The global wood pellets market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for renewable energy and supportive government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. According to Grand View Research, the global wood pellets market size was valued at USD 9.7 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further fueled by rising adoption in residential heating, industrial co-firing, and power generation, particularly in Europe and North America. As demand for sustainable biomass intensifies, bulk manufacturers play a pivotal role in ensuring supply chain efficiency and cost-effective distribution. In this expanding landscape, identifying the top wood pellet producers becomes critical for energy providers, distributors, and procurement specialists. Based on production capacity, global reach, and market reputation, the following nine manufacturers stand out as leaders in the bulk wood pellets industry.
Top 9 Wood Pellets Bulk Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 O’Malley Lumber Company
Domain Est. 1998
Website: omalleylumber.com
Key Highlights: O’Malley Lumber is one of the East Coast’s largest pallet manufacturers and wholesale lumber companies, with locations in Pennsylvania, Maryland, and Virginia….
#2 Enviva Biomass
Domain Est. 2010
Website: envivabiomass.com
Key Highlights: Our wood pellets provide biogenic carbon solutions for power and heat generation, industrial processes, chemicals, and advanced biofuels worldwide. A ……
#3 About Balcas Energy and our Wood Pellets Story
Domain Est. 2019
Website: balcasenergy.com
Key Highlights: We are the largest manufacturer and distributor of high quality wood pellets in the UK and Ireland. Providing fuel services to commercial and domestic customers ……
#4 Sale of wood pellets – retail and wholesale
Domain Est. 2019
Website: pellet-dg.pl
Key Highlights: Buy wood pellets directly from the manufacturer. We offer retail and wholesale, personal collection, delivery and online purchase….
#5 Producer
Website: enplus-pellets.eu
Key Highlights: Below you will find a frequently-updated list of all pellet producers certified under the ENplus scheme along with detailed information related to their ……
#6 Animal Feeds & Supplements for Quality Nutrition
Domain Est. 1996
Website: kentfeeds.com
Key Highlights: Kent Feeds and Blue Seal provide high-quality nutrition with animal feeds for a variety of species, from hobby farmers to competitive owners….
#7 Traeger Grills®
Domain Est. 1996
Website: traeger.com
Key Highlights: Our premium wood pellets are made from 100% natural, cooking quality hardwood. Traeger pure wood pellets grant the perfect burn for optimal wood fired flavor….
#8 About us
Domain Est. 2007
Website: badgerpellets.com
Key Highlights: We are committed to producing 100% natural wood fuel pellets (BADGER Pellets®), of high certified quality, consistently and making sure to use environmentally- ……
#9 LumberJack BBQ: of the Real BBQ Wood Pellets
Domain Est. 2012
Website: bbqlumberjack.com
Key Highlights: BBQ Simply Unmatched · Competition grade grilling pellets with exceptional flavor and performance for the backyard BBQ to the professionals….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Wood Pellets Bulk
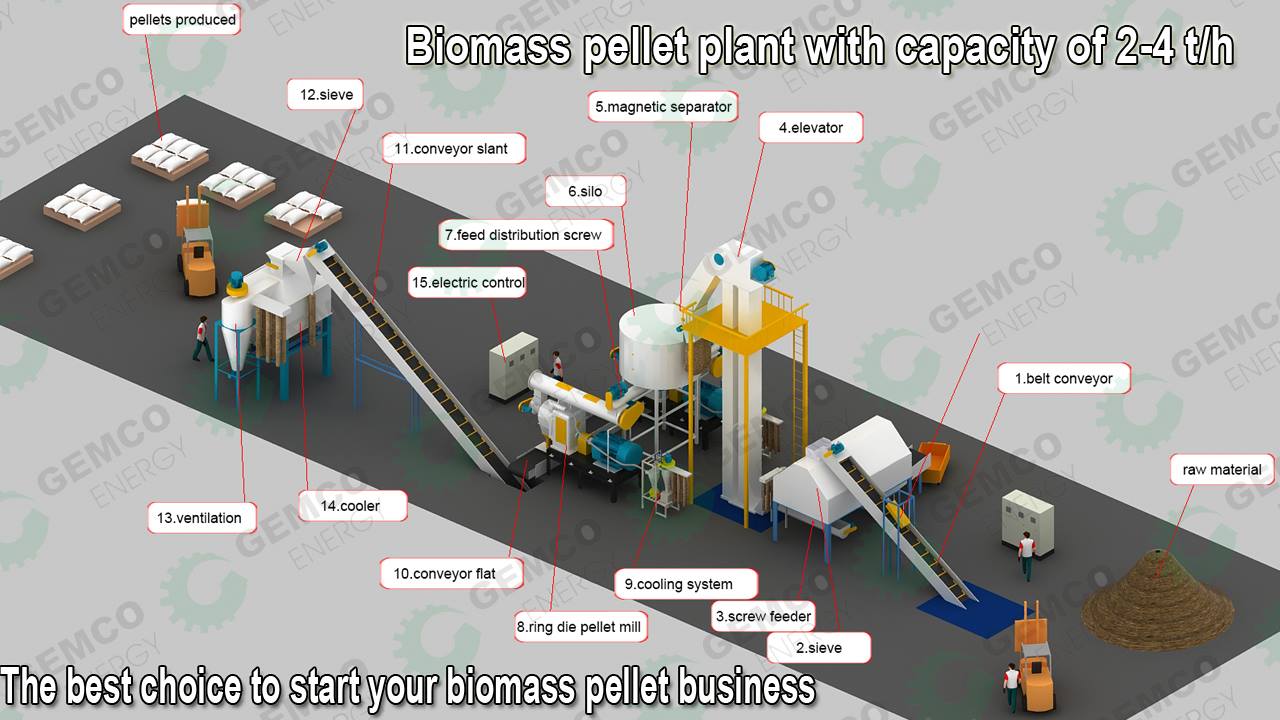
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Wood Pellets in Bulk
The global market for bulk wood pellets is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by increasing demand for renewable energy, evolving environmental policies, and advancements in supply chain logistics. As nations intensify efforts to reduce carbon emissions and transition away from fossil fuels, wood pellets—particularly in bulk—are emerging as a key bioenergy source for residential heating, industrial power generation, and co-firing in coal plants.
-
Growing Demand in Energy Transition
By 2026, demand for bulk wood pellets is projected to rise steadily, especially in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. The European Union’s Renewable Energy Directive (RED III) is expected to reinforce biomass as a sustainable energy source, supporting increased procurement of industrial-grade wood pellets. In the UK and EU, power utilities continue to rely on imported bulk pellets from North America and the Baltics to meet renewable targets, creating a stable demand outlook. -
Expansion in Asian Markets
Japan and South Korea are anticipated to become major importers of bulk wood pellets by 2026. These countries are investing heavily in biomass power generation as part of their decarbonization strategies, with government subsidies encouraging utilities to adopt wood pellets as a co-firing fuel. This shift will diversify global trade flows and potentially elevate prices due to increased competition for supply. -
Sustainability and Certification Pressure
Environmental concerns over deforestation and carbon neutrality are prompting stricter sustainability criteria. By 2026, major importers are expected to enforce robust certification requirements (e.g., SBP, FSC, PEFC), influencing sourcing practices. Producers who prioritize sustainable forestry and transparent supply chains will gain a competitive advantage, while uncertified or controversial sources may face market exclusion. -
Supply Chain and Logistics Developments
The bulk wood pellet market will see infrastructure improvements in loading, shipping, and storage technologies. Dedicated bulk terminals and larger vessels are expected to reduce transportation costs and improve delivery efficiency. Additionally, nearshoring trends may encourage regional pellet production in Asia and Eastern Europe to minimize logistics risks and carbon footprints. -
Price Volatility and Market Consolidation
Energy price fluctuations, raw material costs (e.g., timber), and geopolitical factors (e.g., trade policies, shipping disruptions) could lead to price volatility in 2026. Market consolidation is also likely, as larger producers with vertical integration and global distribution networks outperform smaller players, leading to increased economies of scale. -
Innovation and Alternative Feedstocks
Research into alternative feedstocks—such as agricultural residues and energy crops—may begin influencing bulk pellet production by 2026. While wood remains dominant, blending with non-wood biomass could enhance sustainability and reduce feedstock dependency, particularly in regions with limited forest resources.
In conclusion, the 2026 bulk wood pellet market will be shaped by policy support for clean energy, expanding international demand, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. Stakeholders who adapt to regulatory changes, invest in efficient logistics, and ensure environmental compliance will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
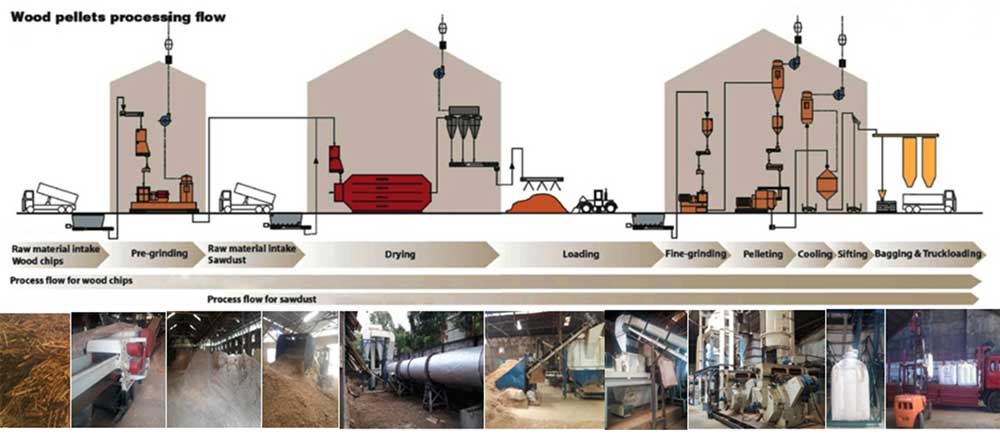
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Wood Pellets in Bulk (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing wood pellets in bulk requires careful attention to both physical quality standards and potential intellectual property (IP) considerations, especially when developing or branding a proprietary product. Overlooking these areas can lead to supply disruptions, customer dissatisfaction, legal risks, and reputational damage.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Inconsistent Moisture Content
One of the most frequent quality issues is variability in moisture levels. High moisture content (typically above 10%) reduces calorific value, increases transportation costs, and can promote mold growth during storage. Sourcing without strict moisture specifications or third-party testing can result in subpar performance and equipment damage.
Poor Ash Content Control
Ash content directly affects combustion efficiency and maintenance frequency in boilers and stoves. Low-grade pellets may have ash levels exceeding 1%, leading to slagging and increased cleaning needs. Failure to verify ash content through lab certification (e.g., ENplus, ISO 17225) can result in non-compliance with appliance requirements.
Inadequate Durability and Fines Production
Low mechanical durability leads to excessive fines (dust) during transport and handling, reducing efficiency and creating safety hazards. Pellets with durability below 97.5% (as per ENplus standards) are prone to breakage. Not specifying durability in contracts may result in receiving material that degrades before reaching the end user.
Contamination and Non-Wood Materials
Contaminants such as bark, soil, or non-wood biomass (e.g., plastics, treated wood) can compromise combustion and emissions. Suppliers using unsorted feedstock may introduce harmful substances. Without rigorous quality audits and material traceability, buyers risk violating environmental regulations or damaging equipment.
Inadequate Certification and Traceability
Relying on suppliers without recognized certifications (e.g., ENplus, Pellet Fuels Institute – PFI) increases the risk of inconsistent quality. Lack of chain-of-custody documentation makes it difficult to trace origin, verify sustainability claims, or address quality disputes effectively.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Unprotected Formulations or Blends
If a buyer develops a proprietary wood pellet blend (e.g., combining wood with agricultural residues or additives for enhanced performance), failing to secure patents or trade secrets can allow suppliers to replicate and market the formula independently. This is especially risky when sharing specifications without non-disclosure agreements (NDAs).
Misappropriation of Branding and Packaging Design
Custom packaging, logos, or labeling developed for branded pellet lines can be copied by unscrupulous suppliers, particularly in international sourcing. Without trademark registration and clear contractual IP ownership clauses, suppliers may sell similar-looking products to competitors.
Lack of IP Clauses in Supply Contracts
Many bulk supply agreements omit explicit terms on IP ownership, confidentiality, and usage rights. This ambiguity can lead to disputes over who owns process innovations, product improvements, or co-developed technologies, especially in long-term partnerships.
Third-Party Infringement Risks
Sourcing pellets that unknowingly infringe on existing patents (e.g., a specific production method or additive technology) exposes the buyer to legal liability. Conducting IP due diligence on both the product and manufacturing process is essential to mitigate infringement claims.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough vetting of suppliers, clear contractual terms, adherence to international quality standards, and proactive IP protection strategies.
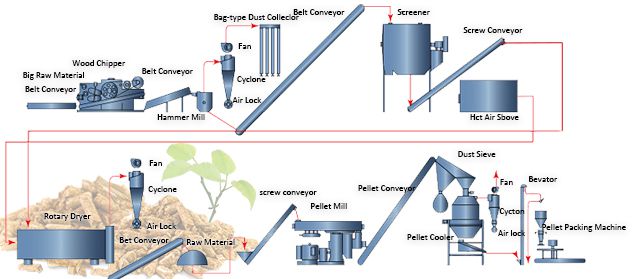
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Wood Pellets (Bulk)
Overview
Transporting bulk wood pellets involves complex logistics and strict compliance requirements due to the nature of the commodity, environmental regulations, and international trade standards. This guide outlines key considerations for the safe, efficient, and compliant handling of bulk wood pellets from production to end-user.
Classification and Characteristics
Wood pellets are classified as a solid biofuel made from compressed wood waste (e.g., sawdust, shavings). When transported in bulk (e.g., in ships, railcars, or bulk trucks), they are considered a Group C solid bulk cargo under the International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes (IMSBC) Code—non-chemically hazardous but may liquefy under certain conditions. Key characteristics include:
– Low moisture content (<10% for safe transport)
– Dust generation risk
– Potential for self-heating and off-gassing (CO, CO₂)
– Susceptibility to moisture absorption, which can degrade fuel quality and risk cargo instability
Packaging and Handling Methods
Bulk wood pellets are typically transported in:
– Bulk carriers (for ocean freight)
– Hopper railcars (for rail transport)
– Bulk pneumatic tankers (for road transport)
Precautions:
– Use closed systems to minimize dust and contamination.
– Avoid exposure to rain or humidity during loading/unloading.
– Clean transport units thoroughly before loading to prevent contamination.
Storage Requirements
Bulk storage (silos, domes, or enclosed warehouses) must:
– Be dry and well-ventilated.
– Prevent water ingress.
– Minimize dust accumulation (explosion risk).
– Include monitoring for temperature and CO levels to detect early signs of self-heating.
– Comply with local fire and safety codes (e.g., NFPA 664 in the U.S.).
Transportation Considerations
Ocean Freight
- Wood pellets must be declared under the IMSBC Code: Group C, UN 1365 (Wood Pallets, Compressed, not otherwise specified).
- Pre-shipment moisture content must be below Transportable Moisture Limit (TML); typically <10%.
- Shippers must provide a moisture content certificate and TML declaration.
- Ventilation during transit is essential to prevent condensation and off-gassing accumulation.
Rail and Road
- Use covered hoppers or enclosed trailers.
- Monitor for dust control and spillage.
- Follow ADR (Europe), 49 CFR (U.S.), or local regulations for hazardous materials where applicable (dust may be classified as combustible).
Regulatory Compliance
International Standards
- IMSBC Code (International Maritime Solid Bulk Cargoes): Mandatory for sea transport.
- ISPM 15 (International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures): Applies if wood packaging materials are used (e.g., for sample containers); bulk cargo itself is generally exempt.
- REACH and CLP (EU): Declare any chemical treatments (rare in pure wood pellets).
- EPA and USDA (U.S.): Compliance with air quality and biofuel sustainability standards (e.g., Renewable Fuel Standard).
Sustainability & Certification
- Many markets require certification for renewable energy eligibility:
- ENplus (Europe): Quality standard for wood pellets.
- Pellet Fuels Institute (PFI) Standard (North America).
- SBP (Sustainable Biomass Program): For industrial-scale biomass supply chains.
- Maintain Chain of Custody (CoC) documentation throughout logistics.
Safety and Risk Management
- Dust Explosion Prevention: Use explosion relief panels, grounding equipment, and inerting systems in enclosed handling areas.
- Gas Monitoring: Install CO and O₂ sensors in holds, silos, and enclosed spaces.
- Fire Response: Have Class D fire extinguishers and emergency shutdown procedures. Water may be used but can exacerbate issues if pellets are wetted excessively.
- Worker Safety: Provide PPE (respirators, goggles) and training for handling bulk biomass.
Documentation and Traceability
Required documents include:
– Bill of Lading
– Certificate of Analysis (moisture, ash, calorific value)
– Moisture Content and TML Declarations (for sea transport)
– Certificate of Origin
– Sustainability Certification (e.g., ENplus, SBP)
– Phytosanitary Certificate (if required by importing country)
Environmental and Sustainability Compliance
- Comply with emissions reporting (e.g., EU ETS if used in power generation).
- Ensure sourcing from sustainably managed forests (FSC/PEFC preferred).
- Minimize transport emissions via route optimization and modal shift (e.g., rail over truck).
Incident Reporting and Emergency Procedures
- Report cargo shifting, heating, or gas accumulation immediately.
- Follow emergency unloading or ventilation protocols.
- Notify port authorities and classification societies if safety issues arise.
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance for bulk wood pellets require coordination across production, storage, transport, and regulatory domains. Adherence to international codes, quality standards, and safety protocols ensures reliable delivery and market access, particularly in environmentally regulated regions. Regular audits and staff training are critical to maintaining compliance and operational safety.
Conclusion: Sourcing Wood Pellets in Bulk
Sourcing wood pellets in bulk offers a cost-effective, efficient, and sustainable solution for heating and industrial energy needs. By purchasing in large quantities, businesses and consumers benefit from reduced per-unit costs, consistent fuel supply, and lower carbon emissions compared to fossil fuels. However, successful bulk sourcing requires careful consideration of pellet quality (such as ENplus certification), reliable suppliers, logistical capabilities, and proper storage to maintain fuel integrity.
Investing time in selecting reputable suppliers, comparing pricing and delivery options, and ensuring compliance with environmental and efficiency standards will maximize the benefits of wood pellet use. As renewable energy demand grows, bulk wood pellets represent a practical and eco-friendly energy alternative, contributing to energy independence and sustainability goals. With proper planning and supplier partnerships, bulk wood pellet sourcing can be a smart, long-term energy strategy.