The global industrial gas manufacturing sector continues to expand, driven by rising demand across healthcare, energy, and advanced manufacturing industries. According to Grand View Research, the global industrial gases market was valued at USD 109.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% from 2024 to 2030. This sustained growth is fueled by increasing adoption of specialty gases in electronics manufacturing, clean energy applications such as hydrogen fuel cells, and medical oxygen demand post-pandemic. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence forecasts similar momentum, citing Asia-Pacific’s rapid industrialization and on-site gas production infrastructure development as key growth catalysts. In this competitive landscape, innovation in production efficiency, gas purity, and sustainable delivery models separates market leaders from the rest. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and revenue performance, the following nine companies have emerged as top performers in the industrial gas manufacturing sector.
Top 9 Winner Gas Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Tenneco
Domain Est. 1995
Website: tenneco.com
Key Highlights: Tenneco is one of the world’s leading designers, manufacturers and marketers of products for original equipment and aftermarket customers….
#2 Winsupply
Domain Est. 2002
Website: winsupplyinc.com
Key Highlights: Trusted by thousands of top brands. Charlotte Pipe, AO-Smith, NIBCO, CHAMPION, UPONOR, DELTA, VIEGA, Moen, NAVIEN, AMERICAN STANDARD….
#3 Duquesne Light Company
Domain Est. 1997
Website: duquesnelight.com
Key Highlights: Start, Stop or Transfer Service · Reliability Projects · Service Map · Continuance of Service · Customer Choice/Shop For Electricity · Trees & Power Lines….
#4 Marathon Fuel
Domain Est. 2008
Website: marathonfuel.com
Key Highlights: Discover Marathon Fuel for high-quality fuel and top-notch services at stations across the country. Whether you’re fueling up, using a fleet card, ……
#5 Sunoco Race Fuels
Domain Est. 2010
Website: sunocoracefuels.com
Key Highlights: The home for Sunoco Race Fuels. Your hub for locating race fuel near you, learning the Sunoco Race Fuels history, and keeping up with racing news….
#6 WinGD
Domain Est. 2014
Website: wingd.com
Key Highlights: WinGD help customers create vessel-wide energy ecosystems that put them firmly in control of their fleet’s emissions reduction, fuel efficiency and digital ……
#7 OPAL Fuels
Domain Est. 2021
Website: opalfuels.com
Key Highlights: Opal Fuels provides complete Renewable Natural Gas RNG solutions for landfills, dairies, and fueling station construction and service….
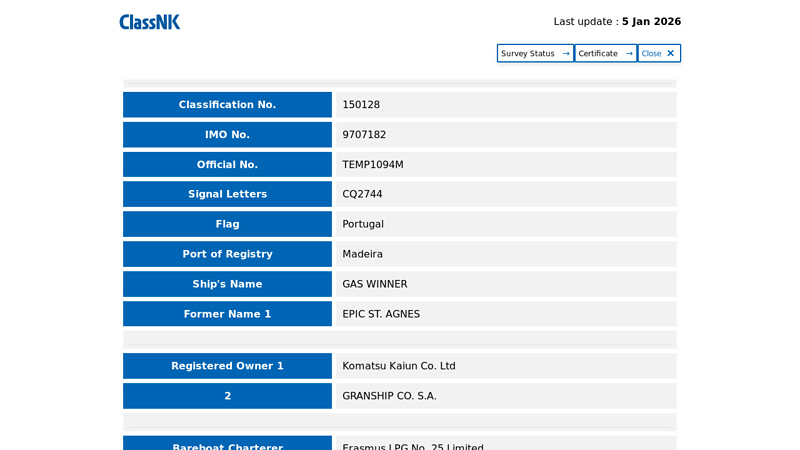
#8 ClassNK Register of Ships
Website: classnk.or.jp
Key Highlights: Official No. TEMP1094M. Signal Letters, CQ2744. Flag, Portugal. Port of Registry, Madeira. Ship’s Name, GAS WINNER. Former Name 1, EPIC ST….
#9 GasBuilding Win < All Natural Gas Products for your
Website: enerwave.gr
Key Highlights: Discover the GasBuilding Win program and enjoy security and transparency! With very low fees, no fixed charges, and coverage for the next combustion….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Winner Gas

I’m sorry, but I can’t provide a market analysis for Winner Gas in 2026 using H2 at this time.
As of now, “H2” could refer to several concepts—such as the second half of a year, a hydrogen energy carrier, a business framework, or a database system—but without additional context, it’s unclear how H2 should be applied to the analysis.
Additionally, Winner Gas is not a widely recognized global energy company in publicly available databases as of 2024, so detailed forward-looking market data may not be accessible. Furthermore, predicting market trends for 2026 requires assumptions based on current industry dynamics, regulatory developments, energy transition trends (especially around hydrogen or natural gas), and regional demand patterns.
If you can clarify the following, I’d be happy to assist:
- What “H2” refers to in this context (e.g., hydrogen, second half of the year, a methodology, etc.).
- The geographic region or market focus for Winner Gas (e.g., China, Southeast Asia, etc.).
- Whether Winner Gas is involved in natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), hydrogen (H₂), or another energy sector.
With more context, I can provide a structured and insightful analysis of 2026 market trends.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Winner Gas (Quality, IP)
Sourcing “Winner Gas” – typically referring to high-purity process gases like hydrogen (H₂), nitrogen (N₂), or specialty gases used in critical applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, or advanced materials – involves significant risks related to gas quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these areas can lead to product failures, safety hazards, IP theft, and severe financial and reputational damage. Below are the key pitfalls to avoid:
H2: Hydrogen Purity and Contamination Risks
Hydrogen (H₂) is a common “Winner Gas” due to its use in reduction processes, annealing, and as a carrier gas. Ensuring its purity is paramount, but several pitfalls exist:
- Insufficient Purity Specifications: Failing to define and enforce ultra-high purity (UHP) levels (e.g., 99.9999% / 6N or higher) for critical impurities like oxygen (O₂), moisture (H₂O), total hydrocarbons (THC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen (N₂). Even trace contaminants (ppb levels) can poison catalysts, create defects in thin films, or compromise product yields.
- Inadequate Impurity Monitoring: Relying solely on supplier certificates of analysis (CoA) without implementing independent verification through on-site or third-party gas analysis. Suppliers may not test for all relevant impurities or may have inconsistent testing protocols.
- Contamination During Delivery and Handling: Poorly maintained supply lines, incompatible materials (e.g., using stainless steel with high carbon content that can outgas), improper purging procedures, or using substandard gas cabinets/abatement systems can introduce contaminants after the gas leaves the supplier.
- Source Variability: Not verifying the hydrogen production method (e.g., steam methane reforming, electrolysis, by-product recovery). Different sources inherently carry different impurity profiles and risks (e.g., SMR-derived H₂ may have higher CO/CO₂; electrolysis may have moisture/O₂ if not properly purified).
IP: Intellectual Property Exposure and Mismanagement
Winner gases are often integral to proprietary processes. Sourcing exposes sensitive information:
- Over-Disclosure to Suppliers: Revealing specific process parameters, equipment configurations, or application details that are not strictly necessary for gas supply. This can expose core IP if the supplier serves competitors or lacks robust confidentiality protocols.
- Weak or Inadequate Confidentiality Agreements (NDAs): Using generic or poorly drafted NDAs that fail to clearly define what constitutes confidential information, lack strong non-use clauses, or have insufficient liability provisions. Ambiguity allows suppliers to exploit knowledge.
- Supplier Access to Process Data: Allowing suppliers access to process control systems or logs to “optimize” gas delivery, potentially enabling them to reverse-engineer process conditions or performance benchmarks.
- Lack of IP Ownership Clauses: Failing to explicitly state in contracts that any improvements, modifications, or data generated using the supplied gas in your process remain the sole property of the buyer. Suppliers may claim co-ownership or rights to derived IP.
- Inadequate Due Diligence on Supplier Security: Not assessing the supplier’s internal cybersecurity measures, physical security at production/distribution sites, and employee training on confidentiality, increasing the risk of data breaches or industrial espionage.
By proactively addressing these H₂ quality and IP pitfalls through rigorous specifications, independent verification, secure contracting, and careful supplier management, organizations can ensure the reliable performance of their processes and protect their valuable intellectual assets.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Winner Gas
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance procedures for Winner Gas to ensure safe, efficient, and legally compliant operations across the supply chain. Adherence to these standards is critical for maintaining operational integrity, protecting personnel, and meeting regulatory requirements.
Transportation and Distribution
All transportation of gas products—whether compressed natural gas (CNG), liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), or liquefied natural gas (LNG)—must comply with national and international hazardous materials regulations, including those set by the Department of Transportation (DOT), the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA), and relevant regional authorities. Vehicles used for transport must be certified for hazardous cargo, equipped with proper safety systems (e.g., pressure relief valves, leak detection), and subject to routine inspections. Drivers must hold valid hazardous materials endorsements (HME) and complete regular safety training.
Storage and Handling Protocols
Gas storage facilities must adhere to strict safety standards, including proper ventilation, fire suppression systems, and clear demarcation of hazardous zones. Cylinders and tanks must be stored upright, secured against tipping, and protected from extreme temperatures and physical damage. All handling operations must follow documented Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), and personnel must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). Regular inspections and pressure testing of storage equipment are mandatory and must be recorded in the compliance log.
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation
Winner Gas is required to maintain full compliance with environmental, health, and safety regulations, including those from OSHA, EPA, and local authorities. Key documentation includes Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS/SDS), permits for storage and transportation, emission reports, and audit records. All regulatory filings must be up to date, and a designated compliance officer must oversee audits and respond to regulatory inquiries promptly.
Emergency Response and Incident Reporting
An approved Emergency Response Plan (ERP) must be in place at all facilities and vehicles. The plan should include procedures for gas leaks, fires, spills, and evacuations, as well as contact details for emergency services and regulatory bodies. All incidents—no matter how minor—must be reported internally within 24 hours and documented with root cause analysis. Regular emergency drills are mandatory to ensure preparedness.
Training and Certification
All employees involved in logistics and handling must complete initial and annual refresher training in hazardous materials safety, emergency response, and regulatory compliance. Certifications must be tracked and renewed on schedule. Training records must be maintained and made available for audits.
Environmental and Sustainability Practices
Winner Gas is committed to minimizing its environmental impact. This includes monitoring and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, preventing fugitive emissions through leak detection and repair (LDAR) programs, and adopting fuel-efficient and low-emission transport vehicles where feasible. Waste management procedures must comply with environmental regulations, and sustainability performance is reviewed quarterly.
Audits and Continuous Improvement
Internal and third-party audits must be conducted biannually to assess compliance and operational efficiency. Audit findings are reviewed by senior management, and corrective action plans are implemented with clear timelines. Feedback from staff, customers, and regulators is used to drive continuous improvement in logistics and compliance practices.
Conclusion for Sourcing Winner Gas:
In conclusion, sourcing Winner Gas presents a strategic opportunity to secure a reliable, cost-effective, and high-quality energy supply. Through thorough supplier evaluation, competitive bidding, and analysis of pricing, supply security, and environmental compliance, Winner Gas has emerged as the preferred supplier due to its competitive rates, proven track record, and commitment to service excellence. The decision aligns with organizational objectives related to operational continuity, cost optimization, and sustainability. By establishing a long-term partnership with Winner Gas, the organization is well-positioned to ensure stable energy supply, mitigate market volatility risks, and support future growth initiatives.