The global broaching machining market is experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand for precision metal components across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment manufacturing. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global machine tools market—under which broaching machining falls—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by advancements in automation and the rising adoption of high-precision machining techniques. Broaching, known for its ability to produce complex, high-tolerance shapes efficiently, remains a critical process in mass production environments. As industries prioritize accuracy, speed, and consistency, leading manufacturers continue to innovate in broach tool design, machine rigidity, and CNC integration. In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers has emerged at the forefront, setting benchmarks in performance, reliability, and technological advancement. Based on market presence, innovation, and customer reach, the following nine companies represent the top players shaping the future of broaching machining technology.
Top 9 What Is Broaching Machining Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 AXISCO
Domain Est. 2007
Website: twaxisco.com
Key Highlights: As the broach machine manufacturer in Taiwan, AXISCO stands with you to find broaching solutions and offers the best experience using our broaching ……
#2 Broaching Machine Specialties
Domain Est. 1996
Website: broachingmachine.com
Key Highlights: BMS stocks over 350 used broaching machines and broach sharpeners. All used machines are available as remanufactured turnkey systems….
#3 Pioneer Broach Company
Domain Est. 1996
Website: pioneerbroach.com
Key Highlights: Pioneer Broach Company designs & manufactures broaching machines in addition to also offering broach sharpening, reconditioning & other services….
#4 Broaches
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nidec.com
Key Highlights: The internal broach can make up the specific shape of work piece internal surface efficiently and with high precision….
#5 Broaching
Domain Est. 2001
Website: mechdev.com
Key Highlights: Mechanical Devices Company has been in the broach business for over 50 years. We also have a supplier network to source shaping, splining or large broaching….
#6 What Is Broaching and How Does It Work?
Domain Est. 2008
Website: tfgusa.com
Key Highlights: Broaching is a versatile and highly effective metal cutting process used to create intricate shapes and precise internal features in various workpieces….
#7 Production Broaching and Machining
Domain Est. 2009
Website: broachingservices.net
Key Highlights: Incorporated in 1946, Broaching Machine Specialties (BMS) provides new and remanufactured turnkey broaching systems for all broaching applications. Serving ……
#8 Gisstec Broaching, Angle Heads, Special Tools
Domain Est. 2011
Website: gisstec.com
Key Highlights: Top Broaching Tools, Live Broaching Units for Lathes, Angle Heads, Slim Angle Heads, Special Turning, Milling and Grooving Tools….
#9 What Is Broaching ? The Process, Uses, and Products
Domain Est. 2023
Website: broachingmach.com
Key Highlights: Broaching is a machining operation that removes material using a toothed tool known as a broach. There are two major forms of broaching: linear ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for What Is Broaching Machining
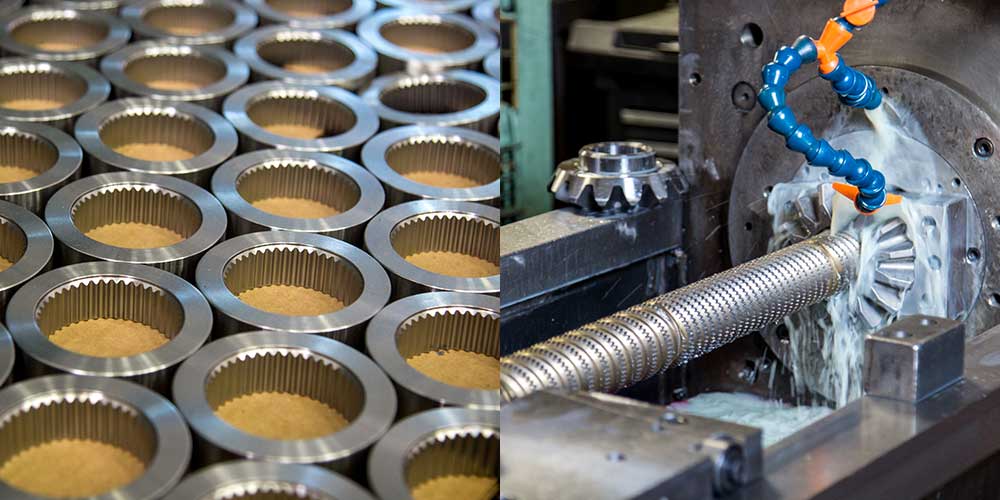

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Broaching Machining
As the manufacturing sector evolves through technological advancements and shifting industrial demands, broaching machining—a precision metal removal process used to produce complex shapes, keyways, splines, and internal/external forms—is anticipated to undergo significant transformation by 2026. Several macroeconomic, technological, and sector-specific trends are expected to shape the future of broaching machining in the coming years.
1. Growth in Automotive and Aerospace Industries
The automotive and aerospace sectors remain key drivers for broaching applications due to their reliance on high-precision components such as gear teeth, turbine blades, and transmission parts. With the continued rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and advancements in aerospace propulsion systems, demand for high-tolerance internal broaching operations is expected to increase. By 2026, manufacturers are projected to invest in advanced broaching solutions capable of handling new alloys and composites used in lightweight vehicle and aircraft design.
2. Integration of Automation and Smart Manufacturing
The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping traditional broaching operations. By 2026, automated broaching systems integrated with IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and predictive maintenance algorithms will become more prevalent. These smart broaching machines will offer improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced precision. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) broaching machines, in particular, are expected to dominate the market, supported by advancements in software for toolpath optimization and adaptive control.
3. Demand for Customization and High-Mix, Low-Volume Production
As industries shift toward customized and specialized components, broaching will benefit from its ability to produce complex geometries in a single pass. This efficiency makes broaching ideal for high-mix, low-volume manufacturing environments, especially in medical device and defense sectors. By 2026, modular broach tooling systems that allow quick changeovers and reconfiguration are expected to gain traction, enabling manufacturers to respond rapidly to evolving customer demands.
4. Advancements in Tool Materials and Coatings
The durability and performance of broach tools are being enhanced through the use of advanced materials such as carbide inserts and polycrystalline diamond (PCD), along with specialized coatings like TiAlN and DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon). These innovations reduce wear, extend tool life, and improve surface finish—critical factors for high-value applications. By 2026, the widespread adoption of these materials will support higher machining speeds and longer production runs, reducing operational costs.
5. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Initiatives
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt greener machining processes. Broaching, while inherently material-efficient due to its high accuracy and minimal waste, is expected to see further optimization in energy consumption and coolant usage. Closed-loop coolant systems, dry broaching techniques, and energy-efficient hydraulic or electromechanical broaching machines are projected to gain market share by 2026.
6. Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Localization
Global supply chain disruptions have prompted a trend toward regionalization of manufacturing, particularly in North America and Europe. This reshoring movement is expected to boost domestic demand for broaching equipment and services. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific—led by China, India, and Japan—will remain a major market due to expanding industrial infrastructure and growing automotive production, supporting continued investment in broaching technology.
7. Rising Adoption in Emerging Applications
Beyond traditional sectors, broaching is finding new applications in renewable energy (e.g., wind turbine components), robotics, and high-performance consumer goods. As these industries scale, the need for precision internal features will drive innovation in specialized broaching tools and machines. By 2026, niche broaching solutions tailored for these emerging markets are expected to represent a growing segment of the industry.
In summary, the broaching machining market in 2026 will be characterized by increased automation, material innovation, and adaptation to evolving industrial needs. While competition from alternative machining processes like milling and EDM persists, broaching’s unique advantages in speed, precision, and surface quality will ensure its relevance—especially in high-performance and custom manufacturing environments.
Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Broaching Machining Services (Quality, IP)
When sourcing broaching machining services, businesses often encounter critical challenges related to quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to costly delays, compromised product performance, and legal risks. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Quality Control Processes
Many suppliers lack robust quality assurance systems tailored to the precision demands of broaching. Broaching produces tight tolerances and complex geometries, making consistent quality essential. Pitfalls include insufficient in-process inspections, lack of certified metrology equipment, and failure to adhere to industry standards (e.g., ISO 9001). Without proper documentation and traceability, defects may go undetected until final assembly, resulting in part rejection or field failures.
Poor Material and Tooling Management
The performance of a broached component heavily depends on correct material selection and tool condition. Some suppliers cut costs by using substandard broach tools or failing to maintain them properly, leading to tool wear, dimensional inaccuracies, and surface finish defects. Additionally, improper material handling or heat treatment prior to broaching can compromise mechanical properties, especially in high-stress applications like aerospace or automotive components.
Incomplete Understanding of Broach Design Requirements
Broaching is highly design-specific—each broach is custom-made for a particular feature. Sourcing partners without deep experience may misinterpret engineering drawings or fail to account for critical factors such as chip load, rake angle, and broach progression. This can result in inefficient cutting, tool breakage, or non-conforming parts. Clear communication and engineering collaboration are essential to avoid costly design iterations.
Intellectual Property Exposure
Broach designs and part specifications often contain proprietary information. When outsourcing, companies risk IP theft if non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are absent or poorly enforced. Some suppliers may replicate tooling or share designs with third parties, especially in regions with weak IP enforcement. Without contractual safeguards and secure data handling practices, businesses may lose competitive advantage or face counterfeit parts in the market.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
High-integrity industries (e.g., medical, defense) require full traceability of materials, processes, and inspections. Some broaching vendors do not maintain detailed records of lot numbers, tooling used, or process parameters. This absence of documentation can lead to compliance failures during audits or product recalls, undermining certification and customer trust.
Choosing Vendors Based Solely on Price
Opting for the lowest-cost provider often leads to compromised quality and hidden costs. Low bids may reflect outdated machinery, untrained operators, or skipped quality steps. Investing in a reputable supplier with proven capabilities, modern broaching equipment, and a strong quality system ultimately reduces total cost of ownership and ensures long-term reliability.
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough supplier audits, require certifications, enforce IP protections, and maintain active engineering oversight throughout the sourcing process.
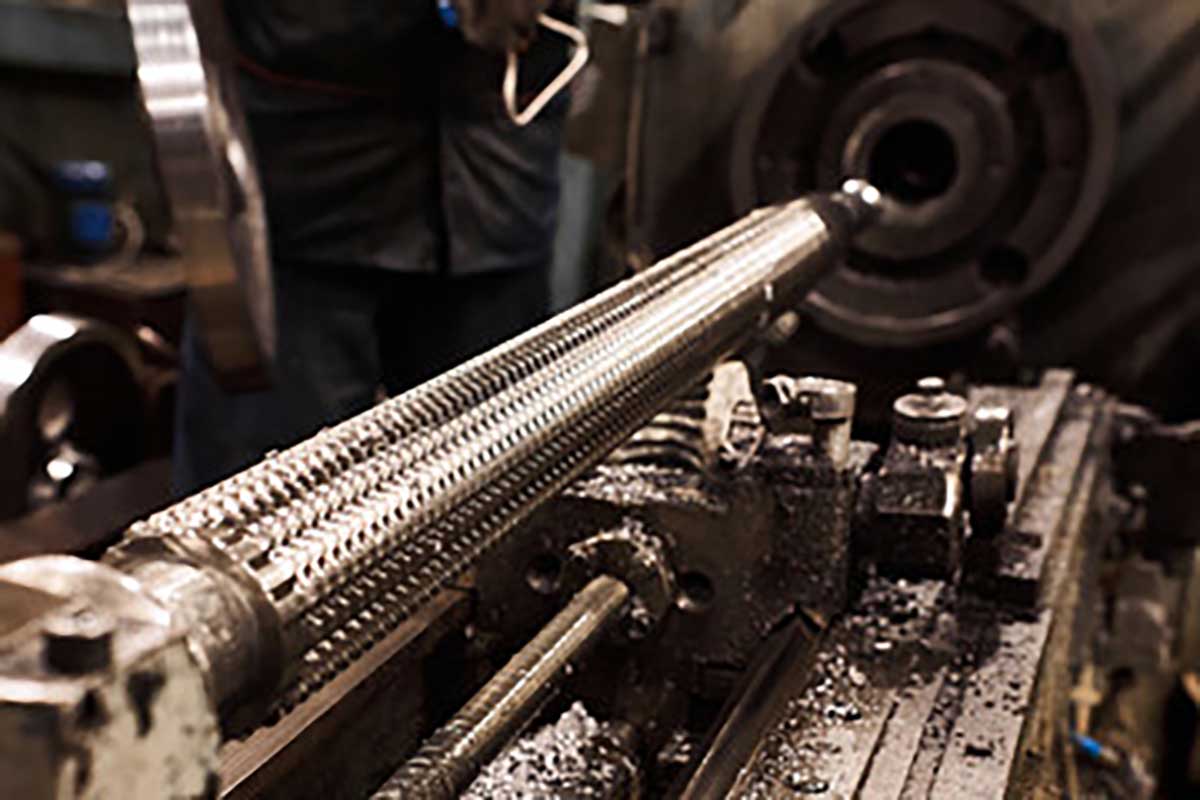

What Is Broaching Machining: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Overview of Broaching Machining
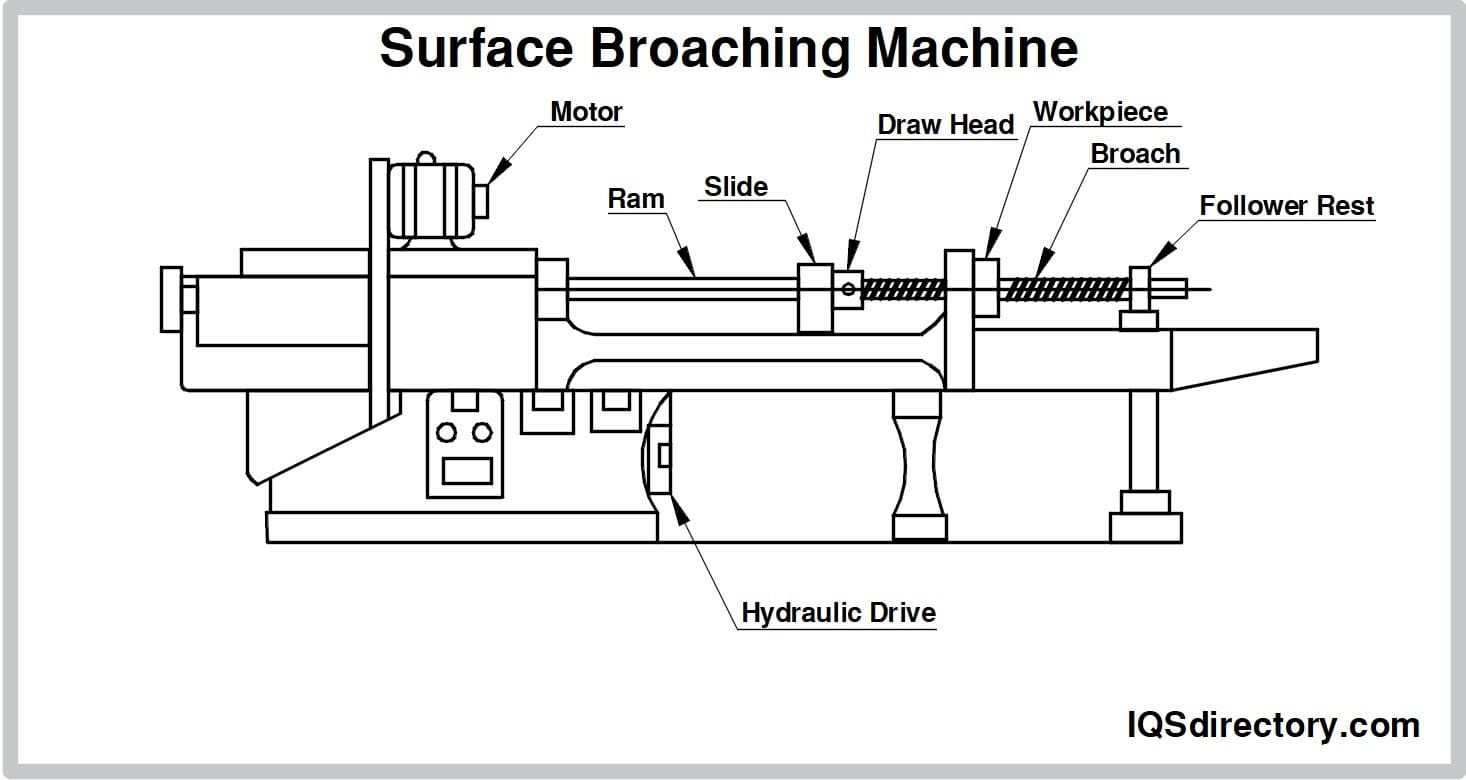
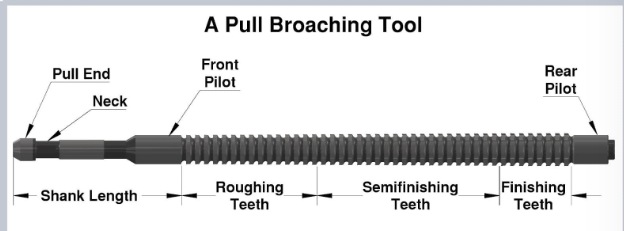
Broaching machining is a precision metalworking process that uses a toothed tool—called a broach—to remove material in a single linear pass. The broach features a series of progressively larger teeth that cut into the workpiece incrementally, achieving the desired shape, size, or surface finish. This method is commonly used for creating internal features such as keyways, splines, and gear teeth, or external forms like flat surfaces and contours.
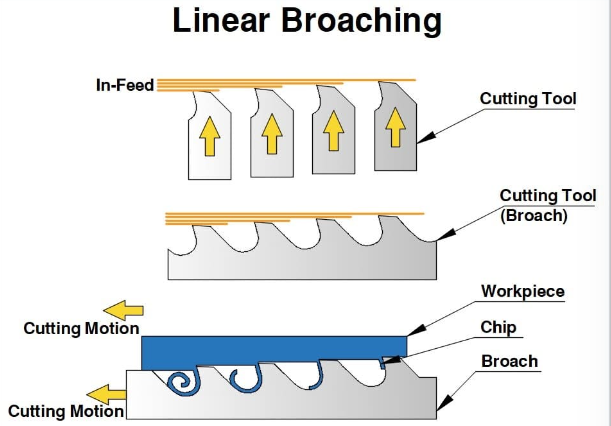
Types of Broaching
Internal Broaching
Used to cut internal shapes such as keyways in gears, splines in shafts, or square/rectangular holes. The broach is pulled or pushed through a pre-drilled hole, and each tooth removes a small amount of material until the final form is achieved.
External Broaching
Involves shaping the outer surface of a workpiece. This method is often used to create flat surfaces, contours, or notches. The workpiece is typically held stationary while the broach moves along it.
Surface Broaching
A specialized form of external broaching used to machine flat or contoured surfaces across multiple parts, often in high-volume production settings.
Equipment and Tooling Requirements
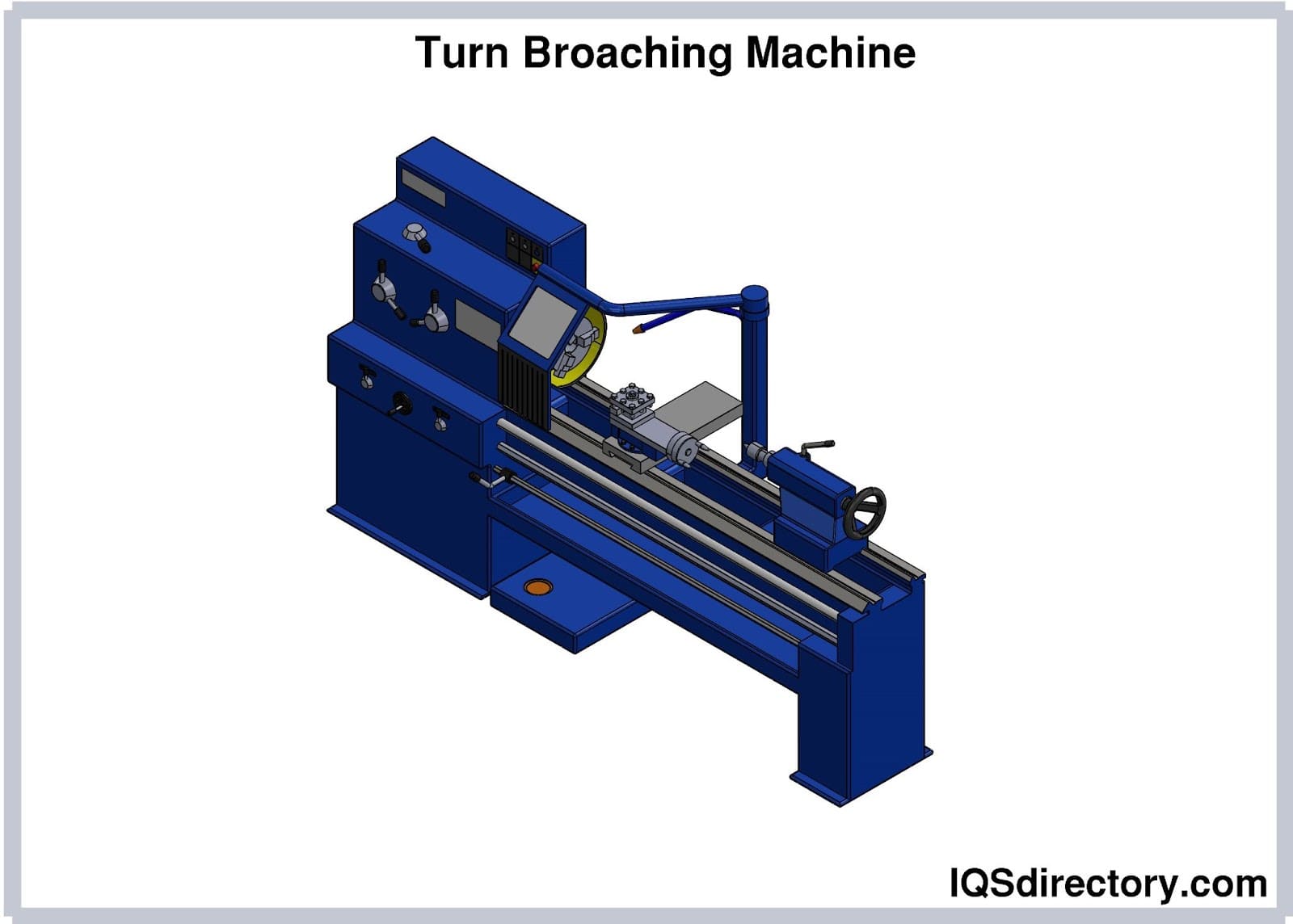
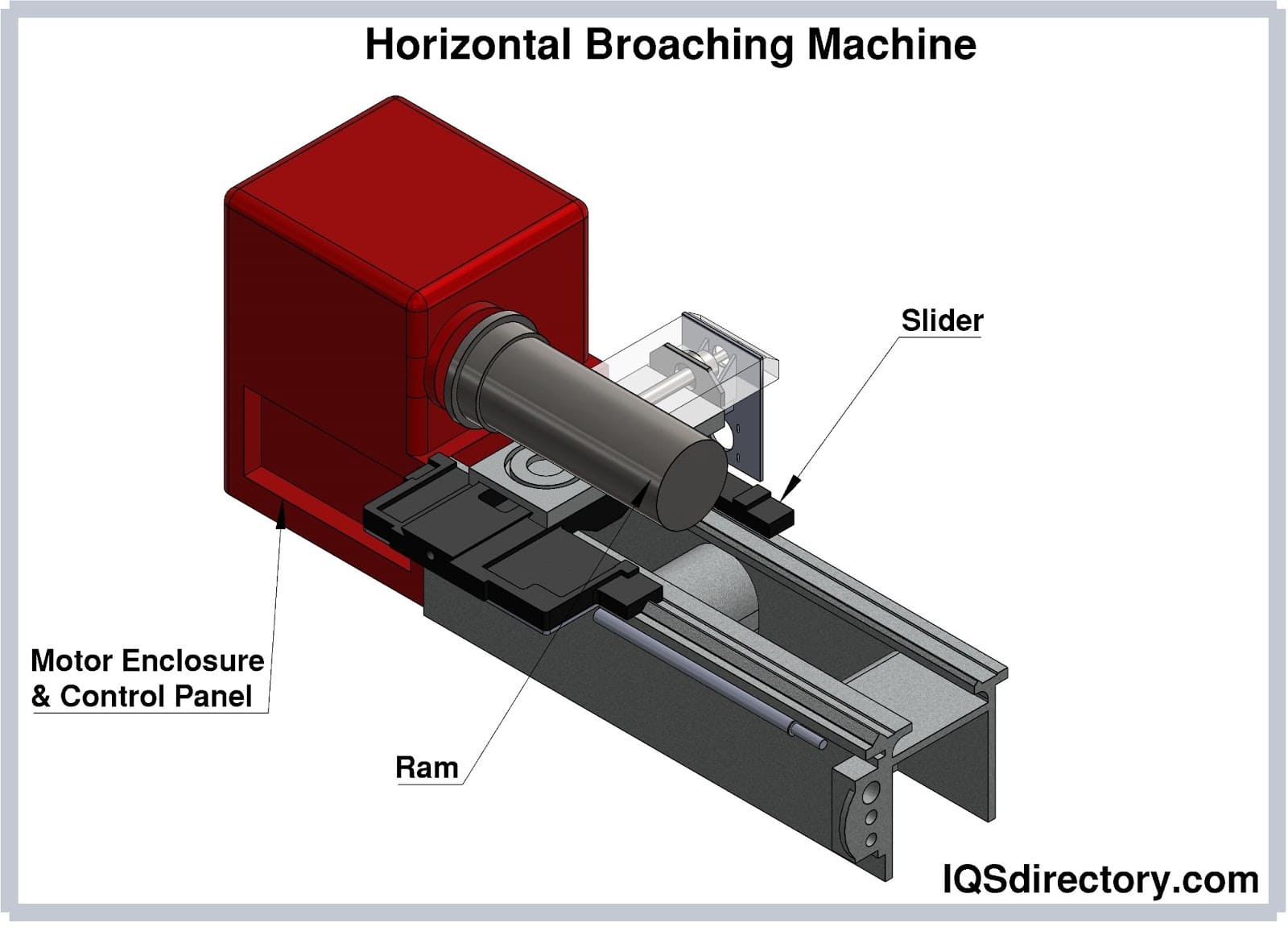
Broaching Machines
Broaching is performed on dedicated broaching machines, which can be vertical or horizontal, hydraulic or mechanical. Key considerations include:
– Stroke length and force capacity
– Machine rigidity and precision alignment
– Tool-holding mechanisms and workpiece fixtures
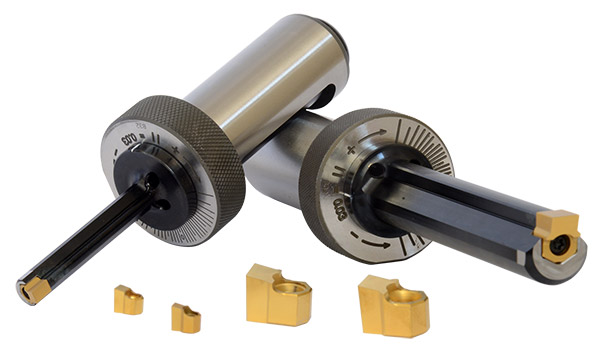
Broach Tooling
Broaches are custom-designed tools made from high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide. They must be precisely manufactured to ensure dimensional accuracy and tool life. Proper storage and handling are critical to prevent chipping or damage.
Material Compatibility
Broaching is suitable for a wide range of metals, including:
– Carbon steel
– Alloy steel
– Stainless steel
– Aluminum
– Brass and bronze
Material hardness should generally be below 35 HRC (Rockwell C scale) for optimal tool life and surface finish. Harder materials may require specialized broaches or pre-heat treatment.
Process Parameters and Best Practices
Cutting Speed
Broaching is typically a slow-speed process due to the high forces involved. Speeds range from 3 to 15 feet per minute (fpm), depending on the material and application.
Lubrication and Coolant
Use of cutting fluids or coolants is essential to:
– Reduce friction and heat
– Extend tool life
– Improve surface finish
– Flush away chips
Common coolants include soluble oil emulsions or synthetic fluids.
Chip Management
Broaching produces continuous chips. Proper chipbreakers on the broach and chip conveyors on the machine help prevent jamming and ensure smooth operation.
Logistics Considerations
Supply Chain and Sourcing
- Broaches are often custom-made; lead times can range from 4 to 12 weeks.
- Source broaches from certified suppliers with ISO 9001 or AS9100 compliance for critical applications.
- Maintain inventory of critical broaches to avoid production downtime.
Shipping and Handling
- Broaches are precision tools; use padded containers and shock-absorbing packaging.
- Clearly label packages as “Fragile – Precision Tools.”
- Track shipments using reliable carriers with tracking capabilities.
Inventory Management
- Store broaches in a dry, temperature-controlled environment.
- Use first-in, first-out (FIFO) rotation to prevent tool aging.
- Implement a tool tracking system (e.g., barcode or RFID) for traceability.
Safety and Compliance
Operator Safety
- Always use machine guards and emergency stop systems.
- Ensure proper training for setup, operation, and maintenance.
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE): safety glasses, gloves, and hearing protection.
Regulatory Compliance
- Comply with OSHA standards for machine guarding and workplace safety (29 CFR 1910.212).
- Adhere to ISO 14120:2015 for safety of machinery – Guards and protective devices.
- Follow local environmental regulations for coolant disposal and metalworking fluid management.
Environmental Compliance
- Recycle used cutting fluids through filtration or reprocessing systems.
- Dispose of metal chips and swarf according to local hazardous waste regulations.
- Implement spill containment procedures for coolants and lubricants.
Quality Control and Inspection
In-Process Monitoring
- Monitor broach wear using force sensors or acoustic emission systems.
- Check dimensional accuracy after every batch using gauges, CMMs, or optical comparators.
Final Inspection
- Verify critical dimensions such as bore diameter, keyway width, and surface finish.
- Use go/no-go gauges for high-volume production.
- Document inspection results for traceability and compliance audits.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Relevant standards include:
– ISO 1328-1:2013 – Cylindrical gears (for spline broaching)
– ANSI B94.19 – Broach tool nomenclature and dimensions
– ASME Y14.5 – Dimensioning and tolerancing for drawing specifications
For aerospace and defense applications, compliance with NADCAP (National Aerospace and Defense Contractors Accreditation Program) may be required.
Conclusion
Broaching machining is a highly efficient and precise method for producing complex shapes in high-volume manufacturing. Ensuring proper logistics, safety, and compliance practices is essential for maintaining quality, minimizing downtime, and meeting industry standards. By adhering to this guide, manufacturers can optimize broaching operations while remaining compliant with regulatory and environmental requirements.
Conclusion on Sourcing Broaching Machining Services
In conclusion, broaching machining is a highly specialized and efficient precision manufacturing process used to produce complex shapes, keyways, splines, and other intricate features in metal and sometimes plastic components. Due to the high initial cost of broach tools and the need for specialized machinery, broaching is most economical for medium to high-volume production runs. When sourcing broaching services, it is essential to partner with experienced manufacturers who possess the right equipment, technical expertise, and quality control processes to ensure dimensional accuracy and surface finish consistency.
Key considerations when sourcing broaching include the material being machined, part geometry, volume requirements, and tolerance specifications. Outsourcing to qualified job shops or contract manufacturers with proven broaching capabilities can provide cost-effective solutions without the need for significant in-house investment. Additionally, early collaboration with suppliers during the design phase can optimize part manufacturability and reduce lead times.
Ultimately, successful sourcing of broaching machining involves balancing precision, cost, and production efficiency—making it a critical process in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery where high-performance components are required.