The global industrial marking and coding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for traceability, product authentication, and regulatory compliance across sectors such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. According to Grand View Research, the global laser marking machines market size was valued at USD 967.2 million in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. This surge underscores the importance of selecting the right marking technology—particularly when comparing traditional pin marking with advanced laser marking systems.
While laser marking offers high precision, permanent non-contact marking, and excellent integration with automated systems, pin marking remains a cost-effective and durable solution for deep engraving on tough materials like metals used in harsh environments. With such strong market momentum and technological divergence, manufacturers must make informed decisions based on application requirements, material types, production volume, and compliance standards. In this context, understanding when to use pin marking versus laser marking—and identifying the top manufacturers capable of delivering reliable, scalable solutions—has become a strategic priority for operational efficiency and product integrity.
Top 9 When To Use Pin Marking Vs. Laser Marking Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
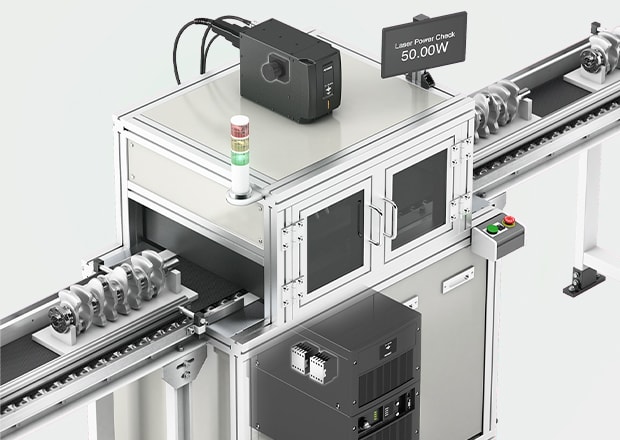
#1 Choosing the right marking technology
Website: pryormarking.com
Key Highlights: Laser markers generally offer higher marking speeds compared to Dot Peen markers. However, the choice between the two technologies will depend ……
#2 5 Considerations for Laser & Dot Peen Part Marking
Website: factronicsusa.com
Key Highlights: Laser marking is among the most popular systems for printing or engraving hard surfaces, used industrially for its speed, productivity, and accuracy….
#3 Laser vs. Dot Peen Marking Machines
Website: lasermarktech.com
Key Highlights: Laser marking is best for intricate designs like branding and QR codes. It’s faster than pin marking and creates highly durable marks on wood, plastic, metal ……
#4 Laser Marking vs Dot Peen Marking Machines?
Website: keyence.com
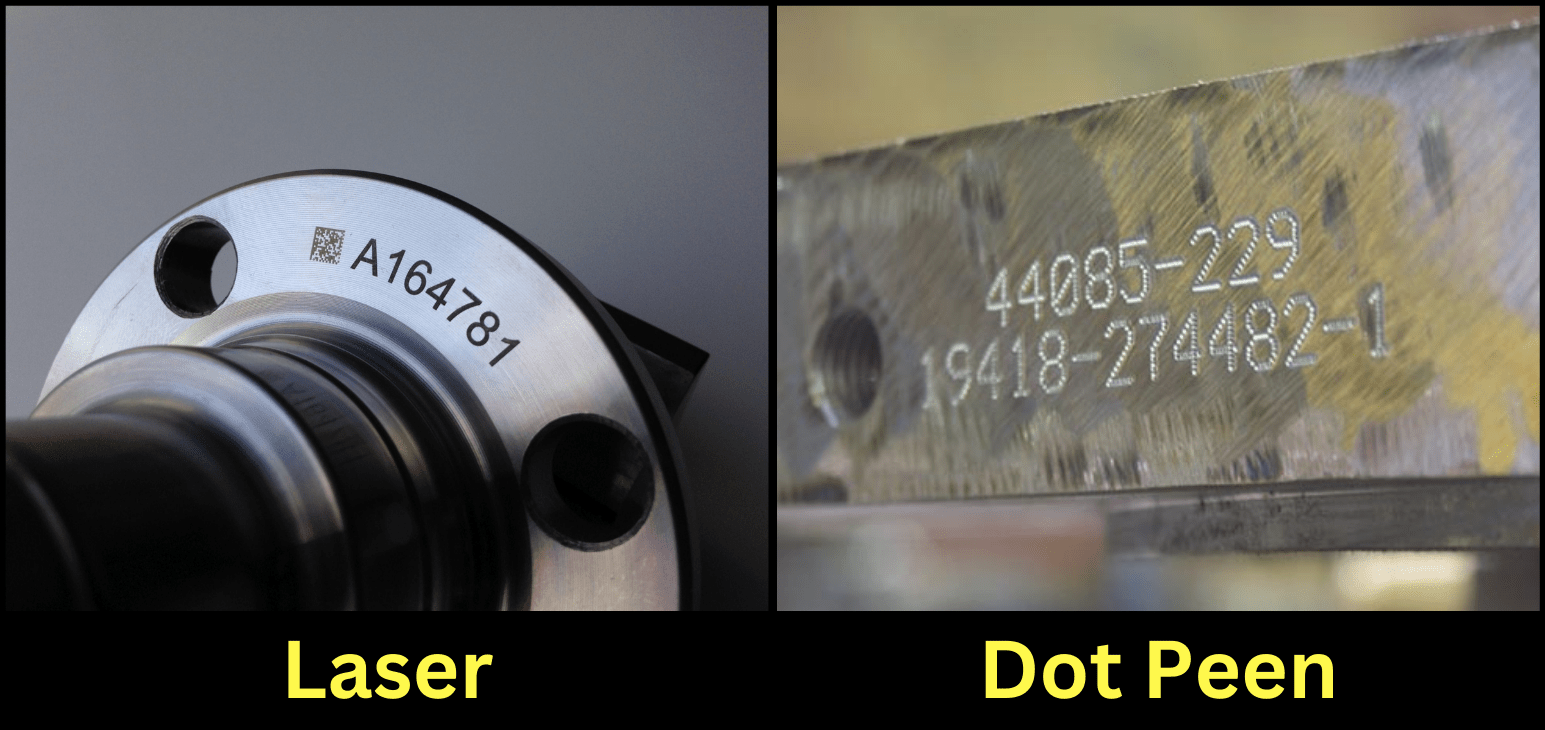
Key Highlights: A laser marking machine discolors the surface for a permanent mark, unlike dot peen marking, which creates an indent that collects contaminates like dust….
#5 Laser Markers vs Dot Peen Marking Machines
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laser marking provides better results. The resolution is fixed by the laser beam size which can be easily modified, allowing markings with lots of details….
#6 What Is the Difference Between Scribe Marking and Dot Peen …
Website: telesis.com
Key Highlights: Scribe and dot peen marking are part-marking methods that support traceability, compliance and operational efficiency….
#7 Types of Marking Technologies: Pin Marking
Website: gtschmidt.com
Key Highlights: Unlike laser marking, pin marking always involves the removal of material. Depending on the marking speed parameters, pin marking can create light, moderate or ……
#8 Laser vs Dot Peen Marking
Website: heatsign.com
Key Highlights: Explore the differences between laser and dot peen marking in our detailed comparison. Discover which technology best suits your industrial marking needs….
#9 A Guide To Laser, Dot
Website: marknstamp.com
Key Highlights: This guide explores three prominent technologies: laser marking, dot pin marking machine, and inkjet marking techniques….
Expert Sourcing Insights for When To Use Pin Marking Vs. Laser Marking
When To Use Pin Marking Vs. Laser Marking: 2026 Market Trends
As industrial manufacturing and product traceability demands evolve, marking technologies such as pin marking and laser marking continue to play crucial roles in part identification, compliance, and brand protection. By 2026, several market trends are expected to influence the decision-making process between pin marking and laser marking. This analysis explores the key factors shaping their applications, cost-efficiency, precision, and adoption across industries.
Rising Demand for Permanent and High-Contrast Marking
In 2026, the demand for permanent, high-contrast markings—especially in automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing—is expected to surge. Laser marking excels in producing high-resolution, durable marks on a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics. Its ability to create 2D data matrix codes, barcodes, and intricate logos without surface contact makes it ideal for traceability and regulatory compliance.
In contrast, pin marking uses mechanical impact to indent characters into the material, producing tactile, deeply engraved marks. It remains favored in high-vibration or harsh environments—such as heavy machinery or military equipment—where abrasion resistance is critical. As industry standards like AS9100 (aerospace) and ISO 13485 (medical devices) emphasize part traceability, both technologies see continued use, but laser marking is gaining traction due to its non-contact precision and minimal maintenance.
Cost and Operational Efficiency Trends
By 2026, operational cost efficiency will heavily influence technology adoption. Laser marking systems have seen significant cost reductions due to advancements in fiber laser technology and increased production scalability. Although initial investment remains higher than pin marking, the long-term savings in tooling, maintenance, and labor make lasers more economical—especially in high-volume production environments.
Pin marking systems, while cheaper upfront, require frequent stylus replacements and mechanical upkeep. They also generate more noise and vibration, contributing to higher facility maintenance costs. In industries moving toward lean manufacturing and Industry 4.0 integration, laser systems offer better compatibility with automated production lines and digital tracking systems, further enhancing their cost-effectiveness.
Material Compatibility and Flexibility
Laser marking offers superior flexibility across diverse materials. In 2026, as manufacturers adopt multi-material components and lightweight composites (e.g., carbon fiber-reinforced polymers), the non-contact nature of laser marking prevents surface damage and allows for precise, clean marks. Fiber and UV lasers can mark sensitive materials like medical implants or electronics without compromising integrity.
Pin marking, however, is generally limited to harder metals such as steel, titanium, and aluminum. It struggles with brittle or thin materials, where impact can cause microfractures or deformation. As product designs become more complex and materials more varied, laser marking is increasingly preferred for its versatility and material-safe operation.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sustainability is a growing concern across global supply chains. Laser marking aligns well with green manufacturing initiatives by eliminating consumables (e.g., styluses, inks) and reducing waste. It operates with minimal energy consumption and does not produce hazardous byproducts.
Pin marking, while mechanically robust, relies on physical tools that wear out and must be replaced, contributing to material waste. Additionally, the mechanical stress from impact can lead to higher scrap rates in delicate components. By 2026, companies aiming for ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) compliance will likely favor laser marking for its cleaner, more sustainable profile.
Industry-Specific Adoption Trends
- Automotive: Increasing use of laser marking for VINs, engine parts, and EV battery components due to precision and integration with smart factories.
- Aerospace & Defense: Both methods are used, but laser marking is growing for internal components requiring fine, readable codes without compromising structural integrity.
- Medical Devices: Laser dominates due to FDA and UDI (Unique Device Identification) requirements, where clean, sterile, and high-contrast marks are mandatory.
- Heavy Equipment & Tooling: Pin marking remains relevant for large, rugged components where deep, tactile marks are needed for field identification.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Technology in 2026
By 2026, laser marking is projected to lead in most high-tech and high-volume applications due to its precision, flexibility, and alignment with digital manufacturing trends. However, pin marking will retain a niche in industries requiring deep, impact-resistant marks on durable metal parts.
The decision between pin and laser marking will ultimately depend on material type, production volume, regulatory demands, and lifecycle cost. As laser technology becomes more affordable and compact, its market share is expected to grow—yet pin marking will persist as a reliable, low-tech solution where simplicity and durability are paramount.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Pin Marking vs. Laser Marking (Quality, IP)
When selecting between pin marking and laser marking for industrial applications, sourcing decisions often overlook critical factors that impact quality, traceability, and intellectual property (IP) protection. Missteps in this process can lead to compromised product integrity, compliance failures, and long-term cost inefficiencies. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Underestimating Material Compatibility and Surface Quality Impact
A frequent sourcing error is assuming both marking methods work equally well across all materials. Pin marking uses physical impact, which can deform softer metals or damage sensitive surfaces, leading to quality defects or part rejection. Laser marking, while non-contact, may alter material properties (e.g., heat-affected zones in stainless steel) or produce inconsistent contrast on certain alloys. Failing to test marking performance on actual production materials can result in unreadable codes, reduced part lifespan, or non-compliance with industry standards (e.g., AS9100, ISO 13485).
2. Overlooking Required Mark Permanence and Environmental Resistance
Sourcing based solely on upfront cost can be a trap. Pin marking generally offers excellent durability in harsh environments (e.g., high vibration, abrasion), making it suitable for automotive or aerospace components. Laser marks can fade or become illegible if the wrong type (fiber vs. CO₂) or settings are used, especially under UV exposure or chemical cleaning. Ignoring the end-use environment may lead to premature mark degradation, jeopardizing traceability and violating IP or regulatory requirements for part identification.
3. Neglecting Intellectual Property and Traceability Needs
Some suppliers fail to consider how marking method impacts IP protection and anti-counterfeiting. Laser marking supports high-resolution, complex codes (Data Matrix, micro-text), enabling secure serialization and digital traceability—critical for IP protection and regulatory compliance. Pin marking is limited in detail and prone to wear over tool life, potentially producing inconsistent or forgeable marks. Choosing pin marking for high-security applications can expose companies to counterfeiting risks and weakened IP enforcement.
4. Misjudging Production Speed and Integration Requirements
Sourcing teams may select a marking technology without evaluating throughput demands. Pin marking is typically faster for simple alphanumeric codes but requires tool changes for different designs, increasing downtime. Laser systems offer flexibility with no tooling changes but may have slower cycle times depending on mark depth and complexity. Poor integration with existing automation or MES systems can disrupt production flow and data collection, undermining quality control and traceability initiatives.
5. Failing to Audit Supplier Capabilities and Process Controls
A critical oversight is not vetting suppliers’ marking processes. Pin marking tools wear over time, leading to inconsistent mark depth or blurring if maintenance schedules aren’t enforced. Laser systems require calibration and parameter validation to ensure mark consistency. Sourcing from vendors without documented quality controls (e.g., SPC, first-article inspection) increases the risk of non-conforming parts and audit failures, especially in regulated industries.
6. Ignoring Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Focusing only on equipment price neglects long-term costs. Pin marking involves ongoing tool replacement and maintenance. Laser systems have higher initial costs but lower consumables and greater versatility. Additionally, poor mark quality leading to rework, recalls, or compliance penalties can far exceed initial savings. A comprehensive TCO analysis—including quality risk, maintenance, and traceability benefits—is essential for informed sourcing.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, sourcing decisions between pin and laser marking must be driven by application-specific requirements: material type, environmental exposure, regulatory needs, traceability goals, and lifecycle costs. Engaging cross-functional teams (engineering, quality, IP, operations) early and conducting rigorous supplier evaluations ensures the selected marking method supports both product quality and long-term business objectives.

When To Use Pin Marking Vs. Laser Marking: A Logistics & Compliance Guide
Choosing the right part marking method is critical for ensuring traceability, meeting regulatory requirements, and maintaining supply chain efficiency. Pin marking and laser marking are two widely used techniques, each suited to different applications based on material, durability needs, regulatory standards, and production environments. This guide outlines key considerations to help logistics and compliance teams determine when to use pin marking versus laser marking.
Material Compatibility and Substrate Requirements
Pin Marking
Best suited for softer metals such as aluminum, brass, and certain steels. It works by physically indenting the surface with a stylus or pin, making it less effective on very hard or brittle materials. Pin marking is not recommended for plastics or composite materials, as it may cause cracking or deformation.
Laser Marking
Highly versatile across a broad range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. Different laser types (fiber, CO₂, UV) can be selected based on material properties. Laser marking excels on hardened steels and heat-treated alloys where pin marking may struggle.
Logistics Insight: Evaluate the full range of materials in your supply chain. Laser marking offers greater flexibility in multi-material production environments.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Pin Marking
Creates a permanent, indentation-based mark that is highly resistant to wear, heat, and chemical exposure. Ideal for parts exposed to harsh environments such as engine components, aerospace hardware, or oil and gas equipment. The physical deformation ensures the mark remains legible even after surface coating or paint.
Laser Marking
Produces durable marks, but longevity depends on the method (annealing, engraving, foaming) and material. Laser engraving removes material and is highly durable, while surface marking may degrade under extreme abrasion or high-temperature cycles. Some laser marks can be affected by post-processing, such as blasting or plating.
Compliance Insight: For MIL-STD, AS9100, or API-compliant parts requiring tamper-proof, permanent identification through lifecycle conditions, pin marking may be preferred in high-stress applications.
Readability and Data Requirements
Pin Marking
Limited in resolution and character size. Best for alphanumeric codes, part numbers, or simple logos. Not ideal for 2D Data Matrix codes or high-density data storage due to lower precision.
Laser Marking
Offers high precision and excellent contrast, enabling small, complex 2D barcodes, QR codes, and serialized data. Ideal for meeting UID (Unique Item Identification) standards such as MIL-STD-130 or ISO/IEC 15415.
Logistics Insight: When integrating with automated tracking systems (e.g., ERP or WMS), laser marking supports efficient scanning and digital traceability.
Speed, Throughput, and Production Integration
Pin Marking
Slower marking speed due to mechanical impact cycles. More suitable for low-to-medium volume production or offline marking stations. Can generate noise and vibration, requiring isolation in automated lines.
Laser Marking
Faster marking speeds with no physical contact, enabling integration into high-speed production lines. Easily automated with robotics and vision systems for inline traceability.
Operational Insight: For high-volume manufacturing or JIT (Just-In-Time) logistics, laser marking reduces bottlenecks and improves throughput.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Pin Marking
Commonly accepted in industries where mechanical permanence is mandated—such as aerospace (SAE AS8035), defense, and heavy machinery. Often required when surface treatments (e.g., anodizing, powder coating) are applied post-marking.
Laser Marking
Widely accepted across industries including automotive (IATF 16949), medical devices (UDI compliance under FDA), and electronics. Must meet readability and permanence standards for 2D codes (e.g., ISO/IEC TR 29158).
Compliance Insight: Confirm industry-specific marking standards. For example, UID compliance often requires high-contrast, machine-readable 2D codes—favoring laser marking.
Total Cost of Ownership and Maintenance
Pin Marking
Lower initial equipment cost but higher maintenance due to stylus wear and replacement. Downtime for tool changes can affect logistics schedules.
Laser Marking
Higher upfront investment but minimal maintenance and consumables. Longer lifespan and reduced operational interruptions enhance supply chain reliability.
Financial Insight: Evaluate lifecycle costs, especially for long-term production programs or global supply chains requiring consistent marking quality.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
- Use Pin Marking when:
- Marking soft to medium-hard metals
- Extreme environmental durability is required
- High-resolution data is not needed
-
Compliance mandates mechanical indentation
-
Use Laser Marking when:
- Working with diverse or hard materials
- High-speed, automated production is critical
- 2D barcodes or UID compliance is required
- Long-term ROI and low maintenance are priorities
Aligning the marking method with material, regulatory, and logistical demands ensures product traceability, reduces compliance risk, and supports seamless supply chain operations.
Conclusion: When to Use Pin Marking vs. Laser Marking in Sourcing
When sourcing components or selecting part marking methods, the choice between pin marking and laser marking depends on several critical factors including material type, durability requirements, production volume, part geometry, traceability needs, and cost considerations.
Pin marking (also known as dot peen marking) is best suited for:
– Metals and durable materials that can withstand mechanical impact.
– High-volume production environments where reliability and low maintenance are key.
– Applications where deep, tactile marks are required for readability over time or under harsh conditions.
– Cost-sensitive projects where initial equipment investment must be minimized.
– Environments with high electromagnetic interference, where non-laser solutions are preferred.
Laser marking, on the other hand, excels in:
– Applications requiring high precision, fine detail, and permanent marks on a wide range of materials—including metals, plastics, and ceramics.
– Industries with strict traceability requirements (e.g., aerospace, medical devices, automotive) where barcodes, data matrix codes, or serialized IDs are essential.
– Production scenarios where non-contact marking preserves part integrity and minimizes contamination (critical in cleanroom environments).
– Complex or delicate components where mechanical force from pin marking could cause damage.
– When branding or aesthetic quality of the mark is important.
Final Recommendation:
In sourcing decisions, opt for pin marking when cost-efficiency, durability, and simplicity are priorities—especially for rugged industrial parts. Choose laser marking when precision, permanence, material versatility, and compliance with high regulatory standards are required. Evaluating the specific application, lifecycle of the part, and long-term traceability needs will guide the optimal selection between these two proven marking technologies.