The global waste compactor market is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing urbanization, stringent environmental regulations, and rising demand for efficient waste management solutions across municipal, industrial, and commercial sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global waste management market size was valued at USD 1.4 trillion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6% from 2023 to 2030, with waste compaction technologies playing a pivotal role in this expansion. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects the waste compactor market to grow at a CAGR of over 6.2% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, fueled by advancements in automation, energy efficiency, and smart waste handling systems. As cities and industries strive to reduce landfill dependency and optimize space utilization, compactors have become indispensable. This growing demand has propelled innovation and competition among manufacturers worldwide, shaping a dynamic landscape. Below are the top 10 waste compactor manufacturers leading the industry through technology, reliability, and global reach.
Top 10 Waste Compactor Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
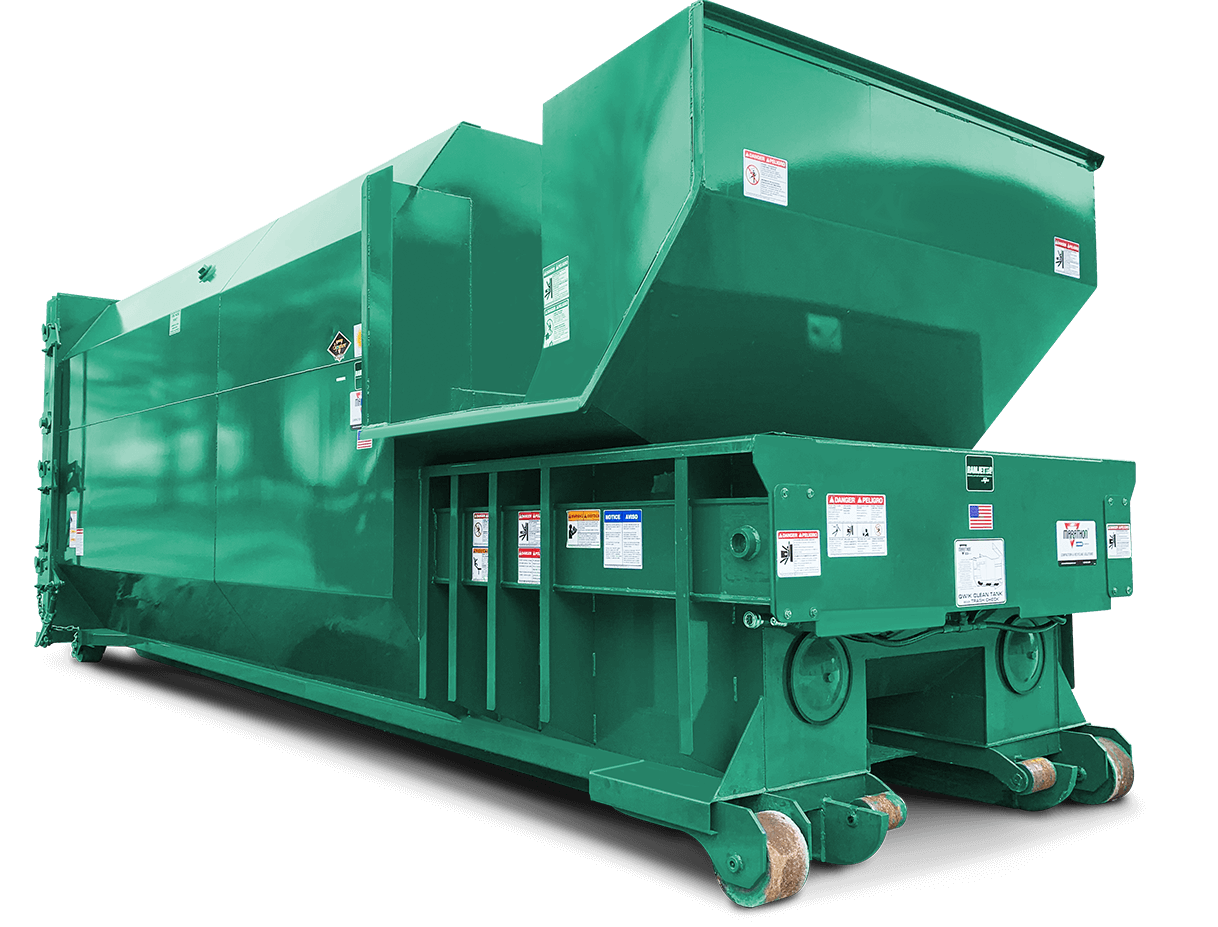
#1 Commercial Trash Compactors, Balers & Recycling Equipment For …
Domain Est. 1998
Website: marathonequipment.com
Key Highlights: Marathon Equipment Company is known throughout the world as a leading manufacturer of onsite commercial/industrial trash compactors, balers, and recycling ……
#2 Refuse compactors
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bomag.com
Key Highlights: BOMAG landfill compactors are hydrostatically driven and equipped with the latest technology and clever assistance systems….
#3 Bramidan
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bramidan.com
Key Highlights: Bramidan offers quality balers and compactors for reliable waste management. Compress waste such as cardboard, plastic, and other recyclable materials….
#4 Commercial & Industrial Trash Compactor Services
Domain Est. 1998
Website: wm.com
Key Highlights: WM offers custom commercial & industrial compactor solutions to help your business improve waste efficiency. Sales, rental and maintenance options ……
#5 BACE
Domain Est. 2006
Website: bacecorp.com
Key Highlights: The world’s leading innovator of recycling and waste industry technology. We infuse intelligence into every baler and compactor we manufacture and service….
#6 Cardboard balers, trash compactors and other recycling equipment …
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cram-a-lot.com
Key Highlights: Our comprehensive product range includes compactors for wet or dry waste, compactors that can be serviced with roll off, front load, or rear load trucks….
#7 Wastequip
Domain Est. 1997
Website: wastequip.com
Key Highlights: Wastebuilt is your One-Stop Source for waste equipment supplies and replacement parts for refuse trucks, roll-off hoists, compactors, containers, and more….
#8 Orwak
Domain Est. 1998
Website: orwak.com
Key Highlights: Orwak is a world leader in compaction and baling solutions for solid waste materials. We make waste management more efficient and more profitable….
#9 U.S. Trash Balers & Compactors
Domain Est. 2008
Website: miltekusa.com
Key Highlights: Mil-tek the U.S. leading provider of Pneumatic trash balers and compactors. Our recycling machines helps companies save space, time and money. Buy or rent….
#10 Smash My Trash: Mobile Waste Compaction Service
Domain Est. 2015
Website: smashmytrash.com
Key Highlights: Transform waste management with our mobile dumpster compaction service. Efficient, eco-friendly solutions that save costs and reduce environmental impact….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Waste Compactor

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Waste Compactors
The global waste compactor market in 2026 is poised for significant transformation, driven by urbanization, tightening environmental regulations, technological innovation, and a growing emphasis on circular economy principles. Here are the key trends shaping the market:
1. Sustainability and Regulatory Pressure as Key Drivers
Stringent environmental regulations, particularly in North America and Europe, are compelling municipalities and businesses to adopt more efficient waste management solutions. Landfill diversion mandates, extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, and carbon reduction targets are pushing demand for compactors that reduce transportation frequency, lower emissions, and improve waste segregation. Compactors enabling better recovery of recyclables (especially plastics and organic waste) will gain prominence, aligning with circular economy goals.
2. Smart and Connected Compactors Gaining Traction
IoT integration is becoming a differentiator. By 2026, smart compactors equipped with fill-level sensors, GPS tracking, and remote monitoring capabilities will see accelerated adoption. These systems optimize collection routes, reduce operational costs, prevent overflow, and provide valuable data analytics for waste stream management. Municipalities and large commercial users are increasingly investing in connected solutions for real-time operational efficiency.
3. Growth in Commercial and Industrial (C&I) Segments
The commercial sector—including retail, hospitality, and food service—will remain a major growth driver. As businesses face rising waste disposal fees and sustainability reporting requirements, high-capacity compactors that reduce labor and hauling costs are essential. In the industrial sector, manufacturing and logistics facilities are adopting specialized compactors for materials like plastics, cardboard, and scrap metal to improve material recovery and streamline operations.
4. Urbanization and Space Optimization
Rapid urbanization, especially in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, is increasing the demand for waste compaction in densely populated areas. Space-constrained environments like high-rise buildings, urban retail centers, and underground facilities are adopting vertical and hybrid compactors to maximize capacity while minimizing footprint. This trend supports the growth of compact, high-efficiency models.
5. Electrification and Energy Efficiency
Environmental concerns and rising energy costs are driving demand for electric and hybrid waste compactors. Municipal fleets and private waste operators are transitioning from diesel-powered units to electric models, especially in emission-sensitive urban zones. Energy-efficient hydraulic systems and regenerative braking technologies will become standard features, enhancing the environmental and economic appeal of modern compactors.
6. Focus on Waste-to-Energy and Organics Processing
While not replacing traditional compactors, integrated systems that combine compaction with pre-processing for waste-to-energy (WtE) or anaerobic digestion are emerging. In regions with advanced WtE infrastructure (e.g., parts of Europe and Japan), compactors designed to densify waste for more efficient incineration or fermentation will see niche growth, particularly for organic waste streams.
7. Market Consolidation and Innovation
The competitive landscape is evolving, with established players investing in R&D for smarter, greener solutions and smaller innovators introducing modular or AI-driven systems. Mergers and partnerships between compactor manufacturers and waste management software providers are likely to increase, offering integrated waste management platforms.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the waste compactor market will be defined by intelligent, sustainable, and data-driven solutions. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to deliver compactors that not only improve operational efficiency but also contribute to broader environmental goals. The convergence of regulatory mandates, technological advancements, and economic incentives will continue to reshape demand, positioning waste compactors as critical components of modern, circular waste ecosystems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Waste Compactors (Quality and IP)
Sourcing waste compactors involves significant considerations around product quality and intellectual property (IP), especially when dealing with international suppliers or private-label manufacturers. Overlooking these areas can lead to operational inefficiencies, legal risks, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Build Quality and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing waste compactors—particularly from low-cost manufacturers—is receiving units constructed with inferior materials and poor workmanship. Thin-gauge steel, inadequate corrosion protection, and low-grade hydraulic components can result in frequent breakdowns, safety hazards, and shortened equipment lifespan. Always verify material specifications and conduct third-party quality inspections before shipment.
Inadequate Performance and Reliability Testing
Many suppliers may provide optimistic performance claims without verifiable test data. Compactors that fail under continuous operation or do not achieve stated compaction ratios can disrupt waste management operations. Ensure suppliers provide documented test results under real-world conditions and request performance guarantees in contracts.
Lack of Compliance with Regional Safety and Environmental Standards
Waste compactors must meet regional safety, noise, and emissions standards (e.g., CE marking in Europe, UL certification in the U.S.). Sourcing non-compliant units can lead to import denials, fines, or liability in case of accidents. Confirm that the compactor meets all applicable regulatory requirements for the target market.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
When sourcing from generic or OEM suppliers, there’s a risk that the design or technology infringes on existing patents or trademarks. Using a compactor that copies protected mechanisms (e.g., hydraulic systems, safety interlocks, or control panels) may expose your company to legal action. Conduct IP due diligence and require suppliers to warrant that their products do not violate third-party rights.
Absence of Original Design Documentation and IP Ownership
In private-label or custom sourcing arrangements, buyers often assume they own the design or have rights to modify and service the equipment. However, without a clear agreement, the supplier may retain full IP rights, limiting your ability to switch manufacturers or make future improvements. Always secure written IP transfer or licensing agreements.
Limited After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Low-cost suppliers may offer attractive upfront pricing but lack reliable technical support, training, or spare parts inventories. This can lead to extended downtime and higher total cost of ownership. Evaluate the supplier’s service network and request a list of available spare parts and support response times.
Misrepresentation of Manufacturing Capabilities
Some suppliers claim in-house production but actually outsource to unvetted subcontractors, leading to inconsistent quality. Conduct on-site audits or require third-party factory assessments to verify actual production processes and quality control systems.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence, clear contractual terms, and proactive quality and IP management throughout the sourcing process.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Waste Compactor
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, installation, operation, and maintenance of a waste compactor. Adhering to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, operational safety, and environmental protection.
Regulatory Compliance
Environmental Regulations
Waste compactors must comply with local, state, and federal environmental laws. Key regulations include:
– Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) – Governs hazardous waste management if applicable. Ensure waste streams processed do not include regulated hazardous materials unless permitted.
– Clean Air Act (CAA) – Compactors that generate dust or emissions may require air quality permits. Use dust suppression systems if needed.
– Clean Water Act (CWA) – Prevent wastewater or leachate from compactors from entering storm drains or waterways. Use containment trays and proper drainage controls.
Local Permits and Zoning
- Obtain required permits from municipal authorities prior to installation.
- Verify zoning regulations allow for waste compaction equipment at the selected site.
- Comply with noise ordinances, especially in residential or mixed-use areas.
Occupational Safety and Health Standards
- Adhere to OSHA regulations for machine guarding, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and worker training.
- Ensure emergency stop mechanisms are accessible and functional.
- Provide personal protective equipment (PPE) for operators.
Transportation and Logistics
Pre-Shipment Preparation
- Confirm compactor dimensions, weight, and power requirements.
- Verify site accessibility (doorways, elevators, pathways) for delivery and installation.
- Coordinate with the supplier for delivery scheduling and site readiness.
Shipping Requirements
- Use certified freight carriers experienced in handling heavy machinery.
- Secure the compactor on flatbed trucks or in containers using chains, straps, and blocking.
- Label cargo with “Heavy,” “This Side Up,” and “Fragile” as appropriate.
On-Site Handling
- Use appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts, cranes) with adequate load capacity.
- Designate a clear path from delivery point to installation site.
- Inspect the unit upon arrival for transit damage; document and report issues immediately.
Installation and Placement
Site Requirements
- Install on a structurally sound, level surface capable of supporting the unit’s weight (including full load).
- Ensure adequate clearance around the compactor for operation, maintenance, and ventilation.
- Install near waste sources to minimize manual transport.
Utility Connections
- Provide correct electrical supply (voltage, phase, amperage) as specified by the manufacturer.
- If hydraulic or water-cooled, ensure proper fluid lines and drainage are in place.
- Ground the unit properly to prevent electrical hazards.
Operational Compliance
Waste Stream Management
- Only compact non-hazardous, non-regulated waste unless specifically permitted.
- Prohibit disposal of prohibited items (e.g., batteries, chemicals, medical waste).
- Label compactor clearly with acceptable and prohibited materials.
Recordkeeping
- Maintain logs of waste volume, compaction frequency, and maintenance.
- Retain manifests if waste is transported off-site by licensed haulers.
- Keep copies of permits, inspections, and training records for at least three years.
Maintenance and Decommissioning
Routine Maintenance
- Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules.
- Inspect hydraulic systems, rams, doors, and safety features regularly.
- Clean compactor and containment area to prevent pest infestations and odor.
Decommissioning and Disposal
- Decontaminate the unit before removal or disposal.
- Recycle metal components where possible.
- Dispose of hydraulic fluids and other waste materials according to hazardous waste rules if applicable.
Training and Documentation
Operator Training
- Train all operators on safe use, emergency procedures, and compliance requirements.
- Document training sessions and maintain personnel records.
- Conduct periodic refresher training.
Compliance Audits
- Perform internal audits annually to ensure adherence to regulations.
- Address deficiencies promptly and update procedures as needed.
- Retain audit reports for regulatory review.
Emergency Procedures
Spill or Leak Response
- Equip the area with spill kits and absorbents for fluid leaks.
- Train staff on spill containment and reporting protocols.
- Report significant spills to environmental authorities per local requirements.
Equipment Malfunction
- Immediately cease operation if safety systems fail or unusual noises occur.
- Follow LOTO procedures before inspection or repair.
- Contact qualified technicians for service.
By following this guide, organizations can ensure the safe, legal, and efficient use of waste compactors while minimizing environmental impact and regulatory risk.
Conclusion:
After a thorough evaluation of available options, sourcing a waste compactor presents a strategic and sustainable solution for efficient waste management. The decision to invest in a waste compactor not only reduces waste volume, lowering disposal frequency and associated transportation costs, but also contributes to improved site hygiene, safety, and environmental stewardship. By selecting a compactor that aligns with operational needs—considering capacity, power source, maintenance requirements, and vendor reliability—the organization can achieve long-term cost savings and demonstrate a commitment to environmental responsibility. Ultimately, sourcing the right waste compactor enhances operational efficiency and supports broader sustainability goals, making it a worthwhile investment for any forward-thinking facility.