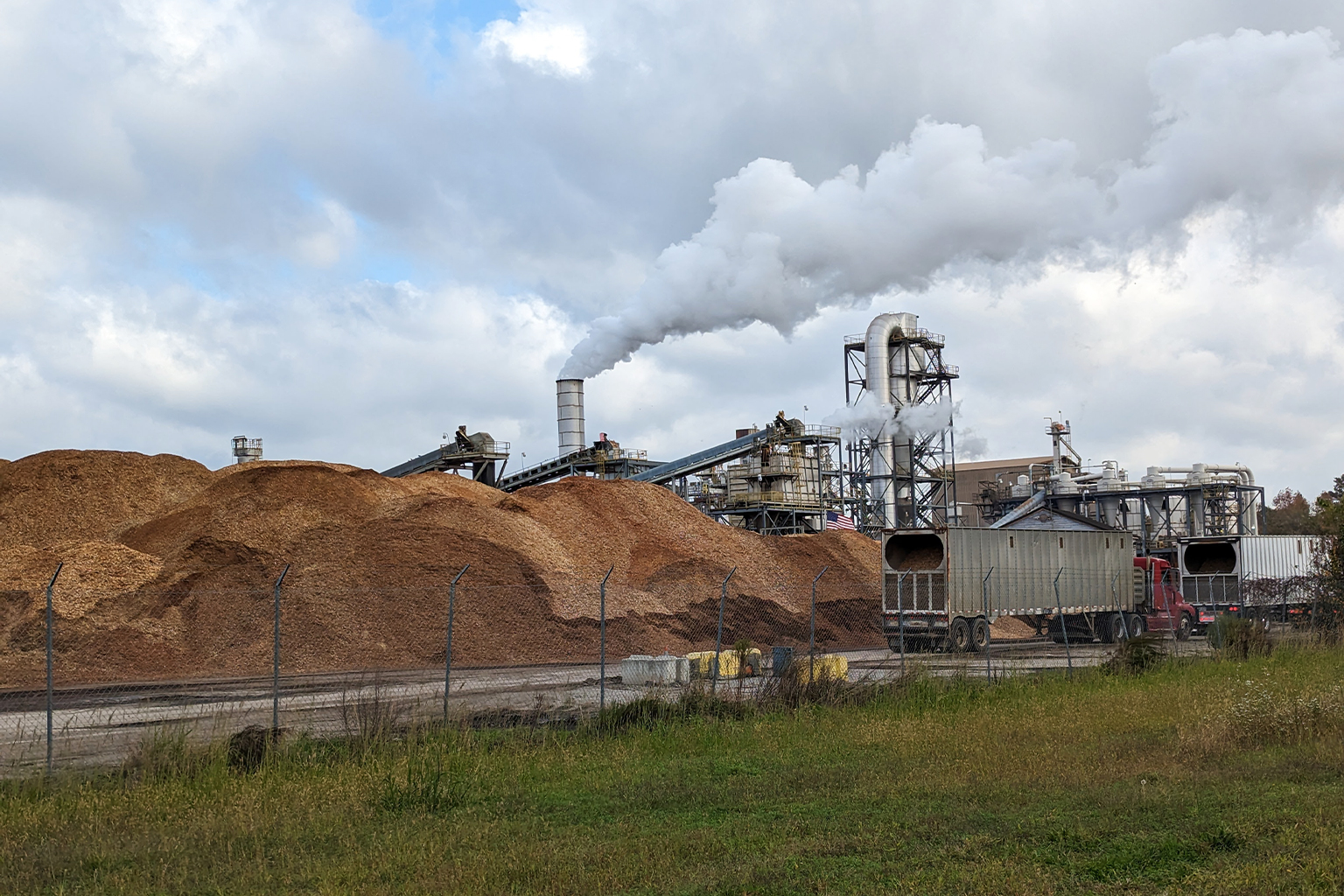
Supply Chain and Production Capacity
Production capacity is expanding, especially in the southeastern United States—the world’s largest exporter of wood pellets. Companies such as Enviva and Pinnacle Renewable Energy are investing in new facilities and efficiency upgrades to meet 2026 demand. Canada and the Baltic states (Latvia, Estonia, Lithuania) are also increasing output, supported by abundant forest resources and favorable logistics.
However, supply chain vulnerabilities—such as transportation bottlenecks, labor shortages, and fluctuations in feedstock availability—could constrain growth. The industry is responding by investing in automation, local sourcing, and rail-port infrastructure to ensure reliability.
Price Trends and Market Dynamics
Wood pellet prices are expected to remain volatile through 2026 due to energy market fluctuations, transportation costs, and weather-related disruptions. In 2023–2024, prices spiked due to supply constraints and high natural gas prices; although some stabilization is expected, long-term contracts and hedging strategies will likely become more common to mitigate risk.
Industrial buyers are increasingly negotiating long-term supply agreements to secure volume and pricing stability, a trend expected to continue through 2026. Additionally, competition from alternative biomass sources and synthetic fuels may pressure margins, pushing producers to focus on cost efficiency and sustainability branding.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
Environmental scrutiny of wood pellets—particularly regarding carbon neutrality and forest management—will intensify by 2026. Critics argue that large-scale pellet production may lead to deforestation and increased carbon emissions if not properly regulated. In response, the industry is investing in traceability technologies (e.g., blockchain) and third-party certifications to prove sustainability.
Consumers and policymakers alike are demanding transparency, pushing producers toward low-impact harvesting, use of sawmill residues, and reduced reliance on whole trees. The integration of circular economy principles—such as using urban wood waste and agricultural residues—may gain traction as a way to enhance sustainability credentials.
Technological and Innovation Trends
Innovation in pellet production and combustion technologies will play a key role in shaping the 2026 market. Advanced densification techniques, improved moisture control, and pellet quality standards (e.g., higher calorific value, lower ash content) are enhancing efficiency and performance.
Additionally, the development of torrefied wood pellets—offering higher energy density and water resistance—is expected to expand into niche industrial applications. Smart heating systems that integrate wood pellet boilers with IoT-enabled controls are also gaining popularity in residential markets, improving user experience and energy efficiency.
Conclusion
By 2026, the wood pellets market is set to be shaped by strong policy support, growing global demand, and a continued emphasis on sustainability. While challenges related to supply chain resilience and environmental concerns persist, technological innovation and strategic investments are positioning wood pellets as a key component of the global renewable energy mix. Stakeholders across the value chain—from producers to policymakers—will need to collaborate closely to ensure a sustainable and scalable future for the industry.

H2. Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Wood Pellets (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing wood pellets involves several potential pitfalls, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Businesses must be vigilant to avoid operational, financial, and legal risks.
1. Inconsistent Quality Standards
One of the most prevalent issues is variability in wood pellet quality. Key quality parameters such as moisture content, ash content, calorific value, and durability can differ significantly between suppliers. Without adherence to recognized standards like ENplus or ISO 17225, pellets may underperform in combustion systems, leading to equipment damage, higher emissions, and increased maintenance costs.
2. Lack of Certification and Traceability
Many suppliers, especially in emerging markets, lack proper certification. Without documentation verifying biomass origin, production methods, and compliance with sustainability criteria, buyers risk sourcing from environmentally harmful or illegal logging operations. This can result in reputational damage and non-compliance with regulatory requirements in regions like the EU.
3. Misrepresentation of Specifications
Some suppliers may falsify test reports or provide samples that do not represent bulk shipments. This misrepresentation can lead to unexpected performance issues upon delivery. Conducting independent third-party testing and requiring batch-specific certifications can mitigate this risk.
4. Supply Chain and Logistics Challenges
Wood pellets are hygroscopic and prone to degradation if exposed to moisture during transport or storage. Poor packaging, inadequate shipping conditions, or long lead times can compromise pellet integrity. Ensuring proper handling protocols and secure logistics agreements is essential.
5. Intellectual Property Risks in Technology and Processes
When sourcing from manufacturers that use proprietary production technologies (e.g., specialized densification processes or additives), there is a potential IP risk. Buyers may inadvertently become involved in disputes if the supplier uses patented methods without authorization. Additionally, custom formulations or branding developed in collaboration with suppliers should be protected through clear IP agreements to prevent unauthorized use or replication.
6. Contractual Ambiguities
Vague contracts that fail to specify quality tolerances, delivery timelines, penalties for non-compliance, or IP ownership can lead to disputes. It is crucial to define all technical and legal terms in writing, including responsibilities for quality control and resolution mechanisms.
In summary, sourcing wood pellets requires due diligence in verifying quality, ensuring sustainability, and safeguarding intellectual property. Establishing strong supplier relationships, conducting audits, and using standardized contracts are key steps to avoid these common pitfalls.
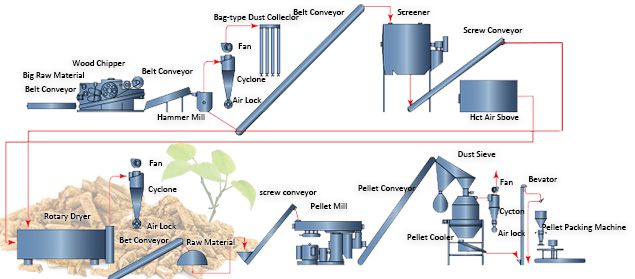
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Wood Pellets
Overview of Wood Pellet Supply Chain
Wood pellets are a renewable energy source made from compressed wood residues such as sawdust, wood chips, and shavings. They are used primarily for residential heating and industrial power generation. The logistics and compliance requirements for wood pellets involve multiple stages—from raw material sourcing to final delivery—each requiring careful management to ensure efficiency, safety, and regulatory adherence.
Key Logistics Considerations
Sourcing and Production
Wood pellets are typically manufactured in facilities located near sustainable forest resources or sawmills to minimize raw material transportation costs. Key logistics factors at this stage include:
- Proximity to raw material suppliers
- Sustainable forestry certification of feedstock (e.g., FSC, PEFC)
- Production capacity and drying efficiency
- Pellet quality control (moisture content, density, durability)
Storage and Handling
Wood pellets are sensitive to moisture, dust, and breakage, making proper storage and handling essential.
- Storage Facilities: Use dry, ventilated silos or covered warehouses with moisture barriers.
- Handling Equipment: Employ low-impact conveyors, screw augers, or pneumatic systems to minimize pellet degradation.
- Dust Control: Implement dust extraction systems to reduce explosion risks and maintain air quality.
Transportation Modes
Transportation logistics depend on shipment volume, destination, and infrastructure availability.
Road Transport
- Ideal for short- to medium-distance deliveries.
- Use covered trucks or silo tankers to protect pellets from moisture.
- Ensure vehicles are clean and dry before loading.
Rail Transport
- Economical for bulk shipments over long distances.
- Utilize covered hopper cars to prevent contamination and moisture absorption.
- Coordinate with rail operators for timely loading/unloading.
Maritime Shipping
- Most common for international exports.
- Pellets are typically shipped in bulk carriers or in containers (big bags or super sacks).
- Use moisture-resistant liners in holds and monitor humidity during transit.
- Comply with the IMO’s IMSBC Code (International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes Code) for safe stowage and handling.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Environmental and Sustainability Standards
Wood pellets must meet sustainability and carbon emission criteria, especially in the European Union and North America.
- ENplus Certification (Europe): The leading quality standard for wood pellets, covering pellet dimensions, moisture, ash content, and durability.
- Pellet Fuels Institute (PFI) Standards (USA/Canada): Defines premium, standard, and utility grades based on quality metrics.
- REACH and CLP Regulations (EU): Ensure safe handling and labeling of chemical substances (relevant for binders or additives).
- Sustainability Certification: Compliance with RED II (Renewable Energy Directive) may be required for pellets used in power generation, mandating proof of sustainable sourcing and carbon lifecycle analysis.
Phytosanitary and Biosecurity Regulations
To prevent the spread of pests and diseases:
- ISPM 15 (International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures No. 15): Applies to wooden packaging used in international shipments. Requires heat treatment or fumigation of wood packaging materials.
- Import Permits: Some countries require phytosanitary certificates or pre-shipment inspections.
- Banned Species: Avoid using wood from invasive or regulated tree species.
Customs and Trade Documentation
Ensure accurate and complete documentation to avoid delays at borders.
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin
- Phytosanitary Certificate (if required)
- Quality and Sustainability Certificates (e.g., ENplus, FSC)
Safety and Hazard Regulations
Although wood pellets are not classified as hazardous goods, they pose specific risks:
- Spontaneous Combustion: Freshly produced pellets may emit heat and carbon monoxide. Allow for off-gassing before sealing storage containers.
- Dust Explosions: High concentrations of wood dust in confined spaces can be explosive. Follow ATEX directives (EU) or OSHA/NFPA guidelines (US) for dust control.
- Asphyxiation Risk: In enclosed spaces, CO and CO₂ emissions from pellet off-gassing can displace oxygen. Ventilate storage areas and use gas detectors.
Quality Assurance and Testing
Regular testing ensures compliance with industry standards and customer expectations.
- Laboratory Analysis: Test for moisture content (<10%), ash content (<0.5–1% for premium grade), calorific value (~4.7–5.2 kWh/kg), and mechanical durability.
- Sampling Procedures: Follow ISO 18135 for sampling and ISO 17225-2 for classification.
- Batch Traceability: Maintain records linking production batches to certification and test results.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management are critical to the successful production, transport, and sale of wood pellets. Adhering to international standards, implementing best practices in handling and storage, and maintaining rigorous documentation will ensure product quality, regulatory compliance, and customer satisfaction in the global wood pellet market.
In conclusion, sourcing wood pellets requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, sustainability, and reliable supply. When selecting a supplier, it is essential to evaluate factors such as pellet grade (e.g., ENPlus or equivalent certification), raw material sourcing, production capacity, logistical capabilities, and adherence to environmental standards. Conducting thorough due diligence—through site visits, sample testing, and reference checks—helps ensure consistency and reliability. Additionally, establishing long-term contracts with transparent pricing and supply terms can mitigate market volatility and supply chain disruptions. Ultimately, choosing the right wood pellet supplier supports not only operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness but also aligns with broader sustainability goals, contributing to a cleaner, renewable energy future.