The global wax filament market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand in prototyping, investment casting, and precision manufacturing across industries such as aerospace, jewelry, and dentistry. According to Mordor Intelligence, the 3D printing materials market—which includes wax filaments—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 20% from 2023 to 2028. With increasing adoption of additive manufacturing for intricate mold-making and lost-wax casting, manufacturers are innovating to deliver high-precision, low-ash, and thermally stable wax filaments. As industries prioritize accuracy and post-processing efficiency, a select group of suppliers has emerged as leaders in performance, consistency, and technical support. Here are the top 8 wax filament manufacturers shaping the future of precision manufacturing.
Top 8 Wax Filament Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 High
Domain Est. 2019
Website: tronhoo3d.com
Key Highlights: 3d Printer Wax Filament Manufacturers, Factory, Suppliers From China, At our firm with quality first as our motto, we manufacture products that are entirely ……
#2 Industrial 3D Printing Materials and Resins
Domain Est. 1996
Website: 3dsystems.com
Key Highlights: Choose from our castable and pressable wax-ups materials, or our direct metal additive alloys, to quickly and economically produce crowns, bridges, veneers, ……
#3 Industrial 3D printers
Domain Est. 2008
Website: enterprise.flashforge.com
Key Highlights: The WaxJet 400 is revolutionizing jewelry manufacturing by transforming traditional wax tree assembly into an efficient, space-saving process through advanced ……
#4 Materials
Domain Est. 2014
Website: raise3d.com
Key Highlights: Easy-to-print resin for prototyping and design. Forward AM Ultracur3D® RG 1100 B Rigid resin with superior stiffness and temperature resistance….
#5 3D Printing Wax
Domain Est. 2007
#6 FormFutura
Domain Est. 2012
Website: formfutura.com
Key Highlights: Discover professional-grade 3D printing consumables including filaments, pellets, resins, and accessories for FDM and SLA applications….
#7 MOLDLAY Filament – 2.85mm – 0.75 kg
Domain Est. 2013
Website: 3dprima.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 14-day returnsThis wax-like filament is designed to enable mold making. With this thermoplastic wax-like filament, molds can be produced. Likewise, the Moldlay filame…
#8 3D printing wax filament
Domain Est. 2023
Website: morsa-wax.com
Key Highlights: 3D printing wax filament. When used for lost wax casting, the burnout is extremely clean (much better than using plastic filament)….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Wax Filament

2026 Market Trends for Wax Filament: Key Drivers and Projections
The wax filament market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in 3D printing technologies, growing demand for high-precision manufacturing, and expanding applications across diverse industries. Here’s a breakdown of the key trends shaping the market:
H2: Rising Adoption in Jewelry and Dental Sectors Fuels Demand
The jewelry and dental industries remain the primary growth engines for wax filament. By 2026, continued adoption of desktop 3D printing for rapid prototyping and direct casting will significantly increase demand. Jewelry designers benefit from the ability to create intricate, customizable designs with high surface finish and minimal post-processing, reducing production time from days to hours. In dentistry, wax filament is increasingly used for fabricating precise surgical guides, crowns, bridges, and orthodontic models. The trend toward digital dentistry and chairside manufacturing solutions will further boost consumption, as dental labs and clinics seek cost-effective, accurate alternatives to traditional wax carving.
H2: Technological Advancements Enhance Material Performance and Printability
Innovation in wax filament formulations is a critical trend for 2026. Manufacturers are focusing on improving thermal stability, dimensional accuracy, and burnout characteristics to meet the stringent requirements of investment casting. New composites incorporating microcrystalline waxes, biopolymers, or reinforcing agents offer better strength, reduced warping, and cleaner burnout with minimal ash residue. Additionally, filament consistency and diameter control have improved, enabling reliable printing on a wider range of FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers. These advancements lower the entry barrier for small studios and educational institutions, broadening the user base.
H2: Expansion into Industrial Prototyping and Foundry Applications
Beyond jewelry and dentistry, wax filament is gaining traction in industrial prototyping and small-batch metal casting. By 2026, sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and art foundries are expected to adopt wax 3D printing for creating complex, one-off metal parts using investment casting. The ability to produce intricate internal geometries unachievable with traditional methods makes wax filament an attractive option for functional prototypes and low-volume production. As industrial 3D printers become more accessible and software integration improves, this segment will contribute to market diversification and growth.
H2: Sustainability and Material Innovation Drive Future Development
Environmental considerations are influencing wax filament development. By 2026, there will be a growing emphasis on bio-based, compostable, or recyclable wax formulations to align with broader sustainability trends in manufacturing. Research into hybrid materials that combine wax with renewable resources or enable easier recovery and reuse will gain momentum. Furthermore, compatibility with automated post-processing systems (e.g., burnout ovens, polishing) will be a key differentiator, enabling end-to-end digital workflows that enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs.
In conclusion, the 2026 wax filament market will be characterized by strong growth in established sectors, technological refinement, and expansion into new industrial applications. As material science and 3D printing ecosystems evolve, wax filament will solidify its role as a critical enabler of precision manufacturing and digital fabrication.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Wax Filament (Quality, IP)
Sourcing wax filament for applications such as lost-wax casting in jewelry, dentistry, or art requires careful consideration to avoid costly errors and ensure successful outcomes. Two major areas of risk are quality inconsistencies and intellectual property (IP) concerns.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inconsistent Melting and Flow Characteristics
Low-quality or poorly manufactured wax filaments often exhibit batch-to-batch variations in melting point and viscosity. This inconsistency can lead to failed prints, poor surface finish, or defects in the final casting, especially in intricate designs where precision is critical. -
Poor Dimensional Accuracy and Warping
Subpar wax filaments may shrink unevenly or warp during cooling, resulting in printed models that do not match the original CAD design. This leads to inaccuracies in the final metal cast, requiring manual corrections or causing rejection of the finished piece. -
Clogging and Print Failures
Contaminants, improper diameter tolerances (e.g., ±0.05 mm not maintained), or inconsistent core composition can cause nozzle clogs or extrusion issues. This not only wastes material but also increases downtime and maintenance costs. -
Residue and Burnout Issues
Inferior waxes may leave behind ash or carbon residue during burnout, contaminating the mold and affecting the surface quality of the final metal casting. High-quality wax filament should fully vaporize without residue when properly processed. -
Limited Post-Processing Compatibility
Some wax filaments are not compatible with common post-processing techniques such as spruing, investing, or burnout cycles. Always verify compatibility with your specific investment materials and kiln schedules.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
-
Unauthorized Replication of Branded Materials
Some suppliers may offer “compatible” or “generic” wax filaments that mimic patented formulations or trademarks of established brands (e.g., Formlabs, Carima). Using such products may expose your business to IP infringement claims, especially if the filament is reverse-engineered or falsely labeled. -
Lack of Transparency in Material Composition
Unreliable vendors may not disclose full material specifications or may misrepresent the composition of their wax filament. This opacity can lead to unintentional use of materials protected by patents or trade secrets, increasing legal risk. -
Counterfeit or Grey Market Products
Sourcing from unauthorized distributors increases the risk of receiving counterfeit filament. These products not only compromise print quality but may also involve IP violations by the manufacturer or distributor, implicating end users in liability. -
Unclear Licensing for Commercial Use
Some wax filaments, particularly those designed for specific 3D printers, come with end-user license agreements (EULAs) that restrict commercial applications. Using such materials for profit-driven casting work without proper licensing may breach IP terms.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
- Source from reputable manufacturers or authorized distributors with verifiable material data sheets.
- Request samples to test print quality, burnout performance, and dimensional accuracy.
- Verify IP compliance—ensure the filament does not infringe on patents or trademarks.
- Document supplier agreements and material certifications to protect against liability.
Taking proactive steps to vet suppliers and understand both technical and legal aspects of wax filament sourcing can safeguard your production process and business integrity.
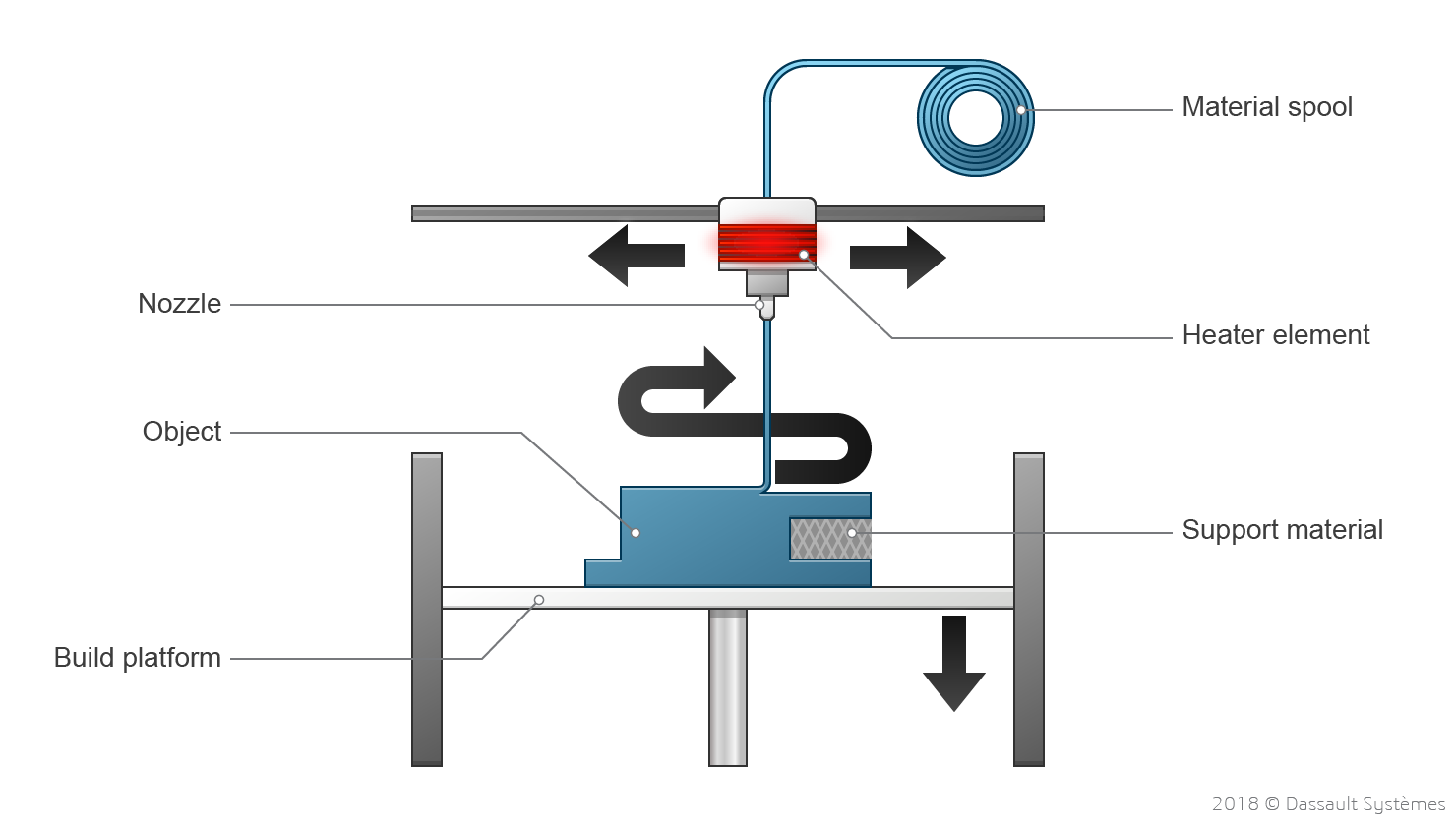
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Wax Filament
Overview
Wax filament is a specialized material used primarily in 3D printing for investment casting and prototyping applications. It typically consists of a wax-based core with a thermoplastic binder, making it suitable for creating sacrificial or burnout patterns. Due to its unique composition and end-use, specific logistics and compliance considerations must be addressed to ensure safe handling, transport, and regulatory adherence.
Classification & Identification
Wax filament is generally classified as a non-hazardous solid material under international transport regulations when packaged correctly. However, classification may vary based on formulation (e.g., presence of additives or solvents). Always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) provided by the manufacturer to determine accurate classification under:
– UN Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods
– IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (for air)
– IMDG Code (for sea)
– ADR (for road in Europe)
Typical UN numbers do not apply unless the wax contains flammable components above threshold limits.
Packaging Requirements
Proper packaging is critical to prevent damage and maintain filament integrity during transit:
– Use original sealed spools inside moisture-resistant packaging (e.g., vacuum-sealed bags with desiccants).
– Place spools in rigid outer containers to prevent crushing or deformation.
– Label packages with product name, net weight, manufacturer details, and storage instructions (e.g., “Keep Dry,” “Protect from Heat”).
– Avoid exposure to temperatures above 40°C (104°F) to prevent softening or deformation.
Storage Conditions
To preserve print quality and material stability:
– Store in a cool, dry environment (15–25°C or 59–77°F).
– Maintain relative humidity below 60%.
– Keep away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
– Use first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory management to prevent aging.
Transportation Guidelines
Wax filament is typically non-regulated for transport when packaged as intended for consumer use:
– Air Freight: Generally permitted as non-hazardous cargo; confirm with carrier if large volumes are shipped.
– Ground & Sea: No special restrictions apply under standard conditions.
– Ensure temperature-controlled transport if ambient conditions exceed recommended storage ranges.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhere to the following regulations based on region and application:
– REACH (EU): Confirm that all chemical components are registered and comply with SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) requirements.
– RoHS (EU): Wax filament is typically exempt, but verify absence of restricted heavy metals if applicable.
– Proposition 65 (California, USA): Check if any constituents require warning labels.
– Customs Documentation: Provide accurate HS codes (e.g., 3916.20 for plastic rods and profiles) and commercial invoices for international shipments.
Handling & Safety
Although wax filament is generally safe, follow best practices:
– Use gloves to avoid skin contamination or print defects from oils.
– Operate in well-ventilated areas during printing to manage potential fumes.
– Follow manufacturer guidelines for printer nozzle temperatures and burnout cycles.
– Dispose of waste filament according to local plastic waste regulations.
Disposal & Environmental Considerations
- Wax filament is not biodegradable and should not be composted.
- Incineration during casting processes should occur in controlled industrial furnaces with proper emission controls.
- Leftover or failed prints may be collected and processed as non-hazardous plastic waste.
Documentation & Traceability
Maintain the following documents for full compliance:
– Safety Data Sheet (SDS) – updated and accessible.
– Certificate of Conformity (CoC) for material specifications.
– Batch/lot tracking for quality control and recall preparedness.
– Import/export declarations where applicable.
Conclusion
Wax filament requires careful attention to storage, packaging, and regional regulations despite its general classification as non-hazardous. By following this guide, businesses can ensure safe logistics operations, regulatory compliance, and consistent product performance in additive manufacturing workflows. Always consult the filament supplier for product-specific guidance.
Conclusion for Sourcing Wax Filament:
Sourcing wax filament requires a careful evaluation of several key factors, including material quality, supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with specific applications such as 3D printing for investment casting or prototyping. After assessing various suppliers and product specifications, it is evident that selecting a reputable supplier who provides consistent filament diameter, low moisture content, and proper packaging is crucial for optimal print performance and end-use results. Additionally, considering lead times, minimum order quantities, and technical support can significantly impact the efficiency of the supply chain. In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach that balances quality, cost, and supplier capabilities ensures a reliable wax filament supply, ultimately supporting successful manufacturing and prototyping outcomes.