The global wind turbine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for renewable energy, supportive government policies, and advancements in turbine technology. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global wind turbine market was valued at USD 107.86 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 171.43 billion by 2029, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by rising energy transition initiatives, declining levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) from wind power, and significant investments in onshore and offshore wind projects across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. As countries intensify efforts to meet climate targets, leading wind generator manufacturers are scaling production, enhancing efficiency, and expanding their global footprint—setting the stage for fierce competition and innovation. In this evolving landscape, the following ten companies stand out as key players shaping the future of wind energy.
Top 10 Wind Generator Companies Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 We are LM Wind Power
Domain Est. 2009
Website: lmwindpower.com
Key Highlights: LM Wind Power is a pioneer in advancing wind turbine blade technology and setting new standards for sustainability, efficiency, and digital industrialization….
#2 Wind turbine manufacturing and service
Domain Est. 1997
Website: us.vestas.com
Key Highlights: Vestas is a wind turbine manufacturer and a global leader in the renewable energy industry for sustainable energy solutions….
#3 Nordex SE
Domain Est. 2000
Website: nordex-online.com
Key Highlights: The Nordex Group is one of the world´s leading OEM´s with 40 years of experience in manufacturing highly efficient wind turbines for global onshore markets….
#4 GOLDWIND
Domain Est. 2000
Website: goldwind.com
Key Highlights: Goldwind is a global leader in clean energy, energy conservation, and environmental protection. As a world-top wind turbine manufacturer, we are committed ……
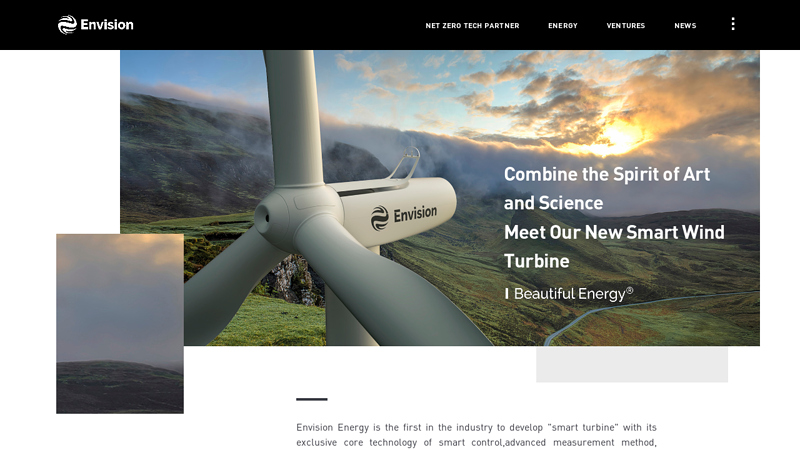
#5 Wind Turbines
Domain Est. 2017
Website: envision-group.com
Key Highlights: Envision Energy is the first in the industry to develop smart turbine with its exclusive core technology of smart control,advanced measurement method, expert ……
#6 ENERCON
Website: enercon.de
Key Highlights: Your leading manufacturer and service provider for onshore wind turbines | We are a partner you can rely on for your wind farm projects all over the world….
#7 Wind Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Domain Est. 1999
Website: energy.gov
Key Highlights: There are more than 500 US manufacturing facilities specializing in wind components such as blades, towers, and generators, as well as turbine assembly across ……
#8 Ørsted
Domain Est. 2004
Website: us.orsted.com
Key Highlights: Ørsted is a leading clean energy company that develops, constructs, and operates renewable projects, including wind, solar, and battery storage….
#9 Wind turbines
Domain Est. 2012
Website: ewtdirectwind.com
Key Highlights: EWT’s DIRECTWIND range of 225kW to 1MW wind turbines is designed and built to provide the most cost-effective long term power….
#10 Siemens Gamesa wind energy
Domain Est. 2017
Website: siemensgamesa.com
Key Highlights: Operating in 81 countries, Siemens Gamesa offers an extensive range of onshore wind turbine technologies to cover all wind classes and site conditions….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Wind Generator Companies

2026 Market Trends for Wind Generator Companies
Global Market Expansion and Policy Drivers
The global wind energy market is projected to experience robust growth by 2026, with wind generator companies at the forefront of this expansion. Governments worldwide are intensifying their commitments to carbon neutrality, with over 140 countries targeting net-zero emissions by mid-century. Policies such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), the European Green Deal, and China’s 14th Five-Year Plan are providing substantial incentives, tax credits, and streamlined permitting processes that favor wind energy deployment. These regulatory tailwinds are expected to drive demand for new wind turbines, particularly in offshore and distributed wind applications.
Offshore Wind as a Key Growth Segment
Offshore wind is anticipated to be one of the most dynamic segments for wind generator companies by 2026. Countries including the UK, Germany, the U.S., South Korea, and Taiwan are aggressively expanding their offshore wind capacity. Technological advancements—such as larger, more efficient turbines (15+ MW models), floating foundations for deep-water sites, and improved grid integration—are reducing the levelized cost of energy (LCOE) and making offshore projects more viable. Leading manufacturers like Vestas, Siemens Gamesa, and GE Vernova are investing heavily in offshore-specific turbine designs, positioning themselves to capture this high-growth market.
Technological Innovation and Efficiency Gains
Wind generator companies are focusing on innovation to improve turbine efficiency, reliability, and digital integration. By 2026, we expect widespread adoption of AI-driven predictive maintenance, digital twins, and smart control systems that optimize turbine performance in real time. Additionally, advances in blade design (e.g., longer, lighter composite materials) and direct-drive generators are helping increase energy yield while reducing mechanical wear and maintenance costs. These innovations are helping wind compete more effectively with solar and fossil fuels on cost and reliability.
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions have prompted a shift toward localized manufacturing and supply chain resilience. By 2026, many wind generator companies are expected to establish regional production hubs—particularly in North America and Southeast Asia—to comply with local content requirements and reduce dependency on single-source suppliers. This trend is supported by government incentives aimed at building domestic clean energy industries, which will benefit companies that can adapt quickly to regional regulatory and logistical demands.
Competitive Landscape and Consolidation
The wind generator market is becoming increasingly competitive, with a few major players dominating global supply. Vestas, Goldwind, Siemens Gamesa, and Ming Yang are expected to maintain strong market positions, but rising competition from Chinese manufacturers—driven by cost advantages and government support—is pressuring margins. This environment may lead to further industry consolidation, strategic partnerships, or vertical integration to achieve economies of scale and secure long-term project pipelines.
Sustainability and Circular Economy Focus
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations are shaping product development strategies. By 2026, wind generator companies are expected to prioritize recyclable materials, modular designs for easier servicing, and end-of-life turbine recycling programs—especially for composite blades. Regulatory pressure and public expectations are accelerating investments in circular economy solutions, with several companies piloting blade recycling technologies and zero-waste manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
By 2026, wind generator companies will operate in a dynamic, policy-driven market characterized by rapid technological advancement, geographic expansion, and increasing competition. Success will depend on innovation, supply chain agility, and the ability to scale offshore capabilities while addressing sustainability challenges. Companies that can navigate these trends effectively will be well-positioned to lead the global transition to renewable energy.
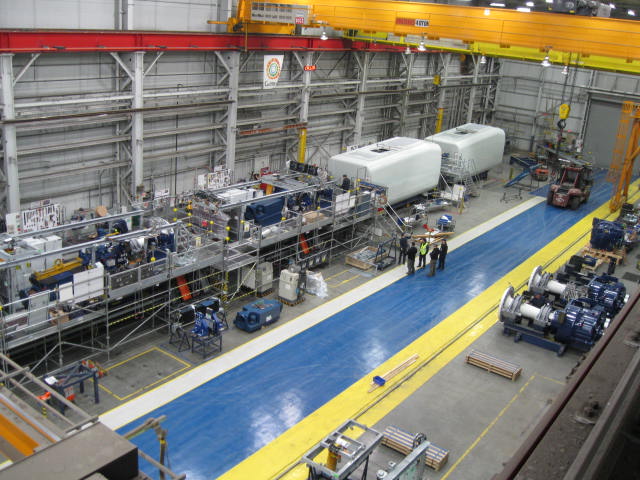
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Wind Generator Companies: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Quality Assurance Challenges
One of the most significant risks in sourcing wind generator companies—especially from emerging markets or lesser-known suppliers—is inconsistent product quality. Many manufacturers may lack rigorous quality control processes, leading to components that fail prematurely under real-world conditions. Issues such as substandard materials, poor welding, imprecise blade alignment, or inadequate testing can result in reduced efficiency, frequent maintenance, and costly downtime. Without third-party certifications (e.g., ISO, IEC, or GL certification), it becomes difficult to verify performance claims or durability. Buyers often discover these shortcomings only after installation, when remediation is expensive and logistically complex.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing from certain regions may expose companies to intellectual property violations, particularly when suppliers replicate patented turbine designs, control systems, or blade technologies without authorization. Using such equipment can lead to legal liabilities, import bans, or reputational damage. Additionally, reverse-engineered products often lack the innovation, reliability, and performance optimization of genuine IP-protected models. Buyers must conduct thorough due diligence on a supplier’s R&D capabilities, patent portfolios, and compliance history to avoid inadvertently supporting counterfeit or infringing technology. Failure to do so may result in project delays, financial losses, or legal disputes.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Wind Generator Companies
Supply Chain and Component Transportation
Wind generator companies rely on a complex global supply chain involving the transportation of massive and specialized components such as turbine blades, nacelles, towers, and hubs. Effective logistics planning must account for oversized load regulations, route surveying, and coordination with transport providers experienced in heavy haulage. Components are typically manufactured in specialized facilities and require multimodal transport—combining road, rail, and sea freight. Early engagement with logistics partners and detailed route analysis are critical to avoid delays and ensure safe delivery to often remote project sites.
Port and On-Site Handling Procedures
Ports serving wind energy projects must be equipped to handle the size and weight of turbine components, including cranes with sufficient lift capacity and laydown areas for staging. Documentation for vessel arrival, customs clearance, and just-in-time delivery to construction sites must be meticulously managed. On-site, components must be stored properly to prevent damage, particularly to sensitive blade surfaces. Handling procedures should follow OEM guidelines and include trained personnel, proper lifting equipment, and site safety protocols to mitigate risks during unloading and assembly.
International Trade Compliance
Wind generator companies operating across borders must comply with international trade regulations, including export controls, customs classifications (HS codes), and import tariffs. Components may be subject to rules under the WTO’s Environmental Goods Agreement or country-specific incentives such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). Accurate documentation—including commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin—is essential. Companies must also monitor changes in trade policies and sanctions that could impact supply chains or market access.
Environmental and Safety Regulations
Transportation and installation of wind turbines must adhere to environmental protection laws, especially in ecologically sensitive or protected areas. Permits may be required for road modifications, temporary access routes, and noise or emissions during transport. Safety compliance includes adherence to OSHA (U.S.), COSHH (UK), or equivalent regional standards during handling and installation. Risk assessments, emergency response plans, and worker training programs are mandatory to ensure operational safety throughout the logistics lifecycle.
Certification and Quality Standards
Wind turbine components and logistics processes must meet international quality and safety standards such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety). Additionally, turbine certification from bodies like DNV, GL, or IEC 61400 series is often required for project financing and grid connection. Logistics providers may also need certification for transporting hazardous materials (e.g., lubricants, batteries) under ADR, IMDG, or IATA regulations, depending on the mode of transport.
Customs and Duty Optimization Strategies
To reduce costs and streamline cross-border movement, wind generator companies should leverage preferential trade agreements and duty drawback programs. Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) may allow for reduced or eliminated tariffs on qualifying components. Utilizing bonded warehouses or temporary importation under bond (TIB) can defer duty payments. Proper classification and valuation of goods, along with proactive customs brokerage, help avoid penalties and delays. Maintaining detailed records supports audits and compliance verification.
Project-Specific Logistics Planning
Each wind farm project requires a customized logistics plan based on site accessibility, infrastructure limitations, and construction timelines. Key considerations include bridge weight limits, road width and gradient, weather conditions, and local permitting requirements. Early site assessments and collaboration with civil engineers, transporters, and local authorities help identify constraints and develop feasible transport routes. Real-time tracking and contingency planning are essential to manage disruptions due to weather, traffic, or regulatory changes.
End-of-Life and Reverse Logistics
As wind turbines reach end-of-life, companies must plan for decommissioning, recycling, and responsible disposal. Logistics for blade recycling, tower dismantling, and transport to recycling facilities are emerging compliance areas. Regulations such as the EU Waste Framework Directive emphasize circular economy principles and producer responsibility. Developing reverse logistics networks and partnerships with certified recyclers ensures compliance and supports sustainability goals, enhancing corporate responsibility and public image.
In conclusion, sourcing wind generator companies requires a strategic approach that balances technical capabilities, financial stability, geographic reach, and long-term sustainability goals. By evaluating key factors such as product quality, certification standards (e.g., IEC, ISO), track record, after-sales service, and innovation capacity, organizations can identify reliable partners suited to their specific energy needs. Additionally, considering the growing importance of corporate social responsibility and environmental impact, prioritizing suppliers with strong sustainability practices enhances overall project value. Engaging with reputable wind turbine manufacturers or suppliers—whether global leaders or proven regional players—ensures access to efficient, durable, and scalable wind energy solutions. Ultimately, a well-researched and due-diligent sourcing process not only mitigates risks but also supports the successful deployment of renewable energy projects contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future.