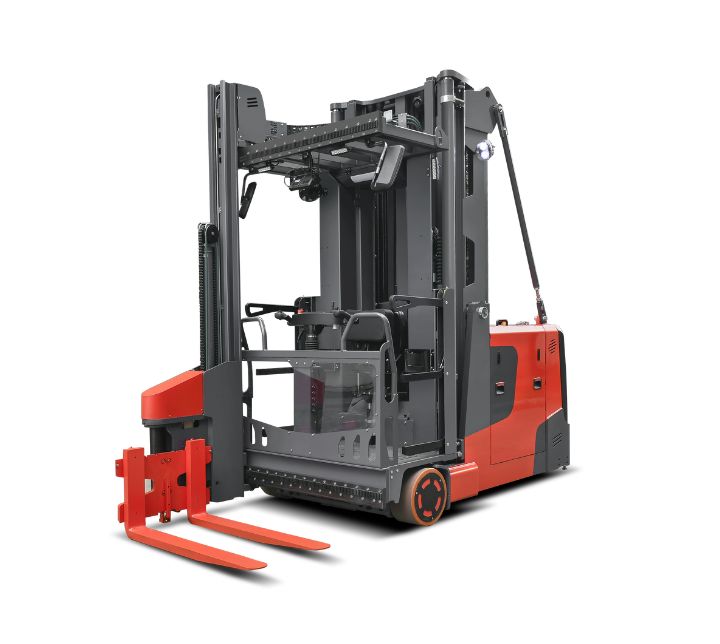
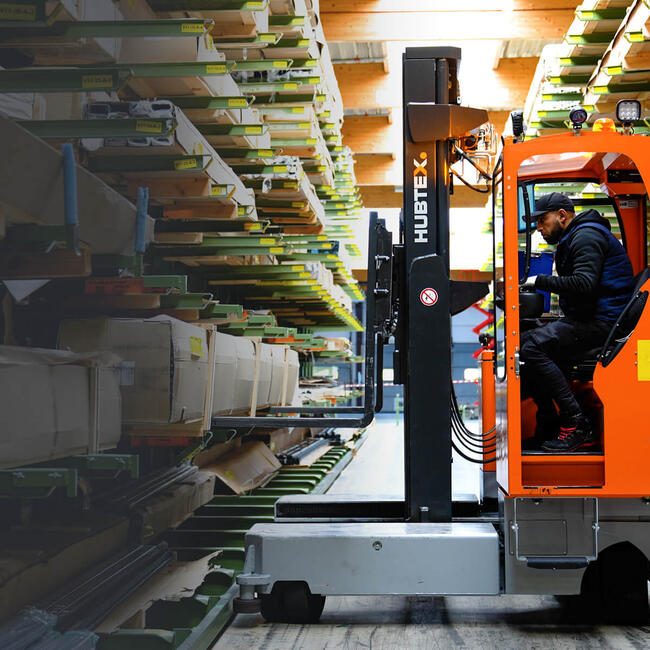
The global very narrow aisle (VNA) forklift market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for high-density warehousing solutions and rising investment in material handling automation. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global forklift trucks market—of which VNA forklifts are a critical segment—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028. The expansion of e-commerce, coupled with limited real estate in urban logistics hubs, is pushing warehouses to maximize vertical storage capacity, making VNA forklifts a strategic asset. These specialized trucks allow aisles as narrow as 1.6 meters, significantly improving space utilization by up to 35% compared to conventional forklifts. With the global VNA forklift segment gaining traction across distribution centers, cold storage facilities, and manufacturing plants, leading manufacturers are intensifying innovation in mast design, guidance systems, and energy efficiency. Based on market presence, technological advancement, and global footprint, the following eight companies stand out as the top manufacturers in the very narrow aisle forklift space.
Top 8 Very Narrow Aisle Forklift Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
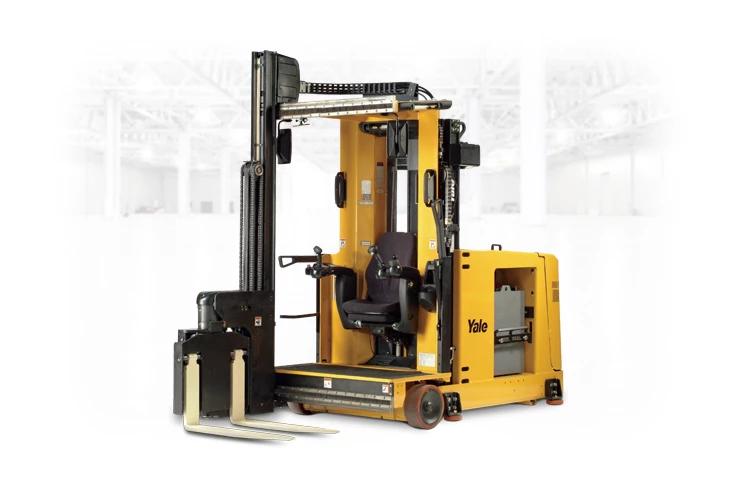
#1 Yale Lift Truck Technologies
Domain Est. 1994
Website: yale.com
Key Highlights: Yale’s forklifts and lift trucks are designed to tackle your biggest challenges. Discover how our technology can boost your warehouse productivity!…
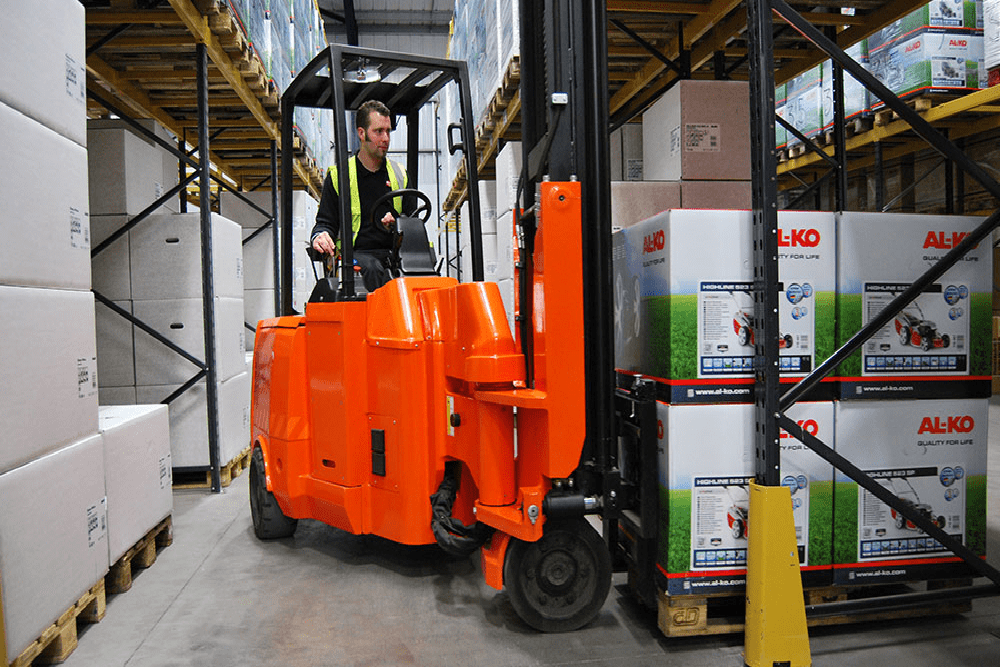
#2 Narrow Aisle Forklifts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: toyotaforklift.com
Key Highlights: Looking for the best forklift for narrow aisles and tight spaces? Toyota Forklift manufacturers multiple narrow aisle solutions for material…
#3 Very Narrow Aisle Forklifts
Domain Est. 1995
Website: raymondcorp.com
Key Highlights: Our trucks can operate in aisles that are less than half the width required by conventional forklifts, with a greater stack height capability….
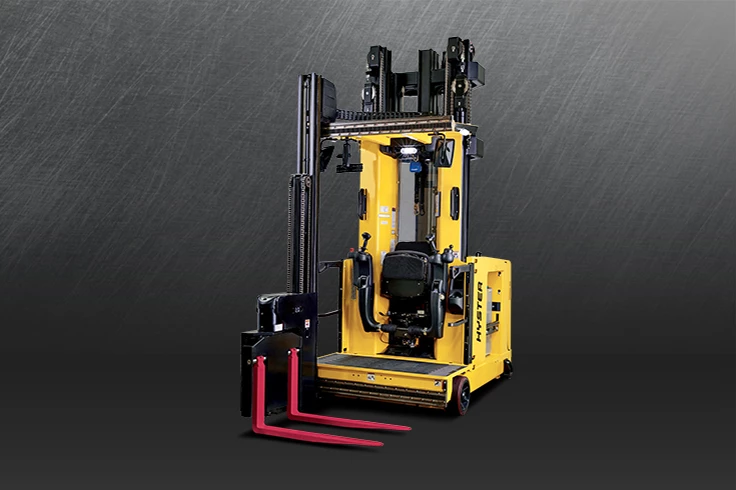
#4 Very Narrow Aisle Forklifts
Domain Est. 1996
Website: hyster.com
Key Highlights: Maximize your storage capacity with Hyster’s narrow aisle forklifts. Our turret forklifts are designed for precision and agility in narrow environments….
#5 Forklifts to Increase Warehouse Storage
Domain Est. 2000
Website: aisle-master.com
Key Highlights: With the ability to operate in very narrow aisles – as narrow as 1.6m – the Aisle-Master articulated forklift increases and maximises storage capacity….
#6 Very narrow aisle trucks
Domain Est. 2001
Website: linde-mh.com
Key Highlights: Very narrow aisle trucks from Linde enable with modern drives and assistance systems a high handling capacity in narrow aisles.» Find out more here!…
#7 Very Narrow Aisle Trucks
Domain Est. 2020
Website: toyotamaterialhandling-international.com
Key Highlights: The very narrow aisle (VNA) trucks come in man-up or man-down versions with fixed or articulated chassis to optimize your storage space….
#8 Bendi International Forklifts
Domain Est. 2023
Website: bendinarrowaisle.com
Key Highlights: Our innovative range of space-saving Forklifts and Warehousing Equipment are designed to give you up to 50% more storage capacity or floor space….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Very Narrow Aisle Forklift
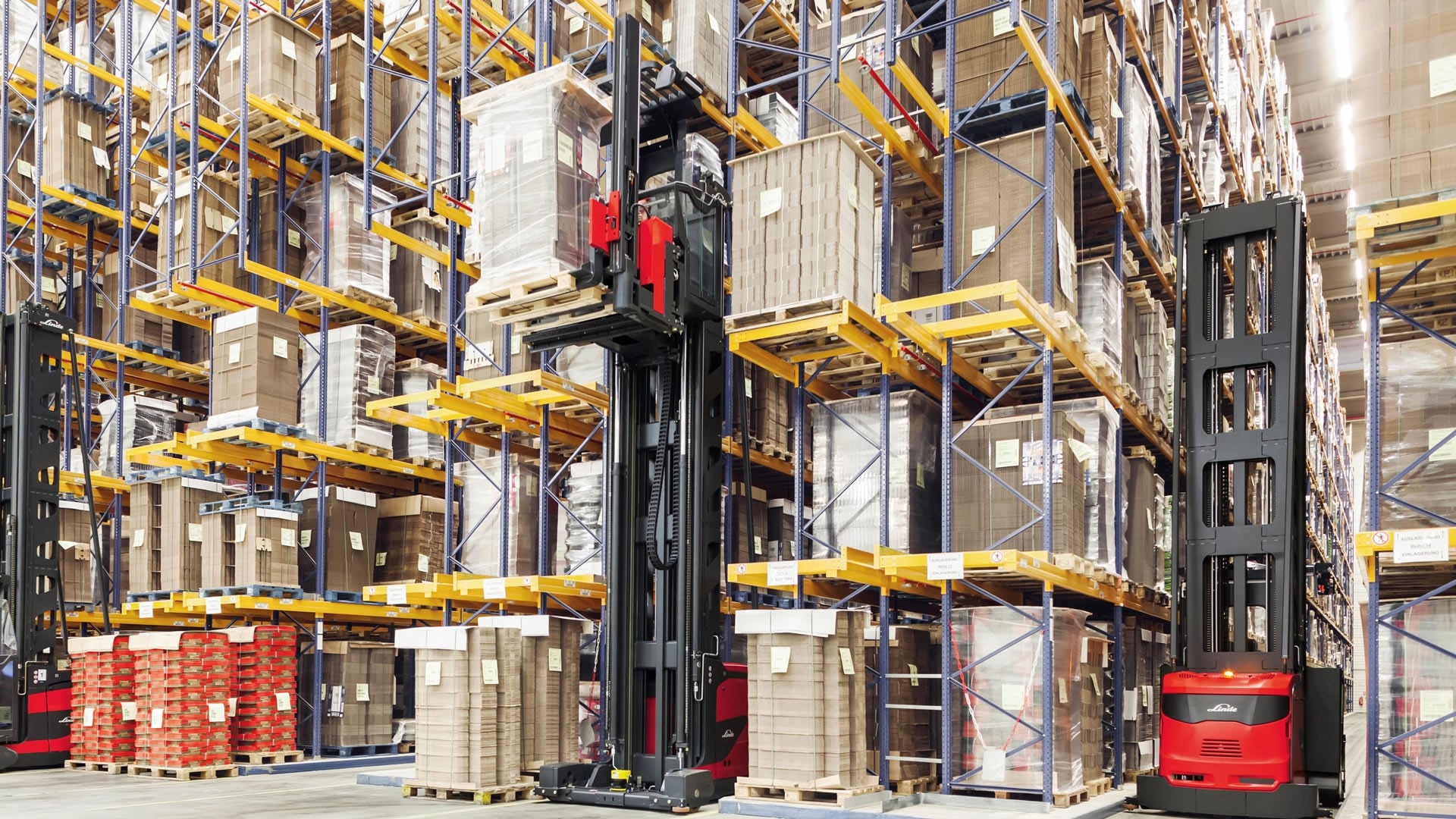

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Very Narrow Aisle (VNA) Forklifts
The global Very Narrow Aisle (VNA) forklift market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in automation, evolving warehouse logistics demands, and a growing emphasis on space optimization and operational efficiency. Key trends shaping the VNA forklift sector include:
-
Increased Adoption of Automation and Robotics
By 2026, the integration of automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) into VNA systems will accelerate. Fully automated VNA forklifts, capable of navigating narrow aisles without human intervention, are gaining traction in high-throughput distribution centers and cold storage facilities. This shift is fueled by labor shortages, rising labor costs, and the need for 24/7 operational capabilities. -
Growth in E-Commerce and Omnichannel Fulfillment
The continued expansion of e-commerce is pushing warehouses to maximize storage density. VNA forklifts, which enable aisle widths as narrow as 1.6 meters, allow for higher rack density and improved inventory turnover. By 2026, demand for VNA equipment will rise in last-mile fulfillment centers and urban logistics hubs where space is at a premium. -
Electrification and Sustainable Operations
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are driving the shift from internal combustion (IC) engines to electric VNA forklifts. Lithium-ion battery technology, with its fast charging, longer lifespan, and minimal maintenance, is becoming the preferred power source. By 2026, a majority of new VNA forklifts sold are expected to be lithium-powered, especially in Europe and North America. -
Integration with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and IoT
Smart VNA forklifts equipped with IoT sensors and real-time data connectivity are enabling predictive maintenance, enhanced fleet management, and improved safety monitoring. Integration with WMS and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems allows for seamless inventory tracking and optimized material flow, a trend that will be standard in mid-to-large scale operations by 2026. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
While North America and Europe remain dominant markets, rapid industrialization and modernization of logistics infrastructure in Asia-Pacific (particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia) will contribute to robust growth in VNA forklift adoption. Governments’ investments in smart warehousing and cold chain logistics are creating new opportunities. -
Focus on Operator Safety and Ergonomics
With increasing regulatory scrutiny and emphasis on workplace safety, manufacturers are enhancing VNA forklift designs with features such as stability control systems, advanced mast cameras, and ergonomic operator cabins. These improvements reduce accident risks and operator fatigue, especially during high-level order picking. -
Rise of Leasing and Fleet-as-a-Service Models
To reduce capital expenditure and adapt to fluctuating demand, more companies are turning to leasing and managed fleet services. By 2026, flexible ownership models will become mainstream, particularly among third-party logistics (3PL) providers and seasonal retailers.
In summary, the 2026 VNA forklift market will be characterized by technological sophistication, sustainability, and integration with digital supply chains. As warehouses evolve into smarter, denser, and more automated environments, VNA forklifts will play a critical role in enabling efficient, high-density material handling.
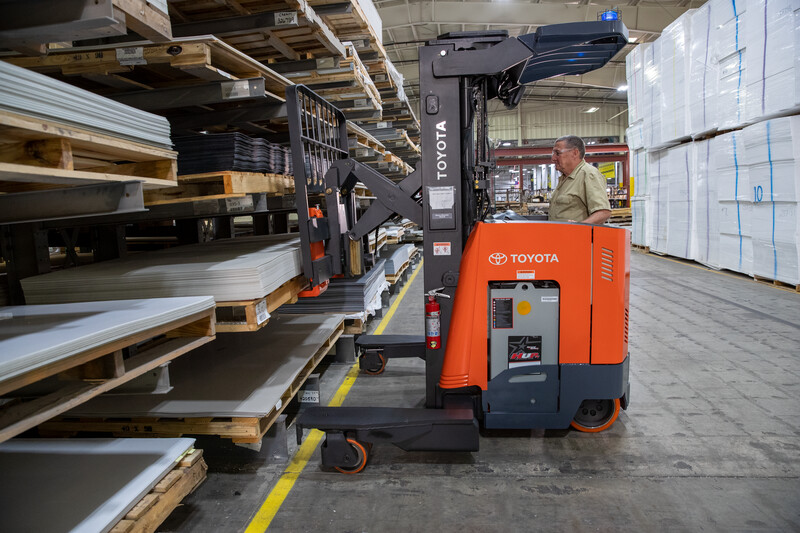

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Very Narrow Aisle (VNA) Forklifts
Sourcing Very Narrow Aisle (VNA) forklifts requires careful consideration due to their specialized nature and high operational demands. Overlooking key aspects can lead to poor performance, safety issues, and increased total cost of ownership. Below are common pitfalls to avoid, particularly around quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns.
Poor Build Quality and Reliability
One of the most significant risks when sourcing VNA forklifts—especially from lesser-known or low-cost manufacturers—is compromising on build quality. VNA trucks operate in tight spaces at considerable heights, placing high stress on components. Poorly manufactured masts, guide systems, or drive trains can result in frequent breakdowns, increased maintenance costs, and safety hazards. Look for proven track records, certifications (e.g., ISO standards), and third-party validation of durability.
Inadequate Safety Features and Compliance
VNA forklifts require advanced safety systems such as mast stabilizers, overhead guards, and automated speed control in narrow aisles. Sourcing models that lack compliance with regional safety standards (e.g., OSHA in the U.S. or CE in Europe) can expose operations to regulatory penalties and accidents. Always verify that the equipment meets local safety and operational regulations before procurement.
Substandard or Proprietary Software and Controls
Many modern VNA forklifts rely on proprietary control systems for stability, guidance, and fleet management. Sourcing trucks with poorly designed or closed software can limit integration with warehouse management systems (WMS), hinder performance monitoring, and reduce operational flexibility. Be cautious of suppliers that do not allow access to diagnostic data or API integration, as this can create long-term dependency and maintenance challenges.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risks in Technology and Design
When considering non-OEM or copycat VNA forklifts, there is a risk of inadvertently sourcing equipment that infringes on patented technologies—such as rail guidance systems, mast designs, or battery management systems. Using such equipment may expose your organization to legal liability, especially in regions with strict IP enforcement. Always source from reputable manufacturers with transparent IP practices and avoid suppliers offering “equivalent” models at suspiciously low prices.
Limited After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
VNA forklifts require specialized parts and trained technicians for maintenance. Choosing a supplier without a robust service network can result in extended downtime. Additionally, some low-cost manufacturers may not honor warranties or may discontinue parts support, especially if they are using copied or reverse-engineered designs with no long-term sustainability.
Lack of Customization and Scalability
VNA applications often require specific configurations based on warehouse layout, lift height, and load capacity. Sourcing from suppliers with limited engineering support may result in a one-size-fits-all solution that doesn’t optimize your operations. Ensure the supplier can tailor the forklift to your exact needs and scale support as your operation grows.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence, supplier vetting, and a focus on total cost of ownership—not just upfront price. Prioritize quality, compliance, and IP integrity to ensure safe, efficient, and sustainable VNA operations.
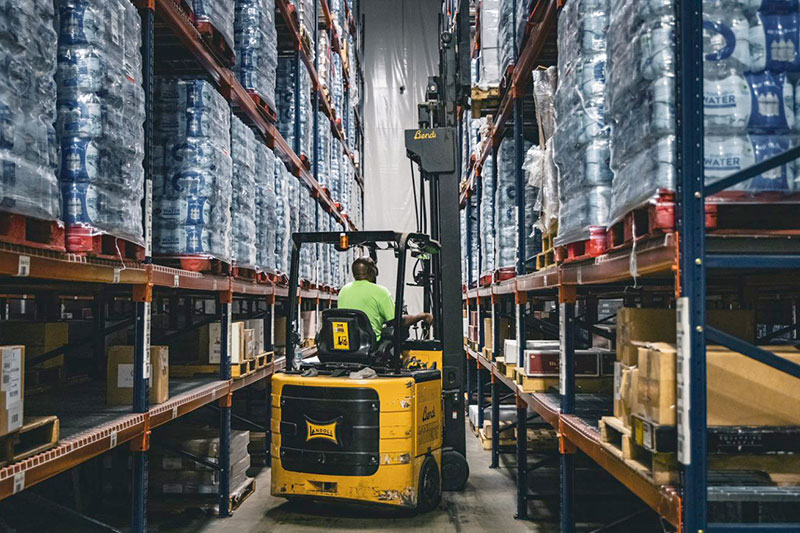

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Very Narrow Aisle (VNA) Forklifts
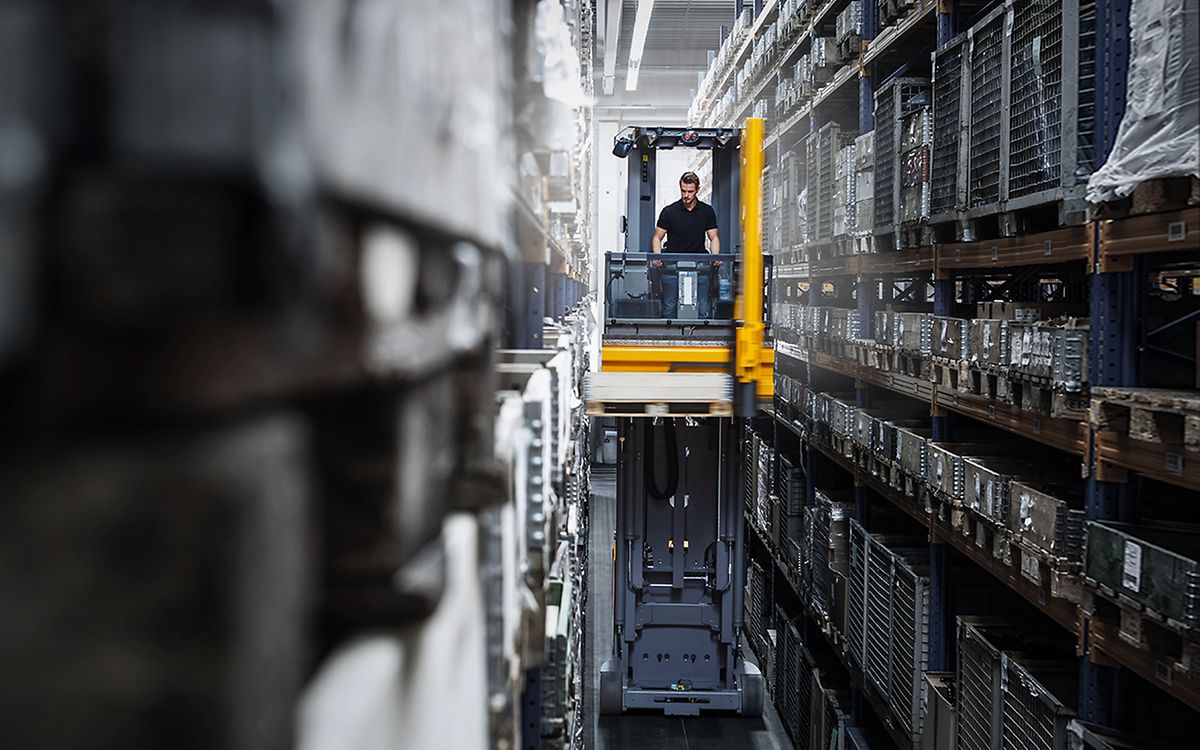
Very Narrow Aisle (VNA) forklifts are specialized industrial trucks designed to operate in tightly spaced warehouse environments, maximizing storage density and operational efficiency. However, their unique design and operating requirements demand strict adherence to logistics best practices and regulatory compliance to ensure safety, productivity, and legal conformity.
Operational Requirements and Facility Design
VNA forklifts require a highly controlled warehouse environment. Racking systems must be engineered to accommodate VNA operations, typically featuring guide rails or wire guidance systems along aisle floors or ceilings to stabilize the forklift during high-lift maneuvers. Aisles are generally between 1.6 to 2.0 meters wide—significantly narrower than those for conventional forklifts. Floor flatness and levelness (measured as FF/FL) must meet stringent standards (e.g., FF 100+/FL 50+) to prevent instability. Additionally, clear overhead clearance is essential to avoid collisions during mast elevation.
Operator Training and Certification
Only trained and certified operators should operate VNA forklifts. Training must go beyond standard forklift certification and include model-specific instruction on stabilization systems, height operation protocols, and navigation in confined spaces. Certification must comply with OSHA 29 CFR 1910.178 in the United States or equivalent national regulations (e.g., PUWER in the UK, CSA B335 in Canada). Refresher training is required at least every three years or following any incident or observed unsafe behavior.
Safety Protocols and Risk Mitigation
Safety is paramount when operating VNA forklifts due to their height and narrow operating space. Key protocols include:
– Mandatory use of seatbelts and fall protection systems when lifting beyond safe operator zones.
– Installation of proximity sensors, overhead obstruction detection, and collision avoidance technology.
– Strict enforcement of pedestrian-free zones in VNA aisles; use of barriers and signage to restrict access.
– Pre-shift inspection of tires, masts, guide systems, and safety devices.
– Prohibition of unauthorized modifications or overrides of safety systems.
Maintenance and Equipment Compliance
Regular preventive maintenance is critical to ensure reliability and safety. Maintenance schedules must follow manufacturer guidelines and include checks on:
– Rail guidance systems (if used)
– Mast alignment and chain tension
– Battery charging and cooling systems (for electric models)
– Hydraulic systems and brake performance
Maintenance records must be documented and retained as part of compliance audits. Equipment must meet ISO 22915-14 (load capacity testing for VNA trucks) and applicable regional standards such as ANSI/ITSDF B56.1 for safety requirements.
Load Handling and Stability
VNA forklifts have specific load capacity limits that vary with lift height and reach. Operators must consult load capacity charts affixed to each truck and never exceed rated capacities. Pallets must be in good condition and evenly loaded. Uneven or overhanging loads increase tipping risk. Operators must always travel with the load tilted slightly backward and at a safe speed, particularly when elevated.
Regulatory and Documentation Compliance
Facilities using VNA forklifts must maintain comprehensive documentation, including:
– Operator certification records
– Equipment inspection and maintenance logs
– Risk assessments and safety procedures
– Incident reports and corrective actions
Regular internal audits should verify compliance with OSHA, ANSI, ISO, and local occupational health and safety regulations. Third-party inspections may be required for insurance or certification purposes.
Integration with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
For optimal logistics performance, VNA forklifts should integrate with the warehouse management system. This enables real-time tracking of inventory movements, task assignment, and route optimization. Some VNA models support wireless communication and telemetry, allowing remote monitoring of usage, performance, and maintenance alerts—enhancing both efficiency and compliance.
By adhering to this logistics and compliance framework, organizations can safely and efficiently leverage the space-saving advantages of Very Narrow Aisle forklifts while maintaining full regulatory compliance and minimizing operational risks.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Very Narrow Aisle (VNA) Forklift
Sourcing a Very Narrow Aisle (VNA) forklift is a strategic investment that can significantly enhance warehouse efficiency, maximize storage capacity, and optimize operational workflow. By enabling access to racking systems in aisles as narrow as 1.6 to 2.0 meters, VNA forklifts allow for higher-density storage, reducing overall facility footprint and associated costs. When selecting a VNA forklift, key considerations include mast height, lift capacity, maneuverability, operator comfort, and integration with existing racking systems and warehouse management systems (WMS).
Additionally, factors such as maintenance requirements, energy efficiency (electric vs. alternative power sources), and supplier support play a critical role in long-term performance and total cost of ownership. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who offer robust after-sales service, training, and spare parts availability.
Ultimately, the successful sourcing of a VNA forklift requires a thorough evaluation of operational needs, site conditions, and future scalability. When implemented correctly, VNA forklifts offer a compelling return on investment through improved space utilization, faster order fulfillment, and enhanced operational safety—making them an ideal solution for modern, high-density warehousing environments.