The global aluminum fabrication market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials across aerospace, automotive, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the aluminum market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% from 2023 to 2028, with 6061 aluminum—one of the most widely used alloys due to its excellent weldability and mechanical properties—accounting for a significant share of this expansion. Grand View Research further underscores this trend, noting that the rising adoption of aluminum in electric vehicles and sustainable infrastructure is accelerating the need for high-precision welding solutions. As demand for reliable 6061 aluminum fabricators intensifies, identifying manufacturers with proven expertise in welding this versatile alloy has become critical for supply chain performance and product integrity. Below are the top 10 welding 6061 aluminum manufacturers leading the industry through innovation, quality control, and scalable production capabilities.
Top 10 Welding 6061 Aluminum Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
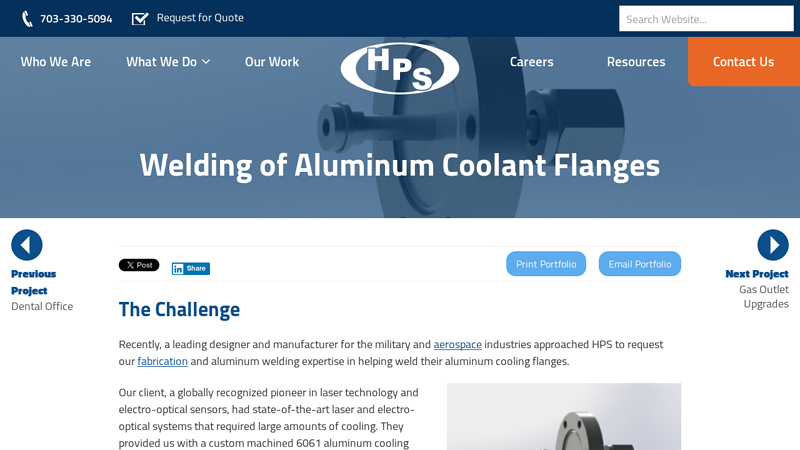
#1 Aluminum Welding Coolant Flanges
Domain Est. 1996
Website: highpurity.com
Key Highlights: They provided us with a custom machined 6061 aluminum cooling flange with 37° aluminum VCR flare fittings, and asked us to weld them together. The Strategy….
#2 6061 Aluminum Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: aluminummanufacturers.org
Key Highlights: Find top USA manufacturers of 6061 aluminum with diverse grades, advanced equipment, custom solutions, and swift delivery….
#3 Alcotec
Domain Est. 1996
Website: esab.com
Key Highlights: AlcoTec aluminum welding wire alloys, aluminum metallizing wires and mechanical wire products are industry-leading aluminum process solutions….
#4 What Are The Considerations When Welding 6061
Domain Est. 1998
Website: howardprecision.com
Key Highlights: Welding 6061-T651 aluminum plates involves a thorough understanding of the alloy’s properties, precise control over the welding process, and careful selection ……
#5 Industry Standards
Domain Est. 1998
Website: aluminum.org
Key Highlights: For 70 years, the Aluminum Association has worked with the industry to develop and maintain technical standards for aluminum production….
#6 6061 TIG Welding TIG Button Aluminum Fabrication
Domain Est. 2002
Website: 6061.com
Key Highlights: Email [email protected] with any questions regarding your order. > >…
#7 6061 Aluminum Sheet
Domain Est. 2011
Website: kloecknermetals.com
Key Highlights: Kloeckner Metals sells 6061 aluminum sheet, a general purpose alloy that strengths through precipitation hardening. Contact us today for a quote….
#8 0.047“ 6061 Aluminum Alloy Welding Wire 4.5 lb Spool (2kg)
Domain Est. 2013
Website: xtool.com
Key Highlights: User-friendly operation. Perfectly adapted to the xTool MetalFab Laser Welder and CNC Cutter. The unique dual-hole design on the welding wire spool ensures ……
#9 6061 Aluminum Flat Coupons
Domain Est. 2018
#10 6061 Aluminum Alloy: Comprehensive Guide
Domain Est. 2009
Website: elkamehr.com
Key Highlights: Common filler materials for welding 6061 aluminum include 4043 and 5356. These fillers help maintain the weld’s strength and corrosion ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Welding 6061 Aluminum

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Welding 6061 Aluminum
The global market for welding 6061 aluminum is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving industrial demands, technological advancements, and sustainability imperatives. As one of the most widely used aluminum alloys due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and weldability, 6061 aluminum remains a cornerstone material in aerospace, automotive, marine, and structural applications. The following trends are expected to shape the welding of 6061 aluminum in 2026:
-
Increased Adoption in Lightweight Transportation
With stringent global emissions regulations and a push toward fuel efficiency and electrification, the automotive and aerospace industries are increasingly adopting lightweight materials. 6061 aluminum, particularly in electric vehicles (EVs), structural frames, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), is seeing higher demand. By 2026, welding processes tailored to maintain the alloy’s mechanical properties post-weld—such as reduced heat-affected zone (HAZ) softening—will be critical. Advanced welding techniques like Cold Metal Transfer (CMT) and pulsed gas metal arc welding (GMAW-P) are expected to dominate due to their precision and low distortion. -
Growth in Automation and Robotics
The integration of robotic welding systems in high-volume manufacturing is accelerating. By 2026, automated welding cells equipped with AI-driven process monitoring and adaptive control systems will become standard for welding 6061 aluminum. These systems enhance consistency, reduce defects, and improve throughput. Collaborative robots (cobots) will also see increased use in smaller fabrication shops, democratizing access to high-quality aluminum welding. -
Advancements in Filler Alloy Development
Welding 6061 aluminum presents challenges due to its tendency to develop micro-cracking and reduced strength in the HAZ. Innovations in filler metals—such as Al-Mg-Si and Al-Zn-Mg based alloys engineered to better match the base metal’s properties—are expected to gain traction. By 2026, proprietary filler alloys designed specifically for 6061 may become commercially mainstream, improving weld integrity and reducing post-weld heat treatment requirements. -
Rise of Hybrid and Alternative Welding Technologies
Traditional TIG and MIG welding will continue to be prevalent, but hybrid processes such as laser-MIG hybrid welding and friction stir welding (FSW) will expand in niche sectors. FSW, in particular, is gaining favor in aerospace and rail applications due to its solid-state nature, which avoids melting and preserves the alloy’s strength. By 2026, portable FSW systems may become more accessible, enabling on-site welding of large 6061 aluminum structures. -
Sustainability and Recycling Focus
The push for circular economy models will drive demand for recyclable materials and energy-efficient processes. Aluminum’s high recyclability aligns with these goals. In welding, this translates to optimized energy consumption in welding equipment and increased use of recycled 6061 aluminum. By 2026, manufacturers may prioritize welding techniques that minimize material waste and emissions, supported by lifecycle assessment (LCA) tools. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will remain dominant in aluminum fabrication due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. North America and Europe will focus on high-precision applications in aerospace and advanced manufacturing, driving demand for certified welding procedures and skilled labor. Regional standards—such as AWS D1.2 (Structural Welding Code – Aluminum)—will see updates to reflect new technologies and safety requirements. -
Workforce Training and Certification
As welding technologies evolve, the demand for skilled welders proficient in aluminum-specific techniques will grow. By 2026, augmented reality (AR)-based training modules and digital certification platforms are expected to become common, improving the speed and quality of workforce development.
Conclusion
By 2026, the welding of 6061 aluminum will be characterized by smarter, cleaner, and more efficient processes. The convergence of automation, advanced materials, and sustainability goals will redefine best practices, positioning 6061 aluminum as a key enabler of next-generation lightweight structures across multiple high-growth industries.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Welding 6061 Aluminum (Quality, IP)
Sourcing high-quality 6061 aluminum for welding applications requires careful attention to material specifications, supplier reliability, and intellectual property (IP) concerns. Overlooking these factors can lead to project delays, compromised weld integrity, safety risks, and legal exposure.
Quality Pitfalls
Incorrect Alloy or Temper
One of the most frequent issues is receiving material that is not genuine 6061 or is in the wrong temper (e.g., T4 instead of T6). Using improperly aged or incorrect alloy grades results in poor weldability, reduced strength, and susceptibility to cracking. Always verify mill test reports (MTRs) that confirm ASTM B221 or AMS 4027 standards and proper temper designation.
Contaminated or Poor Surface Condition
Surface oxides, oils, or improper storage can compromise weld quality. 6061 aluminum is prone to oxide layer formation, which hinders fusion. Material stored in humid or corrosive environments may develop pitting or intergranular corrosion, weakening weld joints. Inspect packaging and surface cleanliness upon delivery.
Inconsistent Chemistry and Impurities
Off-spec chemical composition—especially elevated iron or silicon levels—can reduce weld ductility and increase hot cracking risk. Sourcing from unqualified mills or brokers increases exposure to inconsistent batches. Require certified chemical analysis and prefer suppliers with ISO 9001 or Nadcap accreditation.
Non-Conforming Dimensions and Tolerances
Out-of-tolerance thickness, flatness, or width impacts fit-up and welding precision. Poor dimensional control leads to gaps, uneven heat distribution, and structural weakness. Specify tight tolerances (e.g., ASTM B221) and conduct incoming inspections.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
Unauthorized Use of Proprietary Designs or Processes
Sourcing components or materials based on patented welding procedures or engineered designs without proper licensing risks IP infringement. This is especially critical in aerospace, defense, or medical applications where weld procedures are often protected.
Supplier Use of Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Materials
Some suppliers may offer “equivalent” materials that mimic 6061 but are reverse-engineered without authorization, potentially violating material composition patents or process IP. This not only affects performance but exposes the buyer to legal liability.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Inadequate material traceability (heat numbers, lot tracking) makes it difficult to prove compliance during audits or failure investigations. Without proper documentation, proving the legitimacy and origin of the material becomes challenging, increasing IP and quality risks.
Third-Party Certification Fraud
Some suppliers falsify MTRs or claim certifications they do not possess. This undermines quality assurance and may involve fraudulent use of registered trademarks or certifications, constituting IP violations.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Source from reputable, certified suppliers with verifiable quality management systems.
- Require full material traceability and mill test reports for every batch.
- Conduct independent material testing (e.g., PMI, mechanical testing) for critical applications.
- Audit suppliers regularly and verify compliance with industry standards.
- Consult legal counsel when sourcing materials involving proprietary designs or processes to ensure IP compliance.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP concerns, organizations can ensure the integrity, safety, and legal compliance of their aluminum welding projects.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Welding 6061 Aluminum Using ER4043 (H2 Filler Alloy)
Overview
Welding 6061 aluminum—a heat-treatable, medium-strength alloy—requires careful attention to material characteristics, weld procedures, safety, and regulatory compliance. This guide outlines best practices for logistics and compliance when using ER4043 (designated as H2 in some legacy or internal systems) as the filler metal. ER4043 is a common choice for welding 6061 due to its good fluidity, crack resistance, and compatibility.
Note: “H2” is not a standard AWS/ISO designation for aluminum filler metals. It may refer internally to ER4043, commonly used with 6061-T6. For this guide, H2 = ER4043.
1. Material Specifications & Compatibility
Base Metal: 6061 Aluminum Alloy
- Common Temper: T6 (solution heat-treated and artificially aged)
- Composition: Mg (0.8–1.2%), Si (0.4–0.8%), Cu (~0.15%), balance Al
- Weldability: Moderate; prone to hot cracking in as-welded condition if not properly controlled
Filler Metal: ER4043 (H2)
- AWS A5.10 Classification: ER4043
- Si Content: ~5% (enhances fluidity and hot cracking resistance)
- Melting Range: ~1065–1170°F (574–632°C)
- Advantages:
- Good crack resistance
- Smooth bead profile
- Suitable for general-purpose welding of 6061
- Limitations:
- Lower strength than base metal
- Not heat-treatable post-weld
- Anodizing mismatch (may appear darker)
✅ Compatibility: ER4043 is acceptable for welding 6061, especially when crack resistance is prioritized over ultimate strength.
2. Welding Process & Parameters
Recommended Process:
- GTAW (TIG) – Preferred for precision, clean welds, and thin sections
- GMAW (MIG) – Suitable for production or thicker sections
Shielding Gas:
- GTAW: 100% Argon (Ar)
- GMAW: 100% Ar or Ar/He mix (e.g., 75% Ar / 25% He) for deeper penetration
Typical Parameters (Adjust based on thickness and joint design):
| Parameter | GTAW (TIG) | GMAW (MIG) |
|———————|—————————–|——————————–|
| Polarity | AC (with high-frequency start) | DCEP (electrode positive) |
| Filler Diameter | 1/16″ (1.6 mm) | 0.035″–0.047″ (0.9–1.2 mm) |
| Travel Speed | 3–6 in/min (75–150 mm/min) | 5–15 in/min (125–380 mm/min) |
| Preheat (if needed) | 250°F max (120°C) | Not typically required |
| Interpass Temp | < 300°F (150°C) | < 300°F (150°C) |
⚠️ Avoid excessive heat input to prevent distortion and loss of base metal strength.
3. Joint Preparation & Cleaning
Cleaning:
- Remove oil, grease, oxides, and moisture using:
- Solvent cleaning: Acetone or alcohol
- Mechanical cleaning: Stainless steel wire brush (dedicated to aluminum)
- Chemical cleaning: Alkaline or acidic etch (per ASTM D2651)
Joint Design:
- Use standard V, square, or U-groove joints depending on thickness
- Ensure proper fit-up (gaps < 1/16″)
- Back purging may be needed for critical welds
4. Post-Weld Considerations
Post-Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT):
- Not recommended for ER4043 on 6061. The weld zone cannot be heat-treated to restore base metal strength.
- Natural aging occurs but does not restore full T6 properties.
Post-Weld Cleaning:
- Remove flux residues (if used) with hot water and brush
- Avoid chlorinated solvents near hot metal
Inspection & Testing:
- Visual Inspection (VT): Check for porosity, cracks, undercut
- Dye Penetrant Testing (PT): For surface defects
- Radiographic (RT) or Ultrasonic (UT): For critical joints
- Bend Tests: For procedure qualification
5. Logistics & Handling
Storage:
- Store filler wire (ER4043) in a dry, clean environment (low humidity)
- Use sealed containers or spool wraps to prevent oxidation
- Label clearly: “ER4043 – For Aluminum Use Only”
Material Traceability:
- Maintain Mill Test Reports (MTRs) for base and filler metals
- Implement a Material Control System (e.g., barcoding, logs)
- Ensure alloy verification via PMI (Positive Material Identification) if critical
Transportation:
- Protect aluminum from contamination (steel dust, moisture)
- Use plastic wraps or protective covers during transit
- Segregate aluminum materials from carbon steel
6. Regulatory & Compliance Standards
Ensure adherence to the following standards:
| Standard | Requirement |
|——–|————-|
| AWS D1.2/D1.2M | Structural Welding Code – Aluminum |
| ASME Section IX | Qualification of Welding Procedures and Personnel |
| ISO 15614-2 | Qualification Testing of Welding Procedures for Aluminum |
| OSHA 29 CFR 1910.252 | Fire prevention, ventilation, PPE requirements |
| NFPA 51B | Fire prevention during welding and cutting |
| ANSI Z49.1 | Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes |
✅ Welder Qualification: All welders must be qualified per AWS D1.2 or ASME IX.
7. Health, Safety & Environmental (HSE)
Ventilation:
- Use local exhaust ventilation (LEV) to remove aluminum oxide fumes
- Monitor for ozone and metal fume exposure (especially in confined spaces)
PPE Requirements:
- Welding helmet with appropriate shade (Shade 10–12 for aluminum)
- Flame-resistant clothing
- Gloves (leather or aluminized)
- Respiratory protection (if ventilation is inadequate)
Fire Safety:
- Remove flammable materials within 35 ft (10 m)
- Have fire extinguisher (Class D for metal fires) nearby
8. Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain records of:
– Welding Procedure Specifications (WPS)
– Procedure Qualification Records (PQR)
– Welder Qualification Records (WQR)
– Inspection reports (VT, PT, RT, etc.)
– Material certifications (MTRs)
– Non-conformance reports (NCRs), if applicable
9. Quality Assurance & Continuous Improvement
- Conduct first-article inspections for new jobs
- Perform weld audits regularly
- Train welders on aluminum-specific techniques
- Review rework rates and adjust procedures as needed
Summary: Key Compliance Checklist
| Item | Requirement |
|——|————-|
| ✅ Filler Metal | ER4043 (H2), certified to AWS A5.10 |
| ✅ Base Metal | 6061-T6, certified with MTR |
| ✅ WPS/PQR | Qualified per AWS D1.2 or ASME IX |
| ✅ Welder Qualification | Valid certification on file |
| ✅ Cleaning | Oxide and contaminant removal verified |
| ✅ Inspection | VT + NDT as required |
| ✅ Recordkeeping | Complete and traceable |
| ✅ Safety | PPE, ventilation, fire watch compliant |
Conclusion
Welding 6061 aluminum with ER4043 (H2) is a common and effective practice when proper procedures, logistics, and compliance measures are followed. Emphasis on cleanliness, heat control, qualified personnel, and documentation ensures structural integrity and regulatory compliance.
Always consult project specifications and engineering requirements before welding. In aerospace, marine, or pressure vessel applications, stricter standards may apply (e.g., AMS, ASME BPVC).
Prepared by: [Your Name/Department]
Date: [Insert Date]
Revision: 1.0
Conclusion for Sourcing Welding 6061 Aluminum:
Sourcing welding materials and services for 6061 aluminum requires careful consideration due to the alloy’s specific properties and challenges. While 6061 aluminum offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and machinability, it is prone to weld cracking and reduced mechanical properties in the heat-affected zone. Therefore, successful welding depends on using appropriate filler alloys (such as 4043 or 5356), precise heat control, and qualified welding procedures (typically TIG or MIG welding).
When sourcing, it is crucial to partner with experienced suppliers or fabricators who understand the metallurgical nuances of 6061 aluminum and adhere to industry standards such as AWS D1.2. Additionally, material certification, quality control processes, and post-weld testing (e.g., visual inspection, dye penetrant testing) should be verified to ensure structural integrity.
In conclusion, while 6061 aluminum can be reliably welded, successful outcomes depend not only on the quality of the base and filler materials but also on the expertise of the welding provider. A strategic sourcing approach that prioritizes technical capability, quality assurance, and compliance will ensure durable, high-performance welded joints suitable for structural and aerospace applications.