The global welding equipment and consumables market is undergoing significant expansion, driven by rising industrialization, infrastructure development, and demand from key sectors such as automotive, heavy machinery, and construction. According to Grand View Research, the global welding consumables market was valued at USD 24.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% from 2024 to 2030. A key driver within this segment is the increasing need for high-performance welding solutions for challenging materials like cast iron — particularly in repair, maintenance, and original equipment manufacturing (OEM) applications.
Cast iron’s brittleness, high carbon content, and susceptibility to cracking make it one of the most difficult metals to weld, necessitating specialized welding rods designed for thermal stability, ductility, and crack resistance. As industries continue to extend the lifecycle of cast iron components—from engine blocks to industrial pumps—the demand for reliable, high-quality welding rods is on the rise. This trend is especially pronounced in the automotive and aerospace sectors, where precision and durability are non-negotiable.
With manufacturers seeking cost-effective, efficient repair solutions, the choice of welding rod directly impacts weld integrity, post-weld machining ease, and component longevity. In this context, evaluating the top-performing welding rods for cast iron applications is essential for ensuring optimal performance and return on investment. The following analysis identifies the 10 most effective welding rods for cast iron, based on technical specifications, real-world performance data, and industry feedback.
Top 10 Welding Rods For Cast Iron Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Cast Iron Rods
Domain Est. 1997
Website: lawsonproducts.com
Key Highlights: 90-day returnsDiscover cast iron rods designed for durability, strength, and precision in industrial applications. Browse online and order top-grade cast iron ……
#2 Victory Welding Alloys*
Domain Est. 2014
Website: victoryweldingalloys.com
Key Highlights: Victory Welding Alloys, Inc. is a wholesale supplier of welding consumables, sold through qualified distributors only, into applications such as:…
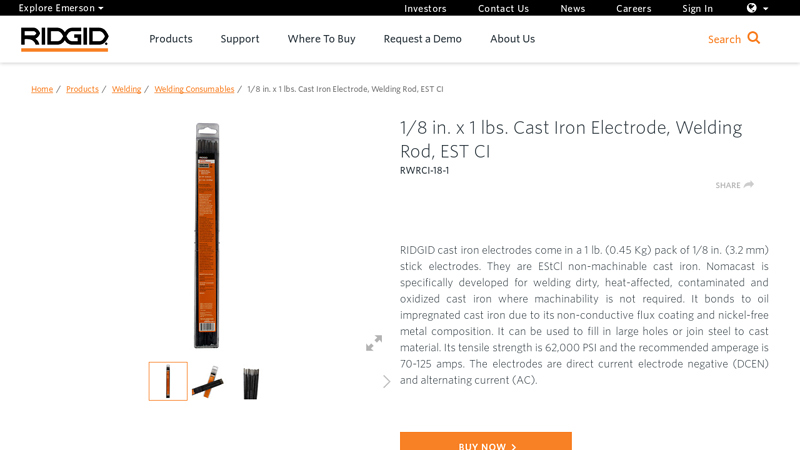
#3 1/8 in. x 1 lbs. Cast Iron Electrode, Welding Rod, EST CI
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ridgid.com
Key Highlights: RIDGID cast iron electrodes come in a 1 lb. (0.45 Kg) pack of 1/8 in. (3.2 mm) stick electrodes. They are EStCl non-machinable cast iron….
#4 NI
Domain Est. 1995
Website: specialmetals.com
Key Highlights: NI-ROD 44 Filler Metal is a solid, nickel-iron-manganese wire designed for automatic and semi-automatic welding of ductile, malleable and gray cast irons….
#5 Ferroweld™
Domain Est. 1996
Website: lincolnelectric.com
Key Highlights: Ferroweld™ ; Features. Deposits may be finished by grinding; Cost effective option for repairing cast iron ; Typical Applications. Repairing pits and small cracks ……
#6 Cast Iron
Domain Est. 1996
Website: sodel.com
Key Highlights: Learn expert tips and methods for mastering cast iron welding. Discover essential precautions, including the right welding processes, filler metals, ……
#7 Products
Domain Est. 1997
Website: crownalloys.com
Key Highlights: Cast Iron Welding Rod for Oxyfuel Gas Welding. SDS TDS. Crown 255. Nickel Alloy Electrode for Cast Iron (E NiFe-CI). SDS TDS. Crown 295. High Nickel Alloy ……
#8 High
Domain Est. 1998
Website: selectarc.com
Key Highlights: Selectarc offers a wide range of welding products: coated electrodes, MIG/MAG wires, TIG rods and wires, special wires, micro-laser range and more….
#9 Cast Iron/Nickel TIG/Stick Alloys
Domain Est. 2006
Website: harrisproductsgroup.com
Key Highlights: Cast Iron/Nickel TIG/Stick Alloys. Harris supplies the highest quality TIG (GTAW) rods and Stick (SMAW) electrodes for welding cast iron and nickel alloys….
#10 electrodes weldcote cast iron rod
Domain Est. 2006
Website: weldcotemetals.com
Key Highlights: Cast Iron Rod is a high quality gray iron oxy-acetylene welding rod designed for gas welding of cast iron, general fabrication or buildup new or worn surfaces ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Welding Rods For Cast Iron

H2: Projected Market Trends for Welding Rods for Cast Iron in 2026
The global market for welding rods specifically designed for cast iron is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving industrial demands, technological advancements, and regional manufacturing shifts. Key trends shaping this niche segment include increasing demand in heavy industries, advancements in welding rod composition, regional growth disparities, sustainability considerations, and the impact of automation.
-
Rising Demand in Repair and Maintenance Sectors
By 2026, the repair and maintenance segment—especially in automotive, heavy machinery, and infrastructure—is projected to be the primary driver of demand for cast iron welding rods. As industries extend the lifecycle of aging equipment to reduce capital expenditures, there will be a surge in the need for reliable, high-integrity weld repairs. Cast iron’s brittleness and susceptibility to cracking make specialized welding rods (e.g., nickel-based or nickel-iron alloys) critical, reinforcing the market for premium-grade consumables. -
Technological Advancements in Rod Formulations
Innovation in electrode composition will continue to be a major trend. Manufacturers are likely to offer enhanced nickel-based rods with improved arc stability, reduced spatter, and better machinability post-weld. By 2026, expect greater availability of low-hydrogen variants and flux-coated rods that minimize pre- and post-weld heat treatment requirements—addressing key challenges in field repairs where controlled heat conditions are difficult to achieve. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia, is expected to dominate growth in the cast iron welding rod market by 2026. Rapid industrialization, expanding manufacturing bases, and aging infrastructure in these regions will fuel demand. Meanwhile, North America and Europe will maintain steady demand, driven by stringent quality standards and a strong presence of high-value repair services in aerospace, energy, and marine sectors. -
Shift Toward Sustainable and Efficient Solutions
Environmental regulations and cost pressures will push suppliers to develop more efficient and eco-friendly welding solutions. This includes longer-lasting rods with higher deposition rates and reduced fume emissions. By 2026, product differentiation may increasingly focus on sustainability metrics, such as recyclability of packaging and lower carbon footprints in production. -
Impact of Automation and Digitalization
While cast iron welding is traditionally performed manually due to material sensitivities, advances in robotic welding with adaptive controls may begin influencing select industrial applications. By 2026, hybrid approaches combining semi-automated processes with specialized cast iron rods could emerge, particularly in high-volume repair facilities, enhancing consistency and reducing labor costs. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Raw Material Volatility
The market will remain sensitive to fluctuations in nickel prices—a key component in most cast iron welding rods. By 2026, leading manufacturers are expected to strengthen supply chain resilience through vertical integration, strategic sourcing, and the development of alternative alloy formulations to mitigate cost volatility.
In summary, the 2026 outlook for welding rods for cast iron reflects a maturing yet adaptive market, with innovation and repair economics at its core. Companies that invest in high-performance materials, regional market penetration, and sustainable practices are likely to gain a competitive edge.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Welding Rods for Cast Iron (Quality, IP)
Sourcing the right welding rods for cast iron requires careful attention to material properties, welding techniques, and supplier integrity. Below are common pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) that buyers and fabricators should avoid.
Poor Quality Control from Suppliers
One of the most frequent issues is receiving welding rods that do not meet advertised specifications. Low-quality rods may have inconsistent core wire composition, inadequate flux coating, or poor moisture resistance—leading to porosity, cracking, or weak welds. Suppliers without proper certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AWS A5.15) or traceability processes may deliver substandard products that compromise weld integrity in critical applications.
Misrepresentation of Rod Type and Compatibility
Cast iron welding requires specialized rods such as nickel-based (Ni-CI, NiFe-CI), nickel-copper, or high-nickel alloys. Some suppliers may mislabel general-purpose rods as suitable for cast iron, or offer “equivalent” alternatives that lack the necessary thermal expansion characteristics and ductility. This mismatch increases the risk of weld failure due to thermal stress and poor fusion.
Lack of Proper Packaging and Moisture Protection
Cast iron welding rods—especially nickel-based types—are sensitive to moisture absorption, which can cause hydrogen-induced cracking. Poor packaging (e.g., non-hermetic containers or reused spools) exposes rods to humidity, degrading performance. Reputable suppliers provide vacuum-sealed or moisture-resistant packaging with clear drying instructions, which is often missing with low-cost or counterfeit products.
Inadequate Traceability and Certification
Industrial and repair applications—especially in oil & gas, power generation, or transportation—require full material traceability and certified test reports (e.g., MTRs). Some suppliers fail to provide proper documentation, making it impossible to verify compliance with standards like AWS A5.15 or EN ISO 1071. This lack of traceability creates liability risks and may fail quality audits.
Intellectual Property Infringement and Counterfeit Products
Reputable welding rod manufacturers invest heavily in R&D to develop proprietary alloys and flux formulations. Counterfeit or imitation rods often copy branding and packaging of well-known brands (e.g., Techweld, Hobart, ESAB) without authorization. These knock-offs may infringe on patents or trademarks and typically offer inferior performance, exposing the buyer to legal and safety risks.
Use of Non-Compliant or Unverified “Generic” Alternatives
While generic rods may appear cost-effective, they often lack independent testing data or compliance verification. Some are reverse-engineered without understanding the original IP, resulting in inconsistent performance. In regulated environments, using non-certified or unapproved substitutes can violate industry codes (e.g., ASME, API), leading to rejected welds or project delays.
Insufficient Technical Support and Application Guidance
High-quality suppliers provide detailed technical data sheets, preheat recommendations, and welding procedures tailored to cast iron repairs. Sourcing from vendors without technical expertise increases the likelihood of improper usage—such as incorrect amperage settings or inadequate peening—leading to weld defects even with good-quality rods.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, always purchase cast iron welding rods from authorized, certified suppliers with full traceability, proper packaging, and technical support. Verify compliance with recognized standards and be wary of unusually low prices, which may indicate counterfeit or substandard products. Protecting both quality and IP ensures reliable welds and reduces operational and legal risks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Welding Rods for Cast Iron
Overview of Welding Rods for Cast Iron
Welding rods designed for cast iron are specialized consumables used to join or repair cast iron components. These rods are formulated to accommodate the unique properties of cast iron, such as its high carbon content, brittleness, and susceptibility to cracking under thermal stress. Common types include nickel-based, nickel-iron, and copper-based rods, each suited for specific applications and service conditions.
Due to their chemical composition and intended use, welding rods for cast iron are subject to various logistics and compliance requirements during storage, transportation, handling, and disposal.
Classification and Regulatory Compliance
Product Classification
Welding rods for cast iron may contain metals such as nickel, iron, copper, and manganese. While not typically classified as hazardous under normal conditions, some formulations may require labeling under occupational safety and environmental regulations due to metal content.
- Globally Harmonized System (GHS): Check Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for classification. Some rods may be labeled with hazard statements related to inhalation of fumes during welding (e.g., H317: May cause allergic skin reaction; H335: May cause respiratory irritation).
- OSHA Hazard Communication Standard (HCS): Employers must maintain SDS and provide training for handling and use.
- REACH (EU): Ensure compliance with registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals, particularly for nickel content.
- RoHS (EU): While not always applicable, verify if specific restrictions apply depending on end-use (e.g., in electrical equipment).
Export and Import Regulations
- HS Code: Typically classified under 8311.10 (Electrodes for arc-welding, cored) or 8311.20 (electrodes with coatings), depending on composition and form.
- ITAR/EAR (USA): Welding rods are generally not controlled under ITAR or EAR unless part of a military or dual-use application.
- Customs Documentation: Provide commercial invoices, packing lists, and SDS as required. Declare accurate weight, value, and country of origin.
Packaging and Labeling Requirements
Packaging
- Primary Packaging: Welding rods are typically sealed in moisture-resistant foil packs or hermetically sealed containers, especially for low-hydrogen or sensitive formulations.
- Secondary Packaging: Pack in sturdy cardboard boxes or wooden crates to prevent damage during transit.
- Moisture Protection: Include desiccants and humidity indicators for hygroscopic rods (e.g., nickel-based types). Store and transport in dry environments.
Labeling
- Product Identification: Include product name, grade (e.g., ENi-CI, Ni99), diameter, length, batch/lot number, and manufacturer.
- Hazard Warnings: If applicable, display GHS pictograms and precautionary statements based on SDS.
- Storage Instructions: Label with “Keep Dry,” “Store in Original Packaging,” or “Protect from Moisture.”
- Compliance Marks: Include CE marking (if sold in the EU), and any relevant certifications (e.g., AWS A5.15 for cast iron electrodes).
Storage and Handling Procedures
Storage Conditions
- Environment: Store in a dry, well-ventilated area with controlled humidity (<50% RH preferred).
- Temperature: Maintain between 10°C and 30°C (50°F–86°F). Avoid freezing or extreme heat.
- Shelving: Keep off the floor on racks to prevent moisture absorption and physical damage.
- Segregation: Store away from acids, oxidizers, and reactive chemicals.
Handling Best Practices
- Use gloves to prevent skin contact, especially with nickel-containing rods.
- Avoid dropping or bending rods to prevent coating damage.
- Use rod ovens to re-dry electrodes if packaging is compromised (follow manufacturer’s baking instructions).
Transportation Guidelines
Domestic Transport (e.g., USA, EU)
- Mode of Transport: Suitable for road, rail, air, and sea freight.
- Hazardous Material Status: Most welding rods are non-hazardous for transport (not regulated under DOT 49 CFR, IATA, or IMDG).
- Exceptions: If rods contain regulated substances or are classified as irritants or sensitizers, consult SDS and apply appropriate regulations.
International Shipping
- IATA/ICAO (Air): Generally permitted as non-dangerous goods when packaged correctly.
- IMDG Code (Sea): Classify under UN3089 (Environmentally hazardous substance, solid, n.o.s.) only if SDS indicates environmental hazards.
- Documentation: Include SDS, commercial invoice, and bill of lading. Declare any applicable certifications (e.g., AWS, ISO 3834).
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Worker Safety (OSHA, EU-OSHA)
- PPE Requirements: Provide gloves, safety glasses, and respiratory protection when handling or using rods, especially during welding operations.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate local exhaust ventilation when welding to control fumes.
Waste Disposal
- Spent or Damaged Rods: Dispose of as non-hazardous industrial waste unless contaminated.
- Regulatory Compliance: Follow local regulations (e.g., RCRA in the USA, Waste Framework Directive in EU). Recycle metal content where possible.
Quality and Certification Standards
Industry Standards
- AWS A5.15: Specification for welding rods and bare electrodes for cast iron.
- ISO 1071: Welding consumables for cast iron.
- EN 1090: If used in construction components in the EU, ensure traceability and CE marking compliance.
Traceability and Documentation
- Maintain lot traceability for quality control.
- Provide Mill Test Certificates (MTC) or Certificate of Conformance (CoC) upon request.
Summary and Recommendations
To ensure smooth logistics and compliance for welding rods for cast iron:
– Verify classification and SDS for hazard communication.
– Use moisture-resistant packaging and proper labeling.
– Store in dry, controlled environments and handle with care.
– Comply with international shipping regulations and customs requirements.
– Train personnel on safe handling and disposal.
– Maintain certifications and documentation for quality assurance.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and product integrity throughout the supply chain.
Conclusion: Sourcing Welding Rods for Cast Iron
Sourcing the appropriate welding rods for cast iron is critical to achieving strong, durable, and crack-resistant welds. Due to the unique properties of cast iron—such as its high carbon content, brittleness, and sensitivity to thermal stress—selecting the right filler material is essential. Nickel-based electrodes (e.g., Ni-CI or Ni-Fe-CI) are often preferred for their excellent machinability, ductility, and compatibility with cast iron’s thermal expansion characteristics. In some cases, special copper-based or iron-based rods may be used depending on cost, strength requirements, and post-weld machining needs.
When sourcing these rods, it is important to consider factors such as the specific type of cast iron (gray, ductile, or malleable), welding process (SMAW being the most common), application requirements, and whether preheating and post-weld heat treatment will be performed. Purchasing from reputable suppliers that provide certified, high-quality materials ensures consistency and reliability.
Ultimately, investing time in selecting the correct welding rod and sourcing it from trusted manufacturers or distributors significantly improves weld quality, reduces repair costs, and extends the service life of cast iron components. Proper storage and handling of the rods are also vital to maintain their integrity and performance.