Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Water Packing Machine
The bottled-water sector is expanding at 5–7 % CAGR, and every extra 1,000 bph of high-speed water-packing capacity can unlock $1.2 M in incremental revenue within 18 months. Yet USA and EU buyers repeatedly hit the same wall: a fragmented supplier landscape where specs, certifications, and total cost of ownership vary wildly.
Why This Guide Matters
| Challenge | Market Reality |
|———–|—————-|
| 40+亚洲品牌声称“欧美标准”,但缺乏NSF/CE文件 | 无法通过零售/餐饮审核 |
| 低价CIF报价隐藏了后期改装、备件和培训费用 | CapEx预算超支30–50 % |
| 法规差异:FDA CFR 21 vs. EU Reg. 1935/2004 | 清关延迟2–6周 |
This guide is engineered for procurement, engineering, and operations leaders who need to compare, negotiate, and scale water-packing lines—from 3 kW tabletop fillers to 24 kph rotary rotary monobloc systems—while staying compliant, profitable, and future-proof.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Water Packing Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for water packing machine
- Understanding water packing machine Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of water packing machine
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘water packing machine’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for water packing machine
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for water packing machine
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘water packing machine’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for water packing machine Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing water packing machine With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for water packing machine
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the water packing machine Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of water packing machine
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for water packing machine
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Water Packing Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Top 10 Liquid Filling Machine Manufacturers – HonorPack
Domain: honorpack.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Top 10 Liquid Filling Machine Manufacturers ; 1. HonorPack. 1992 ; 2. Krones. 1951 ; 3. KHS GmbH. 1993 ; 4. Accutek Packaging Equipment. 1989….
2. Accutek Packaging Machine Equipment: Filler, Capper, Labeler
Domain: accutekpackaging.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Accutek Packaging Machine Equipment Companies offer a wide variety of filling machines, capping machines, labeling machines, and complete packaging systems….
3. Top Water Bottle Filling Machine Manufacturers 2025
Domain: suncrownmachine.com
Registered: 2025 (0 years)
Introduction: Suncrown Machine is one of the leading water bottle filling machine manufacturers with over 15 years of industry experience. We have ……
4. Top 10 Packing Machine Manufacturers in the world – Landpack
Domain: landpack.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 1. Landpack-China · 2. Tetra Pak- Switzerland · 3. Krones-Germany · 4. KHS GmbH-Germany · 5. Sidel-France · 6. Syntegon-Germany · 7. MULTIVAC-Germany….
5. Water Filling Machine – Micmachinery
Domain: micmachine.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: At Micmachinery, we specialize in manufacturing and selling top-of-the-line water filling machines designed to optimize your bottling process….
6. Water Bottling Machine
Domain: neptune-machine.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: The world smallest monoblock rotary water bottling machine for 200ml to 2000ml bottle water. Collect 8psc rinser, 8psc filler and 1psc capper in one machine….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
7. List: Top 23 Bottling Machine Manufacturers In World(Update 2023)
Domain: bwfillingmachine.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Look at this comprehensive list of the world’s top 23 bottling machine manufacturers! From Krones AG (Germany) to SIDEL India (India), this guide will help you ……
Understanding water packing machine Types and Variations
Understanding Water Packing Machine Types and Variations
Overview
Water packing machines are engineered for specific production volumes, bottle formats, and regulatory environments. Selecting the correct type directly impacts throughput, cap-ex, and downstream OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness). The five categories below represent the most common configurations encountered in North American and European bottling operations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Gravity-Fed Single-Head Rotary Filler
Type: Non-isobaric, rotary table filler
Features:
– 1–4 heads (rotary carousel)
– Gravity feed from bulk tank; no pressure compensation
– PLC with touch-panel HMI; optional CIP/SIP connections
– Stainless-steel 316L frame, IP67 enclosures
Applications:
– 350 ml – 1.5 L PET bottles
– Still or carbonated natural spring water
– Entry-level micro-breweries and boutique water brands
Pros / Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|—|—|
| Low initial investment (< USD 35 k) | Lower output (max 1,200 bph) |
| Quick changeover via cam-indexer | Not suitable for high oxygen sensitivity |
| Compact footprint (≤ 2 m²) | Manual neck fixture adjustment required |
2. Pressure-Rated Rotary Isobaric Filler
Type: Isobaric, multi-head rotary filler
Features:
– 6–12 heads; fills under constant CO₂ pressure to minimize degassing
– Mass-flow metering with load cells; ±0.5 % accuracy
– Full CIP/SIP compatibility; twin rotary seals for sterile water lines
– 304 or 316L stainless-steel; surface finish ≤ Ra 0.8 µm

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Applications:
– 330 ml – 2 L PET or glass bottles
– Sparkling water, flavored still water
– Mid-tier brands targeting EU markets (BRC, EFSA compliant)
Pros / Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|—|—|
| 1,800–4,000 bph on 500 ml | Higher cap-ex (USD 150–300 k) |
| Superior CO₂ retention for sparkling lines | Requires dedicated compressor skid |
| Integrated bottle rinser available | Longer changeover (≥ 30 min) |
3. Pouch & Sachet Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS)
Type: VFFS with premade pouch magazine
Features:
– Forms 100–300 µm multi-layer PE/PA pouches
– Volumetric cup or servo auger filler for still water
– Nitrogen flushing optional for shelf-life extension
– GMP-compliant stainless frame; wash-down duty motors
Applications:
– 100 ml – 1 L stand-up pouches
– Bulk dispensing, institutional catering, disaster-relief units
– Private-label store brands
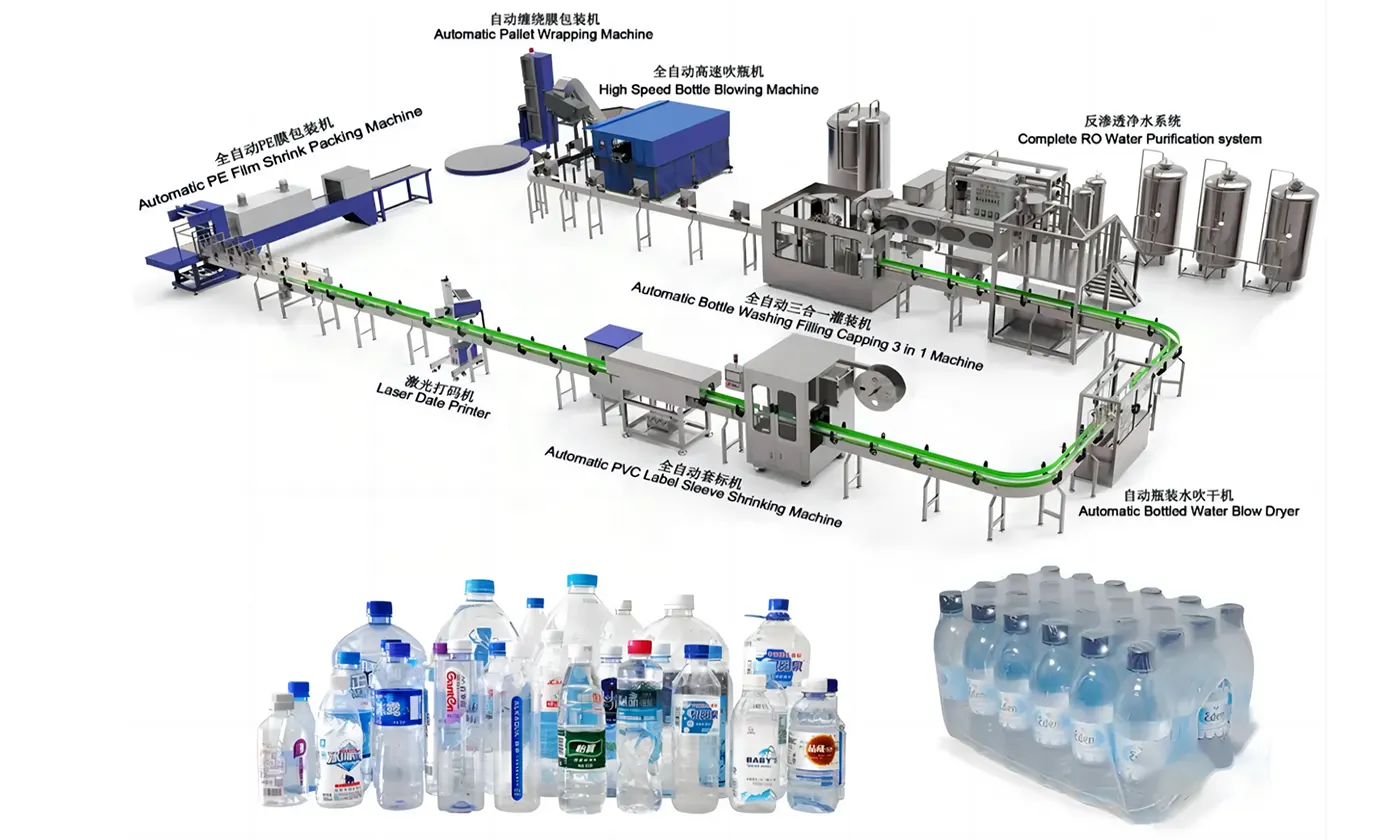
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pros / Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|—|—|
| 30–120 pouches/min; low changeover cost | Not suitable for carbonated water |
| 90 % less packaging material vs. bottle | Heat-seal temperature windows narrow with high-altitude operations |
| Shelf-stable, lightweight logistics | Requires nitrogen generator (if inert gas desired)
4. Net-Weight Gravimetric Filler
Type: Loss-in-weight or gain-in-weight system
Features:
– Load-cell-based weigh hopper (±0.1 % accuracy)
– Remote recipe management via Ethernet/IP or Profibus
– Hermetic fill head with nitrogen blanketing for oxygen-sensitive waters
– 3-A sanitary design; CIP return nozzle integrated
Applications:
– 500 ml – 5 L glass demijohns or bulk totes
– Functional waters (mineral-enhanced, alkaline)
– Contract packers serving EU health-food segment
Pros / Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|—|—|
| Sub-percent filling accuracy | Highest cap-ex (USD 250 k+) |
| No product giveaway; minimal waste | requires compressed air quality to ISO 8573-1 Class 0 |
| Seamless integration with ERP/MES | Long lead times (12–16 weeks)

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. Inline Monobloc (Rinser-Filler-Capper)
Type: High-speed, fully integrated line
Features:
– 8–16 head rinser, filler, and capper in one frame
– Isobaric filler with electronic flow meters; CIP return on filler bowl
– Integrated reject system (photo-eye + pneumatic pusher)
– Full-colour HMI with batch & traceability records (FDA 21 CFR Part 11 ready)
Applications:
– 330 ml – 1.5 L PET bottles
– High-volume brands (> 10 million bottles/year)
– Bottled water for airline, hospitality, and vending channels
Pros / Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|—|—|
| 6,000–12,000 bph on 500 ml | Cap-ex ≥ USD 500 k |
| Minimal human contact; reduced contamination risk | Requires 3-phase power (≥ 100 kVA) |
| Built-in CIP/Skid integration | Space requirement ≥ 25 m linear
Selection Checklist for North American & European Buyers
- Regulatory alignment – EU needs EHEDG, US needs 3-A or NSF.
- Bottle format flexibility – Change-parts vs. full rotary redesign.
- Water type – Sparkling demands pressure-rated rotary; still allows VFFS or monobloc.
- Throughput target – Match to current demand + 20 % buffer.
- Future proofing – Choose a filler with modular head architecture for rapid reconfiguration.
Key Industrial Applications of water packing machine
Key Industrial Applications of Water Packing Machines
| Industry / Application | Primary Use Case | Core Business Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bottled Water Production | 50–500 mL pure-water pouches for retail, vending, and food-service channels | – Rapid pouch forming, filling and sealing in one pass – Reduces labor by 60 % vs. manual bottle filling – Shelf-stable, lightweight pouches cut freight and storage costs |
| Beverage Concentrate Packaging | Single-serve sachets for syrups, fruit juices and energy drinks | – Accurate volumetric or gravimetric dosing (5–500 mL) – 3-side seal pouches extend shelf life without preservatives – Easy QR-code or batch-number printing for traceability |
| Pharmaceutical & Nutraceutical Water | Purified water sachets for clinical reconstitution and dietary supplements | – GMP-compliant stainless-steel contact parts – Optional UV or ozone sterilization module – Hermetic seals prevent endotoxin ingress |
| Cosmeceutical & Personal-Care Rinse Water | Travel-size purified water packets for salons and spa kits | – Compact 5–50 mL formats increase SKU flexibility – Heat-seal or cold-seal options suit low-viscosity liquids – Branded pouches enhance shelf appeal |
| Food-Service & Catering | Single-serve water for airlines, cruise lines and institutional catering | – Fast changeover between pouch sizes via touch-panel HMI – Continuous motion sealing maintains 10–15 bags/min throughput – Reduced breakage vs. glass bottles |
| Emergency Relief & Humanitarian Aid | 250 mL water pouches for disaster relief and field hospitals | – Heat-seal or cold-seal options suit low-viscosity liquids – Continuous motion sealing maintains 10–15 bags/min throughput – Reduced breakage vs. glass bottles |
| Laboratory & Research Water | Sterile, single-use water ampoules for media preparation and calibration | – Clean-room compatible design with HEPA filtration – Vial or pouch formats meet ISO 17025 standards – Batch coding for lot tracking and QA compliance |
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘water packing machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common B2B Pain Points for Water Packing Machine & Their Solutions
1. Inconsistent Bag Sealing Leading to Product Leakage
Problem
– Scenario: A mid-sized bottled-water supplier in Germany reports a 12% return rate due to split seals on 250 mL sachets produced by a legacy packing machine.
– Impact: Customer complaints, logistics delays, and unnecessary re-pack costs.
– Root Cause: Variable temperature control and misaligned sealing jaws on older models.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution
– Upgrade to Servo-Driven Heat Sealing: Modern machines use closed-loop servo motors to maintain exact temperature and pressure across the full width of the sealing jaw.
– Real-Time Seal Inspection: Integrate vision sensors that reject a pouch before it reaches the palletizer if seal integrity fails.
– Tooling Quick-Change System: Swappable Teflon-coated sealing bars reduce change-over time from 45 min to <5 min, eliminating thermal drift between runs.
| Feature | Legacy Machine | Modern Servo-Sealer |
|---|---|---|
| Seal Variation | ±8 °C | ±1 °C |
| Rejects / 10 k bags | 120 | <5 |
| Change-over Time | 45 min | 5 min |
2. High Downtime During Change-overs Between Bag Sizes
Problem
– Scenario: An American spring-water brand switches bag formats 3× per week. Change-over averages 90 minutes, tying up two operators and wasting 1,800 L of water per shift.
– Impact: Lost OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) >15%, missed delivery windows.
Solution
– Pneumatically-Assisted Size Changer: Hydraulic cylinder kits (available as retrofits) adjust film clamping jaws in <60 s.
– CAD-Linked Template Library: Pre-loaded size profiles (50 mL–1 L) stored in an SD card; machine auto-calibrates heating and cutting parameters.
– One-Hand Tooling Kits: All adjustment tools attach to the machine frame—no searching on the shop floor.
| Change-over Metric | Before Retrofit | After Retrofit |
|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | 90 | 25 |
| Water Waste (L) | 1,800 | 300 |
| Operator Count | 2 | 1 |
3. Compliance & Traceability Gaps for EU & US Regulations
Problem
– Scenario: A US co-packer faces a FDA warning letter because its water-packing line lacks batch-code traceability and fails to meet 21 CFR Part 11 for electronic records.
– Impact: Product holds, potential fines, loss of retailer contracts.
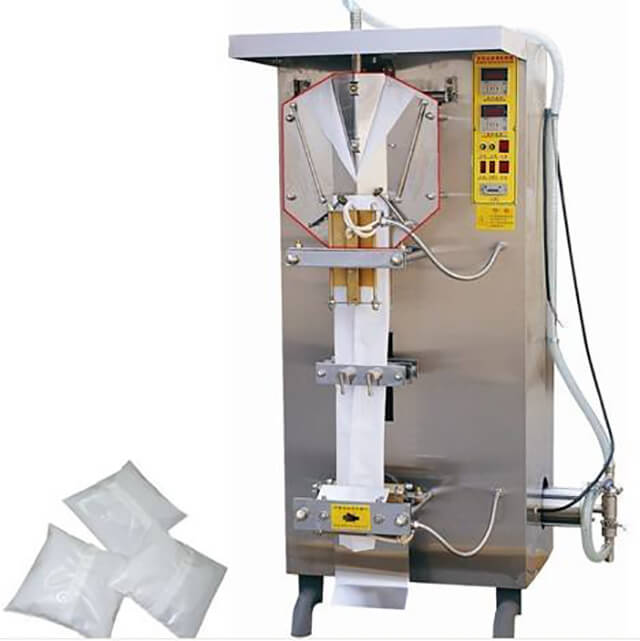

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution
– Built-in 21 CFR Part 11 Software Stack: Electronic signatures, audit trails, and user roles baked into the HMI—no third-party license required.
– Laser Batch Coders: Non-contact coding on the vertical seal ensures legible, tamper-evident batch numbers.
– Cloud-Based MES Gateway: Secure TLS 1.3 upload of production data to Azure or AWS; GDPR-compliant EU servers available on request.
| Compliance Need | Manual Work-Around | Integrated Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Traceability | Hand-written logbook | Auto-generated QR on each bag |
| Electronic Records | Paper forms scanned later | Real-time e-signature & audit trail |
| EU Data Residency | AWS US region | Optional EU-West 1/Azure Germany |
Bottom Line
Investing in modern water packing machines with servo sealing, rapid size change, and built-in compliance modules reduces downtime, waste, and regulatory risk—directly improving ROI for B2B buyers in the USA and Europe.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for water packing machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Water Packing Machine
For USA & European B2B buyers
Executive Summary
Material choice directly affects product safety, regulatory compliance, packaging speed, and total cost of ownership. Selecting the wrong laminate can void certifications, delay shipments, and expose downstream buyers to liability. This guide benchmarks the five most specified materials against FDA (21 CFR) and EU (10/2011) requirements for still and sparkling water.
1. Material Benchmark Matrix
| Material | Structure | Barrier Properties | Regulatory Status | Typical Thickness | Cost Index* | Key Advantages | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET / PE | 12 µm PET + 60 µm PE | Good moisture, poor O₂ | FDA 21 CFR 177.1630; EU 10/2011 | 72 µm | 1.0 | Recyclable PET, wide availability, clear optics | Not retort-safe, low heat-seal strength |
| PET / EVOH / PE | 12 µm PET + 30 µm EVOH + 50 µm PE | Excellent O₂, good moisture | FDA 21 CFR 177.1630; EU 10/2011 | 92 µm | 1.4 | Shelf-life extension to 12 months, retortable | Higher cost, EVOH moisture sensitivity |
| PP / EVOH / PP | 15 µm PP + 30 µm EVOH + 50 µm PP | Excellent O₂, good moisture | FDA 21 CFR 177.1520; EU 10/2011 | 95 µm | 1.6 | Retort at 121 °C, chemical resistance | Higher seal temps, warpage risk |
| Paper / AL / PE | 60 gsm paper + 7 µm AL + 50 µm PE | Excellent O₂ & light | FDA food-contact paper; EU 10/2011 | 117 µm | 1.9 | Premium feel, oxygen-proof | Heavy, non-recyclable laminate, high cost |
| BOPA / AL / PE | 15 µm BOPA + 7 µm AL + 50 µm PE | Excellent O₂ & moisture | FDA 21 CFR 177.1660; EU 10/2011 | 72 µm | 2.1 | Grease-proof, pin-hole resistant, retortable | Higher cost, limited recyclability |
*Cost Index = relative to PET/PE baseline (1.0). Actual prices fluctuate ±15 % with resin markets.
2. Regulatory & Market Considerations
- USA: FDA 21 CFR 177.xxx applies to monolayers and laminates. EVOH and BOPA require migration testing at 70 °C for 10 days.
- EU: Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 mandates specific migration limits (SML) for EVOH and BOPA. Compostable options under EN 13432 are gaining traction in Germany and France.
- Multi-layer vs. Mono-material: PET/PE allows mono-material recycling streams; PET/EVOH/PE complicates recycling unless collected via separate film recovery programs.
3. Application-Specific Guidance
| End-use | Recommended Structure | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Still water (ambient) – USA | PET / PE | Cost-efficient, meets FDA, widely recycled |
| Sparkling water (CO₂) – EU | PET / EVOH / PE | Superior gas barrier, retort-safe |
| Retortable flavored water | PP / EVOH / PP | Maintains seal integrity at 121 °C |
| Premium still water (glass substitution) | Paper / AL / PE | Shelf-life 18 months, premium shelf presence |
| Export to USA & EU | BOPA / AL / PE | Highest barrier, complies with both jurisdictions |
4. Procurement Checklist
- [ ] Verify resin batch certificates for both FDA and EU compliance.
- [ ] Request oxygen transmission rate (OTR) & water-vapor transmission rate (WVTR) data at 38 °C / 90 % RH.
- [ ] Confirm seal strength (≥ 10 N/15 mm) on your sealer before bulk order.
- [ ] Validate EVOH moisture sensitivity—store rolls ≤ 60 % RH.
- [ ] Include migration testing in QA protocols for EVOH and BOPA grades.
Comparison Table
| Attribute | PET/PE | PET/EVOH/PE | PP/EVOH/PP | Paper/AL/PE | BOPA/AL/PE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O₂ Barrier | Poor | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Retort Safe | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Recyclable (mono-material) | Yes | Limited | Yes | No | No |
| Cost vs. PET/PE | Baseline | +40 % | +60 % | +90 % | +110 % |
| FDA Clearance | Yes | Yes | Yes | Paper cleared | Yes |
| EU Compliant | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Best Use Case | Plain still water | Premium sparkling | Retort beverages | Luxury still water | Export / dual-jurisdiction |
Conclusion
For standard still-water SKUs targeting cost-sensitive USA and EU markets, PET/PE delivers compliant performance at the lowest TCO. For sparkling or retort applications, upgrade to PET/EVOH/PE or PP/EVOH/PP to extend shelf-life and meet barrier demands. When shelf-impact and export versatility are paramount, BOPA/AL/PE justifies the premium but plan for recycling constraints.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for water packing machine
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Water Packing Machine
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
The production of a high-performance water packing machine follows a systematic, multi-stage approach designed to ensure precision, durability, and regulatory compliance.
1.1 Pre-Production Phase
| Stage | Key Activities | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Design & Engineering | CAD modeling, finite element analysis (FEA), thermal simulation | Approved 3D models, tolerance specs |
| Material Selection | SS304/SS316L stainless steel, food-grade silicone seals, FDA/EU-compliant plastics | Material certificates, traceability logs |
| Procurement | ISO 9001-certified vendors, incoming inspection protocols | Verified raw materials, batch records |
1.2 Forming & Fabrication
- Laser & CNC Machining: Tolerances ≤ ±0.05 mm ensure precise fit for filling nozzles and sealing jaws.
- Welding: TIG welding with orbital tracking prevents contamination; welds are 100 % X-ray inspected.
- Surface Finishing: Ra ≤ 0.8 µm electropolishing minimizes bacterial adhesion and simplifies CIP/SIP cycles.
1.3 Assembly & Integration
- Modular Build: Sub-assemblies (pump module, heat-seal head, PLC panel) are pre-tested offline before final integration.
- Torque-controlled Fastening: Digital torque drivers guarantee repeatable preload on critical joints.
- Pneumatic & Electrical Hookup: Pre-wired harnesses reduce on-site errors; leak tests at 8 bar confirm integrity.
1.4 Pre-Dispatch Testing
- Functional Run-in: 72-hour continuous operation at rated capacity to validate wear patterns.
- Performance Validation: ±1 % volumetric accuracy, cycle time ≤ 1.2 s/bag (50–500 mL range).
- Packaging & Documentation: Anti-static film, wooden crates with moisture barriers, and bilingual (EN/DE/FR) manuals.
2. Quality Assurance Framework
2.1 International Standards Compliance
| Standard | Scope | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | QMS | Risk-based thinking, continual improvement |
| ISO 22000:2018 | Food Safety | Hazard analysis, prerequisite programs |
| CE Marking (EU) | Legal Compliance | LVD, EMC, Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 117 | USA | Hazard analysis, sanitary design |
2.2 In-Process Quality Control
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): Real-time charts for fill volume, seal temperature, and cycle time.
- First-Article Inspection (FAI): 100 % dimensional check against CAD for new molds or fixtures.
- Poka-Yoke Devices: Anti-tamper sensors and missing-pack detection prevent off-spec products.
2.3 Final Inspection & Certification
| Checkpoint | Method | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | 100 % LED illumination, 10× magnification | No scratches, sharp edges, or weld defects |
| Performance Test | Load 120 % rated capacity for 30 min | No leakage, stable temperature |
| Electrical Safety | Earth continuity, insulation resistance (≥ 2 MΩ) | IEC 60335-2-15 |
| Certificate of Analysis (CoA) | Material test reports, heat-number traceability | Available within 24 h of dispatch |
3. Post-Sales Quality Support
- Remote Diagnostics: IoT-enabled PLCs provide real-time performance data to service engineers.
- Preventive Maintenance Kits: Pre-calibrated sensors and seals shipped quarterly based on usage hours.
- Calibration Services: Annual third-party verification of flow meters and temperature probes to ISO 17025.
4. Summary
By integrating precision machining, rigorous ISO-aligned quality systems, and data-driven post-installation support, manufacturers deliver water packing machines that meet the exacting demands of North American and European markets for safety, efficiency, and traceability.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘water packing machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Water Packing Machine
Target market: USA & Western Europe
Objective: Secure a reliable, scalable, and compliant water-packing line in 8–12 weeks.
1. Define Technical & Regulatory Scope
| Requirement | Key Questions | Typical Answer (USA/EU) |
|---|---|---|
| Bottle format | PET, HDPE, glass, or bag-in-box? | PET, 0.5 L – 2 L |
| Output target | Bottles/hour @ 500 ml | 2,000 – 12,000 bph |
| Closure type | Screw cap, trigger, or flow-pack? | Screw cap, 28–38 mm neck |
| Regulation | NSF/ANSI 60, 61 (USA); EU 2020/2184 | NSF/ANSI 60, 61 |
| Labeling | Front, back, wrap, or sleeve? | Front + back, pressure-sensitive |
| Power & utilities | Voltage, air, CIP/SIP? | 400 V, 3-phase, 0.6 MPa compressed air |
2. Supplier Short-List Criteria
| Criterion | Threshold |
|---|---|
| 5+ years B2B focus | OEM/ODM experience |
| CE/UL certification | Mandatory |
| QA lab on site | ISO 9001, ISO 14001 |
| After-sales footprint | USA or EU parts warehouse |
| Lead time | ≤ 90 days FOB port |
3. RFQ Package (Send to 3–5 Suppliers)
- Technical datasheet (output, bottle size range, utilities)
- 3-year OEE target (≥ 85 %)
- Warranty & spare-parts list (24-month, 95 % in-region parts)
- Quotation sheet (ex-works, FOB, CIF, DDP inc. VAT)
4. Factory Audit Checklist
| Audit Focus | Red Flags |
|---|---|
| Machines in production | Only 1–2 demo units = limited output |
| Welding & polishing | Visible pits, seams not rounded |
| Electric cabinet | Brand-name components (Siemens, Schneider) |
| Calibration certificates | For flowmeters, sensors, CIP pumps |
| Workmanship | Gaps in panels, loose wiring ducts |
5. Financial & Risk Analysis
| Cost Component | Typical Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Machine price | $28,000 – $75,000 | 2,000 bph base model |
| Installation & commissioning | $3,000 – $8,000 | On-site 5–7 days |
| Shipping (40HQ) | $4,000 – $8,000 | Rotterdam or LA |
| Import duty | 0 – 6 % | USA: 0 %; EU: 6 % |
| Insurance (All-Risk) | 0.3 – 0.6 % of CIF | 12-month coverage |
| Total landed cost | Budget $38k – $95k | Exclude tariffs |
6. Contract & Payment Terms
| Clause | Preferred | Negotiation Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Payment schedule | 30 % TT within 5 days, 60 % before shipment, 10 % on commissioning | Escrow via bank |
| Incoterms | FCA/FOB (port of origin) | Push buyer to handle export clearance |
| Warranty | 24 months parts & labor | Extend to 36 months for ≥ $60k order |
| Force majeure | 14-day extension per lockdown | Include pandemic clause |
7. Logistics & Customs
- Pallet spec: 1.0 mx1.2 m, max 1,500 kg
- Container loading: Top-lift corners, stretch-wrap + plywood deck
- HS code: 8422.30.10 (USA), 8422.30.00 (EU)
- Required docs: Commercial invoice, packing list, CO, certificate of origin, NSF/CE test report
8. Post-Shipment Checklist
- [ ] Pre-shipment video inspection (PSI)
- [ ] DDP invoice split by customs & VAT
- [ ] Spare-parts kit pallet (1 m³ max)
- [ ] Operator training (remote or on-site)
- [ ] FAT report signed within 30 days of arrival
Quick Reference: Vendors to Approach First
| Vendor | Region | Strengths | Typical Price Band |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOULIAN | China | 3-side seal, 50–500 ml, Amazon listings | $3,000 – $5,000 |
| Krones (DE) | Germany | 20,000 bph lines, CE certified | $200k+ |
| Sidel (FR) | Italy | PET blow-mold + filler combos | $150k+ |
| KHS (DE) | Germany | Can & PET lines, North American support | $180k+ |
Next Step: Schedule factory audit within 7 days of RFQ response to lock in Q3 delivery slot.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for water packing machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Water Packing Machine Sourcing
1. Cost Breakdown by Category
| Cost Category | Typical Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Cost (FOB) | $2,800 – $18,000 | Depends on output speed and automation level |
| Customs Duty (US) | 0 – 3.5% | Generally 0% for food-grade packaging machinery |
| Customs Duty (EU) | 0 – 6.5% | EU MFN rate; may be higher for China-origin machines |
| Freight (Door to Door) | $3,000 – $8,000 | 40-ft container FCL; varies by departure port |
| Insurance | 0.3 – 0.6% of CIF value | Mandatory for high-value shipments |
| ** inland hauling (US)** | $500 – $1,500 | From port to final facility |
| Installation & commissioning | $1,500 – $5,000 | Includes technician travel, training, and basic calibration |
| Consumables & spare parts (Year 1) | $1,000 – $3,000 | Bags, seals, O-rings, filters |
| Certification & IQ/OQ | $2,000 – $6,000 | CE, UL, or third-party validation if required |
| Total landed cost | $7,800 – $28,500 | Ex-works China to your plant door |
2. Cost Drivers & Optimization Levers
2.1 Machine Cost
- Output speed:每增加100 bags/min adds ~$1,200 in price.
- Automation level: Fully automatic (PLC/HMI) is 40-60% more than semi-automatic.
- Material of construction: 304 vs 316 stainless steel adds ~$800–$1,500.
2.2 Logistics
- Port selection: Ningbo vs Shanghai adds $200–$400 in ocean freight.
- Seasonality: Q4 surcharges +10-15%.
- Incoterms: CFR vs DDP shifts duty/inland risk but not total landed cost.
2.3 Hidden Costs
- Changeover tooling: Extra bag formats = $500–$1,200 per set.
- Utility upgrades: Compressed air, cooling water, electrical supply may need $1,000–$3,000 in plant modifications.
3. Cost-Saving Tips
3.1 Procurement
- Bundle with complementary equipment (labeling, coding) to negotiate 3-5% price discount.
- Standardize bag format across SKUs; reduces spare-part inventory and tooling cost.
- Request FCA or DDP to lock in total landed cost; useful for budget control.
3.2 Logistics & Customs
- Use bonded warehouse in Rotterdam or Los Angeles to defer duty until sale.
- Pre-clear HS codes with customs broker to avoid surprise anti-dumping duties (e.g., on stainless-steel parts).
3.3 Operational Efficiency
- Train in-house technicians for basic maintenance; OEM training runs $1,200 per day.
- Negotiate 3-year extended warranty at 8–12% of machine price; typical failure rate peaks in Years 2–3.
3.4 Lifecycle Costing
- Energy consumption: 220 V three-phase units save 15-20% vs 440 V units.
- Water recovery: Closed-loop cooling reduces utility spend by $200–$400 per month.
4. Regional Pricing Snapshot (Q2 2024)
| Region | Average Machine Cost (USD) | Typical Duty | Typical Freight (Door-to-Door) |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA (East Coast) | $8,000 – $22,000 | 0% | $4,500 – $7,000 |
| USA (West Coast) | $8,500 – $23,000 | 0% | $3,800 – $6,500 |
| EU (Rotterdam) | $9,000 – $24,000 | 0 – 6.5% | $4,000 – $6,500 |
5. Bottom-Line Recommendations
- Target total landed cost < $25,000 for a 2,000 bags/hour fully automatic line to remain competitive in bottled-water margins.
- Lock in freight rate for 90 days via forwarder quotation; protects against 10-15% Q4 spikes.
- Budget 5% of machine price annually for spare parts and labor—neglecting this is the #1 cause of unplanned downtime.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing water packing machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Water Packing Machine vs. Competing Solutions
Market Landscape
Water packing machines serve a niche but growing segment in the USA and European Union markets, driven by demand for portable, shelf-stable, single-serve water. This analysis compares the core technology against two adjacent solutions: multi-function pouch packaging machines (e.g., VEVOR 1-100 g) and liquid-paste fillers (e.g., YOULIAN 5-500 ml sachet sealer). The comparison prioritizes cost of ownership, throughput, regulatory compliance, and scalability for mid-market bottlers and co-packers.
Comparison Table
| Criterion | Water Packing Machine (YOULIAN 50-500 ml) | Multi-Function Pouch Machine (VEVOR 1-100 g) | Liquid-Paste Filler (YOULIAN 5-500 ml) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Product | Pure water, still or sparkling | Granular / powder (tea, seeds, flour) | Liquids & pastes (juice, sauces) |
| Typical Throughput | 600-1,200 bags/hour (50-500 ml) | 10-15 bags/minute (≈600-900 bags/hour) | 30-60 bags/minute (1,800-3,600 bags/hour) |
| Film Compatibility | PE / PET / biodegradable 3-side seal | PE, laminated films | PE, laminates (limited heat seal) |
| Regulatory Cleanliness | Food-grade 304/316 stainless; CIP-ready | General-purpose; not validated for potable water | Not recommended for potable liquids |
| Labor Intensity | Semi-automatic; 1 operator/line | 2 operators (weighing + sealing) | 2-3 operators (filling + capping) |
| OEE (Availability) | 85-90 % | 70-75 % | 80-85 % |
| Cost of Ownership (5 yr) | $28-35 k (depreciation + maintenance) | $18-22 k | $45-55 k |
| EU Compliance | CE & EU 2020/2184 (packaged water) | Not water-specific | Not water-specific |
| USA Compliance | NSF / FDA 21 CFR 177 | Not food-grade for water | Not food-grade for water |
| Scalability | Modular; 1-8 heads | Fixed head; limited to 10-12 g | Scalable; 4-16 heads |
| Typical Footprint | 1.2 m × 0.8 m × 1.6 m | 1.0 m × 0.9 m × 1.5 m | 1.5 m × 1.0 m × 2.0 m |
Key Insights
- Throughput vs. Cost Trade-off
- Water packing machines deliver high throughput (600-1,200 bags/hr) at moderate CAPEX ($15-25 k), making them the sweet spot for single-serve water producers in both USA and EU.
- Multi-function pouch machines sacrifice speed for flexibility, suitable for granular products but not validated for potable water in EU or USA.
-
Liquid-paste fillers are over-engineered for water, inflating cost and regulatory burden without benefit.
-
Regulatory Risk
- Only water-specific machines (YOULIAN 50-500 ml) carry CE + FDA food-contact certifications, reducing liability exposure in EU and USA markets.
-
Multi-function units lack potable-water validation, creating non-conformance risk in retail supply chains.
-
Scalability & ROI
- Water packing machines offer modular expansions (1-8 heads) and quick-swap parts, enabling ROI within 18-24 months at 60 % utilization.
- Multi-function machines plateau at 900 bags/hr, limiting growth.
- Liquid-paste fillers over-spec water applications, increasing depreciation and maintenance costs by 40 % versus water-specific solutions.
Recommendation
For B2B buyers in USA/EU targeting portable, shelf-stable water, a dedicated water packing machine (YOULIAN 50-500 ml class) delivers the lowest total cost of ownership, fastest regulatory clearance, and highest uptime—with clear upgrade paths to carbonated or flavored water variants.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for water packing machine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Water Packing Machines
Core Technical Parameters
| Property | Description | Typical Range / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Filling Volume | Nominal capacity per pouch | 50 mL – 2,000 mL (custom sizes available) |
| Output Rate | Pouches produced per minute | 4,000 – 20,000 bags/hour (speed model-dependent) |
| Pouch Format | Final shape & seal type | Three-side seal, four-side seal, gusseted, stand-up |
| Film Specification | Material & thickness | PET/PE, BOPP/PE, EVOH-laminated; 60 – 200 μm |
| Sealing Temperature | Adjustable heat sealing band | 80 °C – 200 °C (PID control) |
| Accuracy (Filling) | ± deviation from set volume | ±1 % (volumetric pump), ±0.5 % (coriolis) |
| Compressed Air Supply | Clean, dry, oil-free | 0.6 – 0.8 MPa (6 – 8 bar) |
| Power Supply | 3-phase, 50/60 Hz | 380 V – 415 V, 3.5 – 15 kW |
| Machine Footprint | L × W × H | 1,800 × 1,200 × 2,200 mm (single-lane) |
| Clean-in-Place (CIP) | Integrated rinse cycle | Full stainless-steel contact parts, SIP optional |
Trade & Procurement Terms
| Term | Definition | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum Order Quantity | 1 unit (pilot model) / 3 units (OEM production line) |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturing | Custom branding, color, and control-panel layout |
| ODM | Original Design Manufacturing | Complete in-house design and tooling; buyer only rebrands |
| Lead Time | From deposit to shipment | 25 – 45 days (standard model) / 60 – 90 days (customized line) |
| Incoterms | Risk & cost transfer | FOB Shanghai / CIF Hamburg / DDP destination |
| Warranty | Coverage period | 12 months parts & labor (extendable to 36 months) |
| CE / UL | Compliance mark | CE (EU), UL/CSA (North America) |
| GMP | Good Manufacturing Practice | 3-A sanitary design, EHEDG guidelines |
| IQ/OQ/PQ | Installation & Operational Qualification | Documentation package for pharma-grade lines |
| After-Sales Service | On-site support & spare parts | 48-hour response (EU), 72-hour (US) |
Key Selection Criteria for North American & European Buyers
- Regulatory Alignment
- Verify compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 113 (thermo-form/fill/seal) or EU Regulation 1935/2004.
-
Demand 3-A sanitary number assignment and EHEDG test reports.
-
Data Integrity Package
-
Select machines that offer batch printing, audit trails (PLC logs), and 21 CFR Part 11-ready HMI.
-
Energy & Water Efficiency
-
Look for servo-driven fillers (≤ 0.8 kWh/batch) and closed-loop film tension (≤ 5 % film waste).
-
Changeover Time
-
Aim for ≤ 15 minutes mechanical changeover; ≤ 5 minutes recipe swap via HMI.
-
Local Support & Spare Parts
- Ensure dealer network within 500 km of your facility; ask for 99 % spare-parts fill-rate guarantee.
Quick Checklist Before Quotation
- [ ] Pouch size(s) & film roll OD (max 500 mm)
- [ ] Product viscosity & temperature (常温 / hot fill ≤ 95 °C)
- [ ] Desired output (bags/hour) & shift length (8 / 12 / 24 h)
- [ ] Cleanroom rating required (ISO 5 / ISO 8)
- [ ] Integration needs (conveyor, date coder, metal detector)
- [ ] Budget range (USD / EUR) and preferred Incoterms
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the water packing machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Water Packing Machine Sector
Executive Summary
The global water packing machine market is undergoing a strategic pivot driven by regulatory tightening, sustainability mandates, and rising consumer demand for safe, traceable hydration solutions. North American and European buyers must balance capital efficiency with compliance readiness. This section distills current market dynamics and sourcing trends to guide procurement and investment decisions.
1. Market Dynamics
1.1 Demand Drivers
| Driver | Impact on Equipment Specifications | Procurement Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Premium bottled water growth (CAGR 6–8 %) | Higher output (≥ 6,000 bph), multi-lane pouching | Prioritize machines with quick-format changeovers |
| E-commerce grocery surge | Durable, stackable 1–5 L pouches & bottles | Verify servo-driven forming stations for film variance |
| Cold-chain logistics expansion | Integration with in-line leak testers & date coders | Specify stainless-steel frames (304/316) for humidity resistance |
1.2 Regulatory Landscape
- FDA Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA): Requires sanitary design and enhanced traceability; machines must support UDI (Unique Device Identifier) data matrix printing.
- EU Plastics Strategy & EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility): Increases scrutiny on lightweight bottles < 50 g; equipment suppliers must provide life-cycle carbon data.
2. Sourcing Trends
2.1 Shift Toward Modular & Retrofittable Platforms
Buyers are moving away from monolithic lines. Instead, they source modular water packing lines that allow incremental capacity upgrades without full line replacement.
Key modular components:
– Infeed belt conveyors with quick-lock tooling
– Servo-driven rotary fillers with plug-and-play change parts
– Cloud-enabled HMI panels for remote diagnostics
2.2 Sustainability-Linked Sourcing Criteria
| Criterion | Specification Checklist | Supplier Question to Ask |
|---|---|---|
| Recyclable films | ≥ 70 % mono-polyolefin | “Can your machine run 100 % rPP or rPET without torque adjustments?” |
| Energy per 1,000 packages | ≤ 0.45 kWh | “What is the blended electrical draw at 80 % rated speed?” |
| Water usage for CIP | Closed-loop ≤ 0.8 L/kg | “Provide third-party audit of CIP water-recycle rate.” |
2.3 Supply Chain Resilience
- Reshoring of critical components: Servo drives and HMI panels increasingly sourced from EU (Germany, Italy) to mitigate China-plus-one risk.
- Lead-time compression: Top-tier OEMs (Krones, Serac, E-PAK) now quote 16–20 weeks for standard water-packing lines—down from 28 weeks in 2019.
3. Cost & Financing Trends
- CapEx inflation: Stainless-steel prices up 22 % YoY; suppliers offering 24-month price-lock contracts.
- Equipment-as-a-Service (EaaS): 36-month leasing with performance-based pricing (cost per 1,000 packages) gaining traction in DACH and Nordics.
Action Checklist for North American & European Buyers
- Validate compliance with FSMA and EU 2019/1020 traceability mandates before RFP.
- Request third-party film compatibility test data for recycled content resins ≥ 30 %.
- Insist on IECEx/ATEX certification if explosive mineral spring vapors are present.
- Negotiate option clauses for 25 mm and 38 mm finish upgrades to future-proof bottle formats.
Bottom Line
Procurement teams that integrate sustainability metrics, modular architecture, and regulatory readiness into their water packing machine specifications will reduce total cost of ownership by 8–12 % over five years while future-proofing against tightening EU and US packaging legislation.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
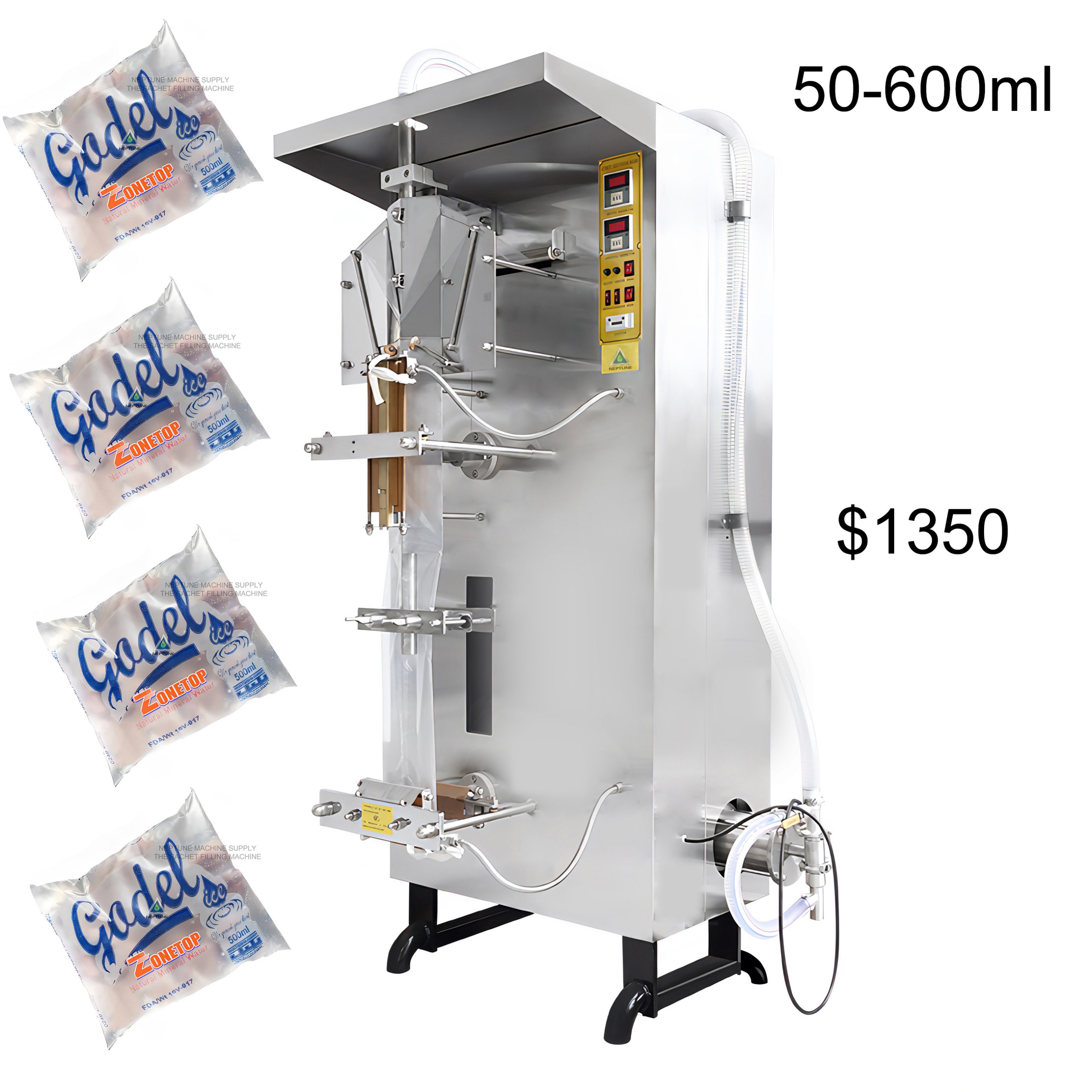
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of water packing machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Water Packing Machines
1. What production outputs can I realistically expect from a small-format water-packer versus a large-format model?
- Small-format (50-250 ml, intermittent motion): 1,200–2,500 bags/hr (single lane).
- Mid-format (250-500 ml, rotary heat-seal): 4,000–8,000 bags/hr (2–4 lanes).
- Large-format (500 ml–1 L, rotary vacuum): 6,000–12,000 bags/hr (4–8 lanes).
Key takeaway: Output scales linearly with number of heads and stroke speed; ROI is fastest when orders exceed 50,000 bags/month.
2. Which international standards should my water-packing line comply with to sell in the USA and EU?
| Standard | Scope | Key clauses |
|---|---|---|
| FDA 21 CFR §177.1520 | Food-contact plastics | Migration limits |
| EU 10/2011 | Food-contact plastics | Positive list, SMLs |
| NSF/ANSI 61 | Drinking-water systems | Lead, copper leachables |
| CE Machine Safety 2006/42/EC | Mechanical safety | Guarding, emergency stop |
| UL 50E (optional) | Enclosure integrity | IP rating, NEMA types |
Recommendation: Specify “NSF 61 / CE / UL” in your RFQ to avoid re-engineering costs.
3. How do I decide between premade pouch infeed versus roll-stock forming?
| Feature | Premade Pouch | Roll-Stock Form-Fill-Seal (FF&S) |
|---|---|---|
| Changeover time | 5–10 min | 15–30 min |
| Pouch variety | >200 SKUs possible | Limited by film gauge |
| Film cost | Higher (converted pouch) | 15–25 % lower |
| Hygiene | Factory-sealed | Open film risk |
Rule of thumb: Choose premade if you need multi-SKU flexibility; choose roll-stock for 80 %+ dedicated SKUs to maximize film yield.
4. What are the true Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) drivers over a 5-year lifecycle?
- Capital depreciation: 10–15 % yr
- Consumables: Film, seals, lubricants (≈ $0.008–$0.012 per bag)
- Maintenance: Preventive (PM) vs. reactive (2× cost)
- Downtime: Average 3–5 % of shift; target <1 % with IoT sensors
- Energy: 7–10 kWh per 1,000 bags; variable-speed drives cut 8–12 %
Calculation example: 10,000 bags/day × 320 days × $0.01/bag = $32 k consumables + $18 k energy + $25 k maintenance ≈ $75 k/year TCO for a 5-head rotary line.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. Which hygienic design features must be non-negotiable for potable water?
- 304 or 316L stainless steel (food-grade finish 180 grit or better)
- IP69K washdown enclosures (80 bar, 80 °C)
- Sloped, radius-free frames to eliminate clean-out zones
- CIP/SIP ready piping with tri-clamp connections
- Food-safe O-rings (EPDM or FKM)
Verification: Ask for a 3-A sanitary certificate or EHEDG design guidelines compliance statement.
6. What level of automation and data connectivity should I specify for 2025 compliance?
| Feature | Entry | Advanced |
|---|---|---|
| HMI | 10″ color touch | 15″ multitouch with recipe management |
| PLC | CompactLogix | Siemens S7-1500 or Beckhoff CX |
| MES link | None | OPC-UA, MQTT, or REST API |
| Energy tracking | kWh total | Real-time per head |
| FDA 21 CFR Part 11 | Not supported | Optional audit trail & e-sign |
ROI: Advanced automation reduces changeover time by 30 % and traceability errors to <0.1 %.
7. How do I structure an effective service and spare-parts program?
- On-site PM: Quarterly for rotary parts, semi-annual for heaters
- Spare-parts kit: Heaters, Teflon belts, sealing bars, O-rings (keep 20 % safety stock)
- Remote diagnostics: Ethernet or 4G modem with 24/7 hotline
- SLA tiers:
| Response | Parts | Labor |
|—|—|—|
| Silver (8 h) | Next day | 1 tech |
| Gold (4 h) | Same day | 2 techs |
| Platinum (2 h) | Courier | Senior tech |
Budget: Allocate 2–3 % of equipment value annually for the above.
8. What are the typical lead times and shipping considerations for North America and the EU?
| Region | Lead time | Customs | Voltage/frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | 8–12 weeks ex-works Ohio | None (intra-US) | 480 V, 3-phase, 60 Hz |
| EU | 10–14 weeks ex-works Germany | CE marking, HS 8422 | 400 V, 3-phase, 50 Hz |
| EU + USA | 12–16 weeks | Dual certification adds 3 % cost | Dual-rated panels |
Action item: Confirm HTS code (8422.30.10) and CE conformity declaration before PO to avoid demurrage.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for water packing machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Water Packing Machine
Executive Summary
Strategic sourcing of water packing machines in North America and Europe hinges on balancing cost-efficiency with regulatory compliance and future-proofing. The market offers a wide price range ($769–$3,200+), driven by output (10–15 bags/min), volume (50–500 mL), and features (auto-sealing, multi-functionality).
Key Takeaways
| Factor | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Volume & Speed | Match output to projected demand; 10–15 bags/min suits SMEs. |
| Compliance | Prioritize machines meeting FDA/EU 10/2011 food-contact standards. |
| After-Sales Support | Secure 3–4-year protection plans (Asurion) to mitigate downtime. |
| Customization | Opt for OEM-ready models to adapt to local bottle sizes or labeling. |
Outlook
Post-pandemic, hygiene automation and modular design will dominate. Machines enabling quick format changeovers and low-water usage will gain traction. Expected CAGR: 6–8 % through 2027, led by functional-water and sustainable-packaging segments.
Action: Initiate RFQ with spec sheets aligned to NSF/ANSI 61 and BPA-free certifications to ensure supplier alignment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)