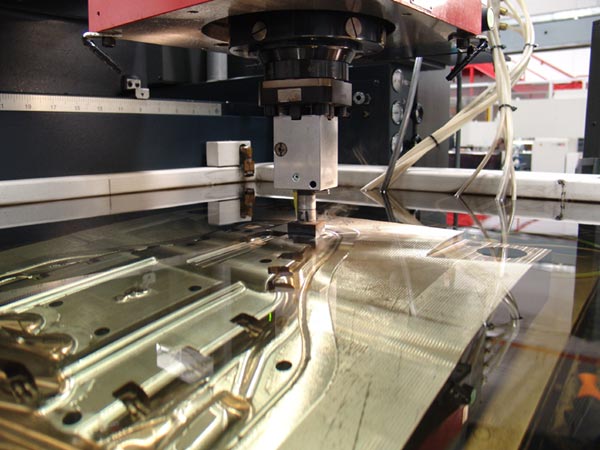
The global Wire Cut EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand for high-precision machining in aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. According to Grand View Research, the global EDM market size was valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% from 2023 to 2030. Mordor Intelligence further highlights that increasing adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies and the need for complex geometries in hard metals are accelerating the uptake of wire cut EDM solutions. As industries prioritize accuracy, efficiency, and minimal material waste, leading manufacturers are investing in next-generation wire EDM machines featuring automation, enhanced control systems, and IoT integration. In this competitive landscape, a select group of innovators are setting benchmarks in performance, reliability, and technological advancement—shaping the future of precision machining.
Top 10 Wire Cut Edm Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Accutex EDM Machines
Domain Est. 2001 | Founded: 2001
Website: accutex.com.tw
Key Highlights: Accutex is the original and professional wire cut EDM manufacturing company. We founded in 2001 by a group of engineers from Industrial Technology Research ……
#2 Chmer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: chmer.com
Key Highlights: CHMER is dedicated to advancing the technology and the quality of the EDM industry in Taiwan and worldwide EDM market….
#3 Leading EDM Machine Manufacturer & Supplier in Taiwan
Domain Est. 2008
Website: excetek.com
Key Highlights: Excetek is a premier EDM machine manufacturer & supplier in Taiwan, specializing in high-precision wire cut EDM and automation. Boost your production with ……
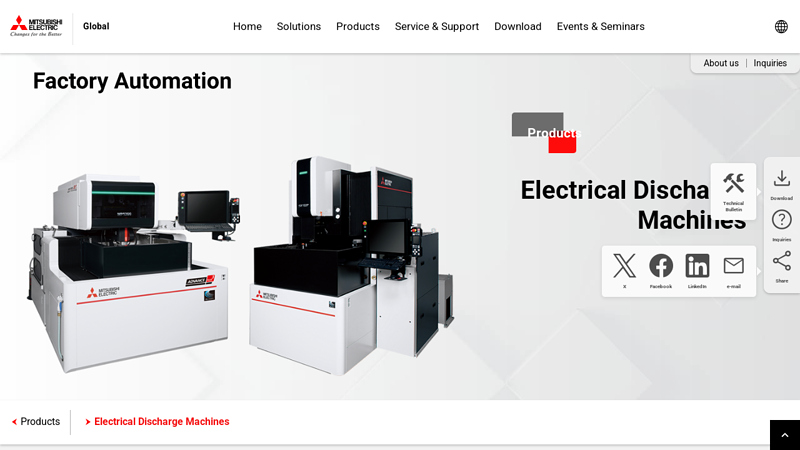
#4 Electrical Discharge Machines
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mitsubishielectric.com
Key Highlights: Mitsubishi Electric Die-sinking EDMs and Wire-cut EDMs enhance productivity with high-speed and high-accuracy. Besides mold making, it is also recognized as a ……
#5 Sodick
Domain Est. 1998
Website: sodick.com
Key Highlights: The Sodick Wire EDM lineup features flat rigid linear motors, maximizing cutting performance, and giving you the highest part accuracy possible. 3D PRINTING….
#6 Metal Fabrication Machinery
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mcmachinery.com
Key Highlights: MC Machinery Systems, a supplier of metal fabrication machines, provides EDM, milling, laser, press brake, finishing, and automation solutions….
#7 Wire
Domain Est. 1999
Website: gfms.com
Key Highlights: The Wire EDM process uses an electrical spark created between two conductive parts, a wire that cuts and a part from which material will be removed. Using a ……
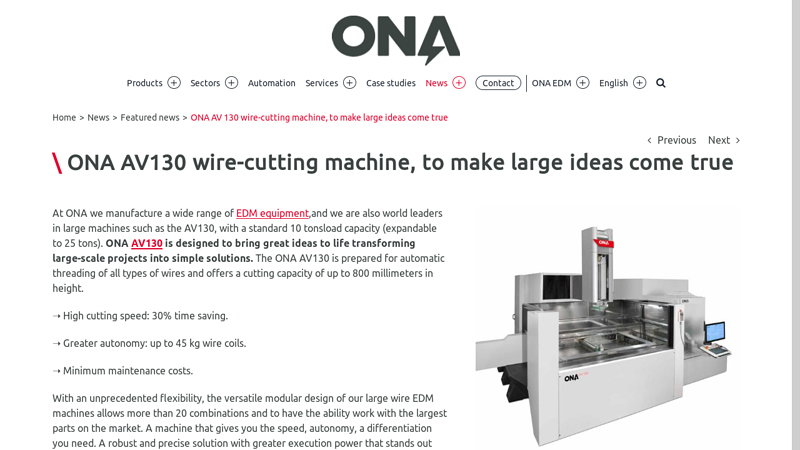
#8 Wire Cut EDM Modular Machine ONA AV130.
Domain Est. 2002
Website: onaedm.com
Key Highlights: At ONA we manufacture a wide range of EDM equipment,and we are also world leaders in large machines such as the AV130, with a standard 10 tonsload capacity ……
#9 Wire Cut Company
Domain Est. 2004 | Founded: 1978
Website: wirecutcompany.com
Key Highlights: Our EDM services offers excellence in electrical discharge machining and has been the industry leader since 1978….
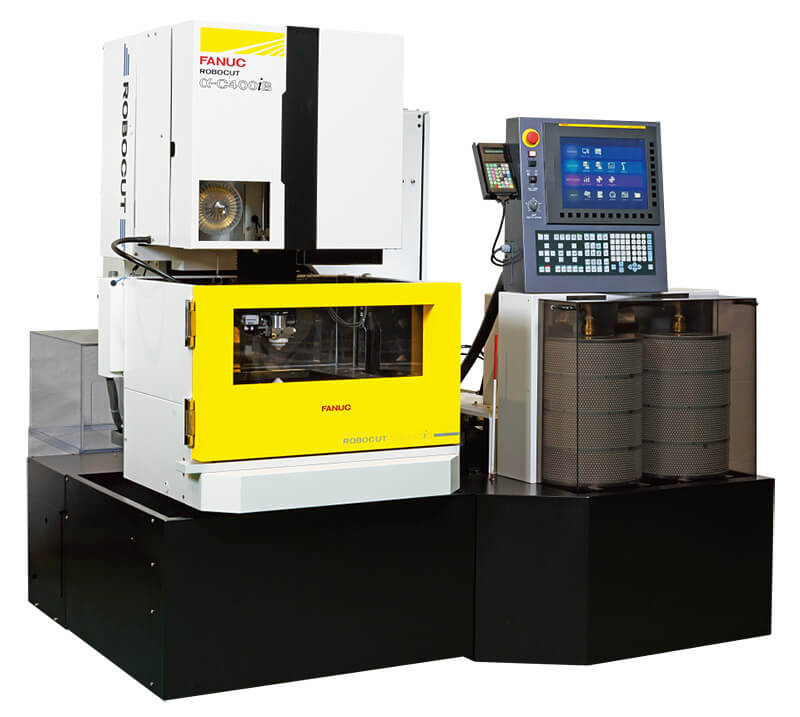
#10 ROBOCUT Wire
Website: fanuc.eu
Key Highlights: FANUC ROBOCUT is our multipurpose wire-cut EDM machine model series, designed for high-precision cutting. Learn more now….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Wire Cut Edm

2026 Market Trends for Wire Cut EDM: A Hydrogen Economy (H2) Perspective
While Wire Cut Electrical Discharge Machining (WEDM) is a mature manufacturing technology, its market trajectory in 2026 will be significantly influenced by broader industrial shifts, particularly the accelerating global push towards decarbonization and the burgeoning hydrogen (H2) economy. Here’s an analysis of key 2026 trends through the lens of H2’s impact:
1. Surging Demand from Hydrogen Infrastructure Manufacturing:
* Core Driver: The massive global investment in H2 production (electrolyzers), storage (high-pressure tanks, cryogenic vessels), transportation (pipelines, tube trailers), and refueling stations creates unprecedented demand for complex, high-precision components.
* WEDM Role: WEDM is uniquely suited for machining the exotic, hard-to-cut materials essential for H2 applications:
* Electrolyzer Stacks: Precision cutting of bipolar plates (often titanium, nickel alloys, stainless steels) with intricate flow field patterns and tight tolerances.
* Seals & Valves: Machining critical sealing surfaces and complex geometries in valve bodies and fittings from superalloys (Inconel, Hastelloy) resistant to H2 embrittlement.
* Sensors & Instrumentation: Fabricating micro-components for H2 purity, pressure, and leak detection systems.
* 2026 Impact: WEDM OEMs and job shops specializing in aerospace/energy will see a significant uptick in orders directly linked to H2 infrastructure. Demand will shift towards machines offering high precision, reliability, and capability with challenging materials.
2. Material Evolution & Machining Challenges:
* Core Driver: H2 applications demand materials with exceptional strength, corrosion resistance (especially to H2S), and resistance to hydrogen embrittlement at high pressures and temperatures. Nickel-based superalloys, advanced titanium alloys, and specialized stainless steels dominate.
* WEDM Role: Traditional machining struggles with these materials due to work hardening, low thermal conductivity, and chemical reactivity. WEDM, being a non-contact thermal process, excels here, enabling precise cuts without inducing significant mechanical stress or altering material properties near the cut.
* 2026 Impact: WEDM will be a critical enabler for manufacturing H2 components. Machine capabilities will be benchmarked on their performance with these specific alloys. Expect advancements in:
* Wire Technology: Development of specialized wires optimized for cutting superalloys and titanium efficiently and with superior surface finish.
* Process Control: Enhanced adaptive control systems to maintain stable cutting in highly variable superalloys, minimizing wire breakage and improving throughput.
3. Precision & Miniaturization Demands:
* Core Driver: Next-generation electrolyzers (especially PEM) and fuel cells require increasingly complex micro-features, tighter tolerances, and higher aspect ratio cuts for efficiency and performance. H2 sensors demand micron-level precision.
* WEDM Role: WEDM’s inherent precision (sub-micron accuracy achievable) and ability to cut intricate shapes and sharp internal corners make it indispensable for these micro-features.
* 2026 Impact: The market will favor WEDM machines with:
* Ultra-High Precision: Machines designed for nanometer-level positioning accuracy and repeatability.
* Improved Surface Integrity: Focus on minimizing the Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) and achieving mirror-like finishes critical for sealing surfaces and minimizing H2 permeation paths.
* Taper Cutting & Skiving: Advanced capabilities for complex 3D geometries in valve components and flow fields.
4. Sustainability & Operational Efficiency Focus:
* Core Driver: The H2 industry itself is built on sustainability. Manufacturers will demand efficient, low-waste processes. Energy consumption and fluid management are key concerns.
* WEDM Role:
* Near-Net Shape: WEDM enables highly efficient material utilization, minimizing expensive scrap from superalloys.
* Fluid Technology: Development and adoption of more environmentally friendly dielectric fluids (biodegradable options) and advanced filtration/reclamation systems will be crucial. Closed-loop systems will gain traction.
* Energy Efficiency: OEMs will focus on reducing machine energy consumption per cut, particularly during high-power operations needed for thick superalloys.
* 2026 Impact: WEDM machine selection will increasingly consider total cost of ownership (TCO), including fluid costs, energy use, and waste disposal. Machines with integrated fluid management and energy-saving features will have a competitive edge.
5. Integration with Digitalization & Automation:
* Core Driver: H2 component manufacturing requires high consistency, traceability, and integration into automated production lines (Industry 4.0).
* WEDM Role: WEDM machines will need seamless integration:
* MES/ERP Connectivity: For production tracking, quality data logging, and supply chain visibility.
* Automated Workholding & Part Handling: Integration with pallet systems and robots for lights-out operation, crucial for high-volume production of standardized H2 parts (e.g., bipolar plates).
* Process Monitoring & AI: Advanced sensors and AI for real-time monitoring of cut stability, wire wear, and surface quality prediction, enabling predictive maintenance and process optimization.
* 2026 Impact: “Smart” WEDM machines with robust connectivity and automation capabilities will be preferred for H2 manufacturing hubs. Standalone machines will become less competitive.
Conclusion for 2026:
The hydrogen economy will be a major growth catalyst for the Wire Cut EDM market in 2026. Demand will be driven by the need to manufacture complex, high-integrity components from challenging materials for H2 infrastructure. Success will depend on:
- Specialization: OEMs and job shops focusing on H2-related materials (superalloys, Ti) and applications.
- Technological Advancement: Machines offering superior precision, surface quality, reliability with difficult materials, and integrated automation/digitalization.
- Sustainability: Emphasis on efficient fluid use, energy consumption, and waste reduction.
WEDM is poised to transition from a precision tool for niche applications to a strategic manufacturing technology underpinning the physical realization of the global hydrogen economy. Companies that align their WEDM capabilities with the specific demands of H2 component production will capture significant market share.
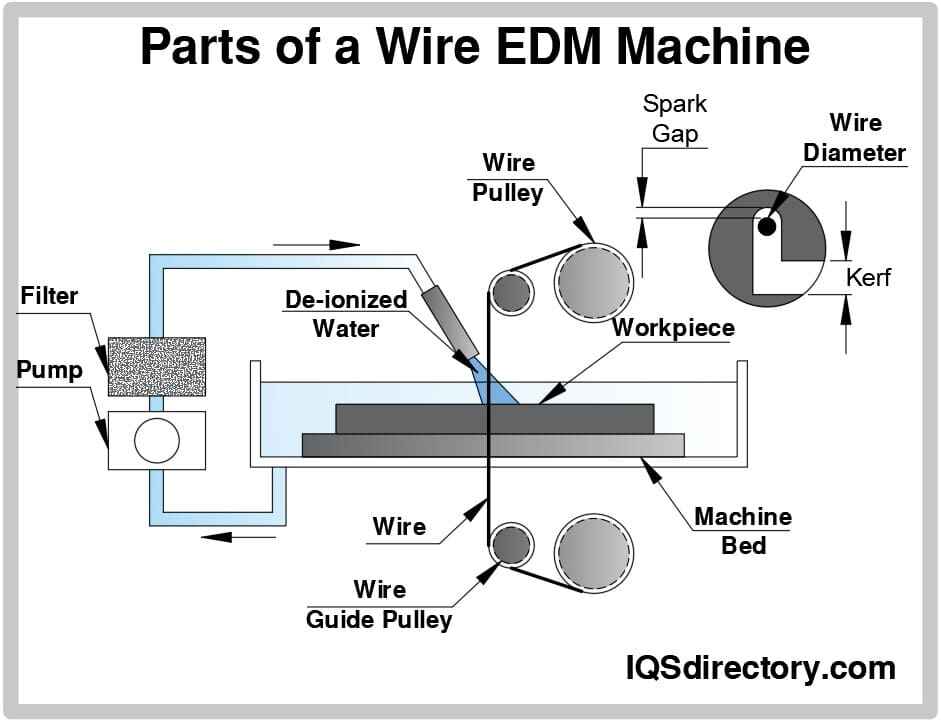
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Wire Cut EDM (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Wire Cut Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) services can present several challenges, particularly concerning part quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can result in defective components, project delays, and exposure of sensitive designs. Below are key issues to watch for:
Poor Surface Finish and Dimensional Inaccuracy
One of the most frequent quality issues in Wire Cut EDM is inconsistent surface finish or deviations from specified tolerances. This often stems from improper machine calibration, worn wires, incorrect cutting parameters (such as voltage, wire tension, or feed rate), or inadequate maintenance. Sourcing from vendors without robust quality control processes increases the risk of receiving parts that require rework or fail inspection.
Inadequate Material Certification and Traceability
Suppliers may not provide proper documentation for the materials used, such as mill test reports or material certifications. This is critical in industries like aerospace or medical devices, where traceability is mandatory. Without verified material data, parts may not meet regulatory standards or performance requirements, leading to compliance risks.
Lack of Process Validation and Repeatability
Wire Cut EDM processes should be repeatable across production batches. However, some suppliers may lack standard operating procedures or fail to conduct process capability (Cp/Cpk) studies. This inconsistency can result in part-to-part variation, especially in high-precision applications, undermining the reliability of the final product.
Insufficient Expertise in Complex Geometry Handling
While Wire Cut EDM excels at intricate shapes, not all providers have the programming and engineering expertise to handle complex contours, tight internal radii, or thin-walled features. Poor path planning or lack of skilled technicians can lead to wire breakage, taper errors, or compromised accuracy.
Weak Intellectual Property Protection Measures
When outsourcing precision machining, you often share detailed CAD models and technical specifications. A major pitfall is partnering with suppliers that lack formal IP protection protocols—such as signed NDAs, secure data handling procedures, or restricted access to design files. This exposes your proprietary designs to unauthorized use, replication, or leakage.
Insecure Data Transfer and Storage
Even with an NDA in place, IP risks remain if the supplier uses unsecured file transfer methods (e.g., public cloud links or unencrypted email) or stores design data on non-protected systems. A breach could lead to theft of design intellectual property or competitive disadvantage.
No Clear Ownership or Usage Rights in Contracts
Some service providers include clauses in their terms allowing them to reuse or showcase your designs as part of their portfolio. Without explicit contractual language defining IP ownership and usage rights, your designs could be used without consent, potentially violating confidentiality or patent strategies.
To mitigate these risks, thoroughly vet potential Wire Cut EDM suppliers for quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), audit their data security practices, and ensure strong legal agreements are in place before sharing sensitive information.
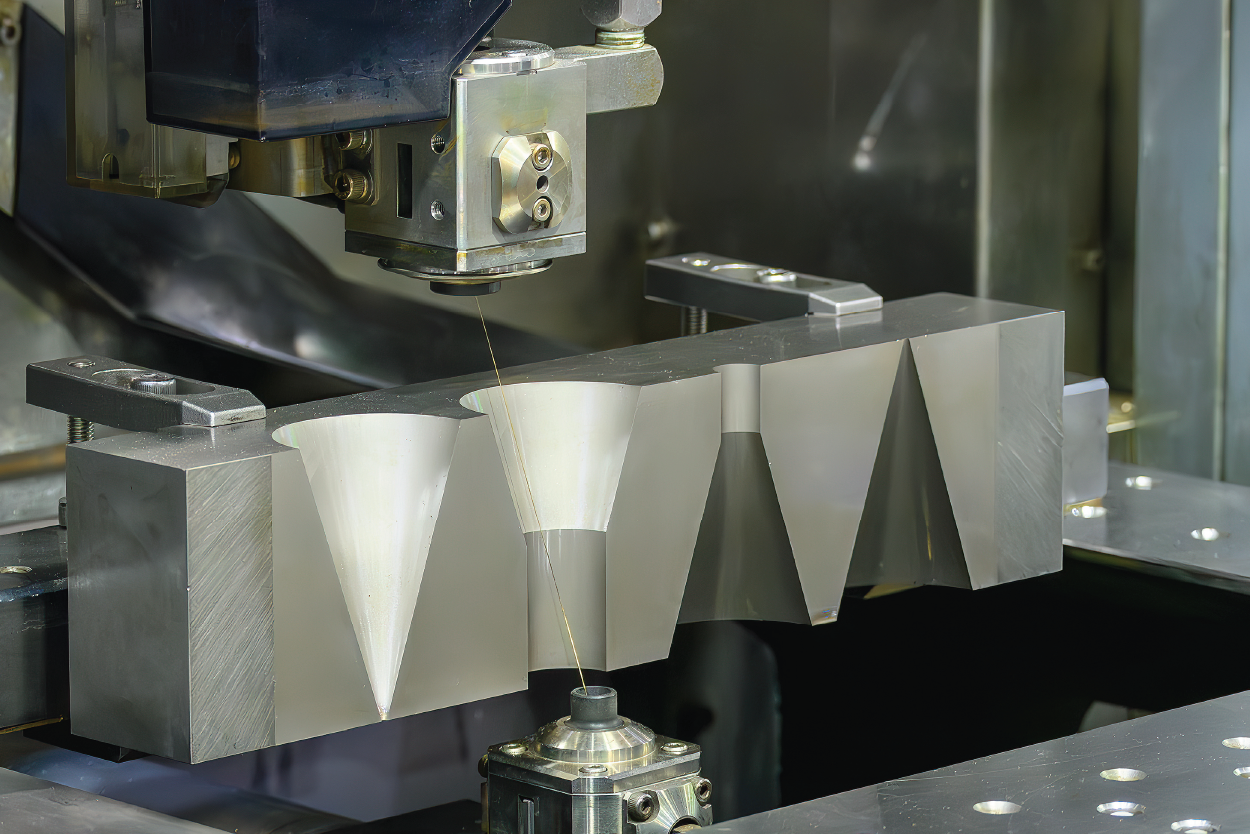
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Wire Cut EDM
Material Handling and Preparation
Ensure raw materials are properly stored in a dry, temperature-controlled environment to prevent warping or corrosion. Use non-marring fixtures and lifting equipment to avoid surface damage during transport to the EDM work area. Verify material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) are on file to meet traceability requirements, especially for aerospace or medical applications.
Machine Setup and Operation
Calibrate wire tension, guide alignment, and dielectric fluid systems prior to each production run. Confirm wire type (brass, zinc-coated, etc.) and diameter match job specifications. Implement documented setup procedures and first-article inspection to validate dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Maintain logs of machine parameters for process traceability.
Dielectric Fluid Management
Use deionized water or specified dielectric fluid as required by the machine and material. Monitor fluid resistivity, filtration efficiency, and contamination levels regularly. Follow local environmental regulations for fluid disposal—never drain used dielectric directly into sewer systems. Recycle or dispose of spent fluid through certified waste management providers.
Waste and Sludge Disposal
Collect metal sludge (primarily from the cut material and wire erosion) in designated containers. Classify waste according to local hazardous waste regulations—some metal sludges (e.g., from beryllium copper or leaded steels) may be regulated. Maintain waste manifests and disposal records to demonstrate regulatory compliance.
Health, Safety, and Environmental (HSE) Compliance
Provide operators with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, gloves, and protective footwear. Ensure proper ventilation to manage mist and fumes generated during cutting. Conduct regular machine maintenance to minimize risk of fluid leaks and electrical hazards. Comply with OSHA (or local equivalent) standards for machine guarding and electrical safety.
Quality Assurance and Documentation
Adhere to ISO 9001 or industry-specific quality standards (e.g., AS9100 for aerospace). Maintain inspection records, including CMM reports, surface finish measurements, and geometric tolerances. Implement a non-conformance reporting system for out-of-spec parts and corrective actions.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Comply with relevant standards such as:
– ISO 25436 (Geometrical product specifications for EDM)
– NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code)
– EPA regulations for wastewater and hazardous waste (e.g., RCRA in the U.S.)
– REACH and RoHS directives if serving EU markets
Ensure all operators are trained and certified per internal and external compliance requirements.
Shipping and Final Packaging
Package finished parts using anti-corrosion materials (e.g., VCI paper) and secure cushioning to prevent damage during transit. Label packages with proper handling instructions and material traceability information. Include compliance documentation (certificates of conformance, material test reports) with each shipment as required by the customer.
Conclusion for Sourcing Wire Cut EDM Services
Sourcing wire cut EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) services is a strategic decision that can significantly enhance precision, efficiency, and quality in manufacturing complex and high-tolerance components. When selecting a wire cut EDM supplier, it is essential to evaluate factors such as technical expertise, machine capabilities, material compatibility, quality control processes, lead times, and cost-effectiveness. Partnering with a reliable and experienced provider ensures consistent accuracy, superior surface finish, and the ability to handle intricate geometries and hard materials that are difficult to achieve with conventional machining methods.
Furthermore, advancements in CNC technology and automation have made wire cut EDM more accessible and efficient, enabling faster production cycles and reduced waste. As industries such as aerospace, medical, mold & die, and electronics continue to demand tighter tolerances and innovative designs, sourcing wire cut EDM services from a capable vendor becomes a competitive advantage.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing strategy that prioritizes technical capability, quality assurance, and responsive service will ensure successful integration of wire cut EDM into your manufacturing process, supporting long-term product excellence and operational success.