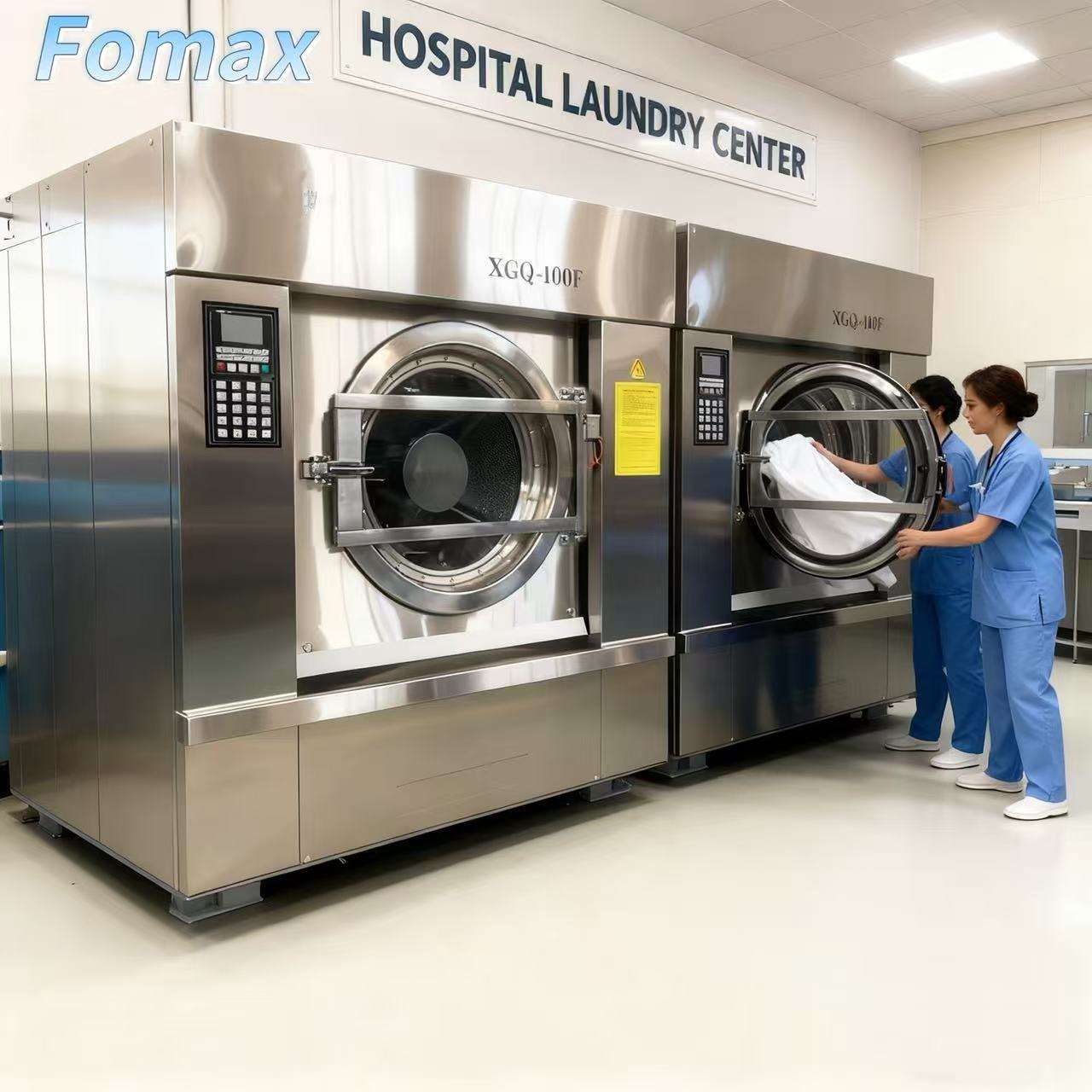
The global washing machine motor market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for energy-efficient and smart home appliances. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the washing machine market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, with motor technology advancements playing a pivotal role in this expansion. As consumers shift toward front-loading and fully automatic models—known for higher performance and lower energy consumption—original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) are increasingly sourcing advanced motors such as brushless DC (BLDC) and direct drive systems. This evolution has intensified competition among motor suppliers, placing innovation, reliability, and efficiency at the forefront. In response to these industry trends, the following list highlights the top 9 washing machine motor manufacturers shaping the future of laundry technology across global supply chains.
Top 9 Washing Machine Motors Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
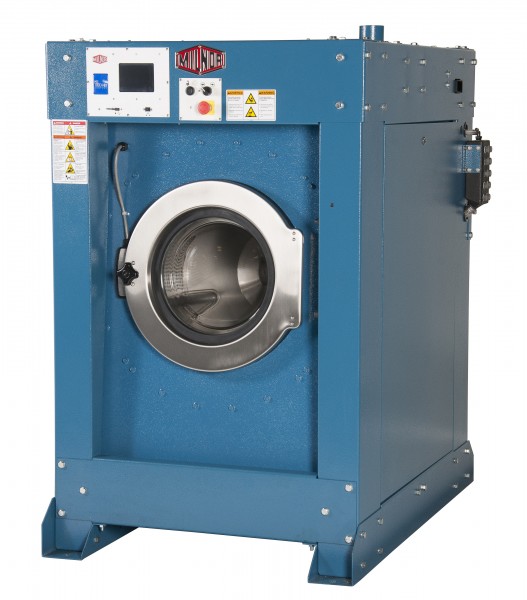
#1 Pellerin Milnor Corporation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: milnor.com
Key Highlights: Pellerin Milnor Corporation is a leading commercial and industrial laundry equipment manufacturer. Our products are designed and tested with the customer in ……
#2 NIDEC MOTOR CORPORATION
Domain Est. 1997
Website: nidec.com
Key Highlights: NIDEC MOTOR is a manufacturer of motors and control equipment for home appliances, industrial use, and consumer use….
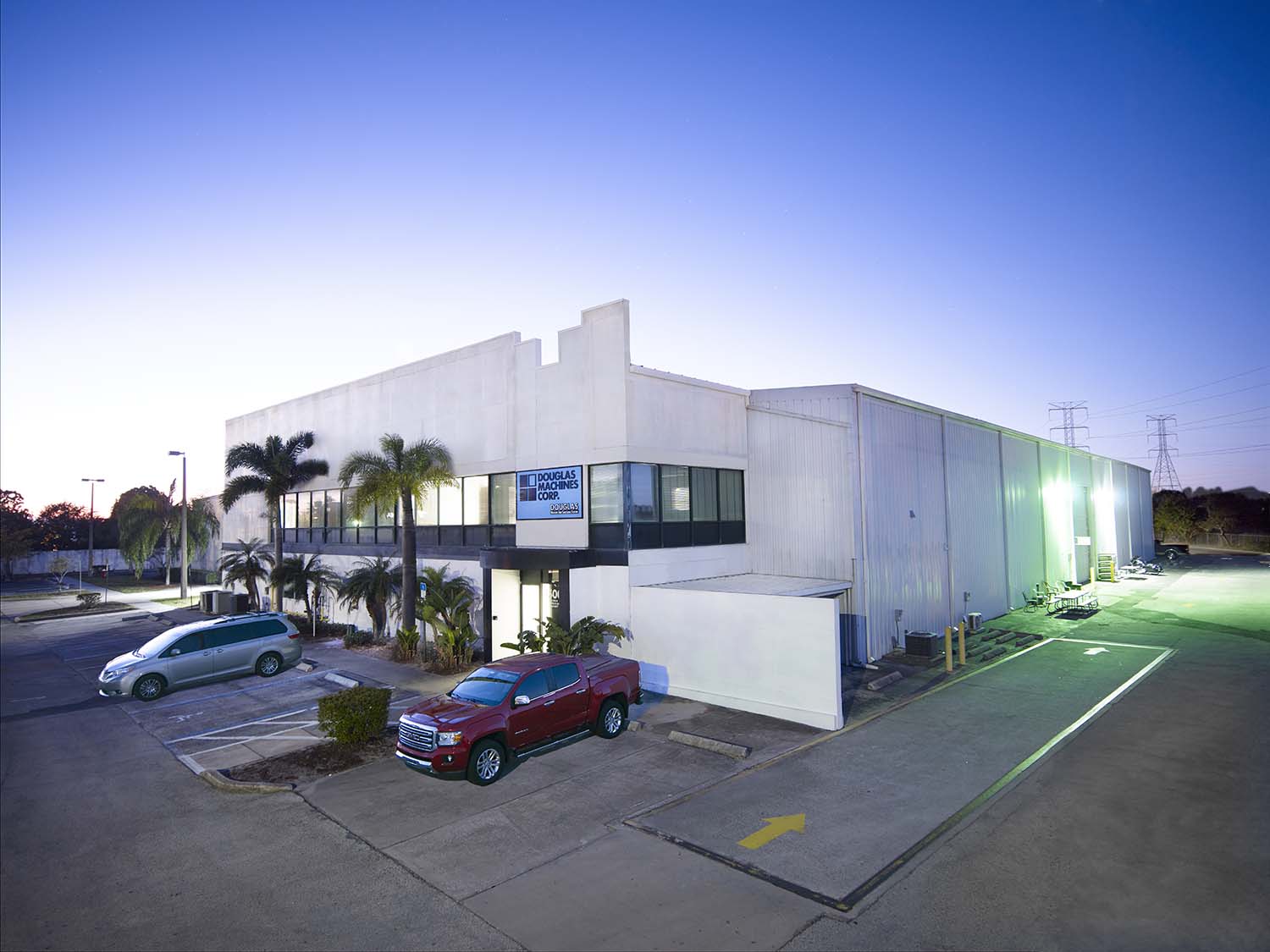
#3 Douglas Machines Corp.
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1979
Website: dougmac.com
Key Highlights: Since 1979, Douglas Machines Corp. has been a specialist in the design and manufacture of automated washing and sanitizing equipment….
#4 Girbau
Domain Est. 1997
Website: girbau.com
Key Highlights: Girbau offers the most comprehensive line of commercial, industrial and vended laundry products in the world. With a commitment to sustainability and innovation ……
#5 Industrial washers
Domain Est. 2007
Website: fivesgroup.com
Key Highlights: RoboWash is a high-precision industrial parts washer featuring a patented removable 6-axis robot and fully automated parts manipulation process….
#6 Washing and drying
Domain Est. 1999
Website: infineon.com
Key Highlights: Implement extremely power-efficient motor control for drums, heat pumps, or water pumps in washing machines or dryers with Infineon solutions….
#7 Welling Motor
Domain Est. 2008
Website: wellingmotor.com
Key Highlights: Welling has developed fixed-speed and variable-frequency products that meet the basic needs of household appliances in various regions around the world….
#8 Wolong
Domain Est. 2019
Website: wolong-electric.com
Key Highlights: Wolong mainly produces all kinds of motors, generators, drive controls, fans, transformers and other products, which are widely used in various industries such ……
#9 LEESON Brand
Domain Est. 2021
Website: regalrexnord.com
Key Highlights: The LEESON band spans thousands of alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) motors, gearmotors, washdown and variable-speed control solutions….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Washing Machine Motors

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Washing Machine Motors
The global washing machine motor market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, sustainability demands, and evolving consumer preferences. Several key trends are shaping the trajectory of motor technology in washing machines, with implications for manufacturers, suppliers, and end-users.
-
Shift Toward Brushless DC (BLDC) Motors
By 2026, BLDC motors are expected to dominate the washing machine motor landscape. Offering superior energy efficiency, quieter operation, and longer lifespan compared to traditional brushed motors, BLDC technology aligns with global energy efficiency regulations such as the EU’s Ecodesign Directive and ENERGY STAR standards. Demand is particularly strong in premium and smart washing machine segments, where performance and reliability are critical selling points. -
Integration with Smart and IoT-Enabled Appliances
As smart home ecosystems expand, washing machine motors are increasingly being integrated with IoT platforms. By 2026, motors will not only drive mechanical functions but also communicate with control systems for predictive maintenance, load optimization, and real-time diagnostics. Motor controllers equipped with sensors will enable adaptive speed and torque adjustments, improving wash efficiency and reducing wear and tear. -
Focus on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Environmental regulations and consumer eco-consciousness are accelerating the adoption of high-efficiency motors. Governments worldwide are tightening energy consumption standards, pushing manufacturers to adopt motors that reduce power usage. In response, motor producers are investing in advanced magnet materials (e.g., rare-earth magnets) and optimized electromagnetic designs to maximize efficiency while minimizing environmental impact. -
Miniaturization and Compact Motor Designs
Space-saving designs are becoming a priority, especially in urban markets with limited living space. Motor manufacturers are developing compact, high-torque motors that allow for slimmer and more versatile washing machine configurations—such as stackable or all-in-one washer-dryer units—without compromising performance. -
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific, led by China, India, and Southeast Asia, will remain the largest market for washing machine motors in 2026 due to rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and increasing penetration of home appliances. However, Europe and North America will lead in adopting premium motor technologies, driven by stricter regulations and higher demand for smart, energy-efficient appliances. -
Supply Chain Resilience and Localization
Geopolitical uncertainties and post-pandemic supply chain disruptions have prompted motor manufacturers to diversify production and localize supply chains. By 2026, increased regional manufacturing—especially in India, Vietnam, and Eastern Europe—is expected to mitigate risks and reduce lead times, benefiting both OEMs and consumers. -
Rise of Direct Drive Motor Technology
Direct drive motors, which eliminate the need for belts and pulleys, are gaining traction for their durability, reduced noise, and improved energy efficiency. Brands like LG have popularized this technology, and by 2026, wider adoption across mid-tier models is anticipated as production costs decline and manufacturing scales up.
In conclusion, the 2026 washing machine motor market will be defined by innovation in efficiency, intelligence, and sustainability. Companies that invest in advanced motor technologies, adapt to regulatory landscapes, and respond to regional consumer needs will be best positioned to capture growth in this evolving sector.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Washing Machine Motors (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing washing machine motors involves navigating several critical challenges related to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) risks. Overlooking these pitfalls can lead to production delays, legal disputes, increased costs, and damage to brand reputation.
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Performance
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing washing machine motors—especially from low-cost regions—is inconsistent quality. Suppliers may offer attractive pricing but lack robust quality assurance systems. This can result in motors with substandard materials, imprecise manufacturing tolerances, or inadequate testing, leading to higher failure rates, reduced efficiency, and increased warranty claims. Without proper audits and performance validation, buyers risk integrating unreliable components that compromise the overall appliance.
Lack of IP Due Diligence and Risk of Infringement
Many motor suppliers, particularly in competitive manufacturing hubs, may produce designs that closely mimic patented technologies from established brands. Purchasing such motors without thorough IP vetting exposes the buyer to legal liability for patent or design infringement. Even if unintentional, using a motor that violates existing IP can result in lawsuits, import bans, or forced product recalls—damaging both finances and market credibility.
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Reliable suppliers should provide comprehensive technical documentation, certifications (e.g., CE, UL, IP ratings), and traceability records. However, some vendors supply incomplete or falsified documentation, making it difficult to verify compliance with safety standards or environmental regulations. This lack of transparency complicates quality audits and increases the risk of non-compliant motors entering the supply chain.
Overlooking Long-Term Support and Scalability
Choosing a supplier based solely on initial cost often neglects long-term considerations. Some vendors may lack the capacity for consistent volume scaling or fail to provide technical support, spare parts, or firmware updates (in the case of smart or inverter motors). This can disrupt production and limit product lifecycle management, especially if the motor design requires future modifications.
Failure to Audit Manufacturing Facilities
Without on-site audits, buyers may not detect poor working conditions, outdated equipment, or non-compliant manufacturing processes. These factors directly affect motor quality and reliability. Additionally, unethical practices or lack of environmental compliance can pose reputational risks, especially for brands committed to sustainability and corporate responsibility.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, buyers should conduct rigorous supplier evaluations, insist on IP clearance documentation, perform independent quality testing, and establish long-term partnerships with transparent, certified manufacturers. Proactive due diligence in both quality and intellectual property safeguards ensures reliable performance and legal compliance in the final product.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Washing Machine Motors
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the international shipment and market entry of washing machine motors. Proper adherence ensures timely delivery, legal compliance, and avoidance of penalties.
Product Classification and Tariff Codes
Accurate classification under the Harmonized System (HS) is critical for customs clearance and duty assessment. Washing machine motors are typically classified under:
- HS Code 8501.10 or 8501.31: Depending on motor type (e.g., single-phase AC motors commonly used in household appliances).
- Additional Country-Specific Codes: Many countries require national subheadings (e.g., HTS in the U.S., TARIC in the EU). Verify destination-specific codes to ensure correct duty rates and eligibility for trade agreements.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Washing machine motors must meet technical and safety standards in the destination market:
- Electrical Safety Standards:
- IEC 60335-1 (General safety for household appliances) and IEC 60335-2-7 (Particular requirements for washing machines).
- Regional certifications: UL (U.S.), CE (EU), PSE (Japan), CCC (China).
- EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility): Compliance with directives such as EU EMC Directive 2014/30/EU or FCC Part 15 (U.S.) to prevent interference.
- RoHS and REACH (EU): Restriction of hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) and chemical registration requirements.
- Energy Efficiency: Some markets may impose efficiency standards under MEPS (Minimum Energy Performance Standards) or eco-design regulations.
Packaging and Labeling Standards
Proper packaging ensures product protection during transit and compliance with labeling laws:
- Packaging: Use anti-static, moisture-resistant materials; secure motors to prevent movement in transit. Include protective foam or dividers for bulk shipments.
- Labeling Requirements:
- Clearly display voltage, frequency, power rating, model number, and manufacturer details.
- Include compliance marks (e.g., CE, EAC, CCC) as required by destination country.
- Barcodes and shipping labels must conform to carrier and customs requirements (e.g., GS1 standards).
Export Documentation
Complete and accurate documentation is essential for customs clearance:
- Commercial Invoice: Must include detailed product description, HS code, value, currency, and Incoterms® (e.g., FOB, EXW).
- Packing List: Itemize contents per package, weight, dimensions, and net/gross weights.
- Certificate of Origin: Required for tariff preferences under trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, RCEP).
- Test Reports and Certificates: Provide copies of safety, EMC, and RoHS compliance documentation.
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill: Legal receipt and contract of carriage; ensure accuracy of consignee and notify party details.
Transportation and Handling
Choose appropriate logistics modes based on volume, urgency, and cost:
- Sea Freight: Ideal for large-volume shipments; use dry containers. Consider container load (FCL) or shared (LCL).
- Air Freight: Faster but more expensive; suitable for urgent or high-value consignments.
- Inland Transport: Use enclosed trucks with shock-absorbing suspension; avoid exposure to extreme temperatures or humidity.
- Handling Precautions: Label packages as “Fragile” and “This Side Up”; avoid stacking heavy items on motor cartons.
Import Regulations by Key Markets
Different regions have specific import requirements:
- European Union: CE marking mandatory; declaration of conformity required. Notify customs via the Import Control System (ICS2).
- United States: Comply with UL standards; file entry through ACE (Automated Commercial Environment). FCC certification may be required.
- China: Obtain CCC certification before import; provide Chinese-language labeling.
- India: BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards) certification may apply; customs requires detailed documentation including import licenses if applicable.
Environmental and Disposal Regulations
Ensure end-of-life compliance:
- WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment): In the EU, producers may be responsible for take-back and recycling.
- Battery and Motor Disposal: Motors may contain materials requiring special handling; comply with local e-waste laws.
Risk Mitigation and Best Practices
- Partner with Certified Suppliers: Ensure all components meet international standards.
- Conduct Pre-Shipment Audits: Verify compliance, packaging, and documentation accuracy.
- Use Licensed Customs Brokers: Engage professionals familiar with appliance motor regulations in target markets.
- Maintain Compliance Records: Retain test reports, certifications, and shipping documents for at least 5–10 years, depending on jurisdiction.
Adhering to this guide ensures smooth logistics operations and regulatory compliance for washing machine motors across global markets.
Conclusion: Sourcing Washing Machine Motors
In conclusion, sourcing washing machine motors requires a strategic approach that balances cost, quality, reliability, and compatibility with the intended application. Whether for replacement parts, appliance manufacturing, or repurposing in DIY and industrial projects, selecting the right motor involves evaluating key factors such as motor type (e.g., induction, direct drive, or brushless DC), power rating, efficiency, durability, and supplier credibility.
Sourcing from reputable manufacturers or authorized distributors ensures compliance with industry standards and provides access to technical support and warranties. Additionally, considering emerging trends—such as the shift toward energy-efficient and smart appliance technologies—can future-proof procurement decisions. Global sourcing offers cost advantages but must be weighed against logistics, lead times, and potential quality risks.
Ultimately, a well-informed sourcing strategy, supported by thorough market research and supplier vetting, enables reliable supply chains and optimal performance of washing machine systems. As the demand for sustainable and high-efficiency appliances grows, strategic motor sourcing will continue to play a critical role in driving innovation and competitiveness in the home appliance industry.