The global renewable energy landscape is undergoing rapid transformation, with wind-powered water pumping systems emerging as a sustainable solution for agricultural, rural, and off-grid water supply needs. According to Mordor Intelligence, the wind energy market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2023 to 2028, driven by increasing investments in decentralized energy systems and off-grid applications. Within this expanding sector, wind-powered water pumps are gaining traction—particularly in arid and remote regions—due to their low operational costs and minimal environmental impact. Supported by favorable government policies and advancements in turbine efficiency, the demand for reliable windmill pumping systems is on the rise. As the market evolves, several manufacturers have distinguished themselves through innovation, durability, and performance. Based on market presence, product scalability, and technological advancement, the following seven companies represent the leading forces in the water pumping windmill industry today.
Top 7 Water Pumping Windmill Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
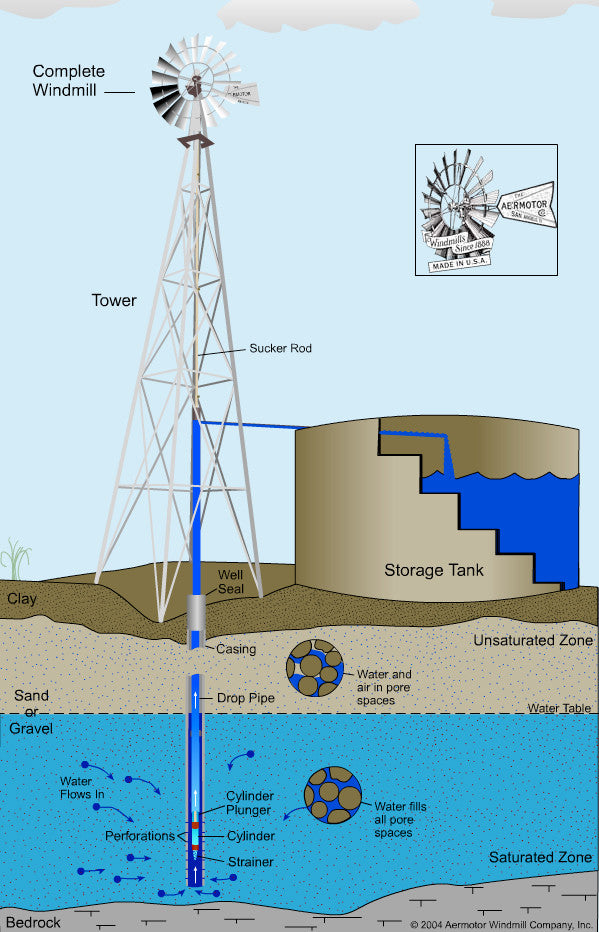
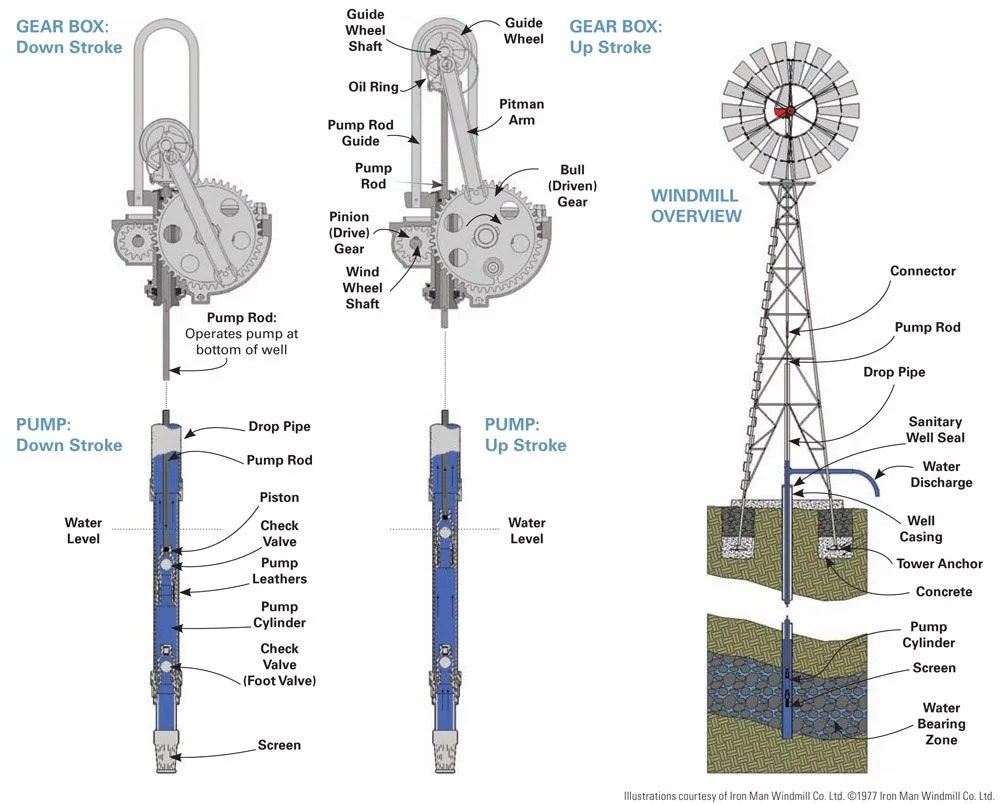
#1 How a Windmill Pumps Water
Domain Est. 1998
Website: aermotorwindmill.com
Key Highlights: Learn how a windmill pumps water from the ground. Aermotor Windmill Company – the only manufacturer of genuine Aermotor Windmills and Parts….
#2 Nebraska City
Domain Est. 2011
Website: kregelwindmillfactorymuseum.org
Key Highlights: The company continued to produce factory-made water pumping windmills until their manufacture ended due to the rationing of raw materials during World War II….
#3 American Windmills
Domain Est. 1998
Website: windmills.net
Key Highlights: American Windmills is dedicated to the preservation, restoration and sale of the Old Farm Style Water Pumping Windmill and Hand Pump systems. Contact us today!…
#4 WEG
Domain Est. 2004
Website: weg.net
Key Highlights: WEG provides global solutions for electric motors, variable frequency drives, soft starters, controls, panels, transformers, and generators….
#5 Farm & Ranch Windmills LLC
Domain Est. 2007
Website: farmranchwindmills.com
Key Highlights: Sales & Service (361)782-5493. A windmill is one of the most energy efficient and ingenious ways ever devised to pump water from under the ground. A ……
#6 Farm Windmills
Domain Est. 2010
Website: hoosierwindmills.com
Key Highlights: New water pumping windmills and towers. Windmill sizes range from 6′ to 16′ in diameter. Tower sizes from 14′ to 47′ in height….
#7 Midwest Windmill Company
Domain Est. 2021
Website: midwestwindmillcompany.com
Key Highlights: At Midwest Windmill Company we offer our signature windmill, the Green Windmill. These water-pumping engines used to be scattered across the Midwest….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Water Pumping Windmill
H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Water Pumping Windmills
The global market for water pumping windmills is expected to experience a resurgence and transformation by 2026, driven by increasing demand for sustainable water solutions, energy efficiency, and off-grid water supply systems. While modern solar-powered pumps have gained prominence, traditional and upgraded wind-powered water pumping systems are regaining attention in specific geographic and economic contexts.
-
Renewed Interest in Off-Grid and Rural Applications
By 2026, water pumping windmills are anticipated to see increased adoption in remote and rural areas—particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and parts of Latin America—where access to electricity and reliable water infrastructure remains limited. Governments and NGOs are investing in decentralized water solutions, and windmills offer a durable, low-maintenance alternative to electric or diesel pumps. -
Integration with Hybrid Renewable Systems
A key trend is the integration of windmills with solar and battery systems to create hybrid renewable water pumping solutions. This hybridization ensures consistent water supply despite variable wind or sunlight conditions. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to offer modular wind-solar pumping units tailored for farms, livestock operations, and community wells. -
Technological Advancements and Material Efficiency
Modern water pumping windmills are incorporating lightweight composite materials, improved blade aerodynamics, and automated control systems to enhance efficiency and reduce maintenance. These innovations are expected to increase reliability and output, making windmills more competitive with other renewable pumping technologies. -
Focus on Sustainability and Climate Resilience
With climate change intensifying water scarcity, especially in arid and semi-arid regions, wind-powered pumps are being recognized for their zero-emission operation and long operational life. In drought-prone areas, they are being promoted as part of climate adaptation strategies by international development agencies. -
Regional Market Growth and Policy Support
Countries like Kenya, India, and Australia are implementing policies and subsidies to support wind-powered water solutions in agriculture and pastoral communities. In the U.S., there is a niche revival in the Great Plains, where wind resources are strong and ranchers seek energy-independent water systems. -
Challenges and Market Constraints
Despite growth potential, the market faces challenges including high initial costs, competition from lower-cost solar pumps, and limited technical expertise in some regions. However, by 2026, increased local manufacturing and training programs are expected to mitigate these issues.
In summary, the 2026 market for water pumping windmills will be shaped by sustainability needs, technological innovation, and targeted deployment in off-grid regions. While not dominating the renewable water sector, windmills are poised to reclaim a strategic role in the global water-energy nexus.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Water Pumping Windmills (Quality, IP)
Sourcing water pumping windmills, especially for critical applications in remote or off-grid locations, requires careful attention to avoid significant pitfalls related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP). Overlooking these aspects can lead to project failures, financial losses, and legal complications.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
- Insufficient Material Durability: Selecting windmills constructed from substandard steel, poorly galvanized components, or inadequate bearings leads to rapid corrosion, mechanical failure, and drastically reduced lifespan, especially in harsh environments. Verify material specifications (e.g., ASTM standards for steel, galvanization thickness) and supplier reputation for durability.
- Poor Manufacturing and Assembly Tolerances: Inconsistent welding, misaligned components, or imprecise machining result in excessive vibration, increased wear, noise, and inefficient energy transfer. This directly impacts pumping performance and reliability. Demand evidence of quality control processes and consider factory audits for large orders.
- Inadequate Design for Local Conditions: Windmills designed for moderate winds or temperate climates will fail in high-wind zones or extreme temperatures. Sourcing a model not rated for the specific wind profile (average and gust speeds) or environmental conditions (dust, sand, humidity, temperature extremes) of the installation site is a major risk. Ensure technical specifications match local requirements.
- Lack of Genuine Spare Parts and Support: Choosing obscure or defunct brands often means spare parts (bearings, rods, vanes, seals) are unavailable when needed. This leads to extended downtime. Prioritize suppliers with proven, long-term spare parts availability and accessible technical support.
- Overstated Performance Claims: Be wary of inflated pumping rate (gallons/liters per minute) or wind speed start-up claims that don’t reflect real-world testing under standard conditions. Request independent test data or verified customer references.
- Compromised Foundation and Tower Components: The tower and foundation are critical structural elements. Sourcing low-quality tower sections, guy wires, anchors, or foundation kits risks catastrophic collapse. Inspect specifications for material strength and corrosion protection.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
- Sourcing Counterfeit or Knock-Off Products: Many reputable windmill designs (e.g., traditional Aermotor, Dempster styles) are frequently copied. These counterfeits often use inferior materials and construction, leading to the quality failures mentioned above. They also infringe on the original manufacturer’s IP rights. Verify the supplier is an authorized distributor or the original equipment manufacturer (OEM).
- Unlicensed Manufacturing and Distribution: Some suppliers may legally operate in regions with weak IP enforcement, producing and selling windmills that copy patented designs, mechanisms, or unique features without permission. Purchasing these supports IP theft and carries risks of poor quality and lack of liability.
- Ambiguous or Missing Design Ownership: For custom or newer windmill designs, unclear IP ownership in contracts can lead to disputes. Ensure agreements explicitly state who owns the design, tooling, and any modifications, especially if co-developing a solution.
- Voided Warranties and Support: Using non-genuine parts or purchasing from unauthorized sources often voids the manufacturer’s warranty. This leaves the buyer without recourse for defects and without access to official technical support or spare parts programs.
- Reputational and Legal Risk: Associating with suppliers involved in IP infringement can damage a project’s or organization’s reputation. In some jurisdictions, importing or using counterfeit goods can also expose the buyer to legal liability or customs seizures.
By diligently addressing these quality and IP pitfalls during the sourcing process—through thorough due diligence, verification of supplier credentials, demanding technical specifications and test data, and prioritizing authorized channels—buyers can secure reliable, efficient, and legally sound water pumping windmill solutions.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Water Pumping Windmills
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the procurement, transport, installation, and operation of water pumping windmills, particularly in rural or off-grid settings.
Regulatory Permits and Approvals
Before installing a water pumping windmill, secure necessary permits from relevant local, regional, or national authorities. Requirements vary by jurisdiction but commonly include land use permits, water rights authorization (especially for groundwater extraction), and environmental impact assessments in ecologically sensitive areas. In some regions, height restrictions or setback rules may apply due to aviation or zoning regulations. Consult with local agricultural extension offices or natural resource departments to determine specific permit needs.
Environmental and Site Compliance
Ensure the proposed installation site adheres to environmental regulations. Avoid protected habitats, wetlands, or conservation areas unless authorized. Conduct a site assessment to evaluate wind resources, soil stability, and proximity to water sources. Compliance with noise ordinances is typically minimal for mechanical windmills, but check local standards. If the system includes storage tanks or piping, ensure spill prevention and runoff controls are in place to avoid contamination of soil or water bodies.
Import and Customs Regulations (International Supply)
For cross-border procurement, verify import regulations applicable to windmill components such as towers, rotors, pumps, and mounting hardware. Key considerations include customs duties, import taxes, and compliance with product safety or engineering standards (e.g., ISO, CE marking, or national standards). Documentation such as commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin must be accurate and complete. Some components may be classified under specific HS codes (e.g., 8413 for pumps or 8502 for wind-powered generators) affecting tariff rates.
Transportation and Handling Logistics
Plan transportation based on component dimensions and weight. Windmill towers and blades can be bulky and may require special handling or oversized load permits for road transport. Use secure packaging and padding to prevent damage during transit, especially for precision pump mechanisms. Coordinate with freight carriers experienced in agricultural or renewable energy equipment. For remote locations, consider modular designs that simplify off-road transport and on-site assembly.
Installation Standards and Safety Protocols
Installation must follow manufacturer guidelines and applicable safety standards (e.g., OSHA in the U.S. or equivalent). Workers should be trained in fall protection, rigging, and mechanical assembly. Anchor foundations must be engineered for local soil conditions and wind loads to prevent structural failure. Electrical components (if present, such as for monitoring systems) should comply with local electrical codes. Keep detailed installation records for compliance audits and warranty claims.
Operational Maintenance and Reporting
Establish a routine maintenance schedule to ensure long-term compliance and efficiency. This includes inspecting tower integrity, lubricating moving parts, checking pump function, and clearing debris from blades. In areas with regulated water use, periodic reporting of extraction volumes may be required. Maintain logs of maintenance, repairs, and water output to demonstrate responsible usage and support compliance with resource management programs.
Decommissioning and End-of-Life Compliance
At end-of-life, plan for responsible decommissioning. Remove and properly dispose of or recycle metal components, plastics, and any hazardous materials (e.g., lubricants). Restore the site to its original condition where required by land use agreements or environmental regulations. Some jurisdictions may require a decommissioning bond or financial assurance before initial installation.
By adhering to these logistics and compliance practices, stakeholders can ensure the sustainable, legal, and efficient deployment of water pumping windmills.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Water Pumping Windmill:
Sourcing a water pumping windmill presents a sustainable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solution for water access, especially in remote or off-grid areas. By harnessing wind energy—a renewable and abundant resource—these systems reduce dependence on fossil fuels and lower long-term operational costs. When properly selected and installed based on local wind conditions, water demand, and site requirements, wind-powered water pumps offer reliable performance with minimal maintenance.
Investing in a durable and well-designed windmill from reputable suppliers ensures longevity and efficiency. Additionally, integrating modern materials and optional backup systems can enhance reliability during low-wind periods. Overall, sourcing a water pumping windmill supports energy independence, promotes sustainable agriculture and livestock management, and contributes to rural development. With careful planning and consideration of technical and environmental factors, wind-powered water pumping stands as a resilient and eco-conscious water solution for the future.