The global printer market continues to expand, driven by evolving printing technologies and sustained demand across home, office, and industrial environments. According to Mordor Intelligence, the printer market was valued at USD 53.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.1% from 2024 to 2029, fueled by advancements in connectivity, energy efficiency, and shifting user preferences between laser and inkjet technologies. As businesses and consumers weigh print quality, cost per page, speed, and durability, the rivalry between leading laser and inkjet manufacturers intensifies. This analysis identifies the top eight manufacturers shaping the competitive landscape—evaluating performance, innovation, and market reach—against the backdrop of this steady industry growth.
Top 8 What’S Better Laser Or Inkjet Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Inkjet vs Laser Printers
Website: brother-usa.com
Key Highlights: Inkjet printers are typically less expensive to purchase while laser printers may cost more to buy initially, but generally have a lower total cost of ownership ……
#2 Laser vs Inkjet Printers
Website: laserfast.com.au
Key Highlights: Laser printers generally excel in speed and handling large volumes. They can print significantly faster, often producing 20-40 pages per minute, ……
#3 Inkjet Printer and Laser Marker
Website: telesis.com
Key Highlights: Laser markers are fast and powerful, and their rapid printing speeds make them the ideal choice for large-scale printing applications….
#4 Laser Printer vs Ink jet Printer
Website: notaryrotary.com
Key Highlights: “Use of a laser printer is preferred over an inkjet printer, since the ink from an inkjet printer ia less permanent and may smudge. The Notary ……
#5 Inkjet printers vs Laser – General/Relocating
Website: vimovingcenter.com
Key Highlights: A laser on the other hand may cost a bit more up front. You can get a color laserjet starting at about $150. The toner costs about double that ……
#6 Know the Difference
Website: blog.chasecorp.com
Key Highlights: It’s important to note that laser printing is ideal for applications that have more text than images, like official documents or books….
#7 Laser vs. Inkjet Printers
Website: newspower.com.au
Key Highlights: Budget and Long-Term Costs: While inkjet printers have lower upfront costs, laser printers may provide more value over time due to lower operational costs….
#8 Inkjet vs. Laser Printers: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing …
Website: sharp.com.hk
Key Highlights: Each type of printer offers unique advantages and disadvantages that need careful consideration, from price and printing speed to print quality….
Expert Sourcing Insights for What’S Better Laser Or Inkjet

H2: 2026 Market Trends – Laser vs. Inkjet Printers: Which Is Better?
As we approach 2026, the debate between laser and inkjet printers continues to evolve, shaped by technological advancements, shifting consumer demands, and workplace transformation. Both printer types maintain strong market positions, but emerging trends indicate a nuanced answer to the question: What’s better—laser or inkjet? The answer increasingly depends on use case, cost structure, and environmental considerations.
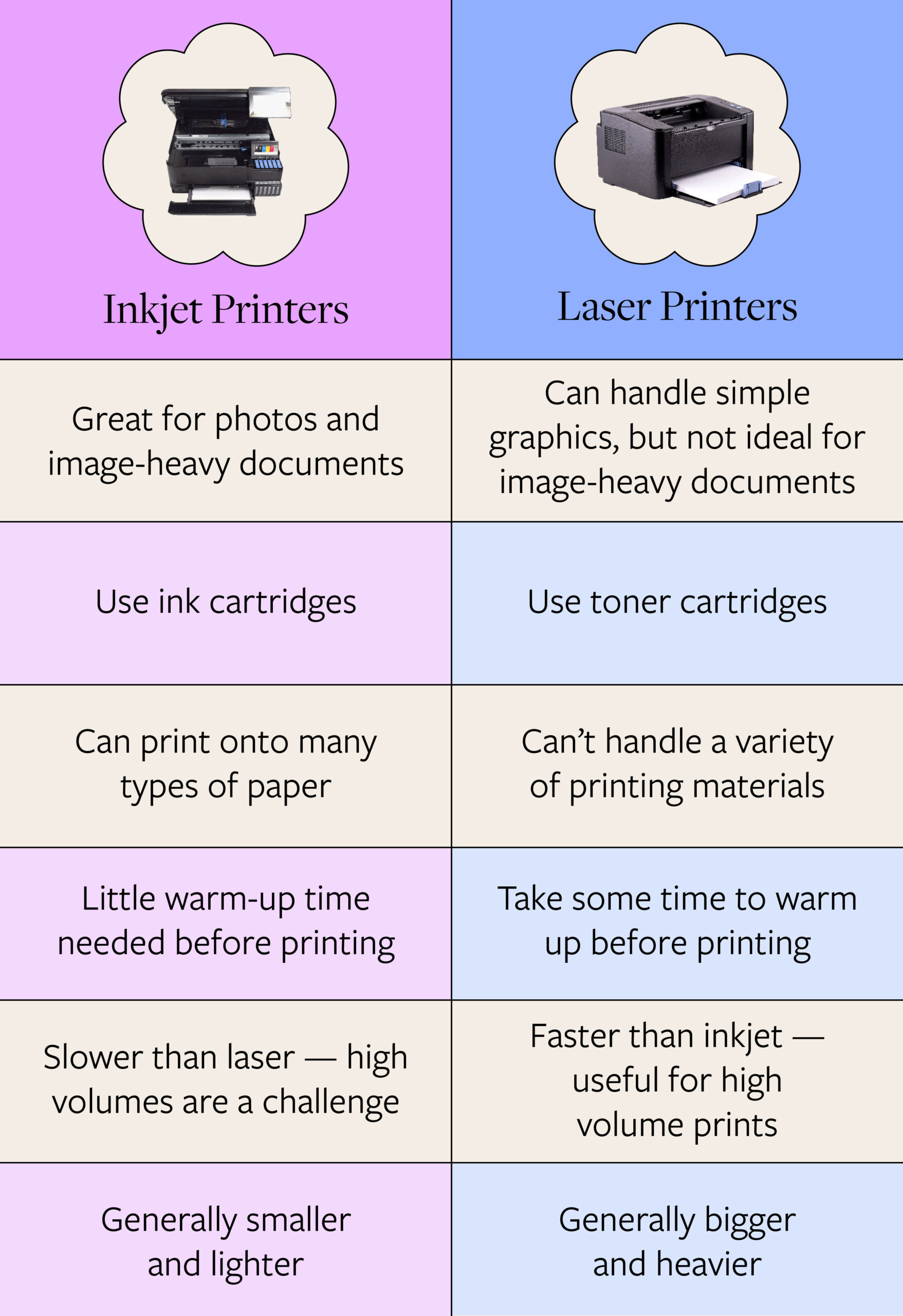
1. Print Volume and Speed: Laser Printers Still Lead for High-Volume Users
Laser printers remain the preferred choice for offices and businesses with high print volumes. Their faster print speeds (typically 20–50 pages per minute) and higher duty cycles make them ideal for environments requiring consistent output. Market analysts project continued dominance of laser printers in corporate and educational sectors through 2026, especially with the rise of hybrid work models increasing demand for reliable in-office printing infrastructure.
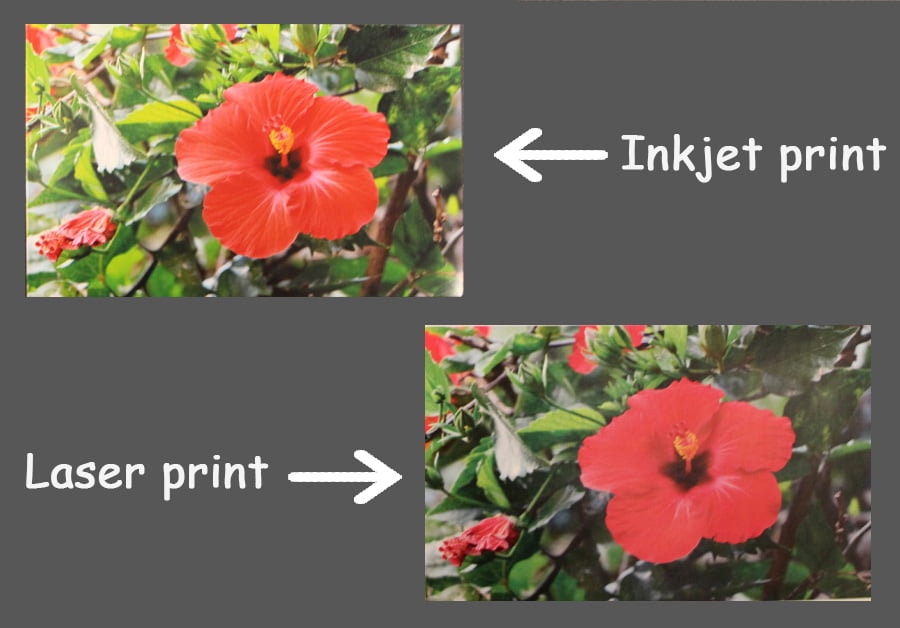
2. Photo and Color Quality: Inkjet Printers Maintain Superiority
Inkjet technology continues to outperform laser printers in color accuracy, photo printing, and fine-art reproduction. With advancements in pigment inks and precision droplet control, inkjet printers now offer near-lab-quality photo output—making them the go-to for photographers, designers, and home users. By 2026, inkjet is expected to further consolidate its lead in the consumer creative market, particularly with the growth of home-based creative businesses and personalized printing.
3. Cost of Ownership: A Shifting Landscape
Traditionally, laser printers had higher upfront costs but lower cost per page, especially for monochrome printing. However, modern inkjet models—especially those using high-capacity ink tanks (e.g., Epson EcoTank, HP Smart Tank)—have dramatically reduced long-term ink costs. By 2026, inkjet printers are projected to offer the lowest total cost of ownership for moderate-volume home and small office users. Meanwhile, laser printers remain cost-effective for high-volume black-and-white printing.
4. Environmental and Sustainability Trends
Sustainability is becoming a key differentiator. Inkjet printers generally consume less energy than laser models, as they don’t require heat to fuse toner. Additionally, cartridge-free ink systems reduce plastic waste. By 2026, eco-conscious consumers and businesses are expected to favor inkjets, especially as manufacturers emphasize recyclable materials and closed-loop ink recycling programs.
5. Connectivity and Smart Features
Both printer types are integrating advanced connectivity—Wi-Fi 6, cloud printing, mobile apps, and AI-powered diagnostics. However, inkjet manufacturers have been more aggressive in targeting smart home integration and app-based printing, appealing to younger demographics. Laser printers are catching up, particularly in secure printing and enterprise IoT integration, but inkjets currently lead in user-friendly smart features.
6. Market Share Projections for 2026
According to industry forecasts:
– The global inkjet printer market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% through 2026, driven by home office expansion and creative applications.
– The laser printer market will grow at a more moderate 3.1% CAGR, sustained by enterprise demand and durability.
Conclusion: It Depends on the Use Case
By 2026, neither laser nor inkjet printers will be universally “better.” Instead:
– Choose laser for high-volume, text-heavy, monochrome printing in offices.
– Choose inkjet for photo quality, color creativity, low operating costs, and eco-friendly printing at home or in small offices.
Ultimately, the best choice hinges on specific needs, volume, and long-term goals—a trend toward personalized, use-case-driven decision-making that defines the 2026 printing landscape.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing: What’s Better, Laser or Inkjet? (Quality, IP)
When deciding between laser and inkjet printers for business or personal use, it’s easy to fall into common sourcing traps—especially when evaluating print quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Understanding these pitfalls helps ensure the right choice based on actual needs rather than assumptions.
Overlooking Total Cost of Ownership
A frequent mistake is focusing solely on the upfront purchase price. Inkjet printers often appear cheaper initially, but ongoing ink costs can be significantly higher per page. Conversely, laser printers have higher initial costs but offer lower cost-per-page, especially for high-volume text printing. Failing to calculate total cost—including toner, ink, maintenance, and paper usage—leads to poor long-term decisions.
Misjudging Print Quality Needs
Many users assume “higher resolution” always means better quality. While inkjets typically excel in photo and color graphics due to smoother gradients and wider color gamuts, laser printers produce sharper text and are more consistent for documents. Sourcing based on marketing claims without testing sample prints for your specific use case (e.g., reports vs. brochures) can result in mismatched performance.
Ignoring Duty Cycle and Volume Requirements
Inkjet printers are often designed for light to moderate use. Using them in high-volume office environments leads to frequent cartridge replacements, clogged printheads, and downtime. Laser printers handle high duty cycles more efficiently. Not aligning printer specs with actual usage volume is a common oversight that impacts productivity and longevity.
Underestimating IP and Security Risks
Both printer types can pose intellectual property risks if not managed properly. Networked printers—especially multifunction devices—can store sensitive documents in internal memory. Some lower-end inkjets and consumer lasers lack robust security features (like data encryption, secure boot, or user authentication), increasing the risk of data breaches. Overlooking built-in security and IP protection, particularly in shared or regulated environments, is a critical pitfall.
Neglecting Environmental and Operational Factors
Inkjets are sensitive to infrequent use, leading to dried ink and nozzle clogs. Lasers generate more heat and may not be ideal for small, poorly ventilated spaces. Additionally, toner and ink cartridges have different environmental footprints and disposal requirements. Ignoring these operational factors affects reliability and sustainability goals.
Assuming All Inkjets or Lasers Are Equal
There’s a wide variance in quality and features across models. Business-grade inkjets (e.g., EcoTank or business inkjet models) offer durability and lower running costs, while entry-level lasers may lack advanced features. Treating “inkjet” or “laser” as monolithic categories without comparing specific models leads to suboptimal sourcing decisions.
Conclusion
Choosing between laser and inkjet requires more than a simple quality comparison. Avoiding these common pitfalls—such as ignoring long-term costs, misjudging print needs, and overlooking IP security—ensures a sourcing decision that supports both performance and protection. Always match the printer type to your specific workflow, volume, security requirements, and quality expectations.
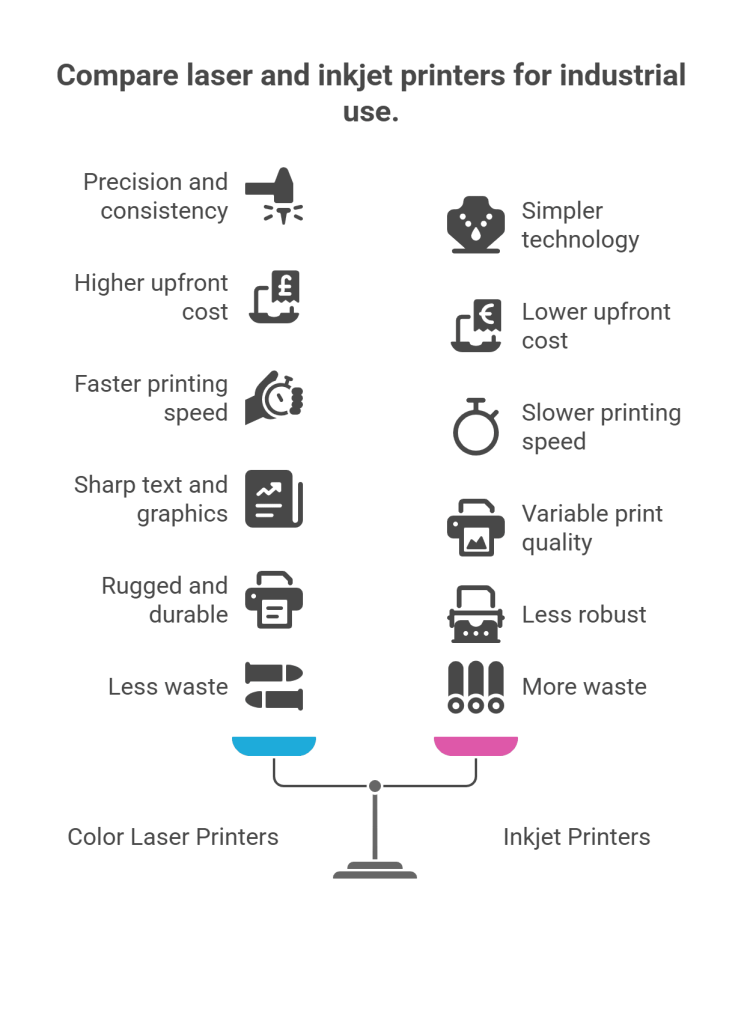
Logistics & Compliance Guide: What’s Better – Laser or Inkjet Printers?
When selecting between laser and inkjet printers for business or personal use, logistics and compliance considerations play a critical role. These factors influence total cost of ownership, environmental impact, safety, and regulatory adherence. Below is a structured comparison to help guide decision-making.
Printer Type Overview
Laser printers use toner powder and electrostatic charges to produce high-speed, high-volume prints, typically favored in office environments. Inkjet printers spray liquid ink onto paper and are commonly used for lower-volume, high-quality color printing, including photos and graphics.
Logistics Considerations
Supply Chain and Consumables Management
- Laser Printers:
- Toner Cartridges: Larger, more durable, and longer-lasting. Fewer replacements needed, reducing shipping frequency and inventory overhead.
- Supply Predictability: Higher yield per cartridge allows for more accurate forecasting and bulk ordering.
-
Storage: Toner is less sensitive to temperature and humidity than ink, simplifying storage logistics.
-
Inkjet Printers:
- Ink Cartridges: Smaller, more frequent replacements required. Higher risk of stockouts due to shorter shelf life.
- Perishability: Ink can dry out or clog if not used regularly, leading to waste and increased replacement needs.
- Shipping Frequency: Higher due to frequent replenishment, increasing transportation costs and carbon footprint.
Maintenance and Downtime
- Laser Printers:
- Generally more reliable for continuous use.
- Less prone to print head clogging, reducing maintenance downtime.
-
Higher initial cost but lower long-term service frequency.
-
Inkjet Printers:
- Prone to nozzle clogging, especially with infrequent use.
- Requires regular cleaning cycles, wasting ink and increasing operational costs.
- Higher support needs may increase technician dispatches and service logistics.
Compliance Considerations
Environmental Regulations
- Waste Management (E-Waste and Consumables):
- Both toner and ink cartridges are classified as hazardous waste in many jurisdictions due to chemical content.
- Laser: Toner cartridges are often larger and contain more waste per unit but are replaced less frequently.
- Inkjet: Higher volume of small cartridges increases collection, recycling, and disposal complexity.
- Compliance Tip: Ensure participation in manufacturer take-back programs (e.g., HP Planet Partners, Brother Cartridge Collection) to meet WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) and local recycling mandates.
Air Quality and Emissions
- Laser Printers:
- May emit ultrafine particles (UFPs) and ozone during operation, especially older models.
-
OSHA and EPA guidelines recommend proper ventilation and use of printers with certified low-emission ratings (e.g., EPEAT, Blue Angel).
-
Inkjet Printers:
- Generally emit fewer airborne particles.
- Solvent-based inks (used in industrial inkjet) may release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), requiring proper ventilation and SDS (Safety Data Sheet) compliance.
Energy Efficiency and Carbon Footprint
- Energy Use:
- Laser printers consume more energy due to heating fusers, especially during warm-up.
- ENERGY STAR® certified laser and inkjet models help meet energy compliance standards.
- Carbon Reporting:
- Organizations tracking Scope 2 emissions should account for printer energy usage.
- Inkjet printers typically have lower energy consumption, favoring sustainability goals.
Regulatory Certifications
Ensure printers meet regional compliance standards:
– FCC (USA): Electromagnetic interference.
– CE (EU): Safety, health, and environmental requirements.
– RoHS (EU): Restriction of hazardous substances in electronics.
– REACH: Chemical safety in printer components and consumables.
Recommendations for Logistics and Compliance Teams
- Assess Print Volume and Use Case:
- High-volume offices: Laser printers reduce logistics burden and compliance risks.
-
Low-volume or color-intensive tasks: Inkjet may suffice but requires tighter inventory control.
-
Implement a Printer Lifecycle Program:
- Track usage, maintenance, and disposal.
-
Use managed print services (MPS) for automated supply replenishment and compliance reporting.
-
Prioritize Certified Equipment:
-
Choose ENERGY STAR, EPEAT, or Blue Angel certified models to ensure regulatory alignment.
-
Train Staff on Proper Handling:
-
Include procedures for cartridge disposal, spill response, and ventilation best practices.
-
Audit Consumables Supply Chain:
- Partner with vendors offering closed-loop recycling and transparent compliance documentation.
Conclusion
While inkjet printers offer flexibility and lower upfront costs, laser printers generally present fewer logistical challenges and stronger compliance alignment for medium to high-volume operations. Their durability, energy efficiency (in newer models), and reduced waste frequency support sustainable and compliant fleet management. However, specific use cases—such as graphic design or remote offices with intermittent printing—may still favor inkjet, provided proper compliance protocols are in place.
When deciding between laser and inkjet printers for sourcing, the better choice depends on your specific needs and usage patterns:
-
Laser printers are generally better for high-volume printing environments, especially in offices. They offer faster print speeds, lower cost per page (particularly for black-and-white documents), and higher reliability for consistent, text-heavy printing. They are more cost-effective over time for large print volumes.
-
Inkjet printers are ideal for users who require high-quality color prints (such as photos, graphics, or marketing materials), print infrequently, or have limited space and budget. While inkjet printers typically have lower upfront costs, they can be more expensive in the long run due to higher ink costs and slower print speeds.
Conclusion:
For high-volume, fast, and cost-efficient document printing—especially in a business setting—laser printers are the better choice. For users needing high-quality color output, versatility, and lower initial cost—such as home users, students, or small creative businesses—inkjet printers may be more suitable. Evaluate your printing needs, volume, and long-term costs to make the most effective sourcing decision.