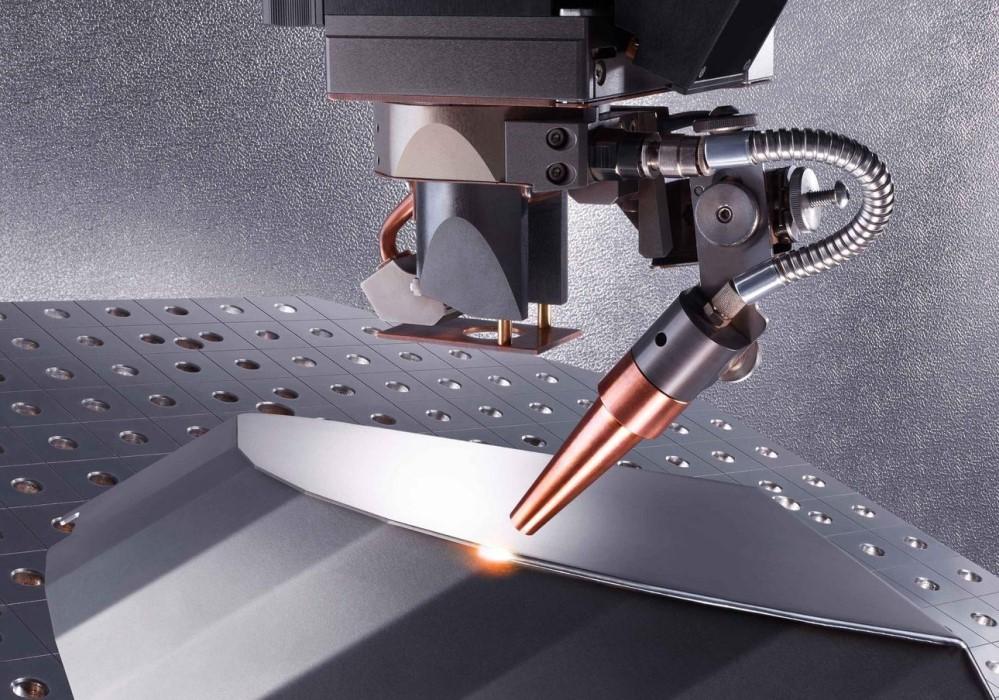
The global laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision joining solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the laser welding market was valued at USD 5.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 8.1 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of approximately 7.6% during the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising automation in manufacturing, and the growing adoption of lightweight materials that require precise, low-distortion welding techniques. As industries prioritize efficiency, speed, and weld quality, leading manufacturers are investing heavily in next-generation laser welding systems. In this evolving landscape, identifying the top players who combine innovation, reliability, and global reach becomes critical for businesses seeking competitive advantage. Below is a data-driven look at the top 10 laser welder manufacturers shaping the future of advanced manufacturing.
Top 10 What Is A Laser Welder Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#2 Laser Technology & Laser Machines from ALPHA LASER
Website: alphalaser.eu
Key Highlights: As a pioneer in the field of mobile laser welding, ALPHA LASER GmbH offers a wide range of high-quality laser welding devices. This includes laser welding ……
#3 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#4 Laser Machines
Website: lclasers.com
Key Highlights: Distribution and manufacture of laser machinery. Sales of laser marking, laser cleaning, laser engraving and welding machines….
#5 Everlast Inverter Welders Equipment
Website: everlastgenerators.com
Key Highlights: Everlast Power Equipment, manufacturers of MIG, TIG & Stick welders. For reliable welding machines and supplies shop Everlast Power Equipment….
#6 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is the process of transferring a laser beam’s energy in the form of heat to fuse or join parts. This transferred heat melts the materials to ……
#7 What is Laser Welding and How Does It Work?
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is a precise process that produces very little deformation compared to traditional welding methods….
#8 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: We specialise in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding, engraving, casting and cutting precious and non-precious metals….
#9 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
#10 Laser Welder
Website: laser-welder.net
Key Highlights: The simplest explanation is that a laser welder is basically a laser cutter with a control system added to move the laser beam in a pattern that distributes the ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for What Is A Laser Welder

H2: 2026 Market Trends for What Is A Laser Welder
As we approach 2026, the understanding and application of laser welders are undergoing significant transformation driven by technological innovation, industrial demand, and evolving manufacturing practices. A laser welder is a high-precision machine that uses a concentrated beam of light (laser) to join materials, typically metals or thermoplastics, by melting and fusing them together. This method offers advantages such as minimal heat distortion, high welding speed, and excellent repeatability—making it ideal for industries requiring precision and efficiency.
The market trends shaping the perception and adoption of laser welders by 2026 include:
-
Increased Automation and Integration with Smart Manufacturing
Laser welding systems are increasingly being integrated into automated production lines, especially within Industry 4.0 environments. By 2026, the convergence of laser welding with robotics, AI-driven monitoring, and Internet of Things (IoT) platforms is expected to enhance real-time quality control and predictive maintenance. This trend is redefining what a laser welder is—not just a standalone tool, but a core component of intelligent manufacturing ecosystems. -
Expansion in Electric Vehicle (EV) and Battery Manufacturing
The rapid growth of the electric vehicle sector is a major driver. Laser welders are essential for high-precision joining of battery components, such as cell tabs and busbars, where reliability and thermal management are critical. By 2026, the demand for compact, high-speed fiber laser welders tailored for EV battery packs is expected to surge, reshaping the market’s view of laser welding as an enabler of sustainable transportation. -
Advancements in Portable and Handheld Laser Welding Systems
Traditionally seen as large, fixed installations, laser welders are becoming more accessible with the rise of handheld and portable units. By 2026, these systems are expected to dominate small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) and field repair applications due to their ease of use, lower cost, and improved safety features. This shift is changing public and industrial perception—laser welders are no longer exclusive to high-tech factories but are becoming tools for broader craftsmanship and maintenance. -
Growth in Adoption Across Aerospace and Medical Devices
High-integrity industries continue to demand non-contact, high-precision joining solutions. In aerospace, laser welders are used for turbine components and lightweight alloys, while in the medical field, they enable micro-welding of surgical instruments and implants. By 2026, stricter regulatory standards and miniaturization trends will further increase reliance on laser welding, reinforcing its reputation for quality and reliability. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
As industries prioritize green manufacturing, laser welding is being evaluated not only for its precision but also for its energy efficiency and reduced material waste. By 2026, laser welders with improved wall-plug efficiency and recyclable component designs are expected to gain market share, aligning with global sustainability goals. -
Regional Market Expansion, Especially in Asia-Pacific
Countries like China, India, and South Korea are investing heavily in advanced manufacturing infrastructure. By 2026, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to lead in laser welder adoption, driven by electronics manufacturing, automotive production, and government initiatives promoting smart factories.
In summary, by 2026, the definition and role of a laser welder are expanding beyond traditional industrial welding. It is increasingly seen as a smart, versatile, and sustainable technology integral to next-generation manufacturing across diverse sectors.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Laser Welder (Quality, IP Protection)
Sourcing a laser welder involves more than just comparing prices and technical specs. Overlooking critical factors related to quality and intellectual property (IP) protection can lead to costly mistakes, operational inefficiencies, and legal risks. Here are the most common pitfalls to avoid:
Overlooking Build Quality and Component Reliability
Many buyers focus solely on laser power or speed, ignoring the overall build quality of the machine. Low-cost laser welders often use substandard materials, inferior optics, and unreliable motion systems, leading to frequent breakdowns, inconsistent welds, and high maintenance costs. It’s crucial to assess the manufacturer’s reputation, examine the quality of core components (like the laser source, cooling system, and control software), and request third-party certifications (e.g., CE, ISO) to ensure long-term reliability.
Ignoring IP Protection and Risk of Technology Leakage
When sourcing from overseas suppliers—especially in regions with less stringent IP enforcement—there’s a significant risk of technology replication or reverse engineering. Sharing proprietary weld parameters, fixture designs, or production processes during the integration phase can expose your competitive advantage. Always implement strict non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), limit the dissemination of sensitive data, and consider working with vendors that have verifiable IP compliance policies.
Failing to Verify Real-World Performance Claims
Suppliers often advertise impressive specifications under ideal lab conditions. However, actual performance in your production environment may differ drastically due to factors like ambient temperature, power stability, and material variability. Avoid taking claims at face value—insist on live demonstrations using your actual materials and joint configurations. Request references and case studies from existing customers in similar industries.
Underestimating After-Sales Support and Service Capabilities
A high-quality laser welder is only as good as the support behind it. Poor after-sales service, long response times, and lack of local technicians can halt production and increase downtime. When sourcing, evaluate the vendor’s service network, availability of spare parts, training programs, and software update policies. Choose a supplier with a proven track record of responsive technical support.
Assuming All “IP” Ratings Are Equal
Ingress Protection (IP) ratings indicate a system’s resistance to dust and moisture. In industrial environments, especially those with metal shavings, coolant, or high humidity, choosing a laser welder with an insufficient IP rating (e.g., IP54 vs. IP65) can result in system failures and safety hazards. Always match the IP rating to your specific working conditions and verify that the rating applies to the entire system—not just the laser head.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence, clear communication with suppliers, and a focus on total cost of ownership—not just initial price. Investing time upfront to assess quality and safeguard IP ensures a reliable, secure, and efficient laser welding solution.
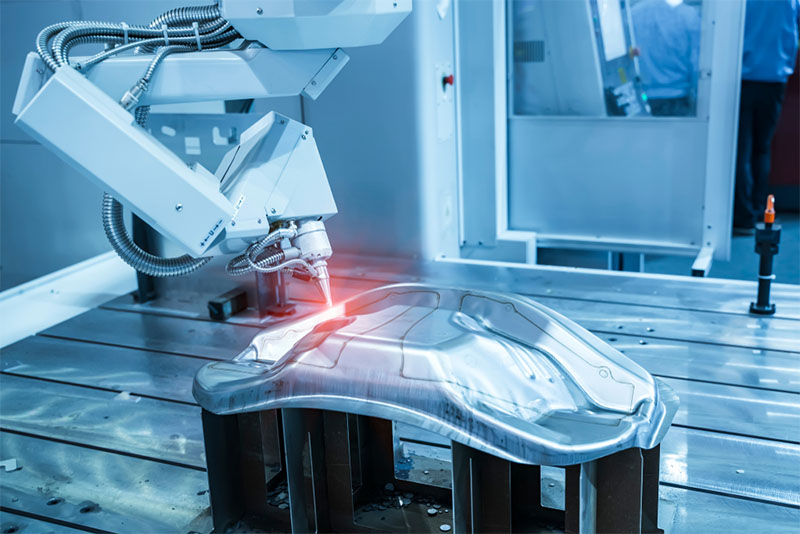

What Is A Laser Welder: Logistics & Compliance Guide
Understanding the logistics and compliance requirements for laser welders is essential for safe transportation, import/export, installation, and operation. This guide outlines key considerations for businesses acquiring or managing laser welding equipment.
Shipping and Transportation
Laser welders are precision industrial machines that require careful handling during transit. Use secure, climate-controlled freight services to prevent damage from moisture, temperature extremes, or physical shock. Ensure the equipment is properly crated with internal bracing and shock-absorbing materials. Clearly label crates with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” indicators. For international shipments, work with freight forwarders experienced in handling high-tech machinery to manage customs documentation and avoid delays.
Import/Export Regulations
Laser welding systems may be subject to export control regulations due to their technological sophistication. In the United States, verify if the laser welder falls under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) or International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR). Most industrial laser systems are classified under the Commerce Control List (CCL), often with an ECCN such as 2B201. Accurate classification is critical to determine licensing requirements for international shipment. Similarly, importing countries may have their own import controls, so ensure compliance with local customs authorities and provide technical specifications as needed.
Safety Standards and Certifications
Laser welders must comply with international and regional safety standards. Key certifications include:
– IEC 60825-1: International standard for laser product safety, classifying lasers by hazard level.
– CE Marking: Required for sale in the European Economic Area, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
– FDA/CDRH Compliance (U.S.): The U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health regulates laser products. Manufacturers must file a product report and include proper labeling.
– OSHA Guidelines: In the U.S., employers must follow OSHA recommendations for safe laser operation, including hazard controls and worker training.
Ensure the laser welder comes with a Certificate of Conformity and meets local regulations where it will be used.
Installation and Facility Requirements
Prepare your facility according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Laser welders often require:
– Stable power supply (voltage and phase compatibility)
– Adequate ventilation or fume extraction systems
– Sufficient space for operation and maintenance
– Laser-safe enclosures or interlocked work areas
– Proper grounding and EMI shielding
Designate a controlled access area with appropriate warning signs (e.g., “Laser in Use”) and install protective barriers to prevent unauthorized exposure to laser radiation.
Operator Training and Workplace Compliance
Only trained personnel should operate laser welding equipment. Provide comprehensive training covering:
– Laser safety procedures
– Emergency shutdown protocols
– Use of personal protective equipment (PPE), including laser safety goggles rated for the specific wavelength
– Maintenance and alignment processes
Maintain training records and establish a Laser Safety Officer (LSO) role if required by local regulations, especially for Class 3B or Class 4 laser systems.
Maintenance and Documentation
Keep detailed logs of maintenance, repairs, and safety inspections. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended service schedule to ensure reliable operation and compliance with warranty terms. Retain all compliance documentation, including user manuals, safety certifications, and calibration records, for audit purposes.
Disposal and End-of-Life
At end-of-life, dispose of the laser welder in accordance with environmental regulations. Components may include hazardous materials (e.g., cooling fluids, batteries, or electronic waste). Recycle or dispose through certified e-waste handlers, and follow local laws regarding the decommissioning of laser equipment.
Adhering to these logistics and compliance guidelines ensures the safe, legal, and efficient use of laser welding technology in your operations.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Laser Welder
In conclusion, sourcing a laser welder requires a thorough understanding of the technology, application needs, and available options in the market. Laser welding offers numerous advantages—including high precision, strong welds, minimal distortion, and automation compatibility—making it ideal for industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. When sourcing a laser welder, key factors to consider include the type of laser (fiber, CO₂, or disk), power output, beam delivery system, integration capabilities, and the level of technical support provided by the supplier.
It is essential to evaluate both the initial investment and long-term operational costs, including maintenance, consumables, and training. Working with reputable manufacturers or suppliers who offer customization, robust warranties, and after-sales service ensures reliability and performance. Additionally, assessing user reviews, requesting demonstrations, and comparing quotes from multiple vendors can lead to a more informed decision.
Ultimately, the right laser welder enhances productivity, improves weld quality, and supports long-term manufacturing goals. By carefully aligning technical specifications with project requirements and business objectives, organizations can successfully source a laser welding solution that delivers efficiency, precision, and a strong return on investment.