The global welding laser machine market is witnessing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for precision, efficiency, and automation across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy manufacturing. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 4.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is fueled by advancements in fiber laser technology, rising adoption of electric vehicles, and the need for high-speed, low-distortion welding solutions. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects steady market growth, citing growing industrial automation and government initiatives to modernize manufacturing infrastructure, particularly in Asia-Pacific and North America. As competition intensifies and technological innovation accelerates, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in delivering high-performance welding laser systems. Here’s a data-informed look at the top 10 welding laser machine manufacturers shaping the future of industrial joining processes.
Top 10 Welding Laser Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Focus on laser
Founded: 1996
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: Han’s Laser Technology Industry Group Co., Ltd, a public company which was established in 1996, has now became the flagship of Chinese national laser industry ……
#2 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#3 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#4 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#5 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#6 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Discover Your Laser Welding Solution IPG is a partner for every stage of production from research and development to full-scale manufacturing….
#7 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: Orotig, with +30 years of experience, specializes in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding engraving and casting metals….
#8 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
#9 Branson
Website: emerson.com
Key Highlights: Laser Plastic Welding. Laser Welding. Perfect for precise, aesthetically pleasing welds, laser welding is ideal for medical applications and filtration devices….
#10 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: FANUCI & FALCON is an innovative high-tech enterprise specializing in the manufacturing of advanced fiber laser machines for metal processing applications ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Welding Laser Machine
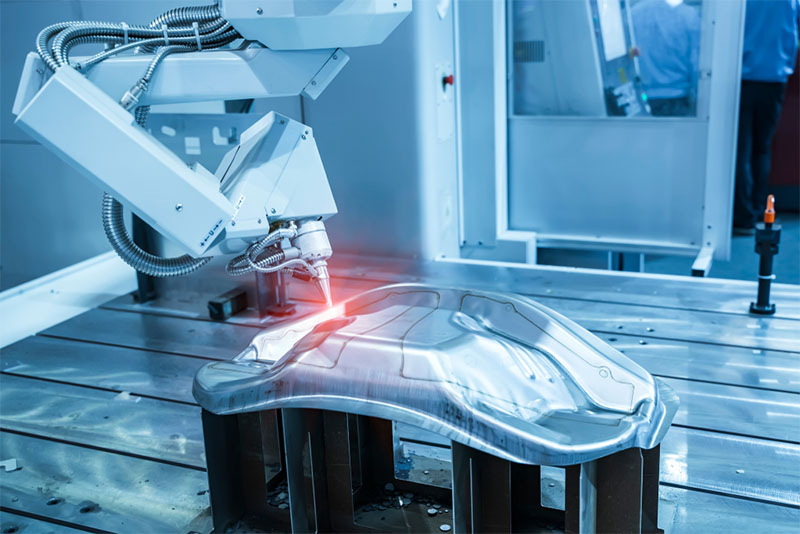

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Welding Laser Machines
The global welding laser machine market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, evolving industrial demands, and a growing emphasis on automation and precision manufacturing. Several key trends are shaping the trajectory of this market, positioning laser welding as a cornerstone technology across multiple high-growth sectors.
1. Rising Adoption in Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing
The automotive industry, particularly electric vehicle production, is becoming a major driver for laser welding machines. By 2026, the demand for lightweight, durable, and energy-efficient vehicle components will continue to grow. Laser welding offers high-speed, precision joining of battery components, power electronics, and structural parts—critical for EV performance and safety. Manufacturers are increasingly investing in high-power fiber laser systems capable of welding dissimilar metals like aluminum and copper, which are prevalent in EV battery packs.
2. Advancements in Fiber and Hybrid Laser Technologies
Fiber laser welding machines are gaining dominance due to their energy efficiency, lower maintenance costs, and superior beam quality. By 2026, innovations in multi-kilowatt fiber lasers and hybrid laser-arc welding systems are expected to enhance weld depth, speed, and stability. These hybrid solutions combine the penetration power of lasers with the gap-bridging capability of arc welding, making them ideal for heavy industrial applications such as shipbuilding and pipeline construction.
3. Growth in Automation and Smart Manufacturing Integration
The integration of welding laser machines with robotics and Industry 4.0 technologies is accelerating. By 2026, smart laser welding systems equipped with real-time monitoring, AI-driven process optimization, and IoT connectivity will become standard in advanced manufacturing facilities. These systems improve consistency, reduce waste, and enable predictive maintenance, thereby increasing overall operational efficiency.
4. Expansion in Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace and defense sectors are increasingly utilizing laser welding for high-integrity components such as turbine blades, engine parts, and fuselage assemblies. The ability of laser welding to produce clean, precise, and minimal-distortion joints is critical in these safety-sensitive industries. As global defense spending rises and commercial aerospace demand rebounds post-pandemic, the need for high-performance laser welding solutions will grow significantly.
5. Increasing Demand in Asia-Pacific Markets
The Asia-Pacific region, led by China, Japan, and South Korea, is expected to dominate the laser welding machine market by 2026. Rapid industrialization, government initiatives promoting advanced manufacturing (e.g., “Made in China 2025”), and expanding electronics and automotive sectors are key regional growth drivers. Local manufacturers are also investing in R&D to develop cost-effective, high-quality laser systems, reducing reliance on imports.
6. Focus on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
With increasing regulatory pressure to reduce carbon emissions, industries are turning to laser welding for its lower energy consumption and reduced material waste compared to traditional welding methods. By 2026, eco-friendly manufacturing practices will favor laser-based solutions, especially in green technologies like wind turbines and solar panel fabrication.
7. Customization and Modular System Designs
End-users are demanding more flexible and modular laser welding systems that can be easily adapted to different production needs. Equipment suppliers are responding with configurable platforms that support various laser sources, optics, and automation interfaces. This trend supports agile manufacturing and short production runs, especially in the medical device and consumer electronics industries.
In conclusion, the 2026 landscape for welding laser machines will be defined by innovation, integration, and industrial transformation. As laser technology becomes more accessible and versatile, its adoption will expand beyond traditional sectors, reinforcing its role as a critical enabler of next-generation manufacturing.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Welding Laser Machines (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing welding laser machines, especially from international or less-established suppliers, involves significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these pitfalls can result in operational inefficiencies, safety hazards, legal disputes, and financial losses.
Poor Build Quality and Performance Inconsistencies
Many low-cost suppliers compromise on critical components such as laser sources, cooling systems, and motion controls, leading to machines that underperform or fail prematurely. Buyers often encounter discrepancies between advertised specifications (e.g., laser power, beam quality, duty cycle) and actual performance. Inadequate quality control processes can result in inconsistent weld quality, increased downtime, and higher maintenance costs. Always request third-party test reports, conduct factory audits, and perform on-site performance validation before finalizing procurement.
Use of Counterfeit or Unlicensed Laser Components
A major quality and IP risk is the integration of counterfeit or reverse-engineered laser sources (e.g., IPG, Trumpf clones) or control systems. These components not only degrade machine reliability but also expose the buyer to intellectual property infringement claims. Unauthorized use of patented technologies may lead to customs seizures, legal liabilities, or forced machine decommissioning. Verify component authenticity through manufacturer certifications and demand transparency in the bill of materials.
Lack of Genuine Software and Embedded IP
Many welding laser machines rely on proprietary control software for precision welding parameters and safety protocols. Suppliers may use pirated or unlicensed software, which poses cybersecurity risks, limits future updates, and violates software licensing agreements. Additionally, copying firmware or user interfaces from established brands constitutes IP theft. Ensure software licenses are legitimate and include access to updates and technical support.
Inadequate Documentation and Missing Compliance Certifications
Low-quality suppliers often provide incomplete or falsified documentation, including missing CE, FDA, or laser safety certifications (e.g., IEC 60825). This can lead to regulatory non-compliance, import restrictions, or workplace safety violations. Poor documentation also hampers maintenance and troubleshooting. Require full compliance dossiers and verify certifications with issuing bodies.
Weak or Unenforceable IP Clauses in Contracts
Procurement agreements frequently lack clear IP ownership terms, especially for customizations or co-developed features. Without explicit clauses, buyers risk losing rights to modifications or facing restrictions on machine resale or servicing. Ensure contracts specify IP ownership, prohibition of reverse engineering by the supplier, and warranties against infringement.
Supply Chain Transparency and Component Traceability
Opaque supply chains make it difficult to trace the origin of critical parts, increasing the risk of inadvertently sourcing components with stolen or disputed IP. Demand component traceability and conduct supply chain due diligence, particularly when dealing with OEMs or white-label manufacturers.
Post-Purchase Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even if initial quality appears acceptable, poor after-sales support and unavailability of genuine spare parts can render machines unusable over time. Some suppliers disappear after delivery, leaving buyers without technical assistance or firmware updates. Evaluate the supplier’s service network, spare parts inventory, and long-term support commitments before purchasing.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—through thorough vetting, contractual safeguards, and technical validation—buyers can mitigate risks and ensure reliable, legally compliant laser welding operations.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Welding Laser Machine
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the international shipping, import, and operation of a welding laser machine. Adhering to these guidelines ensures legal compliance, safety, and smooth transportation.
Product Classification & Documentation
Accurate classification and comprehensive documentation are critical for customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
– HS Code Assignment: Identify the correct Harmonized System (HS) code for the welding laser machine (e.g., 8515.21 or 8515.31, depending on type and power). Consult local customs authorities or a trade expert for precise classification.
– Commercial Invoice: Include detailed specifications such as model number, power output, weight, dimensions, country of origin, and declared value.
– Packing List: Provide a breakdown of contents, packaging type, gross/net weights, and dimensions per package.
– Certificate of Origin: Required by many countries to determine tariff eligibility; may be preferential (e.g., under USMCA, RCEP) or non-preferential.
– Technical Specifications & User Manual: Submit in the destination country’s official language(s), including safety warnings and maintenance instructions.
Regulatory & Safety Compliance
Welding laser machines are subject to stringent safety and technical regulations due to their high-power operation.
– Laser Safety Certification: Ensure compliance with IEC 60825-1 (Safety of Laser Products) and obtain necessary certification (e.g., FDA 21 CFR 1040.10 in the U.S., CE marking under the EU Machinery Directive and EN 60825 in Europe).
– Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Comply with EMC directives (e.g., EU EMC Directive 2014/30/EU, FCC Part 15 in the U.S.).
– Machine Safety Standards: Adhere to relevant machinery safety standards such as ISO 12100 and ISO 13849 for risk assessment and control systems.
– Local Registration: Some countries require pre-shipment inspection, registration, or type approval (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil, KC mark in South Korea).
Packaging & Transportation
Robust packaging and proper handling are essential to prevent damage during transit.
– Shock-Resistant Packaging: Use wooden crates or reinforced containers with internal bracing and vibration-dampening materials.
– Climate Protection: Include desiccants and moisture barriers, especially for sea freight, to prevent condensation and corrosion.
– Handling Labels: Clearly mark packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Do Not Drop,” and laser warning symbols.
– Secure Mounting: Bolt the machine inside the crate to prevent movement during transport.
Import & Customs Clearance
Prepare for customs procedures in the destination country to avoid delays.
– Duty & Tax Calculation: Verify applicable import duties, VAT, and other taxes based on the HS code and trade agreements.
– Import Licenses: Determine if special permits are required (e.g., for high-power lasers or dual-use technology under export control regimes).
– Customs Broker: Engage a licensed customs broker in the destination country to facilitate documentation and clearance.
– Restricted Components: Confirm that optical components, power supplies, or software do not fall under export control lists (e.g., ITAR, EAR).
Installation & Operational Compliance
Ensure safe and compliant operation post-delivery.
– Site Preparation: Verify electrical supply compatibility (voltage, phase, grounding), ventilation, and safety zones per manufacturer specifications.
– Laser Safety Officer (LSO): Appoint an LSO if required by local regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S.) to oversee laser safety programs.
– Protective Equipment & Training: Provide appropriate PPE (e.g., laser safety goggles) and conduct operator training on safe handling and emergency procedures.
– Local Inspections: Schedule required inspections by local authorities or safety bodies before commissioning.
Environmental & Disposal Considerations
Manage end-of-life responsibly in accordance with environmental regulations.
– Waste Electrical Equipment (WEEE): Comply with WEEE directives in applicable regions for proper recycling or disposal.
– Hazardous Materials: Identify and handle any hazardous components (e.g., batteries, cooling fluids) according to local environmental laws.
– Documentation Retention: Keep compliance records, certifications, and maintenance logs for audit purposes.
Following this guide ensures the safe, legal, and efficient delivery and use of welding laser machines across global markets. Always consult with legal, logistics, and regulatory experts for jurisdiction-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Welding Laser Machine
In conclusion, sourcing a welding laser machine is a strategic investment that can significantly enhance manufacturing precision, efficiency, and product quality. After evaluating various suppliers, technologies, and machine specifications, it is evident that selecting the right laser welding system requires a thorough assessment of production needs, material types, welding accuracy requirements, and long-term operational costs.
Key factors such as laser power, beam quality, automation compatibility, service support, and total cost of ownership must be carefully balanced to ensure optimal performance and return on investment. Additionally, partnering with reputable manufacturers or suppliers who offer technical expertise, training, and reliable after-sales support is crucial for seamless integration and sustained operation.
Ultimately, the successful sourcing of a laser welding machine not only improves manufacturing capabilities but also strengthens competitiveness in the global market by enabling high-quality, high-speed, and repeatable welding processes. A well-informed procurement decision will lay the foundation for innovation, scalability, and long-term growth in advanced manufacturing operations.