The global automotive repair tools market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising vehicle ownership, increased maintenance demand, and the expansion of aftermarket services. According to Mordor Intelligence, the automotive tools market was valued at USD 15.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% through 2029. A key segment within this space is wheel bearing hub removal tools—an essential solution for mechanics performing precision axle and hub assemblies. With the rise in both light-duty and commercial vehicle fleets, demand for durable, efficient removal tools has intensified. As OEMs and aftermarket service providers prioritize time-efficient and damage-free maintenance, manufacturers specializing in high-quality hub removal systems are gaining traction. Drawing on market insights and product performance data, this list highlights the top nine wheel bearing hub removal tool manufacturers leading innovation, reliability, and global reach in this niche but critical sector.
Top 9 Wheel Bearing Hub Removal Tool Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 ConMet
Domain Est. 1996
Website: conmet.com
Key Highlights: We supply the commercial vehicle industry with wheel ends, hub assemblies, brake drums, hubs, rotors, aftermarket wheel products & OEM genuine products….
#2 Automotive Light & Commercial Vehicles
Domain Est. 1994
Website: timken.com
Key Highlights: We offer an extensive line of premium wheel hub units, tapered roller bearings, seals and driveline products designed to cover most light passenger vehicles on ……
#3 NSK Global
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nsk.com
Key Highlights: Global leader in Motion & Control. NSK keeps the world moving with bearings, ball screws, linear guides, auto parts, and precision machinery solutions….
#4 Bearing Extractors
Domain Est. 1998
Website: wheelsmfg.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $99.99 30-day returnsIndividual bearing extractors and tools used to remove sealed cartridge bearings from bottom brackets, hubs and suspension frame components….
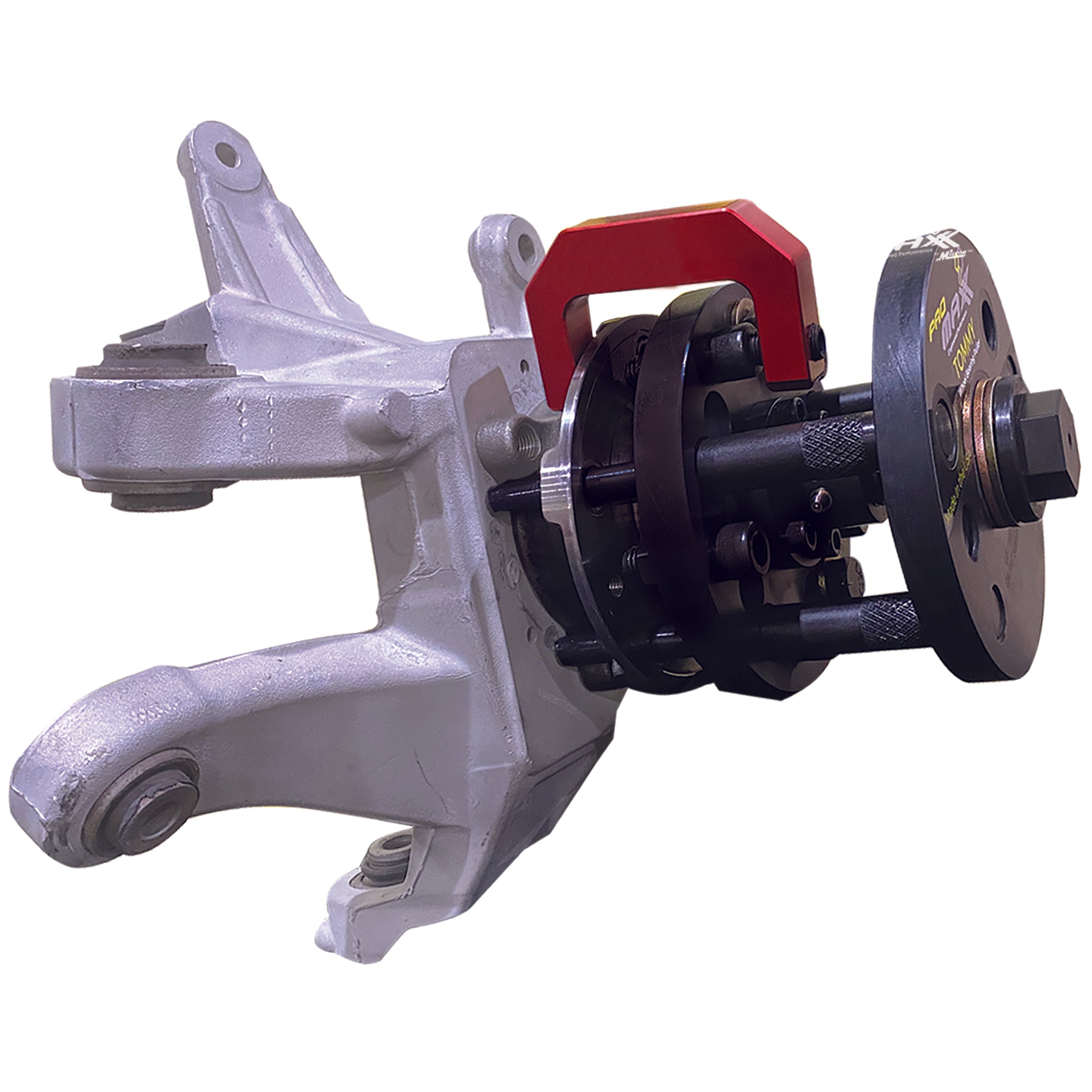
#5 Wheel Bearing Puller Hub Removal Kits
Domain Est. 1998
Website: steckmfg.com
Key Highlights: Unlock ultimate performance with the Tommy Wheel Bearing Hub Puller, engineered specifically for select Ford and Subaru models….
#6 Pullers & Installers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: lislecorp.com
Key Highlights: The alternator decoupler pulley tool kit includes all of the tools required for removal and installation of ADP (one way and overriding/freewheeling)….
#7 Wheel Bearing Press Tool Kit
Domain Est. 2004
#8 Wheel Bearing Puller Removal Tools
Domain Est. 2012
Website: orionmotortech.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $59With Orion Motor Tech’s bearing tools like bearing puller tools, bearing splitter, you’ll tackle bearing problems more safely, easily, and efficiently….
#9 Wheel bearings
Domain Est. 2017
Expert Sourcing Insights for Wheel Bearing Hub Removal Tool
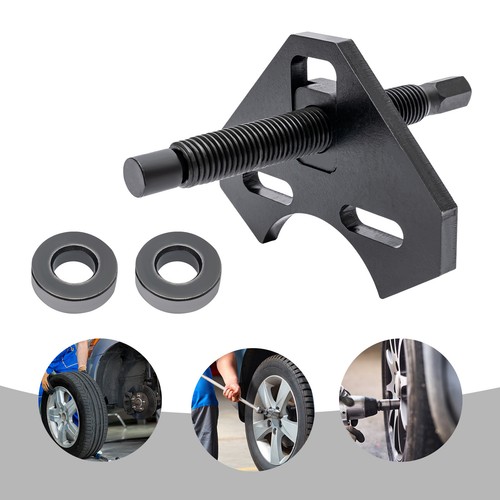

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Wheel Bearing Hub Removal Tool
The global market for wheel bearing hub removal tools is projected to experience steady growth and notable transformation by 2026, driven by evolving automotive service demands, technological advancements, and shifts in vehicle manufacturing. Several key trends are expected to shape the industry landscape in the coming years.
1. Rising Demand from the Automotive Aftermarket
As vehicle ownership continues to rise globally—especially in emerging economies—the automotive aftermarket is expanding. Increased vehicle age and mileage are leading to higher maintenance and repair frequency, particularly for components like wheel bearings. This trend is fueling demand for specialized tools such as wheel bearing hub removal tools, as both professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts seek efficient and reliable solutions.
2. Growth in Electric and Hybrid Vehicle Maintenance
With the accelerated adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles (EVs/HEVs), repair shops are adapting to new maintenance requirements. Although EVs have fewer moving parts, they still utilize wheel bearings that require servicing. However, their heavier weight due to batteries can lead to faster wear on suspension and wheel components. This necessitates robust, heavy-duty removal tools, prompting tool manufacturers to innovate for high-torque applications compatible with EV platforms.
3. Technological Advancements in Tool Design
By 2026, wheel bearing hub removal tools are expected to incorporate advanced materials (such as high-strength alloys and composite handles) and ergonomic designs to improve user safety and efficiency. Hydraulic and powered variants are gaining market share over traditional manual tools, offering faster operation and reduced labor intensity. Integration with digital diagnostics or smart tools may also begin to emerge, especially in professional repair environments.
4. Expansion of E-Commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Sales
Online marketplaces like Amazon, eBay, and specialized automotive tool retailers are becoming dominant sales channels. This shift enables broader access to professional-grade tools for independent mechanics and hobbyists. Brands are investing in digital marketing and customer education to capture online demand, with an emphasis on product compatibility, ease of use, and durability.
5. Regional Market Growth Dynamics
Asia-Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing region due to increasing vehicle production and repair infrastructure in countries like China, India, and Indonesia. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand, supported by well-established automotive service networks and stringent safety regulations requiring regular wheel system inspections. Latin America and the Middle East are also emerging as promising markets due to rising vehicle fleets and growing technical service capacity.
6. Focus on Multi-Vehicle Compatibility and Universal Kits
Tool manufacturers are increasingly offering universal or adaptable wheel bearing hub removal kits that support a wide range of vehicle makes and models. This trend responds to the need for cost-effective solutions in multi-brand repair shops and aligns with the growing diversity of vehicles on the road.
7. Emphasis on Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Workplace safety standards are tightening globally, prompting demand for tools that reduce injury risk during hub removal—a process that involves high pressure and force. Tools with built-in safety mechanisms, clear usage instructions, and compliance with ISO or ANSI standards will gain preference among professional users and fleet maintenance providers.
Conclusion
By 2026, the wheel bearing hub removal tool market will be defined by innovation, accessibility, and responsiveness to changing vehicle technologies. Stakeholders—including manufacturers, distributors, and service providers—must align with these trends to remain competitive, focusing on quality, versatility, and customer-centric design to meet the evolving needs of the global automotive repair ecosystem.
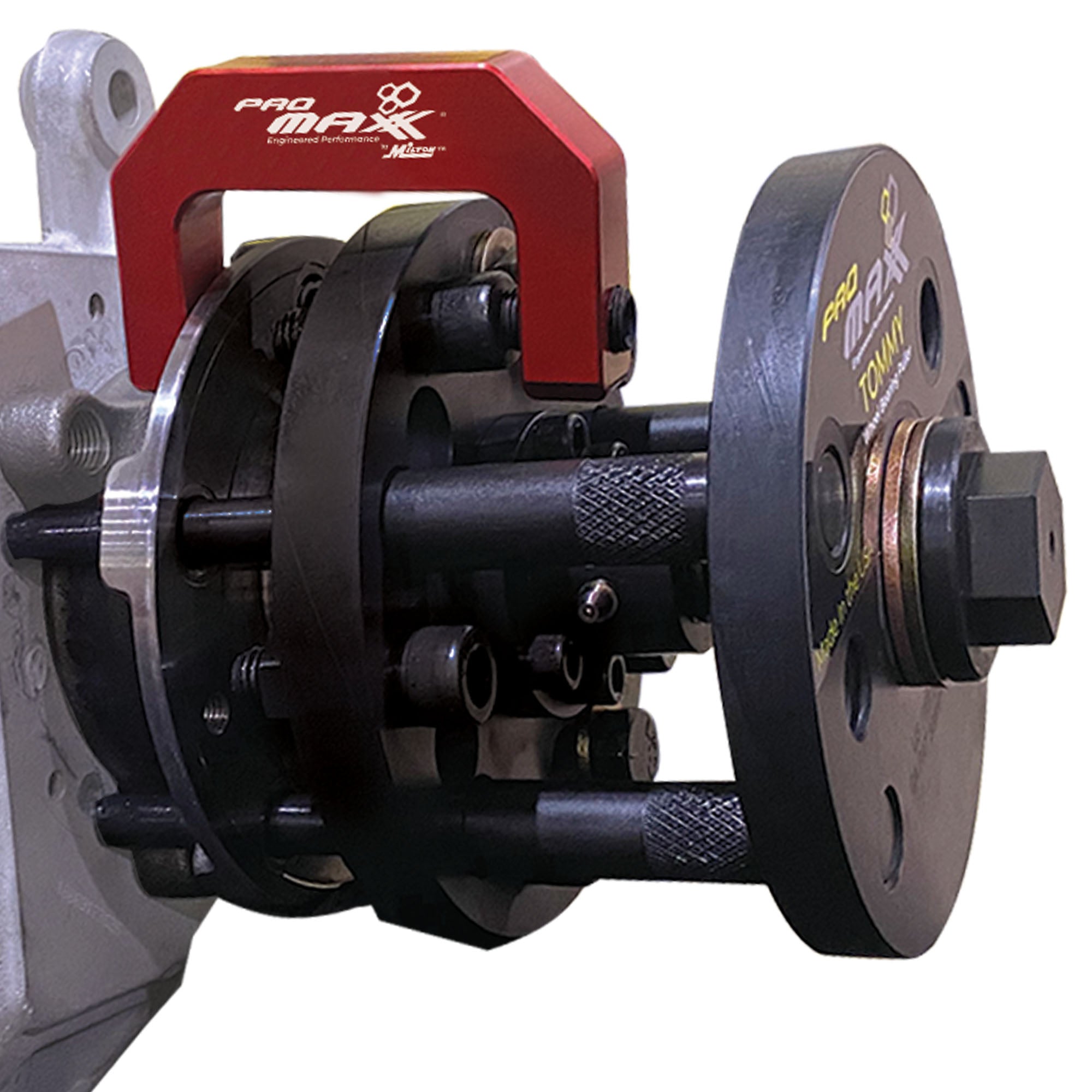

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Wheel Bearing Hub Removal Tool (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a wheel bearing hub removal tool involves more than just finding the lowest price—overlooking quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns can lead to costly failures, safety risks, and legal complications. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Material Quality and Construction
Many low-cost tools are made from substandard steel or lack proper heat treatment, resulting in tools that deform, crack, or fail under pressure. This not only reduces tool lifespan but also poses safety hazards during use. Always verify material specifications (e.g., chrome vanadium steel) and look for signs of robust manufacturing, such as precise threading and clean welds.
Inaccurate Dimensions and Compatibility Issues
Off-brand or counterfeit tools often have dimensional inaccuracies, leading to improper fitment with common hub assemblies (e.g., Ford, GM, Toyota). This can damage the hub, spindle, or surrounding components. Ensure the tool is designed to meet OEM specifications and supports a wide range of vehicle applications.
Lack of Load Capacity Certification
High-force applications require tools rated for specific tonnage. Tools without load testing or certification may collapse under pressure, risking injury. Confirm that the supplier provides load capacity data and compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO or DIN).
Intellectual Property Infringement
Some suppliers produce tools that closely mimic patented designs from reputable brands (e.g., OTC, Arcan, or Lisle). Using or distributing such tools can expose your business to legal action for IP infringement. Always source from legitimate manufacturers and request proof of IP compliance or licensing when necessary.
Inadequate Branding and Traceability
Rebranded or unbranded tools from gray-market suppliers may lack traceability, making warranty claims or quality investigations difficult. Tools without clear manufacturer markings or batch numbers hinder accountability in case of defects.
Overlooking Safety Design Features
High-quality tools include safety features such as retaining rings, threaded collars, or overload protection. Cheaper alternatives often omit these, increasing the risk of sudden component ejection during operation. Prioritize tools engineered with user safety in mind.
Insufficient Supplier Vetting
Sourcing from unknown or unverified suppliers—especially on open marketplaces—increases the risk of receiving counterfeit or non-compliant products. Conduct due diligence: request samples, audit manufacturing facilities, and verify certifications like ISO 9001.
By addressing these pitfalls early, businesses can ensure they procure reliable, safe, and legally compliant wheel bearing hub removal tools that support efficient operations and protect brand integrity.
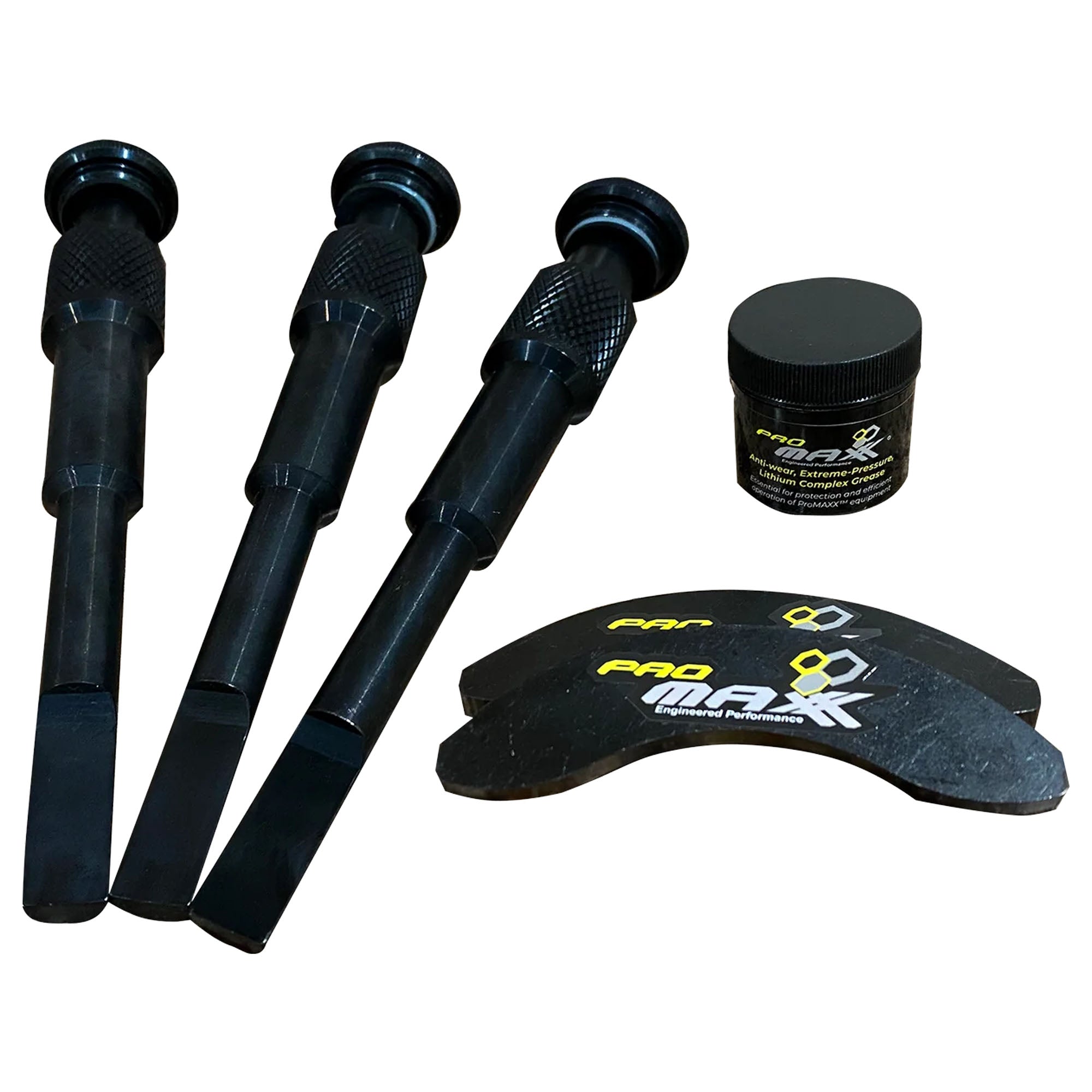

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Wheel Bearing Hub Removal Tool
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the distribution, handling, and use of a Wheel Bearing Hub Removal Tool. Adherence to these guidelines ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and efficient supply chain operations.
Product Classification & Regulatory Compliance
The Wheel Bearing Hub Removal Tool is classified as an automotive mechanical repair tool. It is not subject to hazardous materials regulations under DOT, IATA, or IMDG when shipped in its standard packaging. Ensure compliance with the following:
- CE Marking (if applicable for EU markets): Confirm conformity with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and applicable EN standards for mechanical tools. Technical documentation must be available upon request.
- REACH & RoHS Compliance: Verify that materials used in manufacturing (e.g., steel, coatings) comply with EU REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives.
- Country-Specific Standards: For markets such as the U.S., ensure alignment with ANSI or other relevant safety standards for hand tools. In Canada, check compliance with CSA Group standards.
Packaging & Shipping Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage during transit and ensure safe handling.
- Packaging Specifications: Ship in sturdy corrugated cardboard boxes with internal foam or molded pulp inserts to immobilize the tool. Include a UPC barcode and product identification label on the exterior.
- Weight & Dimensions: Standard unit dimensions: 12” x 6” x 3” (LxWxH), weight: 3.2 lbs (1.45 kg). Palletized shipments should not exceed 50 units per pallet (max load: 160 lbs).
- Shipping Classification: Non-hazardous goods. Suitable for standard ground and air freight. No special handling required.
- Labeling: Each package must display:
- Product name and model number
- Manufacturer/supplier information
- “Fragile – Handle With Care” if applicable
- Barcodes for inventory tracking
Import/Export Documentation
For international shipments, ensure all required documentation is complete and accurate.
- Commercial Invoice: Must include product description, HTS code (e.g., 8207.90.90 – Tools for working in the hand, other), country of origin, unit value, and total shipment value.
- Packing List: Itemize quantity, weight, and dimensions per package.
- Certificate of Origin: Required for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU FTAs).
- HTS Code Guidance: Confirm local tariff classification; typical classification falls under Chapter 82 (Tools) of the Harmonized Tariff Schedule.
Storage & Handling Guidelines
- Storage Conditions: Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (40°F to 90°F / 4°C to 32°C). Avoid exposure to moisture or corrosive chemicals to prevent rust.
- Handling: Use appropriate lifting techniques for pallets. No special protective gear required for handling packaging, but gloves are recommended during unpacking to prevent cuts from cardboard edges.
- Shelf Life: Indefinite, provided storage conditions are maintained. Inspect tools periodically for signs of corrosion or damage.
Safety & User Compliance
While the tool itself poses minimal risk when packaged, end-user safety is critical.
- Instruction Manual: Include a multilingual instruction sheet outlining proper use, torque specifications, and safety warnings (e.g., wear eye protection, ensure vehicle is securely lifted).
- Compliance with OSHA/Workplace Safety: Distributors and repair shops must follow local occupational safety regulations when using the tool. Ensure users are trained in safe automotive repair practices.
- Product Liability: Maintain records of design validation, quality control, and customer complaints. Register product with relevant safety authorities if required.
Warranty & Recalls
- Standard Warranty: 1-year limited warranty against manufacturing defects. Exclude damage from misuse or improper installation.
- Recall Protocol: In the event of a safety issue, follow ISO 10397 or equivalent recall procedures. Notify distributors, customers, and relevant authorities (e.g., CPSC in the U.S.) promptly. Maintain traceability via batch/lot numbers.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
- End-of-Life Disposal: The tool is made primarily of recyclable steel. Advise users to dispose of through metal recycling programs in accordance with local waste regulations.
- Sustainability: Packaging materials should be recyclable. Avoid single-use plastics where possible.
Adherence to this logistics and compliance guide ensures safe, legal, and efficient movement of the Wheel Bearing Hub Removal Tool from manufacturer to end user. Regular audits and updates to regulatory requirements are recommended.
In conclusion, sourcing a reliable wheel bearing hub removal tool is essential for efficient and safe automotive maintenance and repair. After evaluating various options, it is clear that selecting a high-quality, durable, and compatible tool—whether manual, hydraulic, or pneumatic—can significantly improve productivity, reduce labor time, and minimize the risk of damage to components. Factors such as vehicle make and model, tool compatibility, build quality, and user reviews should all be considered when making a purchase. Investing in a reputable brand or professional-grade kit not only ensures long-term value but also supports precise and consistent results. Whether for a professional mechanic or a dedicated DIY enthusiast, the right wheel bearing hub removal tool is a worthwhile addition to any toolkit.