Elon Musk’s investment portfolio in the manufacturing sector reflects a strategic alignment with high-growth, transformative industries poised to redefine global infrastructure. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global electric vehicle market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 22.6% from 2023 to 2028, driven by policy support, declining battery costs, and rising consumer demand for sustainable transportation—sectors directly benefiting Tesla, Inc., one of Musk’s primary manufacturing ventures. Additionally, the industrial automation market, a cornerstone of advanced manufacturing, is expected to expand at a CAGR of 10.8% from 2023 to 2030, as reported by Grand View Research, a trend amplified by Tesla’s Gigafactories and their use of robotics and AI-driven production lines. Musk’s manufacturing interests extend beyond electric vehicles, encompassing next-generation transportation with The Boring Company and sustainable energy integration via Tesla Energy. These investments are not only vertically integrated but also positioned at the convergence of megatrends—decarbonization, smart infrastructure, and automation—where market expansion is both validated and accelerating. The following six companies represent the core of Musk’s manufacturing ecosystem, each playing a pivotal role in scaling disruptive technologies with multi-billion-dollar addressable markets.
Top 6 What Companies Does Elon Musk Invest In Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Elon Musk’s ventures drive new industrial investment in Texas
Domain Est. 2008
Website: canada.constructconnect.com
Key Highlights: Rocket and spacecraft company SpaceX is one of Elon Musk’s major high-tech investments in Texas. Perhaps no single company has made more impact on the economy ……
#2 CNBC Daily Open
Domain Est. 1997
Website: cnbc.com
Key Highlights: Elon Musk is seeing positive activity in his companies. His brain tech startup Neuralink announced a $650 million funding round….
#3 7 Companies Owned By Elon Musk
Domain Est. 2005
Website: slashgear.com
Key Highlights: 7 Companies Owned By Elon Musk · Tesla · X, formerly Twitter · xAI · SpaceX · The Boring Company · The Musk Foundation · Neuralink · Recommended….
#4 Elon Musk’s SpaceX and Suppliers Bet Big on Vietnam
Domain Est. 2007
Website: vietnam-briefing.com
Key Highlights: SpaceX invests US$1.5 billion in Vietnam to expand Starlink services, with suppliers boosting high-tech manufacturing….
#5 Elon Musk
Domain Est. 2023
Website: investinmusk.com
Key Highlights: Elon Musk is an entrepreneur, founder of SpaceX and Tesla, aiming to change the world through innovations in space, energy, and AI, inspiring millions….
#6 List of Elon Musk Companies
Domain Est. 1994
Website: observer.com
Key Highlights: Elon Musk serves one or more leadership roles at at least six companies: Tesla, SpaceX, Neuralink, The Boring Company, Twitter (X) and xAI….
Expert Sourcing Insights for What Companies Does Elon Musk Invest In

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Companies Elon Musk Invests In
As we approach 2026, the market landscape for companies associated with Elon Musk reflects a convergence of technological innovation, regulatory shifts, and evolving consumer demand. Elon Musk’s influence extends across several high-growth sectors, including electric vehicles (EVs), space exploration, artificial intelligence (AI), and renewable energy. While Musk does not traditionally function as a venture capitalist, his leadership roles and significant equity stakes in key companies position them as bellwethers for future trends. The following analysis examines the projected market dynamics for the core companies Elon Musk is most directly involved with: Tesla, Inc., SpaceX, Neuralink, The Boring Company, and xAI.
1. Tesla, Inc. – Accelerating the EV and Energy Transition
By 2026, Tesla is expected to solidify its position as a dominant force in the global electric vehicle market, though facing intensified competition from legacy automakers and Chinese EV manufacturers like BYD and NIO. Market trends suggest slower growth in vehicle sales compared to previous years due to market saturation in key regions and economic headwinds. However, Tesla’s energy division—encompassing solar, Powerwall, and Megapack—is projected to become a major growth driver. With increasing global demand for grid-scale energy storage and distributed renewable systems, Tesla’s energy revenue could grow at over 25% annually through 2026. Additionally, advancements in 4680 battery technology and potential breakthroughs in structural battery packs may improve margins and vehicle range, enhancing competitiveness. Full Self-Driving (FSD) software, if approved for broader deployment, could unlock a high-margin subscription revenue stream, potentially positioning Tesla as a leader in autonomous mobility services.
2. SpaceX – Dominance in Commercial Space and Satellite Broadband
SpaceX is on track to maintain its leadership in the commercial space sector through 2026. The Starlink satellite internet constellation, with over 5,000 operational satellites by early 2025, is expected to achieve profitability by 2026, serving millions of subscribers in rural and underserved regions globally. As global demand for low-latency broadband grows, especially in emerging markets and maritime/aviation sectors, Starlink’s revenue could exceed $10 billion annually. Meanwhile, the Starship program—aimed at deep-space missions and eventually Mars colonization—is anticipated to conduct its first orbital refueling tests by 2026, paving the way for NASA’s Artemis lunar missions and future commercial space tourism. SpaceX’s reusable rocket technology continues to lower launch costs, maintaining its competitive edge and capturing over 60% of the global launch market.
3. Neuralink – Advancing the Frontier of Brain-Computer Interfaces
Neuralink, focused on developing implantable brain-machine interfaces (BMIs), is poised for significant clinical and regulatory milestones by 2026. Following successful early human trials in 2024–2025, the company aims to secure FDA approval for broader medical applications, such as restoring mobility and communication for patients with paralysis. Market trends indicate growing investor interest in neurotechnology and AI-augmented healthcare, with the global brain-computer interface market projected to reach $5–7 billion by 2026. While commercial adoption remains limited to medical use cases in the near term, long-term implications for human augmentation and cognitive enhancement could open new markets. Partnerships with healthcare institutions and research organizations are likely to expand, although ethical and privacy concerns will remain key challenges.
4. The Boring Company – Urban Mobility and Infrastructure Innovation
The Boring Company’s vision for underground tunnel-based transportation continues to evolve, with several pilot projects—such as the Las Vegas Convention Center Loop—demonstrating feasibility. By 2026, the company is expected to expand operations to additional cities, focusing on freight transport and last-mile urban logistics. While mass passenger transit remains a longer-term goal, partnerships with municipalities and private developers may accelerate adoption in congested metropolitan areas. The company’s focus on reducing tunneling costs through automation and improved drilling techniques could disrupt traditional infrastructure development, particularly as urban congestion and sustainability concerns grow. However, regulatory approvals and public skepticism remain barriers to widespread deployment.
5. xAI – Challenging the AI Status Quo
Founded in 2023, xAI aims to develop artificial intelligence systems that better understand the universe’s fundamental nature. By 2026, xAI is projected to emerge as a serious competitor to industry leaders like OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and Anthropic. Leveraging Musk’s vision of “truth-seeking” AI and concerns about AI safety, xAI’s Grok model is expected to gain traction, particularly within the X (formerly Twitter) ecosystem. Integration with real-time data from social media could enable unique applications in sentiment analysis, content moderation, and personalized information delivery. With massive investments in computational infrastructure and talent acquisition, xAI may capture a niche in transparent, less-censored AI models, appealing to users seeking alternative platforms. Market trends suggest increased demand for open, auditable AI systems, positioning xAI as a disruptor in the ethical AI space.
Conclusion: Interconnected Innovation Driving Market Shifts
By 2026, companies associated with Elon Musk are expected to shape critical technology trends across transportation, energy, space, healthcare, and artificial intelligence. While each operates in distinct sectors, synergies between them—such as AI integration in Tesla’s FSD and SpaceX operations, or data sharing between xAI and X—could amplify their collective impact. Market success will depend on execution, regulatory navigation, and sustained innovation. Investors and industry watchers should monitor not only financial performance but also technological milestones and Musk’s evolving strategic focus, which continues to drive disruption across multiple frontiers.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Information on What Companies Elon Musk Invests In: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
When researching the companies Elon Musk invests in or is affiliated with, individuals and organizations often encounter several pitfalls related to data quality and intellectual property (IP) issues. These challenges can lead to misinformation, legal risks, or flawed business decisions if not properly addressed.
1. Confusing Affiliation with Investment
A common mistake is conflating leadership roles or public statements with actual financial investment. Elon Musk is the CEO or CTO of companies like Tesla and SpaceX, but that doesn’t always mean he holds significant equity in every venture he promotes. For example, his public support for Dogecoin or Neuralink does not necessarily equate to personal investment in all aspects of those ventures. Relying on media headlines without verifying ownership records can result in inaccurate conclusions.
2. Overreliance on Unverified Sources
Many online articles, blogs, and social media posts claim to list Musk’s investments, but they often lack credible sourcing. Websites may republish unverified claims, leading to the spread of outdated or false information. This low-quality data can mislead researchers, investors, or journalists. Always prioritize primary sources such as SEC filings (e.g., Form 4 or 13F), official company announcements, or regulatory disclosures.
3. Misinterpretation of Indirect Investments
Elon Musk’s investment activities are sometimes indirect—made through trusts, shell companies, or venture funds (e.g., SpaceX’s funding rounds involve institutional investors, not always Musk personally). Without access to detailed financial disclosures, it’s easy to attribute funding or ownership incorrectly. This lack of transparency increases the risk of drawing false inferences about his direct involvement.
4. Intellectual Property Misuse in Content Creation
When compiling reports or content about Musk’s investments, creators may inadvertently violate IP rights by using copyrighted company logos, financial charts, or proprietary data from paid databases (e.g., Crunchbase, PitchBook). Reproducing such material without proper licensing or attribution can lead to legal consequences, even if the intent is informational.
5. Outdated or Incomplete Data
Investment portfolios evolve. Musk may divest from certain companies or increase stakes over time. Relying on static or outdated sources (e.g., articles from several years ago) can present a distorted picture. Real-time updates are rare in public data, so periodic re-verification using updated filings is essential to maintain accuracy.
6. Assumption of Public Disclosure for All Ventures
Not all investments are publicly disclosed, especially private or early-stage ventures. Musk may hold stakes in startups through non-public funding rounds. Assuming full transparency can create gaps in research. Additionally, privacy laws and corporate confidentiality limit the availability of certain ownership details, making comprehensive sourcing difficult.
Best Practices to Avoid These Pitfalls
- Use authoritative sources: Rely on SEC filings, corporate websites, and verified financial disclosures.
- Cross-check information: Validate claims across multiple reputable outlets.
- Respect IP rights: Use only licensed or public domain materials; cite sources appropriately.
- Clarify investment vs. affiliation: Distinguish between personal investment, company funding, and public endorsement.
- Update regularly: Reassess sources periodically to reflect changes in ownership or involvement.
By recognizing these common pitfalls, researchers and content creators can improve the reliability and legality of their work when exploring Elon Musk’s investment landscape.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Companies Elon Musk Invests In
Understanding the logistics and compliance requirements for companies associated with Elon Musk requires examining the unique operational, regulatory, and supply chain challenges each entity faces. Musk’s investments span diverse industries—from aerospace and automotive to energy and artificial intelligence—each with distinct logistical complexities and compliance obligations. Below is a breakdown of key companies and the associated logistics and compliance considerations.
Tesla, Inc.
Logistics Overview:
Tesla operates a vertically integrated supply chain, managing everything from raw material procurement (e.g., lithium, nickel) to vehicle production and global delivery. Its Gigafactories in Nevada, Shanghai, Berlin, and Texas serve as central production hubs, requiring efficient inbound logistics for components and outbound distribution for finished vehicles and energy products.
Compliance Considerations:
– Environmental Regulations: Compliance with EPA standards, REACH (EU), and RoHS for hazardous substances.
– Safety Standards: Adherence to NHTSA (U.S.) and equivalent international vehicle safety regulations.
– Trade Compliance: Managing export controls, tariffs, and sanctions, especially for battery technology and international sales.
– Labor Laws: Compliance with OSHA (U.S.) and local labor regulations across global facilities.
– Data Privacy: GDPR and CCPA compliance for customer data collected via connected vehicles.
SpaceX
Logistics Overview:
SpaceX manages the design, manufacturing, and launch of reusable rockets and spacecraft. Logistics involve transporting large rocket components via specialized transport (e.g., barges, custom trailers), managing launch schedules across multiple sites (Cape Canaveral, Vandenberg, Starbase), and coordinating satellite deployments.
Compliance Considerations:
– ITAR/EAR Compliance: Strict adherence to International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) and Export Administration Regulations (EAR) due to the defense-sensitive nature of space technology.
– FAA Licensing: Launch and re-entry permits from the Federal Aviation Administration’s Office of Commercial Space Transportation.
– Environmental Review: NEPA (National Environmental Policy Act) compliance for launch site operations.
– International Regulations: Coordination with global space agencies and adherence to Outer Space Treaty obligations.
– Workplace Safety: Compliance with federal and state safety standards for high-risk aerospace manufacturing.
Neuralink
Logistics Overview:
Neuralink develops implantable brain-machine interface devices. Logistics involve secure transport of medical devices, sterile manufacturing environments, and coordination with research hospitals and clinical trial sites.
Compliance Considerations:
– FDA Regulations: Compliance with U.S. Food and Drug Administration requirements for investigational device exemptions (IDE) and eventual market approval (PMA).
– HIPAA: Protection of patient health information in clinical trials.
– Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): Adherence to FDA 21 CFR Part 820 for medical device production.
– Animal Welfare: Compliance with Animal Welfare Act and IACUC protocols for preclinical research.
– Data Security: Strong cybersecurity measures to protect neural data and ensure patient privacy.
The Boring Company
Logistics Overview:
Focused on tunnel construction and infrastructure, logistics include transporting heavy machinery (e.g., tunnel boring machines), managing construction materials, and coordinating urban excavation with municipal authorities.
Compliance Considerations:
– OSHA Standards: Workplace safety in high-risk tunneling and construction environments.
– Environmental Regulations: Compliance with local, state, and federal rules on noise, emissions, soil disposal, and water runoff.
– Urban Zoning and Permits: Coordination with city planning departments for right-of-way and construction permits.
– Transportation Safety: DOT compliance for oversized equipment movement on public roads.
X (formerly Twitter)
Logistics Overview:
As a digital platform, X’s logistics are primarily data-driven, involving cloud infrastructure, content delivery networks (CDNs), and global data centers. Physical logistics include office operations and hardware for internal tech infrastructure.
Compliance Considerations:
– Data Privacy Laws: Compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other regional data protection regulations.
– Content Moderation: Adherence to local speech laws and regulatory frameworks (e.g., EU Digital Services Act).
– Cybersecurity: Implementation of SOC 2, ISO 27001 standards to protect user data.
– Employment Law: Compliance with labor regulations across international offices, including remote work policies.
– Financial Regulations: SEC reporting obligations as a publicly traded company (prior to privatization) and ongoing corporate governance standards.
xAI
Logistics Overview:
xAI focuses on artificial intelligence research, requiring high-performance computing infrastructure, data storage, and secure collaboration across global research teams. Logistics involve procurement of GPUs, cloud computing resources, and data center operations.
Compliance Considerations:
– Export Controls: Compliance with EAR regulations on advanced AI chips and software.
– Data Ethics and Privacy: Ensuring responsible use of training data and avoiding bias in AI models.
– Intellectual Property: Protection of proprietary algorithms and research under patent and copyright law.
– Cybersecurity: Secure handling of sensitive datasets and AI models to prevent misuse.
– Emerging AI Regulations: Monitoring and adapting to new frameworks such as the EU AI Act.
General Cross-Company Compliance Best Practices
- Board Oversight: Establish dedicated compliance committees for risk assessment and regulatory monitoring.
- Third-Party Audits: Regular audits of supply chains, data practices, and safety protocols.
- Whistleblower Systems: Secure channels for employees to report compliance concerns.
- Training Programs: Ongoing training for employees on industry-specific regulations and ethical standards.
- Geopolitical Risk Management: Assessing sanctions, trade restrictions, and political instability in global operations.
This guide provides a foundational understanding of the logistical and compliance landscape across Elon Musk’s key investments. Each company must tailor its approach to meet evolving regulatory demands while maintaining operational efficiency and innovation.
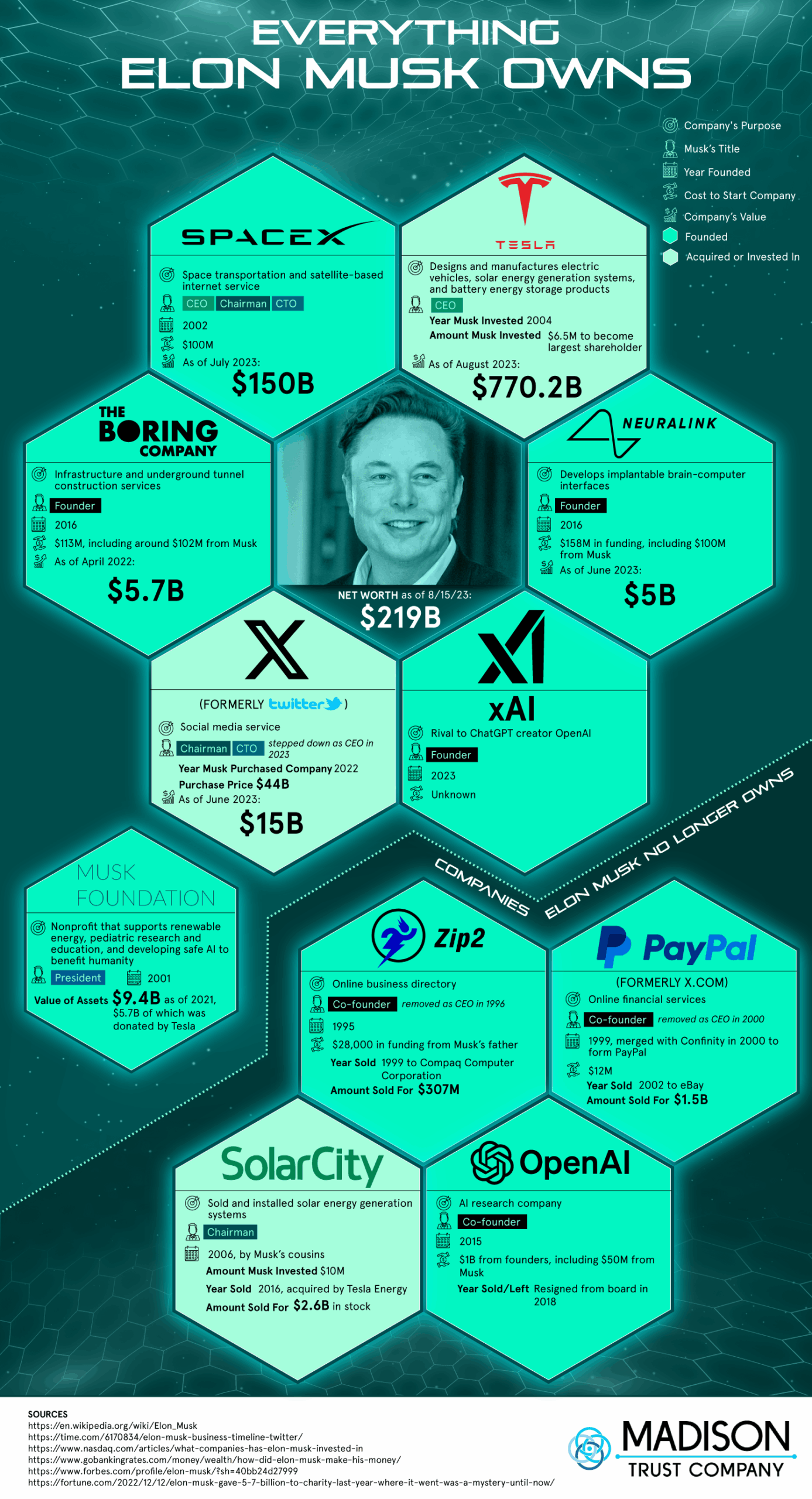
Elon Musk is involved with and invests in a range of innovative, technology-driven companies, typically focused on transforming major industries such as transportation, energy, space exploration, and artificial intelligence. The key companies he is most directly associated with include:
-
Tesla, Inc. – A leader in electric vehicles and clean energy, where Musk serves as CEO and a major shareholder. He has played a pivotal role in advancing sustainable transportation and energy solutions.
-
SpaceX (Space Exploration Technologies Corp.) – Founded by Musk, this aerospace company aims to reduce space travel costs and enable the colonization of Mars. He is the CEO and lead engineer, investing significant personal funds and time.
-
Neuralink – A neurotechnology company developing brain-machine interface devices. Musk co-founded the company and is actively involved in its vision of merging the human brain with AI.
-
The Boring Company – Focused on infrastructure and tunnel construction to alleviate urban traffic congestion. Musk founded the company and continues to guide its development.
-
xAI – Musk’s newest venture, an artificial intelligence company launched in 2023 with the goal of understanding the universe and developing AI systems that can reason at or beyond human levels.
While Musk occasionally makes personal investments in other startups or emerging technologies, his primary focus remains on these core companies. His investments are usually strategic, aligning with his long-term vision of advancing humanity through technology, sustainability, and interplanetary expansion.
Conclusion: Elon Musk invests primarily in companies he either founded or leads, with a consistent focus on disruptive innovation and solving global challenges. These ventures reflect his ambition to reshape transportation, energy, space exploration, and the future of human-AI integration.