The global wastewater treatment market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing industrialization, stringent environmental regulations, and rising concerns over water scarcity. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at USD 103.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 143.7 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period. Similarly, Grand View Research projects a CAGR of 6.1% from 2023 to 2030, citing advancements in membrane technologies, increased municipal infrastructure investments, and growing adoption of water reuse practices as key growth catalysts. With over 80% of global wastewater still discharged untreated into the environment, per UN-Water estimates, the demand for reliable and innovative treatment solutions has never been more pressing. As industries and municipalities seek scalable, efficient, and compliant systems, a select group of manufacturers are leading the charge in technological advancement and global deployment. Below are the top 10 wastewater treatment companies shaping the future of water sustainability.
Top 10 Wastewater Treatment Companies Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Nviro
Domain Est. 1996
Website: nviro.com
Key Highlights: Nviro delivers a full-service water and wastewater offering, from design and manufacturing to operations, compliance, and technology….
#2 Xylem Water Solutions & Water Technology
Domain Est. 1999
Website: xylem.com
Key Highlights: Xylem is a leader in developing innovative water solutions through smart technology. Learn more about Xylem’s water, wastewater and energy solutions….
#3 Cloacina
Domain Est. 2004
Website: cloacina.com
Key Highlights: Cloacina is a manufacturer and purveyor of stainless steel package wastewater treatment plants and equipment located on the Central Coast of California….
#4 Aquacycl
Domain Est. 2018
Website: aquacycl.com
Key Highlights: Industrial Wastewater Treatment Made Simple. We solve your toughest wastewater challenges, so you can focus on your core business. Get Started See How It’s Done….
#5 WesTech Engineering
Domain Est. 2020
Website: westechwater.com
Key Highlights: WesTech offers solutions and equipment to clean water and wastewater for municipal, and a variety of industrial and mining applications….
#6
Domain Est. 1999
Website: jetincorp.com
Key Highlights: If you want to experience honest, dependable, responsive, service-oriented wastewater treatment specialists, you want Jet—a company founded on innovation and ……
#7 Gradiant
Domain Est. 2002
Website: gradiant.com
Key Highlights: Gradiant deploys advanced water treatment solutions and technologies to solve the toughest water challenges for the world’s critical industries….
#8 AUC Group
Domain Est. 2003
Website: aucgroup.net
Key Highlights: Along with conventional filtration, we also offer membrane processes including: Microfiltration; Ultrafiltration; Reverse Osmosis. Water Treatment Plant….
#9 Inframark
Domain Est. 2013
Website: inframark.com
Key Highlights: Our business is protecting & providing the world’s most valuable resource, water. Inframark provides top quality water management and infrastructure ……
#10 Infiltrator Water Technologies
Domain Est. 2015
Website: infiltratorwater.com
Key Highlights: Infiltrator Water Technologies has been a market leader within the onsite wastewater treatment industry for over 35 years….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Wastewater Treatment Companies

2026 Market Trends for Wastewater Treatment Companies: A Comprehensive Analysis
The global wastewater treatment market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by escalating environmental concerns, stringent regulations, technological innovation, and growing water scarcity. Wastewater treatment companies must navigate a complex landscape characterized by both substantial challenges and compelling opportunities. Here’s a detailed analysis of the key trends shaping the industry:
1. Stringent Environmental Regulations and the Rise of Circular Economy Mandates
Governments worldwide are tightening discharge standards for pollutants (nutrients, microplastics, PFAS, pharmaceuticals) and setting ambitious water reuse targets. The EU’s Zero Pollution Action Plan, the US EPA’s PFAS Strategic Roadmap, and similar initiatives in Asia-Pacific are forcing industries and municipalities to upgrade treatment capabilities. Concurrently, the circular economy model is gaining traction, transforming wastewater from a disposal problem into a resource stream. By 2026, regulations will increasingly mandate or incentivize:
* Energy Recovery: Widespread adoption of advanced anaerobic digestion and thermal hydrolysis to generate biogas for power/heat.
* Nutrient Recovery: Commercial-scale extraction of phosphorus and nitrogen for fertilizer production.
* Water Reclamation: Mandates for non-potable (irrigation, industrial cooling) and increasingly, indirect/direct potable reuse, particularly in water-stressed regions.
* Impact: Companies specializing in resource recovery technologies (e.g., struvite precipitation, membrane bioreactors for high-purity reuse) will see accelerated demand. Compliance services and system retrofits will be major revenue drivers.
2. Digitalization, AI, and the Smart Water Plant Revolution
The integration of digital technologies will be pervasive by 2026, moving beyond basic SCADA systems towards truly intelligent operations:
* AI-Powered Process Optimization: Machine learning algorithms will predict influent loads, optimize chemical dosing (aeration, coagulants), minimize energy consumption, and prevent equipment failures in real-time, significantly reducing OPEX.
* Digital Twins: Widespread use of virtual replicas of treatment plants for simulation, scenario planning, predictive maintenance, and operator training.
* Advanced Sensing and IoT: Proliferation of real-time sensors (e.g., for nutrients, pathogens, emerging contaminants) feeding data into central platforms for instant decision-making and regulatory compliance reporting.
* Cybersecurity: As plants become more connected, robust cybersecurity measures will be non-negotiable.
* Impact: Companies offering integrated digital solutions (software platforms, sensors, analytics) will gain a competitive edge. Traditional EPC (Engineering, Procurement, Construction) firms must partner with or acquire digital expertise. Data analytics will become a core service offering.
3. Decentralized and Modular Treatment Solutions Gain Prominence
Centralized wastewater treatment faces challenges in rapidly urbanizing areas, remote communities, and industrial sites with high-strength waste. By 2026:
* Modular Systems: Factory-built, scalable units (e.g., membrane bioreactors, MBBRs, advanced oxidation) will be favoured for faster deployment, lower capital costs, and easier expansion.
* On-Site/Industrial Treatment: Industries (food & beverage, pharma, textiles) will increasingly treat wastewater on-site to meet zero liquid discharge (ZLD) goals, recover resources, and reduce reliance on municipal systems.
* Small Community Solutions: Affordable, robust decentralized systems will be crucial for rural and peri-urban areas lacking sewer infrastructure.
* Impact: Manufacturers of standardized, containerized treatment units will thrive. Service models shifting from pure equipment sales to long-term operational contracts (O&M) for decentralized systems will grow.
4. Focus on Energy Efficiency and Carbon Neutrality
Wastewater treatment is energy-intensive. The push for net-zero emissions is a major driver:
* Energy-Neutral/Positive Plants: Advanced processes (high-rate anaerobic treatment, thermal hydrolysis, energy recovery from sludge) will enable more plants to generate more energy than they consume.
* Renewable Integration: On-site solar, wind, and biogas co-generation will become standard.
* Low-Carbon Technologies: Adoption of energy-efficient pumps, blowers, and membranes; exploration of alternative processes like anammox for nitrogen removal.
* Impact: Companies providing energy-efficient equipment, renewable integration solutions, and carbon footprint assessment/services will be in high demand. Energy performance will be a key selection criterion.
5. Addressing Emerging Contaminants and Micropollutants
PFAS (forever chemicals), microplastics, pharmaceuticals, and endocrine disruptors are a growing threat to water quality and public health. By 2026:
* Regulatory Pressure: Stricter limits on these contaminants will necessitate advanced treatment.
* Technology Adoption: Wider deployment of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs – UV/H2O2, ozone), advanced filtration (nanofiltration, reverse osmosis), and activated carbon (especially for PFAS) will be essential.
* Sludge Management: Contaminated biosolids will require specialized treatment (e.g., thermal destruction for PFAS) or restricted land application.
* Impact: Significant growth in the market for AOPs, niche membrane technologies, and specialized sludge treatment. Companies with proven solutions for emerging contaminants will command premium pricing.
6. Water Scarcity Driving Reuse and Desalination Integration
With increasing droughts and population pressure, water reuse is no longer optional but essential:
* Non-Potable Reuse Expansion: Industrial reuse (cooling, process water) and agricultural irrigation will be major drivers.
* Indirect/Direct Potable Reuse (IPR/DPR): Projects will move beyond pioneers (e.g., Singapore, California) to more regions, requiring ultra-advanced treatment (e.g., multiple barriers: MBR, RO, AOP, UV).
* Synergy with Desalination: Brine management from desalination plants and wastewater reuse will be integrated for holistic water security, particularly in coastal areas.
* Impact: Massive growth in markets for high-recovery membranes (RO, NF), advanced disinfection (UV, ozone), and comprehensive reuse system design. Public acceptance campaigns will be crucial.
Conclusion: Navigating the 2026 Landscape
By 2026, successful wastewater treatment companies will be those that transcend traditional roles. They must be:
* Technology Integrators: Seamlessly combining biological, physical, chemical, and digital solutions.
* Resource Recovery Experts: Turning waste into water, energy, and nutrients.
* Data-Driven Service Providers: Offering intelligent O&M and performance guarantees.
* Sustainability Partners: Helping clients achieve environmental and carbon goals.
The market will reward innovation, adaptability, and a holistic approach to the water-energy-nutrient nexus. Companies failing to embrace digitalization, resource recovery, and advanced contaminant removal risk obsolescence. The wastewater sector is evolving from a necessary cost center to a strategic, value-generating component of sustainable infrastructure and the circular economy.
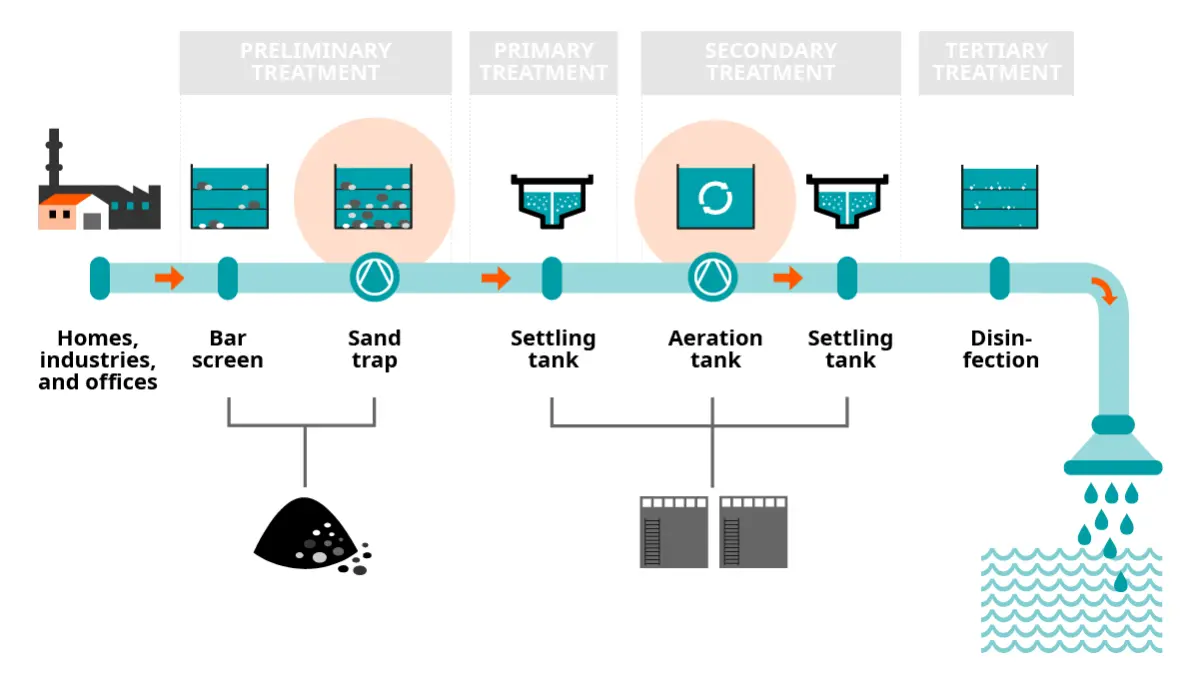
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Wastewater Treatment Companies: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing wastewater treatment companies—whether for technology licensing, equipment procurement, or project execution—exposes organizations to significant risks if due diligence is insufficient. Two critical areas prone to pitfalls are quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Failing to address these can lead to project delays, regulatory non-compliance, financial losses, and legal disputes.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
One of the most prevalent risks in sourcing wastewater treatment solutions is compromising on quality, often due to vendor misrepresentation, lack of standardized validation, or inadequate performance verification.
-
Inconsistent Technology Performance: Many suppliers claim high treatment efficiency under ideal lab conditions, but real-world performance can vary significantly due to influent variability, climate, or operational challenges. Without verified case studies or third-party testing data, buyers risk selecting underperforming systems.
-
Substandard Materials and Construction: Some vendors cut costs by using inferior materials (e.g., non-corrosion-resistant metals, low-grade polymers), leading to premature system failure, increased maintenance, and safety hazards. This is particularly common with offshore or low-cost manufacturers.
-
Lack of Certifications and Compliance: Reputable wastewater technologies should meet environmental and safety standards (e.g., ISO 14001, NSF, local discharge regulations). Sourcing from companies without proper certifications increases the risk of non-compliance and regulatory penalties.
-
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Training: Quality extends beyond the physical product. A lack of proper installation guidance, operator training, or responsive technical support can undermine treatment efficiency and system longevity, even with a well-designed solution.
Intellectual Property-Related Pitfalls
Intellectual property issues are often overlooked during procurement but can result in costly litigation, technology limitations, or loss of competitive advantage.
-
Unclear IP Ownership in Custom Solutions: When co-developing or customizing a treatment process, ambiguous contracts may leave IP ownership unresolved. This can prevent the buyer from freely using, modifying, or transferring the technology in the future.
-
Use of Infringing Technology: Some vendors may incorporate patented components or processes without proper licensing. If the buyer deploys such technology, they could be held liable for infringement, even if unaware.
-
Overly Restrictive Licensing Terms: For licensed technologies (e.g., proprietary bioreactor designs or chemical formulations), restrictive usage rights may limit scalability, geographic deployment, or integration with other systems, reducing long-term flexibility.
-
Inadequate Protection of Buyer’s Own IP: During technical evaluations or pilot projects, buyers may disclose sensitive operational data or process details. Without robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and data handling protocols, this information could be misused or disclosed to competitors.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, organizations should:
– Conduct thorough technical audits and request performance data from existing installations.
– Verify certifications and conduct on-site factory acceptance tests (FAT).
– Engage legal and technical experts to review IP clauses in contracts.
– Require warranties, performance guarantees, and clear service-level agreements.
– Use comprehensive NDAs and define IP ownership upfront in joint development agreements.
Proactively addressing quality and IP concerns ensures reliable wastewater treatment performance and protects the buyer’s legal and commercial interests.
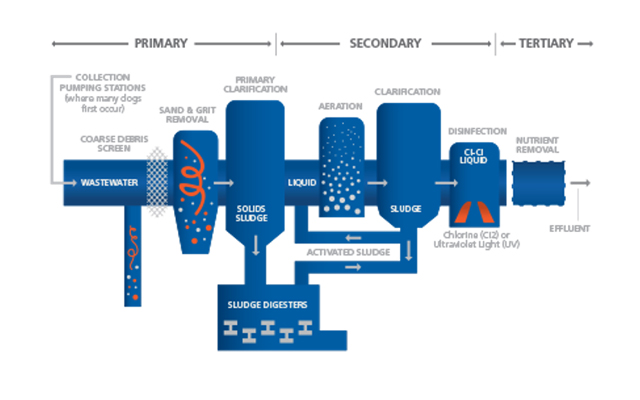
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Wastewater Treatment Companies
Regulatory Framework Overview
Wastewater treatment operations are governed by a complex network of federal, state, and local regulations. Key federal laws include the Clean Water Act (CWA), which establishes discharge standards and requires National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permits. Compliance also involves adherence to the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) for hazardous waste handling, the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) for worker safety, and state-specific environmental codes. Staying current with regulatory updates and permit requirements is essential to avoid penalties and operational disruptions.
Wastewater Transport & Handling Protocols
Safe and compliant transportation of wastewater and biosolids requires strict adherence to Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations. All vehicles must be properly labeled, equipped with spill containment systems, and operated by trained personnel. Transport manifests must be completed accurately and maintained for recordkeeping. Routing should minimize risks to sensitive environmental areas and populated zones. Regular vehicle inspections and maintenance logs are mandatory to ensure mechanical integrity and prevent leaks or spills during transit.
Storage & Disposal Compliance
On-site storage of wastewater and residuals must comply with containment standards to prevent groundwater contamination and surface runoff. Storage tanks and lagoons should be constructed with impermeable liners, secondary containment, and leak detection systems. Sludge and biosolids must be treated and disposed of according to EPA 40 CFR Part 503 standards, including pathogen reduction, metal limits, and land application restrictions. Records of storage duration, volume, and treatment methods must be retained for at least five years.
Monitoring, Reporting & Recordkeeping
Routine monitoring of influent, effluent, and process parameters is required to verify compliance with NPDES permit limits. Parameters typically include biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), total suspended solids (TSS), pH, ammonia, and specific pollutants. Data must be collected using calibrated equipment and analyzed by certified laboratories. Discharge Monitoring Reports (DMRs) must be submitted monthly or quarterly to regulatory agencies. All operational logs, maintenance records, monitoring data, and personnel training documentation should be stored securely and made available for audits.
Spill Prevention & Emergency Response
Facilities must have a Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) plan if they store oil or hazardous substances above threshold quantities. A comprehensive emergency response plan should outline procedures for leaks, equipment failure, or natural disasters. This includes immediate containment actions, notification protocols for regulatory agencies and the public, and coordination with local emergency services. Regular drills and employee training ensure preparedness and regulatory compliance under the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (EPCRA).
Personnel Training & Safety Compliance
All employees must undergo regular training on hazardous materials handling, confined space entry, lockout/tagout procedures, and chemical safety (per OSHA 29 CFR 1910). Wastewater operators should hold valid certifications issued by state licensing boards, with continuing education to maintain compliance. Safety data sheets (SDS) must be accessible for all chemicals used, and personal protective equipment (PPE) should be provided and enforced based on job-specific risk assessments.
Third-Party Contractor Management
When outsourcing services such as sludge hauling, equipment maintenance, or lab testing, companies must vet contractors for regulatory compliance and proper licensing. Contracts should specify compliance responsibilities, insurance requirements, and data-sharing obligations. Third-party transporters must provide valid manifests and disposal certifications. Regular audits of contractor performance and documentation help ensure alignment with company and regulatory standards.
Sustainability & Environmental Stewardship
Beyond compliance, wastewater companies are encouraged to adopt sustainable practices such as energy recovery (e.g., biogas from anaerobic digestion), water reuse programs, and nutrient recycling. Implementing a formal environmental management system (EMS) aligned with ISO 14001 can improve operational efficiency and demonstrate commitment to environmental responsibility. Public reporting on sustainability metrics enhances transparency and community trust.
In conclusion, sourcing wastewater treatment companies requires a comprehensive evaluation of technical expertise, regulatory compliance, cost efficiency, and long-term sustainability. It is essential to select a partner that not only meets current treatment needs but also aligns with environmental goals and future scalability. By prioritizing proven experience, innovative technologies, and strong customer support, organizations can ensure reliable, compliant, and environmentally responsible wastewater management. A thorough due diligence process, including site assessments, reference checks, and performance reviews, will ultimately lead to a successful and sustainable partnership in addressing wastewater challenges.