The global welding equipment market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing industrialization, infrastructure development, and demand across automotive, construction, and manufacturing sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global welding market size was valued at USD 27.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% from 2024 to 2030. This growth is further fueled by advancements in portable welding technologies, including the rising adoption of welding battery machines that offer greater flexibility and efficiency in field operations. As industries shift toward lightweight, energy-efficient solutions, battery-powered welding systems are gaining traction, especially in remote or mobile applications. With this increasing demand, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, reliability, and performance, shaping the future of arc welding through cutting-edge battery technology. The following list highlights the top 10 welding battery machine manufacturers leading this transformation, selected based on market presence, technological advancements, and product scalability.
Top 10 Welding Battery Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
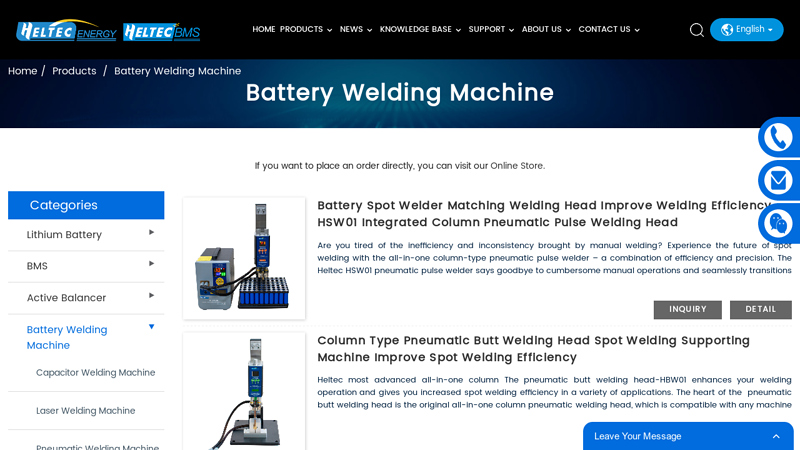
#1 China Battery Welding Machine Factory
Website: heltec-energy.com
Key Highlights: Wholesale spot welding machine from a leading manufacturer and supplier. Reliable and efficient, get the best deals directly from the factory….
#2 Battery Industry
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: AMADA WELD TECH offers a production solution: resistance welding, laser welding, laser marking, laser surface cleaning or laser cutting….
#3 Welding Equipment
Website: esab.com
Key Highlights: Explore ESAB welding equipment including cordless, engine driven, MIG, TIG and multi process welders for shop or field use….
#4 Arc Welding, Battery Chargers & Body Repair
Website: gys-welding.com
Key Highlights: GYS is a French family-owned manufacturing group that engineers, designs and sells arc welding, collision repair and automotive battery service equipment….
#5 Fronius USA
Website: fronius.com
Key Highlights: New and innovative welding, solar energy, and battery charging solutions. Perfect efficiency in every Fronius USA product….
#6 TIG welding solutions from BTS, the leading battery machine supplier
Website: btscl.com
Key Highlights: BTS TIG welding machines are optimized for energy efficiency and low gas consumption. Thermal overload protection is provided by a water-based cooling system….
#7 Branson
Website: emerson.com
Key Highlights: Branson offers state of the art plastic and metal welding and precision cleaning technologies and equipment….
#8 ESAB Debuts its First Battery
Website: esabcorporation.com
Key Highlights: The VOLT is a highly portable option for off-the-grid welding across key industries like maintenance and repair, construction, shipyard, rail, power generation….
#9 Car Battery Welding Machine
Website: wirtzusa.com
Key Highlights: Leko’s intercell welding machines can process a variety of battery sizes. The Leko BW series of equipment is fully automatic equipment….
#10 Path Robotics
Website: path-robotics.com
Key Highlights: Path Robotics’ Intelligent Welding Cells solve the skilled labor shortage with Obsidian-1 AI. 4x productivity, 30%+ lower cost, $0 capex….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Welding Battery Machine
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Welding Battery Machines
The global market for welding battery machines is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in battery technology, rising demand for portable welding solutions, and a growing emphasis on sustainability in industrial applications. As industries shift toward more energy-efficient and mobile equipment, welding battery machines—also known as battery-powered arc welders—are gaining traction across construction, automotive repair, maintenance, and field service sectors.
1. Surge in Demand for Portability and Off-Grid Welding
One of the most prominent trends shaping the 2026 outlook is the increasing need for portable welding solutions. Battery-powered welding machines offer unmatched mobility, allowing welders to operate in remote locations, construction sites, and emergency repair scenarios without access to a direct power supply. This trend is being amplified by improvements in lithium-ion battery technology, which now enables longer runtimes, faster recharging, and lighter equipment designs.
2. Advancements in Lithium-Ion and Solid-State Battery Technology
By 2026, ongoing innovations in battery chemistry are expected to enhance the performance of welding battery machines. Lithium-ion batteries continue to dominate due to their high energy density and cycle life, while early-stage research into solid-state batteries may begin influencing premium product lines. These advancements will lead to machines with higher output stability, improved thermal management, and reduced weight—making them more competitive with traditional AC/DC welders.
3. Integration with Smart Features and IoT
The convergence of welding technology and digitalization is driving the integration of smart features in battery welding machines. By 2026, many models are expected to include Bluetooth connectivity, mobile app integration, real-time performance monitoring, and predictive maintenance alerts. These smart capabilities not only improve user experience but also enhance safety and operational efficiency, especially in industrial and commercial settings.
4. Growth in Renewable Energy and Green Infrastructure Projects
With global investments in renewable energy infrastructure—such as wind turbines, solar farms, and electric vehicle (EV) charging stations—there is a rising need for flexible and eco-friendly welding tools. Battery-powered machines align well with green construction practices, producing zero emissions during operation and supporting sustainability goals. Governments and private firms investing in clean energy projects are increasingly adopting these tools, boosting market demand.
5. Expansion in Emerging Markets
Developing economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are expected to contribute significantly to market growth by 2026. Rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and government support for manufacturing are creating new opportunities for battery welding machines. Local production and cost-optimized models tailored to regional needs will likely expand accessibility and adoption rates.
6. Competitive Landscape and Product Innovation
Leading manufacturers such as Lincoln Electric, Miller Electric, and EVO-Tech are intensifying R&D efforts to differentiate their battery welding offerings. By 2026, competition will center on power output (measured in amps), battery life, multi-process capabilities (e.g., MIG, TIG, stick welding), and ruggedness for harsh environments. The market will also see increased collaboration between battery suppliers and welding equipment makers to co-develop integrated power systems.
7. Regulatory and Safety Standards Evolution
As battery-powered welding machines become more widespread, regulatory bodies are expected to update safety and performance standards specific to portable, high-energy devices. Compliance with international certifications (e.g., CE, UL, ISO) will be critical, particularly concerning battery safety, thermal runaway prevention, and electromagnetic compatibility.
Conclusion
By 2026, the welding battery machine market will be characterized by rapid technological evolution, expanding applications, and strong growth across both developed and emerging regions. Driven by the need for mobility, energy efficiency, and smart functionality, these machines are transitioning from niche tools to essential equipment in modern welding operations. Companies that innovate in battery integration, digital features, and sustainability will be best positioned to capture market share in this dynamic landscape.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Welding Battery Machines (Quality & IP)
Sourcing welding battery machines, especially from new or unfamiliar suppliers, involves significant risks related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to operational failures, safety hazards, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Here are the most critical issues to watch for:
H3: Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Misrepresented Specifications & Performance:
- The Pitfall: Suppliers may exaggerate key metrics like peak welding current, battery capacity (Ah), charge/discharge cycles, duty cycle, or welding speed. Machines might fail to deliver claimed performance under real-world conditions.
- The Risk: Inadequate weld strength, premature battery failure, overheating, inability to handle required workloads, leading to rework, downtime, and safety incidents.
- Mitigation: Insist on independent third-party testing reports (e.g., TÜV, UL, CE certifications with test data), conduct rigorous on-site performance testing with your specific materials, and demand detailed technical documentation.
-
Substandard Component Quality:
- The Pitfall: Use of low-grade batteries (prone to swelling, fire, short lifespan), inferior power electronics (IGBTs, MOSFETs), poor-quality connectors/wiring, or flimsy mechanical construction.
- The Risk: Catastrophic failures (thermal runaway/fires), frequent breakdowns, inconsistent weld quality, short product lifespan, and high maintenance costs.
- Mitigation: Require detailed Bills of Materials (BOMs) specifying component brands/models (especially batteries and power semiconductors), conduct factory audits to inspect component sourcing and assembly processes, and sample destructive testing.
-
Inadequate Safety Protections & Certifications:
- The Pitfall: Lack of essential safety features (overcharge, over-discharge, over-current, over-temperature, short-circuit protection, robust BMS) or reliance on fake/invalid safety certifications (CE, UL, KC, PSE).
- The Risk: Severe safety hazards including battery fires, electric shock, and equipment damage. Non-compliance with local regulations can lead to import bans, fines, or liability.
- Mitigation: Verify certifications through official databases, demand test reports from accredited labs, physically inspect safety circuits and BMS functionality during audits, and ensure compliance with destination market regulations.
-
Poor Build Quality & Reliability:
- The Pitfall: Rushed manufacturing, lack of quality control (QC) processes, inconsistent assembly, and poor workmanship (e.g., loose connections, inadequate strain relief, poor cable management).
- The Risk: High field failure rates, unpredictable downtime, inconsistent weld results, and difficulty in maintenance/repair.
- Mitigation: Conduct thorough factory audits focusing on QC procedures (incoming inspection, in-process checks, final testing), request MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) data, and demand warranties with clear repair/replacement terms.
-
Insufficient After-Sales Support & Spare Parts:
- The Pitfall: Suppliers with no local presence, lack of technical support, or inability/unwillingness to provide spare parts (especially batteries, control boards) long-term.
- The Risk: Extended downtime, machines becoming obsolete quickly, high costs for third-party repairs, and stranded investment.
- Mitigation: Negotiate service level agreements (SLAs), confirm spare parts inventory and pricing for at least 5-7 years, assess supplier’s technical support capabilities (response time, language), and consider local service partners.
H3: Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
-
Design & Technology Infringement:
- The Pitfall: The machine is a direct copy (“knock-off”) of a competitor’s patented or copyrighted design, circuitry, software, or unique features (e.g., specific welding algorithms, user interface).
- The Risk: Your company could be named in infringement lawsuits by the original IP holder, facing injunctions, damages, destruction of infringing goods, and reputational harm. Customs seizures are also possible.
- Mitigation: Conduct IP due diligence: request proof of ownership (patents, design registrations), perform freedom-to-operate (FTO) searches, include IP indemnification clauses in contracts, and be wary of prices significantly below market.
-
Counterfeit Components:
- The Pitfall: Use of counterfeit semiconductor chips, controllers, or other critical electronic components that mimic genuine parts but fail prematurely or malfunction.
- The Risk: Unreliable performance, safety hazards, voided warranties, and potential IP infringement if the counterfeit chips replicate protected designs.
- Mitigation: Require suppliers to use only genuine components from authorized distributors, conduct component authenticity verification (e.g., visual inspection, data logging, X-ray), and include component sourcing requirements in contracts.
-
Lack of Clear IP Ownership in Customization:
- The Pitfall: Developing custom features or modifications with the supplier, but the contract fails to explicitly assign IP ownership (designs, software code, specifications) to your company.
- The Risk: The supplier could claim ownership or reuse your custom designs for competitors. You lose control over your investment and innovation.
- Mitigation: Use clear development contracts stating that all IP created specifically for your project is your sole property. Include detailed specifications and require assignment of rights.
-
Software & Firmware IP Issues:
- The Pitfall: Proprietary welding control algorithms, user interfaces, or BMS software embedded in the machine may be unlicensed, pirated, or infringe on third-party software IP.
- The Risk: Legal liability for software piracy or infringement, potential for malware, inability to update or modify software, and security vulnerabilities.
- Mitigation: Require software license documentation, conduct source code reviews (if possible), ensure compliance with open-source licenses, and include software IP warranties in contracts.
Key Takeaway: Avoiding these pitfalls requires proactive due diligence. Prioritize transparency, demand verifiable proof (certificates, test reports, BOMs), conduct on-site audits, and secure strong contractual protections regarding quality, specifications, IP ownership, and indemnification. Never compromise on safety certifications or ignore red flags related to pricing or supplier responsiveness.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Welding Battery Machine
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, handling, installation, and operation of a welding battery machine. Adhering to these guidelines ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and efficient deployment across international and domestic supply chains.
Regulatory Classification and Documentation
Identify the welding battery machine according to relevant international and national regulations. Classify the equipment under the appropriate Harmonized System (HS) Code for customs clearance—typically under HS 8515 (electroplasma and other welding machinery). Ensure all documentation, including commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, and certificate of origin, is complete and accurate. Include technical specifications and safety certifications (e.g., CE, UL, or IEC standards) to facilitate customs processing.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Package the machine in a robust, moisture-resistant crate with internal bracing to prevent movement during transit. Use anti-static materials if electronic components are exposed. Clearly label the packaging with handling instructions such as “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack.” Include weight, dimensions, and center-of-gravity indicators for safe lifting. For battery-integrated models, ensure battery terminals are insulated and secured per IATA/IMDG regulations if shipped with batteries installed.
Transportation Modes and Restrictions
Choose transportation mode based on machine size, weight, and destination. For air freight, comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if lithium batteries are included—this may require UN38.3 testing certification and proper labeling. For sea freight, follow IMDG Code requirements, especially for lithium battery shipments. Road and rail transport must adhere to ADR/RID regulations in applicable regions. Confirm carrier-specific restrictions and ensure secure loading to prevent shifting.
Import/Export Compliance
Verify export control classifications (e.g., ECCN under the U.S. Commerce Control List) to determine if licenses are required. Check destination country import restrictions, including conformity assessment procedures and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. Some countries may require pre-shipment inspections or local representative registration. Ensure compliance with environmental directives such as RoHS and REACH if applicable.
On-Site Delivery and Installation
Coordinate delivery with site availability and ensure unloading equipment (e.g., forklift, crane) is ready. Conduct a site inspection to verify floor load capacity, power supply compatibility (voltage, phase, grounding), and ventilation. Follow manufacturer’s installation procedures and involve certified technicians. Retain installation records for compliance audits. Isolate the machine during setup to prevent accidental activation.
Safety and Operational Compliance
Ensure the welding battery machine meets applicable safety standards such as ISO 5182 (resistance welding equipment) and IEC 60974 series (arc welding equipment). Verify that protective features—including emergency stops, interlocks, and fume extraction—are operational. Provide operator training on safe use, maintenance, and emergency procedures. Maintain logs for inspections, repairs, and safety checks.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
Dispose of packaging materials according to local waste management regulations. At end-of-life, handle the machine and any integrated batteries in compliance with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) and battery recycling directives. Use authorized recyclers for proper dismantling and material recovery.
Recordkeeping and Audits
Maintain comprehensive records including shipping documents, compliance certifications, maintenance logs, and training records. These documents support regulatory audits and demonstrate due diligence in supply chain management. Update compliance status regularly in response to regulatory changes.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and adherence to compliance requirements are critical for the safe and legal deployment of welding battery machines. Always consult local regulations and involve qualified compliance officers or consultants when entering new markets.
Conclusion:
After a thorough evaluation of various suppliers and options for sourcing a welding battery machine, it is evident that selecting the right unit requires a balanced approach considering performance, reliability, cost-efficiency, and after-sales support. Battery-powered welding machines offer significant advantages in terms of portability, energy efficiency, and usability in remote or off-grid locations, making them ideal for fieldwork, construction, and maintenance applications.
Based on the assessment of technical specifications, brand reputation, user feedback, and total cost of ownership, sourcing from reputable manufacturers with proven experience in battery technology and welding solutions is recommended. Key factors such as weld quality, battery life, charging time, durability, and warranty should guide the final procurement decision.
In conclusion, investing in a high-quality welding battery machine from a trusted supplier not only enhances operational efficiency but also reduces long-term maintenance and downtime costs. It is advisable to establish partnerships with suppliers who provide comprehensive technical support and service networks to ensure sustained performance and user satisfaction.