The global laser welding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for precision manufacturing across automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global laser welding market size was valued at USD 4.7 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% from 2023 to 2030. This surge is attributed to the increasing adoption of automation, advancements in high-power laser technologies, and the push for energy-efficient manufacturing processes. As industries prioritize accuracy, speed, and lower operational costs, laser welding has emerged as a preferred alternative to traditional welding methods. In this competitive landscape, a select group of manufacturers are leading innovation, scalability, and technological integration. Based on market presence, R&D investment, and product performance, here are the top 9 laser welding manufacturers shaping the future of industrial fabrication.
Top 9 Weld Laser Manufacturers (2026 Audit Report)
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Focus on laser
Founded: 1996
Website: hanslaser.net
Key Highlights: Han’s Laser Technology Industry Group Co., Ltd, a public company which was established in 1996, has now become the flagship of Chinese national laser ……
#2 LaserStar Technologies
Website: laserstar.net
Key Highlights: LaserStar Technologies designs and manufactures high-performance laser welding, marking, and cutting systems for industrial, jewelry, ……
#3 Equipment & Systems
Website: amadaweldtech.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturer of equipment and systems for welding, cutting, marking, micromachining, sealing, and bonding. Resistance welding. Laser….
#4 Denaliweld
Website: denaliweld.com
Key Highlights: We Specialize in Laser Welding & Cleaning. DenaliWeld INC, is a proud employee-owned fiber laser welding machine manufacturer based in Chicago, USA. Bolstered ……
#5 Laserax
Website: laserax.com
Key Highlights: Laserax works with the world’s leading manufacturers to implement laser cleaning, welding, texturing, and marking solutions….
#6 Laser Welding
Website: ipgphotonics.com
Key Highlights: Laser welding is the process of transferring a laser beam’s energy in the form of heat to fuse or join parts. This transferred heat melts the materials to ……
#7 Orotig: Laser Machinery
Website: orotig.com
Key Highlights: Orotig, with +30 years of experience, specializes in engineering and manufacturing laser solutions for welding engraving and casting metals….
#8 Laser Welding Machines
Website: coherent.com
Key Highlights: Get manual to fully automated laser welding machines that weld plastics and metals with speed and precision while improving throughput….
#9 Sunstone Welders
Website: sunstonewelders.com
Key Highlights: Sunstone designs and manufactures high-tech micro welding and engraving solutions for many different industries. In short, wherever a very small spot weld ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Weld Laser

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Weld Laser
The global weld laser market in 2026 is poised for significant evolution, driven by technological advancements, shifting industrial demands, and a strong push toward automation and sustainability. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
1. Accelerated Adoption of High-Power and Multi-Kilowatt Fiber Lasers:
By 2026, high-power fiber lasers (exceeding 10 kW) will dominate heavy-duty industrial applications, particularly in automotive, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery. The demand for faster processing speeds, deeper penetration, and improved energy efficiency is driving the shift from traditional CO2 and lower-power lasers. Innovations in beam quality and modulation will enable more precise control, expanding applications in thick-section welding.
2. Integration with AI and Smart Manufacturing (Industry 5.0):
Laser welding systems in 2026 will increasingly feature embedded AI and machine learning for real-time process monitoring, defect prediction, and adaptive control. Integration with digital twins and IoT platforms will enable predictive maintenance, optimize weld parameters dynamically, and ensure consistent quality—critical for high-mix, low-volume production environments. This trend supports the broader Industry 5.0 movement toward human-machine collaboration and resilient supply chains.
3. Growth in Battery and EV Manufacturing:
The electric vehicle (EV) revolution will continue to be a major growth driver. Laser welding is essential for high-precision, high-speed joining of battery components (e.g., busbars, cell tabs, and enclosures). Demand will surge for specialized systems capable of welding dissimilar materials (e.g., copper to aluminum) and ultra-thin foils with minimal heat input, ensuring safety and longevity of battery packs.
4. Expansion into New Materials and Hybrid Processes:
As industries adopt advanced materials like high-strength steels, aluminum alloys, and composites, laser welding technologies will evolve to handle their unique thermal and mechanical properties. Hybrid laser-arc welding (HLAW) will gain traction, offering deeper penetration and greater tolerance to joint fit-up, especially in the aerospace and energy sectors.
5. Regional Market Shifts and Supply Chain Localization:
Asia-Pacific, led by China and India, will remain the largest market due to rapid industrialization and government initiatives promoting advanced manufacturing. However, North America and Europe will see renewed investment in onshoring and nearshoring, boosting demand for automated laser welding solutions in reshored EV and clean energy production facilities.
6. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Focus:
With increasing regulatory and corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) pressures, manufacturers will prioritize laser systems with lower energy consumption, reduced emissions, and recyclable components. Advances in laser source efficiency and closed-loop cooling systems will support greener production footprints.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the weld laser market will be characterized by smarter, faster, and more adaptable systems, deeply integrated into next-generation manufacturing ecosystems. Companies that invest in AI-driven automation, sustainability, and application-specific innovations—particularly in EVs and clean tech—will lead the market. Success will depend on agility, technological differentiation, and alignment with global decarbonization goals.
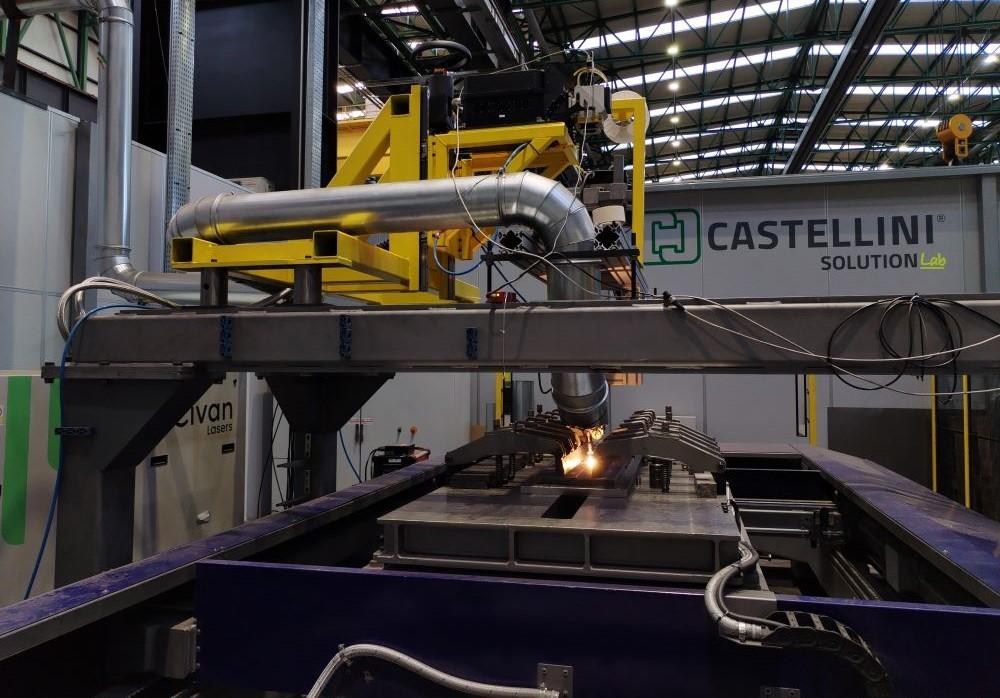

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Weld Lasers: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing weld lasers—especially high-power fiber or diode lasers for industrial applications—can present significant challenges. While cost and lead time are often primary concerns, overlooking quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks can lead to long-term operational, legal, and financial consequences. Below are key pitfalls to avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inadequate Performance Verification
Many suppliers provide laser specifications based on ideal lab conditions. Buyers often assume these translate directly to real-world performance. However, factors like beam quality (M²), power stability, duty cycle, and thermal management may degrade under continuous operation. Without third-party testing or on-site validation, companies risk receiving lasers that fail to meet production requirements.
2. Poor Component Sourcing and Build Quality
Low-cost manufacturers may use substandard optical components (e.g., collimators, focusing lenses) or cooling systems, leading to premature failure or inconsistent weld quality. Counterfeit or recycled diodes, in particular, can result in unpredictable output and shorter lifespans. Lack of transparency in the supply chain exacerbates this risk.
3. Insufficient After-Sales Support and Calibration
Weld lasers require regular maintenance, recalibration, and technical support. Sourcing from suppliers without local service networks or documented service level agreements (SLAs) can result in prolonged downtime. Moreover, absence of traceable calibration certificates undermines quality control in regulated industries (e.g., automotive, aerospace).
4. Non-Compliance with Industry Standards
Lasers used in industrial welding must comply with safety and performance standards such as IEC 60825 (laser safety), ISO 11553 (safety of laser processing machines), and ISO 13849 (functional safety). Sourcing non-compliant units exposes companies to safety hazards and regulatory penalties.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
1. Risk of IP Infringement
Some suppliers—particularly in regions with weak IP enforcement—may offer lasers that incorporate patented technologies (e.g., beam delivery systems, modulation techniques) without proper licensing. Purchasing such equipment can expose the end user to legal liability, especially if the laser is used in markets with strong IP protection (e.g., U.S., EU).
2. Lack of IP Ownership Clarity in Custom Solutions
When working with suppliers on customized laser systems, contracts often fail to clearly define who owns the resulting IP. Without explicit agreements, companies may lose rights to modifications, integration designs, or process optimizations developed during the project.
3. Reverse Engineering and Technology Leakage
Sharing detailed requirements or system designs with unvetted suppliers increases the risk of technology leakage. In some cases, suppliers may reverse engineer or replicate proprietary welding processes, especially if non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) are weak or unenforceable in the supplier’s jurisdiction.
4. Embedded Software and Licensing Risks
Modern weld lasers include proprietary control software. Buyers may unknowingly accept restrictive licensing terms that limit usage, prevent integration with third-party systems, or allow remote deactivation. Additionally, software may contain unlicensed or open-source code, creating compliance risks.
Mitigation Strategies
- Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including audits of manufacturing processes and quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001).
- Require independent performance testing and factory acceptance tests (FAT) before shipment.
- Verify compliance with relevant international standards and obtain documentation.
- Engage legal counsel to review contracts for IP ownership, warranties, and liability clauses.
- Use robust NDAs and IP assignment agreements, especially for custom developments.
- Source from reputable suppliers with established track records and enforceable service agreements.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, organizations can minimize risks and ensure reliable, legally sound integration of weld lasers into their manufacturing processes.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Weld Laser
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legally compliant handling, transportation, storage, and operation of Weld Laser systems. Adherence ensures workplace safety, regulatory compliance, and equipment longevity.
Shipping & Receiving
Ensure all Weld Laser units and components are shipped using qualified carriers experienced in handling sensitive industrial equipment. Use original packaging or equivalent protective materials to prevent damage during transit. Upon receipt, immediately inspect the shipment for visible damage, verify contents against the packing list, and document any discrepancies with photos and written reports. Report damages to the carrier and supplier promptly.
Storage Requirements
Store Weld Laser systems and optical components in a clean, dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 10°C–30°C) with low humidity (<60% non-condensing). Protect equipment from dust, vibrations, and direct sunlight. Keep laser modules and optics in sealed protective containers until installation. Avoid storing near corrosive chemicals or high-EMI sources.
Installation & Site Preparation
Verify that the installation site meets electrical specifications (voltage, phase, grounding) and has adequate cooling capacity (chiller requirements, ventilation). Ensure the area is free of obstructions and has secure, level flooring. Confirm access to required utilities (compressed air, water, exhaust). Install warning signs and establish a designated laser-controlled area compliant with ANSI Z136.1 or IEC 60825 standards.
Regulatory Compliance
Comply with all applicable local, national, and international regulations, including but not limited to:
– Laser Safety: ANSI Z136.1 (USA), IEC 60825 (International)
– Electrical Safety: NFPA 70 (NEC), IEC 60204
– Machine Safety: ISO 13849, OSHA 29 CFR 1910
– EMC: FCC Part 15 (USA), CE EMC Directive (EU)
Maintain documentation of certifications, risk assessments, and compliance records.
Hazard Communication
Clearly label all Weld Laser systems with appropriate hazard warnings, including laser class (e.g., Class 4), high-voltage indicators, and interlock warnings. Provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for any consumables or coolants used. Train personnel on interpreting labels and responding to warnings.
Personnel Training & Authorization
Only trained and authorized personnel may operate, maintain, or service Weld Laser systems. Training must include laser safety, emergency procedures, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and equipment-specific operation. Maintain training records and conduct periodic refresher courses.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Mandatory PPE includes laser safety eyewear with the correct optical density (OD) for the laser wavelength and power used. Additional PPE may include flame-resistant clothing, face shields, hearing protection, and gloves when handling hot components. Inspect PPE regularly and replace damaged items immediately.
Operational Safety Procedures
Always perform a pre-operation check of interlocks, emergency stops, cooling systems, and beam enclosures. Never bypass safety interlocks. Ensure the work area is clear of unauthorized personnel before initiating laser operation. Use beam shutters and enclosures to minimize exposure risk. Follow lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance.
Maintenance & Servicing
Schedule regular maintenance per the manufacturer’s recommendations. Use only approved replacement parts and calibrated tools. Qualified technicians must perform all internal servicing. Keep detailed maintenance logs, including dates, tasks performed, and parts replaced. Verify system performance and safety features after any service.
Waste & Environmental Compliance
Dispose of laser-generated airborne contaminants (fumes, particulates) through certified filtration systems (e.g., fume extractors with HEPA and activated carbon filters). Handle and dispose of coolant fluids, batteries, and electronic waste in accordance with RCRA (USA), WEEE (EU), or local environmental regulations. Document disposal procedures and retain records.
Incident Reporting & Emergency Response
Establish clear procedures for reporting laser-related incidents, including exposure, fire, or equipment malfunction. Post emergency contact numbers and evacuation routes. Equip the area with fire extinguishers rated for electrical and metal fires (e.g., Class D). Conduct regular emergency drills and maintain an accessible first aid kit.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records including:
– Equipment manuals and schematics
– Safety certifications and compliance reports
– Training logs
– Maintenance and calibration records
– Incident reports
– Risk assessments and safety audits
Ensure all documents are up-to-date and accessible to authorized personnel.
Conclusion for Sourcing Weld Lasers
Sourcing weld lasers requires a strategic approach that balances technical requirements, cost-efficiency, reliability, and long-term support. After evaluating various suppliers, laser technologies (such as fiber, CO₂, and disk lasers), and integration capabilities, it is evident that fiber lasers emerge as the preferred choice for most industrial welding applications due to their high efficiency, low maintenance, superior beam quality, and excellent weld precision.
Key factors in successful sourcing include assessing the supplier’s expertise, after-sales service, customization options, and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—rather than upfront price—ensures sustainable operational benefits. Partnering with reputable manufacturers or integrators who offer training, technical support, and scalability will enhance productivity and reduce downtime.
In conclusion, a well-informed sourcing strategy for weld lasers, centered on application needs and supplier reliability, enables businesses to improve welding performance, achieve consistent quality, and maintain a competitive edge in manufacturing processes.