The global laser welding machine market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-precision joining solutions across industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 2.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6% from 2023 to 2028, reaching an estimated USD 4.3 billion by the end of the forecast period. This expansion is fueled by the rising adoption of automation, advancements in fiber laser technology, and the need for energy-efficient manufacturing processes. Additionally, Grand View Research highlights the surge in electric vehicle (EV) production as a key market catalyst, given the extensive use of laser welding in battery and powertrain components. As industries prioritize speed, accuracy, and repeatability, leading manufacturers are investing heavily in R&D to enhance laser welding capabilities. In this competitive landscape, the following ten companies have emerged as top-tier producers of laser welder machines, setting benchmarks in innovation, reliability, and global market presence.
Top 10 Welder Laser Machine Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Focus on laser
Founded: 1996
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: Han’s Laser Technology Industry Group Co., Ltd, a public company which was established in 1996, has now become the flagship of Chinese national laser ……
#2 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#3 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#4 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#5 Everlast Inverter Welders Equipment
Website: everlastgenerators.com
Key Highlights: Everlast Power Equipment, manufacturers of MIG, TIG & Stick welders. For reliable welding machines and supplies shop Everlast Power Equipment….
#6 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Discover Your Laser Welding Solution IPG is a partner for every stage of production from research and development to full-scale manufacturing….
#7 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: We specialise in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding, engraving, casting and cutting precious and non-precious metals….
#8 Fanuci & Falcon
Website: fanuci-falcon.com
Key Highlights: FANUCI & FALCON is an innovative high-tech enterprise specializing in the manufacturing of advanced fiber laser machines for metal processing applications ……
#9 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
#10 Sunstone Welders
Website: sunstonewelders.com
Key Highlights: Sunstone designs and manufactures high-tech micro welding and engraving solutions for many different industries. In short, wherever a very small spot weld ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Welder Laser Machine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Welder Laser Machines
The global welder laser machine market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing automation across industries, and the rising demand for precision manufacturing. As industries prioritize efficiency, energy savings, and high-quality welds, laser welding technology continues to displace traditional welding methods. Below are key trends expected to shape the welder laser machine market in 2026:
-
Growing Adoption in Automotive and Electric Vehicle (EV) Manufacturing
The shift toward lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength steel in automotive design is accelerating the demand for laser welding. With the EV market expanding rapidly, manufacturers are increasingly using laser welder machines for battery assembly, motor components, and structural parts due to their precision, speed, and minimal heat-affected zones. By 2026, the integration of laser welding in EV production lines is expected to become standard practice. -
Advancements in Fiber Laser Technology
Fiber laser systems are becoming more efficient, compact, and cost-effective, making them the preferred choice for industrial welding applications. In 2026, expect higher power outputs (up to 30kW and beyond) and improved beam quality, enabling deeper penetration and faster welding speeds. Innovations in beam shaping and modulation will allow greater control over weld characteristics, supporting complex joint geometries and dissimilar metal joining. -
Integration with Automation and Industry 4.0
Laser welder machines are increasingly being integrated into smart manufacturing ecosystems. By 2026, the use of AI-driven monitoring, real-time process control, and IoT-enabled diagnostics will enhance weld quality and reduce downtime. Collaborative robots (cobots) equipped with laser welding heads will become more prevalent in small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs), improving flexibility and lowering entry barriers. -
Rise in Demand from Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace industry continues to demand high-precision, reliable joining solutions for turbine blades, fuselage components, and engine parts. Laser welding offers advantages such as reduced distortion and excellent repeatability. By 2026, increased investments in next-generation aircraft and defense systems will drive the adoption of advanced laser welding systems, particularly hybrid laser-arc technologies. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Countries in Asia-Pacific (especially China, India, and Southeast Asia), Latin America, and Eastern Europe are witnessing rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. These regions are expected to account for a growing share of the laser welder machine market by 2026, fueled by expanding manufacturing bases and government initiatives to promote high-tech industries. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus
As sustainability becomes a top priority, laser welding is gaining favor due to its lower energy consumption and reduced material waste compared to traditional methods. Manufacturers are investing in energy-efficient laser sources and closed-loop cooling systems. Regulatory pressures and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals will further boost the adoption of eco-friendly welding technologies. -
Increased Competition and Price Optimization
With more players entering the market—particularly from China and South Korea—competition is intensifying. This is expected to drive price reductions and innovation, making high-quality laser welder machines more accessible to a broader range of industries. However, premium systems with advanced features will continue to command higher margins.
In conclusion, the 2026 welder laser machine market will be characterized by technological sophistication, deeper industry integration, and global expansion. Companies that invest in R&D, embrace digitalization, and cater to sector-specific needs—especially in EVs, aerospace, and smart factories—are likely to lead the market.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Welder Laser Machines (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a welder laser machine presents significant opportunities for improved precision and efficiency, but it also comes with critical risks—especially concerning quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational disruptions, financial loss, and legal exposure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
Many suppliers, particularly in competitive low-cost markets, use substandard materials and inferior components to reduce prices. This includes low-grade optics, unreliable cooling systems, and underpowered laser sources. These compromises result in inconsistent weld quality, frequent breakdowns, and high maintenance costs over time. Always verify the specifications of core components (laser source, optics, motion system) and request third-party test reports or certifications.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Service Network
Laser welding systems require ongoing maintenance and technical support. Sourcing from suppliers without a local service presence or clear support structure leads to extended downtimes. Be cautious of vendors who offer attractive upfront pricing but lack service agreements, spare parts availability, or trained technicians in your region.
Misrepresentation of Machine Capabilities
Some suppliers exaggerate performance metrics such as maximum power, welding speed, or material thickness capacity. Without independent verification or on-site testing, buyers may receive machines that cannot meet production requirements. Always conduct a live demonstration with materials representative of your actual use case and review machine logs or performance data.
Lack of Quality Control and Certification Standards
Suppliers without ISO 9001 certification or equivalent quality management systems may lack consistent manufacturing processes. This increases the risk of variability between units. Ensure the manufacturer adheres to recognized international standards and conducts comprehensive in-house testing before shipment.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
One of the most serious risks involves unintentionally sourcing machines that incorporate patented technologies without proper licensing. Some manufacturers reverse-engineer or clone designs from leading brands, exposing the buyer to potential IP litigation. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s reputation and request documentation confirming legal use of key technologies (e.g., laser source licensing, software copyrights).
Use of Counterfeit or Unlicensed Software and Components
Low-cost machines may include pirated control software or unlicensed firmware, which can cause operational instability and legal issues. Additionally, counterfeit laser sources (e.g., falsely branded IPG or Raycus) are common and offer poor reliability. Confirm software authenticity and verify component brands with original equipment manufacturer (OEM) documentation.
Insufficient Training and Documentation
Even high-quality machines underperform without proper operator training and technical documentation. Suppliers may omit comprehensive manuals, safety guidelines, or training programs, leading to misuse, safety hazards, and reduced machine lifespan. Ensure training is included in the purchase agreement and materials are provided in your working language.
Hidden Costs and Unclear Warranty Terms
Initial quotes may exclude installation, calibration, import duties, or software updates. Warranty terms can be vague or exclude critical components like the laser source. Clarify all costs upfront and insist on a detailed warranty covering parts, labor, and response time.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—prioritizing verified quality, robust support, and IP compliance—buyers can mitigate risks and ensure a reliable, legally sound investment in laser welding technology.
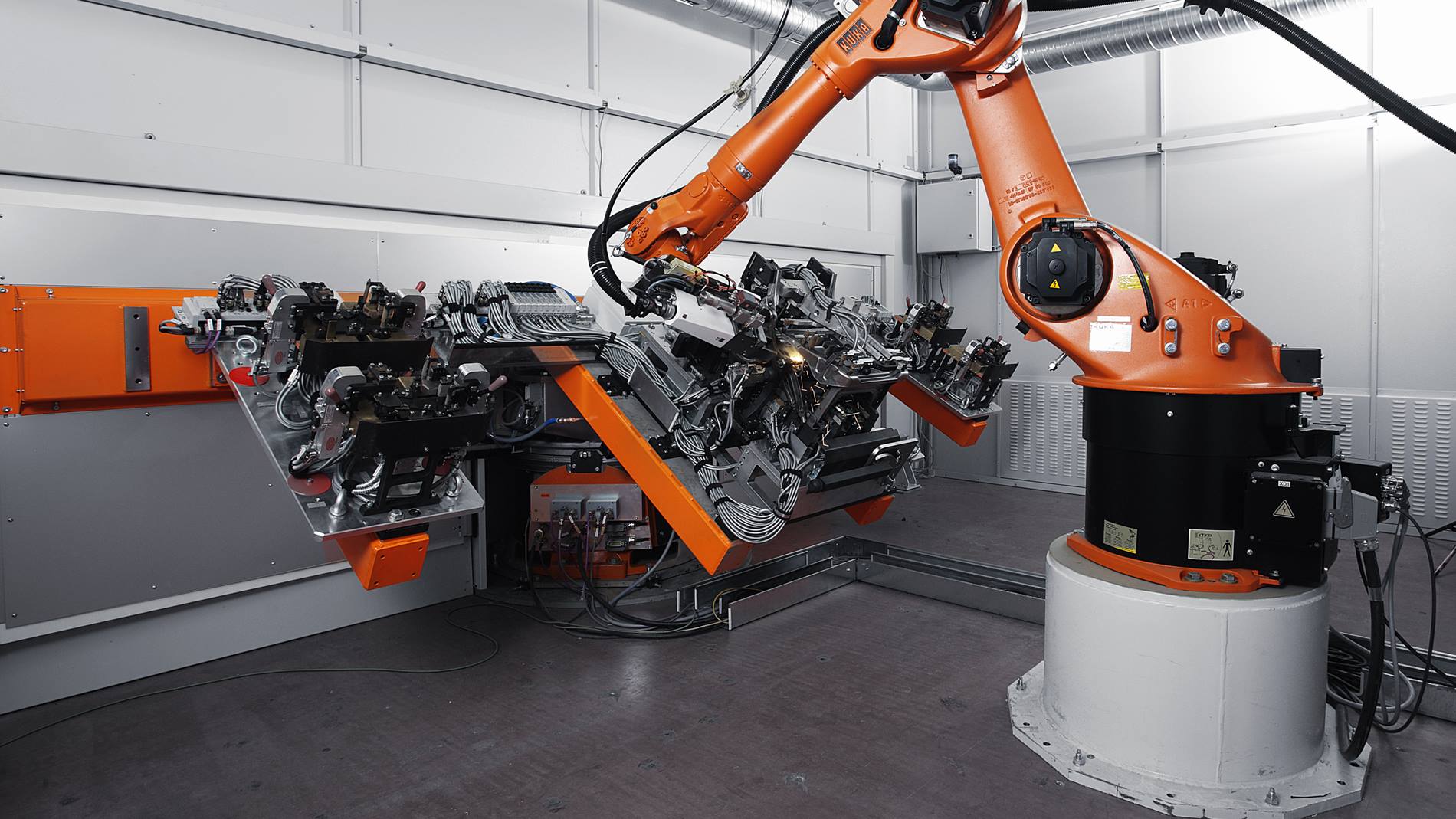
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Welder Laser Machine
Overview
This guide provides essential information for the safe and compliant logistics handling, transportation, import/export, and operation of industrial Welder Laser Machines. Adherence to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, minimizes risks, and supports efficient supply chain operations.
Classification & Documentation
Ensure accurate product classification using the Harmonized System (HS) Code. Welder Laser Machines typically fall under HS 8515.21 or 8515.31, depending on type and power. Required documentation includes:
– Commercial Invoice
– Packing List
– Certificate of Origin
– Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB)
– Technical Specifications Sheet
– CE, FDA, or other regional compliance certificates, as applicable
International Regulations & Compliance
Comply with international and local regulations:
– CE Marking (EU): Conformity with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, EMC Directive 2014/30/EU, and LVD 2014/35/EU.
– FDA Registration (USA): Class I or II laser products must comply with 21 CFR 1040.10 and 1040.11; registration with FDA is mandatory.
– RoHS & REACH (EU): Ensure materials meet substance restrictions.
– IEC 60825-1: Laser safety standard for classification and labeling.
Verify country-specific import requirements (e.g., import licenses, customs bonds).
Packaging & Handling Requirements
Use robust, shock-resistant packaging with:
– Wooden crates or reinforced cardboard with internal foam or custom inserts
– Moisture barriers to prevent condensation
– Clearly labeled orientation and fragile indicators
– Protection for optical components and electrical connectors
Secure internal components to prevent movement during transit.
Transportation & Shipping
- Mode of Transport: Air freight (urgent), sea freight (cost-effective for large units), or road transport (regional).
- Labeling: Apply hazard labels: “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “Laser Radiation” (Class 3B or 4), and “Do Not Stack.”
- Environmental Controls: Maintain temperature (5°C–40°C) and humidity (<80% non-condensing) during transit.
- Battery Handling: If equipped with batteries, follow IATA/IMDG regulations for lithium batteries (UN3480 or UN3481).
Import & Customs Clearance
- Submit complete documentation to customs authorities.
- Pay applicable duties, VAT, and anti-dumping fees.
- Provide proof of conformity (e.g., EU Declaration of Conformity, FCC ID).
- Engage a licensed customs broker in destination country for efficient clearance.
Safety & Risk Mitigation
- Laser Safety: Class 3B and 4 lasers require protective housings, interlocks, and emission indicators.
- Electrical Safety: Comply with local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in USA, IEC 60204-1 globally).
- Operator Training: Ensure personnel are trained in laser safety (e.g., ANSI Z136.1).
- Insurance: Obtain cargo insurance covering damage, theft, and liability during transit.
Installation & On-Site Compliance
- Conduct pre-installation site audit (power supply, ventilation, space, grounding).
- Follow manufacturer’s installation manual.
- Perform safety checks: beam alignment, emergency stops, interlock functionality.
- Register equipment with local occupational safety authorities if required (e.g., OSHA in USA).
Maintenance & Record Keeping
- Maintain service logs, calibration records, and safety inspections.
- Keep copies of compliance certificates, import documents, and training records for minimum 5 years.
- Update compliance status for software/firmware upgrades affecting safety.
Disposal & End-of-Life
Dispose of the machine in accordance with WEEE (EU), EPA (USA), or local e-waste regulations.
Deactivate laser components before disposal. Recycle metals and electronic parts through certified vendors.
Contact & Support
For logistics or compliance inquiries, contact:
– Manufacturer’s Technical Support
– Authorized Import Agent
– Local Regulatory Body (e.g., OSHA, HSE, ANVISA)
– Freight Forwarder or Customs Broker
Note: Regulations vary by country. Always verify requirements with local authorities prior to shipment or operation.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Laser Welding Machine:
After a thorough evaluation of technical specifications, production requirements, supplier credentials, and cost considerations, sourcing a laser welding machine represents a strategic investment in enhancing manufacturing precision, efficiency, and product quality. The selected machine aligns with our operational needs, offering advanced capabilities such as high welding speed, minimal heat distortion, and consistent seam quality—all critical for maintaining competitive advantage in high-precision fabrication.
Furthermore, factors such as after-sales support, serviceability, training availability, and long-term maintenance costs were carefully assessed to ensure operational continuity and maximize return on investment. By partnering with a reputable supplier and selecting a reliable, scalable laser welding solution, we position our production line for improved throughput, reduced rework, and greater flexibility in meeting future manufacturing demands.
In conclusion, the sourcing decision supports both immediate production goals and long-term technological advancement, reinforcing our commitment to innovation, quality, and operational excellence.