The global ball bearings market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand across automotive, industrial machinery, aerospace, and consumer electronics sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 26.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.1% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by rising industrial automation, the expansion of electric vehicles (EVs), and the need for high-efficiency rotating components. Grand View Research also underscores this trajectory, citing advancements in precision engineering and the escalating adoption of miniaturized bearings in smart devices as key market drivers. As competition intensifies, a handful of manufacturers have emerged as industry leaders, combining innovative design, global supply chain reach, and consistent quality to dominate the landscape. The following list highlights the top 10 ball bearing manufacturers shaping the future of motion control and mechanical efficiency worldwide.
Top 10 What Are Ball Bearings Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 New Hampshire Ball Bearings, Inc.
Domain Est. 1995
Website: nhbb.com
Key Highlights: (NHBB) is a leading manufacturer of precision bearings and complex bearing assemblies for the global aerospace, defense, medical, and high technology markets….
#2 Precision Roller Bearings Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1997
Website: rbcbearings.com
Key Highlights: RBC Bearings Incorporated Announces Acquisition of Specline, Inc., a manufacturer of precision bearings for the commercial and defense aerospace markets….
#3 Mounted Ball Bearings
Domain Est. 2001
Website: amibearings.com
Key Highlights: AMI Bearings, Inc. is a World Class Manufacturer of Mounted Ball Bearings Serving the North American Market. Featuring the broadest possible combination of ……
#4 AST Bearings: Ball Bearings
Domain Est. 1998
Website: astbearings.com
Key Highlights: AST Bearings is a premier supplier of high-precision, miniature, and industrial ball bearings, roller bearings, bushings, and related bearing services….
#5 PEER Bearing
Domain Est. 1999
Website: peerbearing.com
Key Highlights: Explore Peer Bearing’s wide range of high-quality bearings and solutions. Trusted reliability for your industrial needs….
#6 Deep groove ball bearing by FAG
Domain Est. 2006
Website: schaeffler.us
Key Highlights: Single-row deep groove ball bearings are available in open and sealed designs. They are designed for high to very high speeds and can accommodate radial as ……
#7 NTN Americas
Domain Est. 2012
Website: ntnamericas.com
Key Highlights: At NTN Bearing Corp., we manufacture and supply the most comprehensive range of ball bearings and other industrial and automotive equipment….
#8 Timken ® Ball Bearings
Domain Est. 1994
Website: timken.com
Key Highlights: The Timken Company designs & manufactures ball bearings for industries all over the world. Browse our full line of bearing products….
#9
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nsk.com
Key Highlights: Shop bearings, linear motion products, and accessories with fast ordering, real-time availability, and trusted NSK quality. Order Now. NSK Online Catalogue for ……
#10 SKF Group homepage
Domain Est. 1996
Website: skf.com
Key Highlights: Bearings, seals, lubrication systems and surrounding equipment for enhanced reliability and performance. View products. Services. Engineering, maintenance, ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for What Are Ball Bearings

H2: Market Trends for Ball Bearings in 2026
As global industrial and technological advancements accelerate, the ball bearings market is poised for significant evolution by 2026. Driven by demand across automotive, aerospace, renewable energy, and industrial automation sectors, several key trends are shaping the landscape of ball bearing applications, production, and innovation.
1. Rising Demand in Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The rapid expansion of the electric vehicle market is a primary driver for ball bearing demand. EVs require high-performance, low-friction bearings for electric motors, gearboxes, and wheel hubs. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to prioritize compact, lightweight, and thermally stable ball bearings capable of withstanding high-speed operation and regenerative braking systems. This shift is prompting innovation in materials such as hybrid ceramic bearings (steel rings with ceramic balls), which offer reduced weight and enhanced efficiency.
2. Growth in Renewable Energy Applications
Wind turbines rely heavily on ball bearings for pitch and yaw control systems, as well as generator support. With global commitments to carbon neutrality, wind energy installations are increasing, especially offshore. By 2026, demand for large-diameter, corrosion-resistant ball bearings designed for harsh environments is projected to grow. Manufacturers are investing in advanced sealing technologies and greases to extend bearing life under extreme conditions.
3. Advancements in Smart and Condition-Monitoring Bearings
The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) and predictive maintenance technologies is transforming traditional ball bearings into smart components. By 2026, smart bearings equipped with embedded sensors for vibration, temperature, and load monitoring are expected to gain widespread adoption in industrial machinery and transportation. These intelligent systems enable real-time diagnostics, reduce downtime, and optimize maintenance schedules, improving operational efficiency.
4. Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly production methods. Trends include the use of recyclable materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and remanufacturing or reconditioning of used bearings. By 2026, companies offering ‘green’ bearing solutions—such as longer-lasting designs and reduced lubricant needs—are anticipated to gain competitive advantage.
5. Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Resilience
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will continue to dominate ball bearing production and consumption due to expanding manufacturing and automotive industries. However, geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions are prompting companies to diversify sourcing and increase local production in North America and Europe. By 2026, nearshoring and digital supply chain integration will be critical strategies for maintaining reliability and reducing lead times.
6. Material and Coating Innovations
To meet the demands of high-speed, high-load, and corrosive environments, advancements in bearing steels, surface coatings (e.g., DLC – Diamond-Like Carbon), and corrosion-resistant alloys are accelerating. These innovations enhance durability, reduce friction, and extend service life—key factors in high-value applications such as aerospace and medical devices.
In conclusion, the ball bearings market in 2026 will be defined by technological innovation, sustainability, and adaptation to emerging industrial needs. Companies that invest in R&D, digital integration, and sustainable practices are likely to lead the next phase of growth in this essential mechanical component sector.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Ball Bearings (Quality, IP)
Sourcing ball bearings may seem straightforward, but overlooking key factors can lead to performance failures, safety hazards, and increased long-term costs. Two critical aspects—quality and IP (Ingress Protection) rating—are often misunderstood or misjudged. Here are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Quality
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting the lowest-cost ball bearings without evaluating material quality, manufacturing precision, or compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, ABEC). Cheap bearings often use inferior steel, imprecise tolerances, and poor heat treatment, leading to early failure, increased friction, and downtime.
Solution: Always source from reputable manufacturers or distributors with certifications. Consider total cost of ownership, not just initial price.
2. Misunderstanding or Ignoring IP Ratings
Ball bearings themselves are not typically assigned IP ratings, but the sealed or shielded units they are integrated into (e.g., housed units or flanged bearings) are. A common mistake is assuming a bearing is dust- or water-resistant simply because it has metal shields.
Pitfall: Assuming rubber seals (e.g., 2RS) provide full water protection. While they offer good protection against dust and some moisture, they may not suffice in wet or washdown environments unless properly rated.
Solution: Verify the IP rating of the complete bearing unit. For harsh environments, select bearings with proper sealing (e.g., IP67 or higher) and ensure compatibility with operating conditions.
3. Overlooking Application-Specific Requirements
Using generic bearings for specialized applications—such as high-speed rotation, extreme temperatures, or corrosive environments—can cause premature wear or failure.
Pitfall: Using standard carbon steel bearings in food processing or marine environments where stainless steel (e.g., AISI 440C or AISI 316) is required.
Solution: Match bearing material, lubrication, and sealing to the operational environment. For example, use stainless steel with FDA-compliant grease in food-grade applications.
4. Assuming All Seals Are Equal
Not all seals offer the same level of protection. Metal shields (ZZ) offer minimal protection against particulates but no moisture resistance. Rubber seals (2RS) are better but may degrade under UV exposure or high heat.
Pitfall: Assuming “sealed” means waterproof. Many sealed bearings resist splashes but not submersion.
Solution: Check seal material (nitrile, silicone, Viton) and design. For high IP protection, ensure the housing and seals are engineered for the intended environment.
5. Failing to Verify Supplier Credentials
Counterfeit or substandard bearings are widespread, especially in online marketplaces. Bearings may be mislabeled with fake ABEC or ISO ratings.
Pitfall: Purchasing bearings from unknown suppliers offering “genuine” brands at suspiciously low prices.
Solution: Buy from authorized distributors, request traceability documentation, and inspect packaging and markings upon delivery.
6. Neglecting Lubrication Compatibility
Improper lubrication—either type or quantity—can lead to overheating, corrosion, or contamination. Some bearings come pre-lubricated for life, and re-lubrication may not be possible or advised.
Pitfall: Assuming all bearings can be re-greased, or using incompatible grease types.
Solution: Confirm lubrication type and re-lubrication intervals with the manufacturer. Ensure compatibility with operating temperature and environment.
Conclusion
Sourcing ball bearings effectively requires more than just matching dimensions. Prioritizing quality, understanding sealing and IP ratings, and aligning specifications with application demands are essential to avoid costly failures. Always verify supplier credibility and application suitability to ensure reliable, long-term performance.
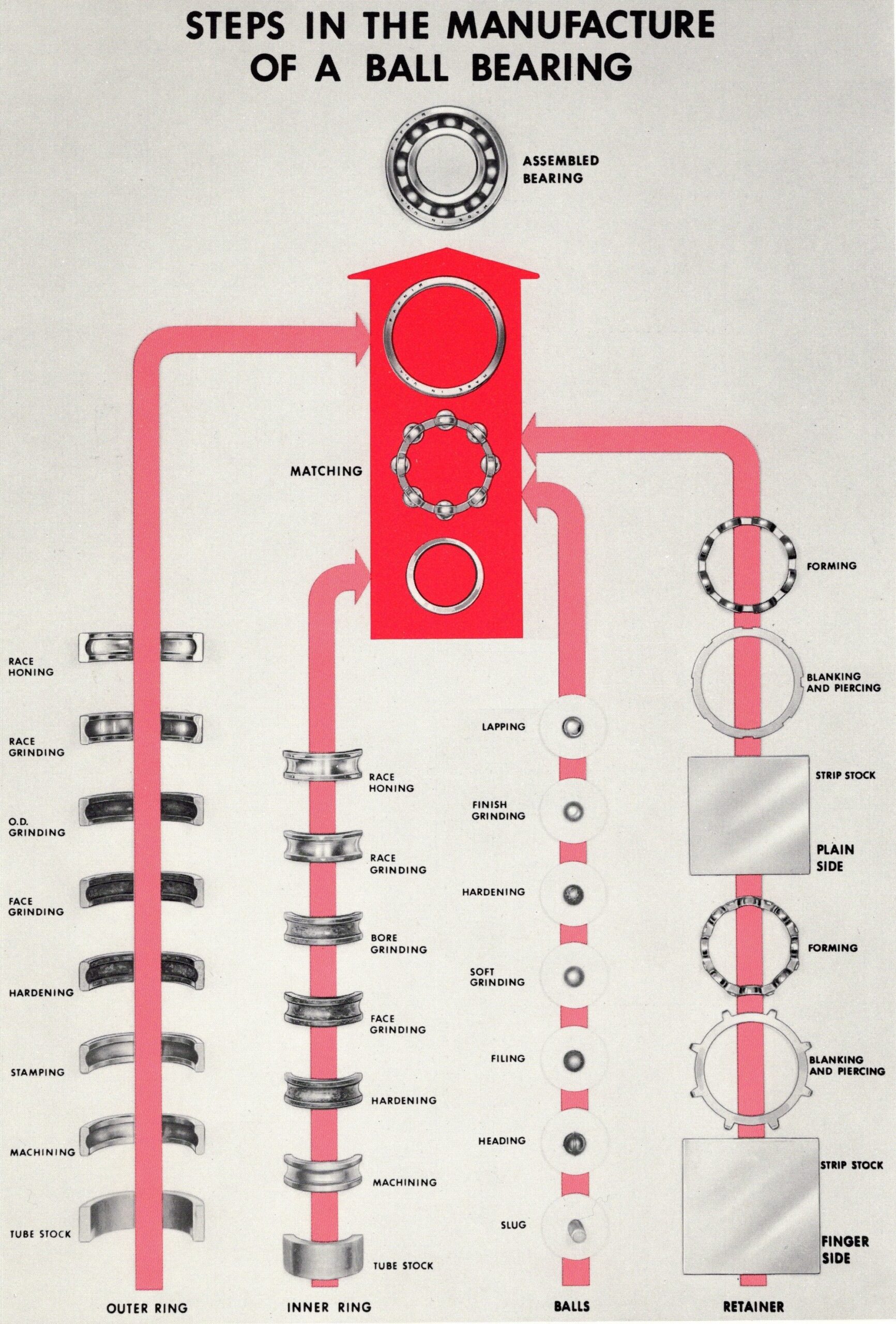
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Ball Bearings
Product Classification and HS Codes
Ball bearings are typically classified under the Harmonized System (HS) code 8482.10 for “Ball bearings, radial.” Accurate classification is essential for international shipping, customs clearance, and determining import duties. Always verify the specific HS code with the destination country’s customs authority, as subcategories may vary (e.g., based on size, material, or intended use).
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Ball bearings must be packed to prevent damage during transit. Use robust, moisture-resistant packaging such as sealed plastic containers or padded cartons with internal dividers. Avoid loose packing to minimize movement. Include desiccants if shipping in humid environments. Label packages with “Fragile” and “Protect from Moisture” warnings. For bulk shipments, use pallets secured with stretch wrap and corner boards to maintain stability.
Transportation and Shipping Considerations
Ball bearings can be shipped via air, sea, or land freight. Ensure proper weight distribution and secure loading to prevent shifting. For air freight, adhere to IATA regulations; for sea freight, follow IMDG Code guidelines if applicable. Avoid extreme temperatures and prolonged exposure to humidity. Use containers with climate control when necessary. Maintain documentation such as packing lists, commercial invoices, and certificates of origin.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with international standards such as ISO 15 (dimensions) and ISO 492 (tolerances) is recommended. In the EU, ball bearings may fall under the Machinery Directive or REACH regulations if containing certain substances. In the U.S., adhere to ASTM standards and FTC labeling rules. Verify if bearings are subject to ITAR or EAR controls, especially if used in defense or aerospace applications.
Import/Export Documentation
Prepare essential documents: commercial invoice, bill of lading/air waybill, packing list, and certificate of origin. Some countries may require a conformity certificate or third-party inspection report. For exports from the U.S., validate if a license is needed through the Department of Commerce. Maintain records for at least five years for audit purposes.
Environmental and Safety Regulations
Dispose of packaging materials according to local environmental regulations. Ball bearings themselves are generally non-hazardous but may contain small amounts of lubricants subject to environmental controls. Ensure workplace safety during handling by using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to prevent injury from sharp edges or small parts.
Quality Assurance and Traceability
Implement a traceability system to track batch numbers, manufacturing dates, and material sources. Conduct regular quality audits to ensure bearings meet industry standards. Provide clients with inspection reports or material test certificates upon request to support compliance and warranty claims.
In conclusion, sourcing ball bearings requires a clear understanding of their function, types, specifications, and application requirements. Ball bearings are essential mechanical components that reduce friction between moving parts and support radial and axial loads in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, manufacturing, and consumer electronics. When sourcing ball bearings, key factors to consider include load capacity, speed requirements, precision grade, material composition (such as stainless steel or ceramic), sealing options, and environmental resistance.
Effective sourcing involves identifying reputable suppliers or manufacturers, comparing product quality and certifications (like ISO or ABEC standards), evaluating cost-effectiveness, and ensuring supply chain reliability. Whether sourcing standard off-the-shelf bearings or custom solutions, proper due diligence ensures optimal performance, longevity, and cost efficiency in the final application. Ultimately, a strategic approach to sourcing ball bearings supports operational reliability and enhances overall system performance.