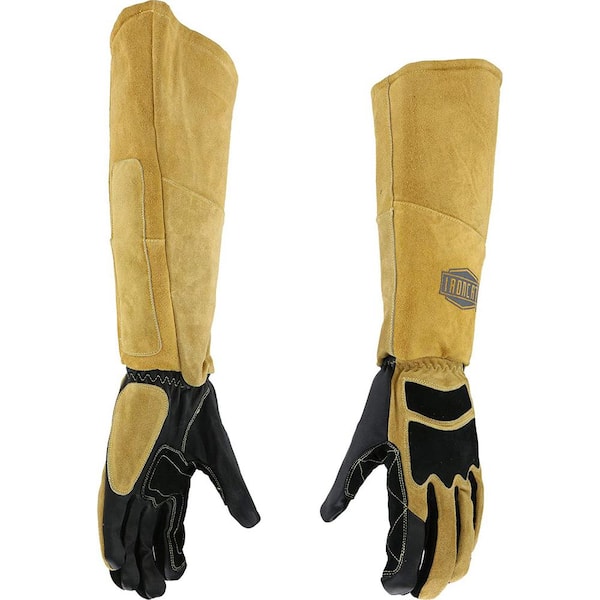
The global personal protective equipment (PPE) market, which includes welder attire, is witnessing robust growth driven by increasing industrial safety regulations and rising awareness of occupational hazards. According to Grand View Research, the global PPE market was valued at USD 56.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2023 to 2030. Welding-specific protective clothing forms a critical segment within this space, fueled by demand from industries such as construction, oil & gas, and manufacturing. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence projects the PPE market to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% during the forecast period 2023–2028, citing stringent workplace safety standards across North America and Europe as key drivers. As safety compliance becomes non-negotiable, the need for high-performance, certified welder attire has led to the emergence of specialized manufacturers focused on durability, heat resistance, and comfort. Below are nine leading manufacturers shaping the future of welding PPE through innovation and quality.
Top 9 Welder Attire Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Steiner Industries
Domain Est. 1997
Website: steinerindustries.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer and supplier of industrial clothing and safety products, all designed to promote safety and increase productivity in the workplace….
#2 HobartWelders
Domain Est. 1999
Website: hobartwelders.com
Key Highlights: Hobart Welders is a leading welding manufacturer in the U.S. Browse a variety of welders, welding equipment, gear and projects to find the best match for ……
#3 RADNOR™ Welding & Safety Products
Domain Est. 1995
Website: airgas.com
Key Highlights: Outfit your welders with RADNOR™ PPE. Shop RADNOR for the biggest selection of rugged, reliable and priced‑right welding PPE to keep your team safe and ……
#4 Miller Welding Apparel and Gear
Domain Est. 1996
Website: millerwelds.com
Key Highlights: Staying comfortable increases productivity and compliance. Explore Miller’s extensive line of welding protection, including jackets, gloves and other ……
#5 Chicago Protective Apparel
Domain Est. 1997
Website: b2b.mechanix.com
Key Highlights: Mechanix Wear/Chicago Protective Apparel offers a wide range of protective garments for various industries including foundry, electrical/utilities, ……
#6 Welding Gloves
Domain Est. 1998
Website: blackstallion.com
Key Highlights: With over 50 years of manufacturing experience, Black Stallion® leads the market in in high-quality, innovative gloves, FR garments and other PPE….
#7 8 Miller Welding Safety Apparel for sale from $14.50
Domain Est. 1998
Website: weldersupply.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $300 · 14-day returns…
#8 Welding Safety
Domain Est. 1998
Website: safetyclothing.com
Key Highlights: We carry a wide selection of workwear for everyday welding activities. Welding clothing is designed to be flame retardant and resistant to hot welding spatter ……
#9 Lincoln Electric Red Line Welding Apparel
Domain Est. 2003
Website: weldfabulous.com
Key Highlights: Free deliveryShop for Lincoln Electric Red Line Welding Apparel at Weldfabulous. From Lincoln welding gloves to Lincoln welding jackets, we have the PPE you ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Welder Attire

H2: Emerging Market Trends in Welder Attire for 2026
H2: Increasing Demand for Smart and Connected Welding Apparel
A major trend shaping the welder attire market in 2026 is the integration of smart technologies into protective clothing. Manufacturers are increasingly embedding sensors and IoT-enabled components into welding jackets, gloves, and helmets to monitor vital signs, heat exposure, and posture in real time. These innovations aim to enhance worker safety and reduce occupational injuries. For example, smart welding jackets with temperature alerts and motion tracking are gaining traction among industrial users. This shift is driven by rising workplace safety regulations and the growing adoption of Industry 4.0 practices across manufacturing and construction sectors.
H2: Focus on Lightweight and Breathable Fire-Resistant Fabrics
As worker comfort becomes a priority, 2026 sees a surge in demand for welder attire made from advanced lightweight, breathable, and flame-resistant (FR) materials such as modacrylic, aramid blends, and treated cotton. These fabrics offer high protection against sparks, UV radiation, and molten metal splatter while improving mobility and reducing heat stress. Innovations in textile engineering are enabling manufacturers to balance durability with comfort, particularly for long-duration welding tasks in hot environments.
H2: Rising Adoption of Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Materials
Environmental concerns are influencing product development in the welder attire market. By 2026, brands are increasingly using recycled fibers, bio-based treatments, and low-impact dyes to reduce the environmental footprint of protective gear. Certifications such as OEKO-TEX and Bluesign are becoming key differentiators. Companies are also launching take-back programs and offering biodegradable packaging, aligning with corporate sustainability goals in industrial supply chains.
H2: Customization and Ergonomic Design Gaining Popularity
Personalization and ergonomic improvements are emerging as competitive advantages. In 2026, welders are seeking attire tailored to specific welding processes (e.g., MIG, TIG, stick) and body types. Features like pre-curved sleeves, adjustable cuffs, and modular padding systems are being incorporated to enhance fit and functionality. Online configurators and 3D body scanning are enabling custom-fit solutions, especially in high-end industrial and aerospace applications.
H2: Growth in E-Commerce and Direct-to-Consumer Sales Channels
The distribution landscape for welder attire is evolving rapidly, with e-commerce platforms and direct-to-consumer (DTC) models gaining prominence in 2026. Online marketplaces offer broader product selections, detailed safety specifications, and customer reviews, empowering buyers to make informed decisions. Major brands are investing in digital marketing, virtual fitting tools, and subscription-based gear replacement services to increase customer retention and streamline procurement for small contractors and independent welders.
H2: Regulatory Compliance Driving Innovation and Market Entry Barriers
Stricter global safety standards—such as updates to ANSI/ISEA 110, EN ISO 11612, and OSHA guidelines—are shaping product design and certification processes in 2026. Compliance is no longer optional; it’s a baseline requirement, prompting companies to invest in R&D for certified, high-performance gear. These regulations are also raising entry barriers for low-cost, non-compliant imports, benefiting established players that prioritize quality and traceability.
H2: Expansion in Emerging Markets and Industrialization Hubs
The welder attire market is experiencing robust growth in regions like Southeast Asia, India, and Africa, driven by infrastructure development, urbanization, and expanding manufacturing sectors. In 2026, multinational suppliers are forming partnerships with local distributors and adapting product lines to regional climate conditions and labor practices. This geographic diversification is creating new revenue streams and reshaping global supply chains.
H2: Integration of Augmented Reality (AR) in Training and Gear Usage
While not directly part of attire, AR-compatible welding helmets and training suits are influencing the broader ecosystem. In 2026, AR-integrated headgear allows welders to access real-time data, welding parameters, and virtual guidance overlays. Apparel manufacturers are collaborating with tech firms to ensure clothing compatibility with AR systems, enhancing precision and reducing training time—especially for novice welders in automated or robotic welding environments.
H2: Increased Focus on Gender-Specific and Inclusive Sizing
The industry is responding to a more diverse workforce by introducing gender-inclusive and anatomically optimized welder attire. In 2026, leading brands offer female-specific cuts with improved shoulder, waist, and hip proportions, addressing long-standing fit and safety issues. This inclusivity trend is supported by labor diversity initiatives and is helping attract a broader talent pool to the welding profession.
H2: Rise of Rental and Subscription-Based Protective Wear Models
To reduce costs and improve gear maintenance, rental and subscription models for high-end welder attire are gaining adoption—particularly among SMEs and project-based contractors. These services often include regular cleaning, safety inspections, and timely replacement of worn gear. In 2026, such models are supported by digital tracking and QR-coded inventory systems, ensuring compliance and traceability across job sites.
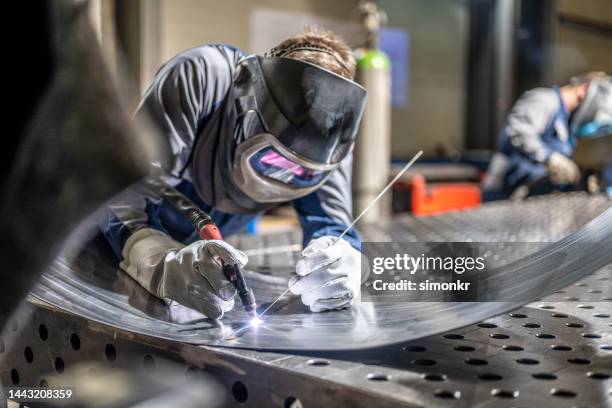

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Welder Attire (Quality and IP)
Sourcing welder attire—such as welding jackets, gloves, aprons, and helmets—requires careful attention to both quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to safety risks, compliance issues, and legal liabilities. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Safety and Durability
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting the lowest-cost option without verifying material quality. Cheap welding attire may use substandard flame-resistant (FR) fabrics or inadequate stitching, increasing the risk of burns or injury. Always ensure materials meet recognized safety standards (e.g., ANSI, NFPA, or EN ISO).
2. Ignoring Compliance with Safety Standards
Welder attire must comply with industry-specific safety regulations. Sourcing products that do not meet required certifications (e.g., ASTM F2675 for gloves or EN 470-1 for protective clothing) can result in non-compliance, workplace incidents, or failed audits.
3. Overlooking Material Composition and Protection Level
Different welding processes (MIG, TIG, stick) produce varying levels of heat, spatter, and UV radiation. Using inappropriate materials—such as cotton blends instead of leather or treated FR cotton—can compromise protection. Always match the attire’s specifications to the welding environment.
4. Inadequate Due Diligence on Suppliers
Sourcing from unverified or offshore suppliers can lead to inconsistent quality and counterfeit products. Conduct thorough supplier audits, request product samples, and verify manufacturing capabilities to ensure reliability and consistency.
5. Neglecting Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Purchasing or distributing welder attire that infringes on patented designs, trademarks, or branded technologies (e.g., branded cooling systems or proprietary stitching methods) can expose your business to legal action. Avoid suppliers offering “replica” or “compatible” branded gear unless properly licensed.
6. Assuming All “Flame-Resistant” Claims Are Equal
Not all flame-resistant materials perform the same. Some may only be temporarily treated and lose effectiveness after washing. Ensure the FR properties are inherent to the fabric and remain durable over time and multiple washes.
7. Failing to Consider Ergonomics and Comfort
Poorly designed attire can reduce mobility and increase fatigue, leading to decreased productivity and safety. Assess fit, weight, breathability, and range of motion—especially for workers in high-heat environments.
8. Overlooking After-Sales Support and Warranty
Low-cost suppliers may not offer warranties, repair services, or replacement policies. This can result in higher long-term costs and downtime if gear fails prematurely.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls, businesses can ensure they source high-quality, compliant, and legally sound welder attire that protects workers and minimizes risk.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Welder Attire
Purpose and Scope
This guide outlines the logistical considerations and compliance requirements for welder attire to ensure worker safety, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency across welding environments. It applies to all personnel involved in welding operations and those responsible for procuring, maintaining, and inspecting protective clothing.
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Welder attire must comply with national and international safety standards, including:
– ANSI/ISEA 101-2014 – Standard for classification of high-visibility safety apparel
– NFPA 2112 – Standard on Flame-Resistant Garments for Protection of Industrial Personnel Against Short-Duration Thermal Exposures from Fire
– OSHA 29 CFR 1910.252 – General Requirements for Welding, Cutting, and Brazing
– ASTM F1506 – Performance Specification for Textile Materials for Wearing Apparel for Use by Electrical Workers Exposed to Momentary Electric Arc and Related Thermal Hazards (if applicable)
Compliance ensures protection from arc flash, molten metal splash, UV/IR radiation, and fire hazards.
Required Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
All welders must wear the following attire:
– Flame-Resistant (FR) Clothing: Long-sleeve shirts and full-length pants made of FR cotton, leather, or treated synthetic materials; no synthetics that can melt (e.g., polyester, nylon)
– Welding Jacket or Apron: Made of leather or heavy-duty FR fabric to protect torso and arms from sparks and spatter
– Welding Gloves: Heat and abrasion-resistant gloves specifically rated for welding tasks (e.g., TIG, MIG, Stick)
– Safety Boots: Steel-toed, high-top boots with heat-resistant soles and metatarsal protection
– Head and Neck Protection: Welding helmet with proper shade lens (auto-darkening preferred), along with a fire-resistant welding cap or balaclava
– Hearing Protection: Earplugs or earmuffs in high-noise environments
– Respiratory Protection: When ventilation is inadequate, use NIOSH-approved respirators to guard against fumes and particulates
Procurement and Inventory Management
- Source attire from certified suppliers meeting OSHA and NFPA standards.
- Maintain an inventory log tracking PPE issuance, inspection dates, and replacement schedules.
- Order in bulk with safety stock levels to prevent shortages; include size diversity to accommodate all workers.
- Use barcoding or digital tracking systems for efficient management and compliance audits.
Inspection and Maintenance Protocol
- Inspect all welder attire before each use for tears, burns, excessive wear, or contamination.
- Establish a scheduled maintenance plan: clean FR clothing per manufacturer instructions (avoid chlorine bleach), repair minor damage promptly, and replace severely damaged items.
- Retire any PPE compromised by heat exposure, chemical contamination, or structural failure.
- Document all inspections and replacements in the safety management system.
Training and Worker Compliance
- Conduct mandatory training on proper use, care, and limitations of welder attire.
- Include hands-on demonstrations and refresher courses annually or after incidents.
- Enforce a zero-tolerance policy for non-compliant attire (e.g., wearing regular cotton shirts or rolled-up sleeves).
- Empower workers to report defective PPE without retaliation.
Environmental and Operational Considerations
- Adapt attire to environmental conditions: use lighter-weight FR garments in hot climates and layered systems in cold environments.
- Ensure proper ventilation when using FR treatments or coatings to avoid inhalation hazards.
- Store attire in dry, clean areas away from direct sunlight and chemicals to preserve material integrity.
Audits and Continuous Improvement
- Conduct quarterly safety audits to verify compliance with this guide.
- Review incident reports involving PPE failure to identify gaps and update protocols.
- Solicit feedback from welders to improve comfort, functionality, and adoption of safety attire.
- Stay updated on new regulations and technological advancements in protective wear.
Recordkeeping and Documentation
- Maintain records of PPE purchases, inspection logs, training attendance, and incident reports for a minimum of five years.
- Ensure documentation is accessible for internal audits and regulatory inspections.
- Include PPE compliance status in site safety reports and management reviews.
Conclusion
Proper welder attire is a critical component of workplace safety and regulatory compliance. By following this logistics and compliance guide, organizations can protect workers, reduce risk, and maintain operational continuity in welding operations. Regular review and adaptation of this guide are essential to address evolving standards and site-specific challenges.
Conclusion for Sourcing Welder Attire:
Sourcing the appropriate welder attire is a critical step in ensuring workplace safety, compliance with health and safety regulations, and the overall efficiency of welding operations. After evaluating various suppliers, material types, and protective features, it is evident that investing in high-quality, flame-resistant clothing—such as jackets, aprons, gloves, and helmets—significantly reduces the risk of burns, sparks, and long-term occupational hazards. Factors such as durability, comfort, proper fit, and adherence to international safety standards (e.g., ANSI, EN, OSHA) should guide procurement decisions. Additionally, considering customizability and supplier reliability ensures long-term value and consistent supply. Ultimately, prioritizing safety through well-sourced welder attire not only protects personnel but also enhances productivity and demonstrates a commitment to maintaining a safe working environment.