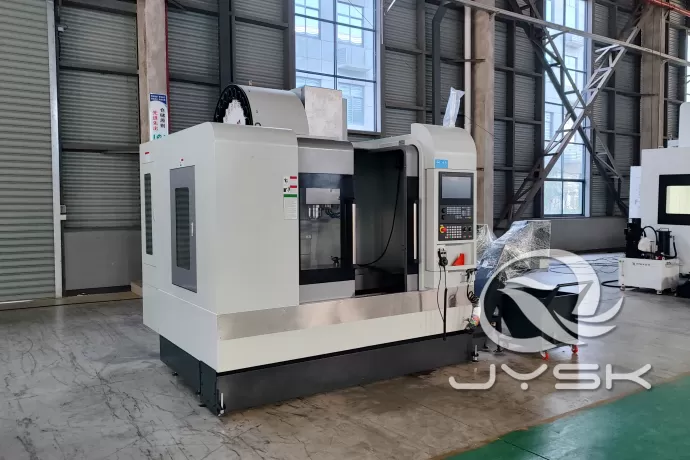
The global vertical milling center market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand for precision machining across aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the CNC machine tools market—of which vertical milling centers are a critical segment—is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 7.5% from 2023 to 2028. Similarly, Grand View Research estimates that the global CNC machine market size was valued at USD 76.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.8% through 2030, fueled by advancements in automation and the rising adoption of smart manufacturing technologies. As industries prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and integration with Industry 4.0 systems, leading manufacturers of vertical milling centers are innovating rapidly to meet evolving production demands. In this competitive landscape, ten companies have emerged as key players, combining technological excellence, global reach, and high-performance engineering to lead the market.
Top 10 Vertical Milling Center Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
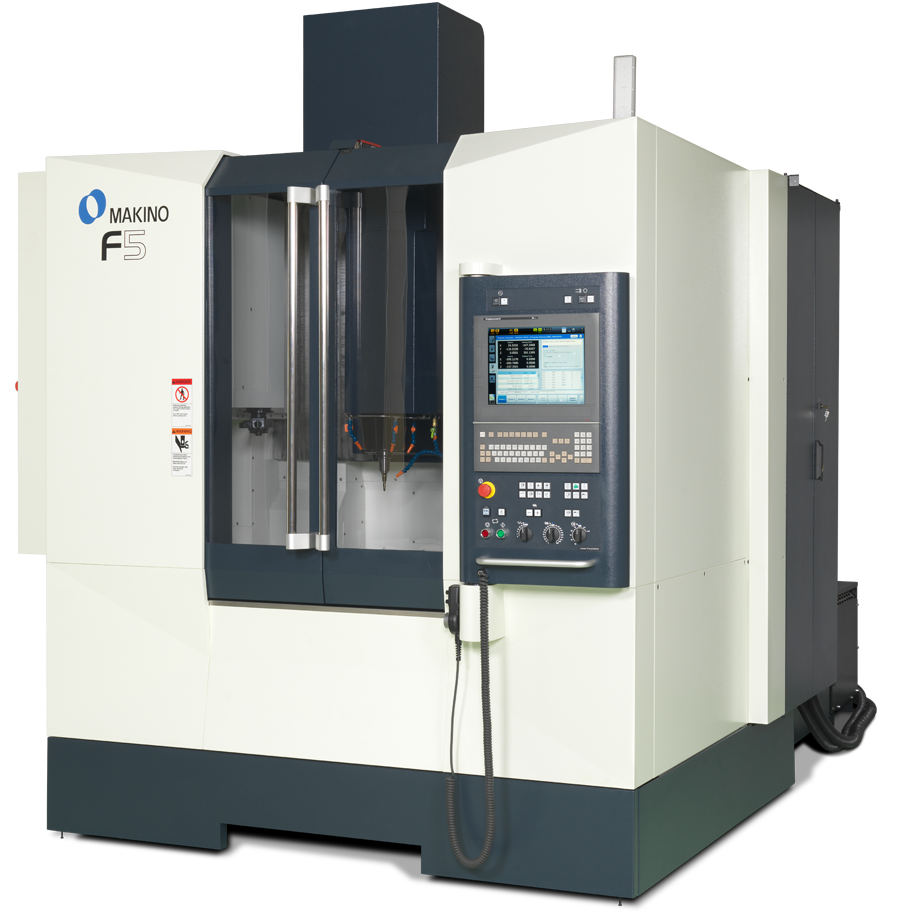
#1 Makino
Domain Est. 1996
Website: makino.com
Key Highlights: Achieve superior results with Makino’s CNC machining. Makino machines and engineering services provide precision and reliability across applications….
#2 Vertical Milling Machines
Domain Est. 1996
Website: haascnc.com
Key Highlights: Get a quick look at the complete vertical mill lineup Haas has to offer. Our vertical mills provide high performance machining for a magnitude of applications….
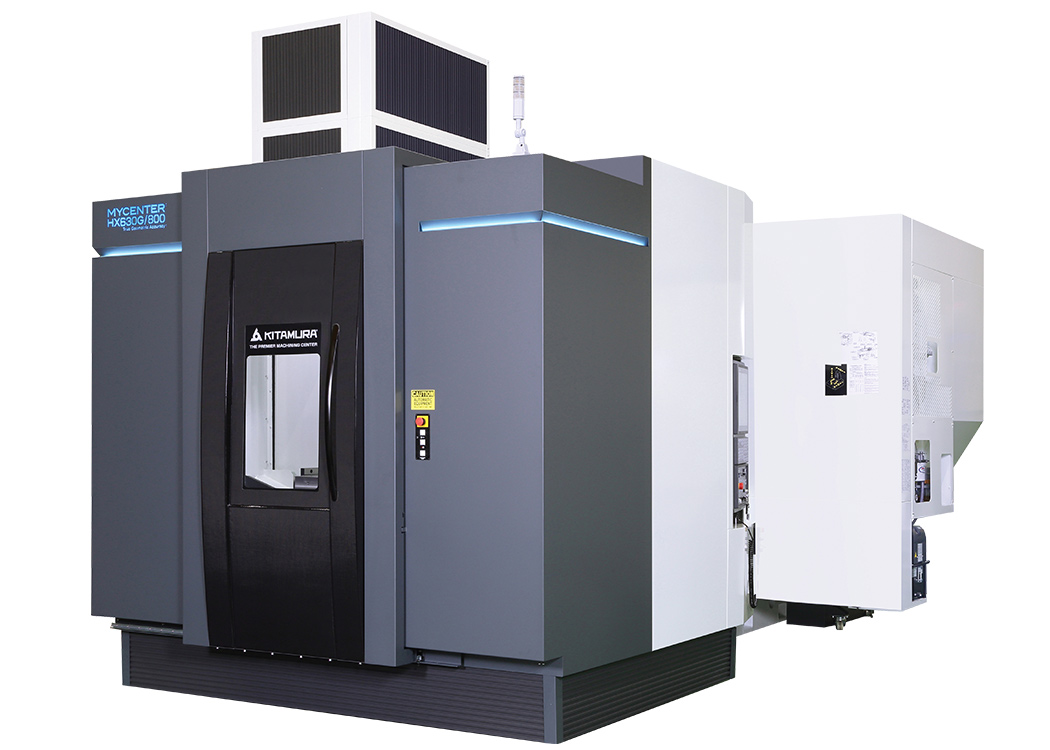
#3 Kitamura Machinery
Domain Est. 2000
Website: kitamura-machinery.com
Key Highlights: Innovating horizontal, vertical & 5-axis machining centers for manufacturers for over 90 years – Kitamura Machinery….
#4 YEONG CHIN MACHINERY INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.
Domain Est. 2005
Website: ycmcnc.com
Key Highlights: Products · Vertical Machining Center · Double Column Vertical Machining Center · Horizontal Machining Center · CNC Turning Center · 5-Axis Vertical Machining Center….
#5 Milltronics
Domain Est. 1995
Website: milltronics.com
Key Highlights: Milltronics offers 50 different models of CNC milling and CNC turning machines for toolroom and production environments….
#6 CNC Machining Centers
Domain Est. 1996
Website: okuma.com
Key Highlights: we offer more than 35 horizontal, vertical, and 5-axis configurations. Many in this product line — which is one of the most extensive in the industry — are ……
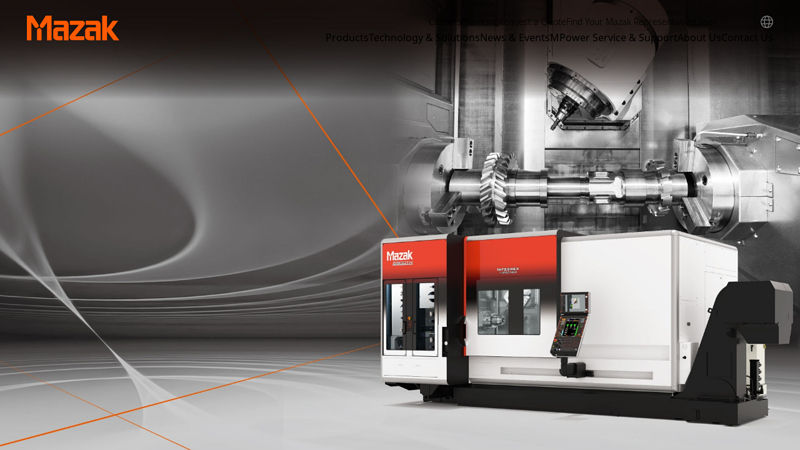
#7 to Mazak Corporation
Domain Est. 1998
Website: mazak.com
Key Highlights: Total Solution for Automation Systems. Automation systems for machining centers. Automation systems for turning centers. Build your Mazak Ez Machine….
#8 Bridgeport Machine Tools
Domain Est. 2005
Website: bridgeportmachinetools.com
Key Highlights: The New Bridgeport XR1000 Vertical Milling Center. The XR1000 VMC is designed to produce the most challenging parts in the tool industry and satisfies the most ……
#9 Vertical Milling
Domain Est. 2013
Website: us.dmgmori.com
Key Highlights: Overview of all Vertical CNC Milling Machines and Vertical CNC Milling Centers by DMG MORI. … Vertical Milling Machines for Quality-Oriented Manufacturing….
#10 DN Solutions
Domain Est. 2017
Website: dn-solutions.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to official website of DN Solutions! Here you can view our wide range of products from the very latest machines to our most popular models….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Vertical Milling Center
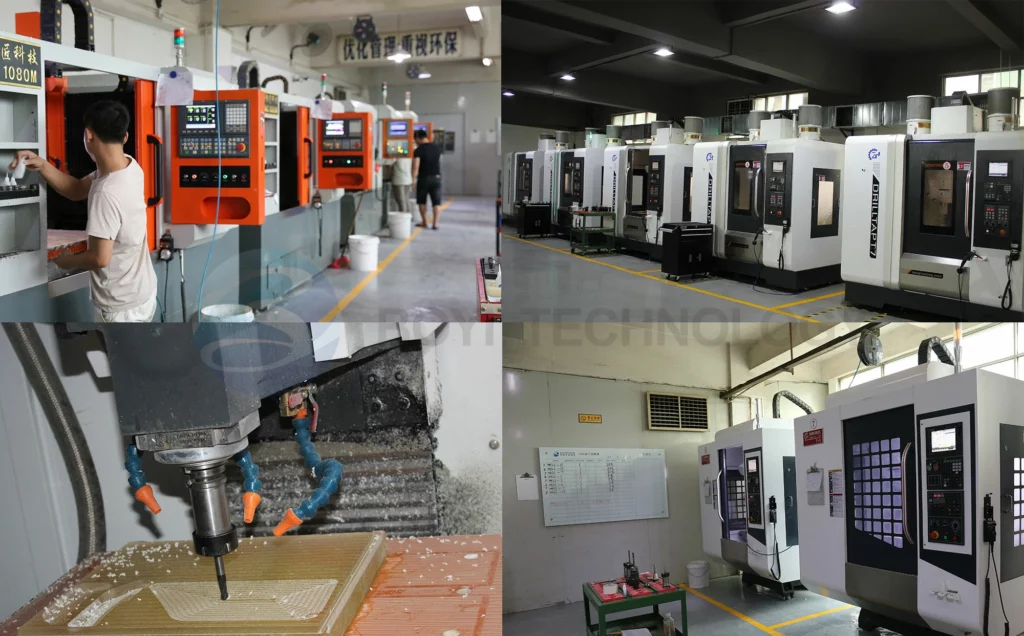

2026 Market Trends for Vertical Milling Centers
The global Vertical Milling Center (VMC) market is poised for significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, shifting industrial demands, and evolving manufacturing paradigms. Key trends shaping the landscape include:
Accelerated Adoption of Automation and Integration
VMCs are increasingly being deployed as core components of fully automated manufacturing cells. By 2026, seamless integration with robotic loading/unloading systems, automated tool changers (ATCs), and pallet changers will become standard, especially in high-volume production environments. This trend is fueled by the need to reduce labor dependency, improve uptime, and maintain consistent quality. Manufacturers are prioritizing VMCs with open communication protocols (e.g., MTConnect, OPC UA) to enable compatibility with factory-wide digital systems.
Rise of Smart Machining and Industry 4.0 Capabilities
Smart VMCs equipped with IoT sensors, predictive maintenance algorithms, and real-time monitoring will gain widespread traction. These machines collect operational data—such as spindle load, vibration, and thermal conditions—to optimize performance, prevent downtime, and extend tool life. Cloud-based analytics platforms will allow remote diagnostics and performance benchmarking. By 2026, VMCs with embedded AI for adaptive control and process optimization will transition from niche offerings to competitive differentiators.
Demand for High-Speed and High-Precision Machining
Industries such as aerospace, medical device manufacturing, and precision tooling are pushing the boundaries of machining performance. This drives demand for VMCs with higher spindle speeds (15,000+ RPM), improved axis rigidity, and advanced linear motor or direct-drive technologies. Enhanced thermal compensation systems and vibration damping will be critical to maintain micron-level accuracy during prolonged operations.
Growth in Hybrid and Multi-Tasking Machines
While traditional 3-axis VMCs remain prevalent, there is growing interest in 5-axis vertical machining centers and hybrid models that combine milling with turning or additive capabilities. These machines enable complex part production in fewer setups, reducing lead times and improving geometric accuracy. By 2026, affordable 5-axis VMCs with user-friendly controls will become accessible to small and medium enterprises (SMEs), broadening market reach.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Imperatives
Environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals are influencing VMC design. Machine tool builders are focusing on energy-efficient motors, regenerative braking systems, and reduced coolant consumption through Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) or air-cooled options. Additionally, modular designs that facilitate refurbishment and component reuse are gaining favor, aligning with circular economy principles.
Regional Market Dynamics and Supply Chain Resilience
Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, will remain the largest VMC market due to industrial expansion and government initiatives promoting advanced manufacturing. However, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions are prompting manufacturers in North America and Europe to reshore or nearshore production. This shift is increasing demand for domestic VMC suppliers and localized service networks, emphasizing machine reliability and ease of maintenance.
Expansion of Digital Twins and Simulation Tools
By 2026, digital twin technology will be integral to VMC deployment and optimization. Manufacturers will use virtual replicas of their machines to simulate machining processes, validate toolpaths, and train operators before physical implementation. This reduces scrap, accelerates setup times, and improves overall operational efficiency.
In conclusion, the 2026 VMC market will be defined by intelligent, connected, and flexible machines that support agile, sustainable, and high-precision manufacturing. Success will depend on vendors’ ability to innovate holistically—combining mechanical excellence with digital intelligence and responsive service ecosystems.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Vertical Milling Center (VMC): Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing a Vertical Milling Center (VMC) is a significant investment, and overlooking critical quality and intellectual property (IP) aspects can lead to substantial financial losses, production delays, and legal risks. Being aware of these common pitfalls is essential for making a sound procurement decision.
Poor Build Quality and Component Selection
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing VMCs, especially from lower-cost suppliers, is substandard build quality. This includes the use of inferior materials in critical components such as cast iron for the machine base, linear guides, ball screws, and spindles. Low-grade components wear faster, reduce machining accuracy, and increase maintenance costs. Buyers may be attracted by a lower upfront price but soon face higher total cost of ownership due to frequent breakdowns and reduced machine lifespan.
Lack of Rigorous Quality Control Processes
Reputable manufacturers implement strict quality control (QC) protocols throughout the manufacturing process, including laser alignment checks, thermal growth testing, and vibration analysis. However, some suppliers—particularly those under pressure to cut costs—may skip or shortcut these tests. Without proper QC documentation and certification (e.g., ISO standards), there’s a high risk of receiving a machine that does not meet specified tolerances or performance benchmarks, leading to scrap, rework, and production inefficiencies.
Inadequate Spindle Performance and Reliability
The spindle is the heart of a VMC, and poor spindle quality directly impacts machining precision and surface finish. Pitfalls include under-specified spindle motors, inadequate cooling systems, and the use of low-grade bearings that lead to premature failure. Additionally, some suppliers may exaggerate spindle speed or power capabilities. Without independent verification or performance testing, buyers may end up with a machine unable to handle required cutting loads or maintain tight tolerances over time.
Insufficient After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality machines require maintenance and occasional repairs. A major pitfall is sourcing from suppliers who lack a robust service network or fail to stock critical spare parts. Delays in obtaining replacement components or technical support can result in extended machine downtime. Furthermore, some manufacturers may go out of business or discontinue support, leaving buyers stranded with obsolete equipment and no recourse.
Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Purchasing a VMC from a supplier that uses copied or reverse-engineered designs poses serious IP risks. Some manufacturers replicate the look and functionality of well-known brands without proper licensing, potentially violating patents or design rights. If a company unknowingly sources such a machine, it could face legal liability, especially if the machine is used in a competitive industry where IP disputes are common. Additionally, counterfeit or cloned machines may lack the innovation, reliability, and safety features of genuine equipment.
Use of Proprietary Software with Limited Licensing or Transparency
Many modern VMCs come with proprietary CNC controls and software. A hidden pitfall is restrictive software licensing that limits functionality, prevents third-party integration, or requires expensive annual renewals. Some suppliers embed non-standard software that locks buyers into their ecosystem, making future upgrades or repairs difficult. Lack of transparency about software ownership and update policies can also hinder long-term usability and data security.
Failure to Verify Compliance with International Standards
Ensuring a VMC meets international safety and performance standards (e.g., CE, ISO, NRTL) is critical. Some suppliers provide falsified or incomplete compliance documentation. Machines lacking proper certification may not be insurable, could pose safety hazards, or fail customs inspections. This is particularly important when sourcing from overseas, where regulatory enforcement may be inconsistent.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence—requesting machine certifications, visiting manufacturing facilities, reviewing service agreements, and consulting independent experts. Investing time upfront to verify quality and IP integrity protects against costly surprises and ensures the VMC delivers long-term value and performance.
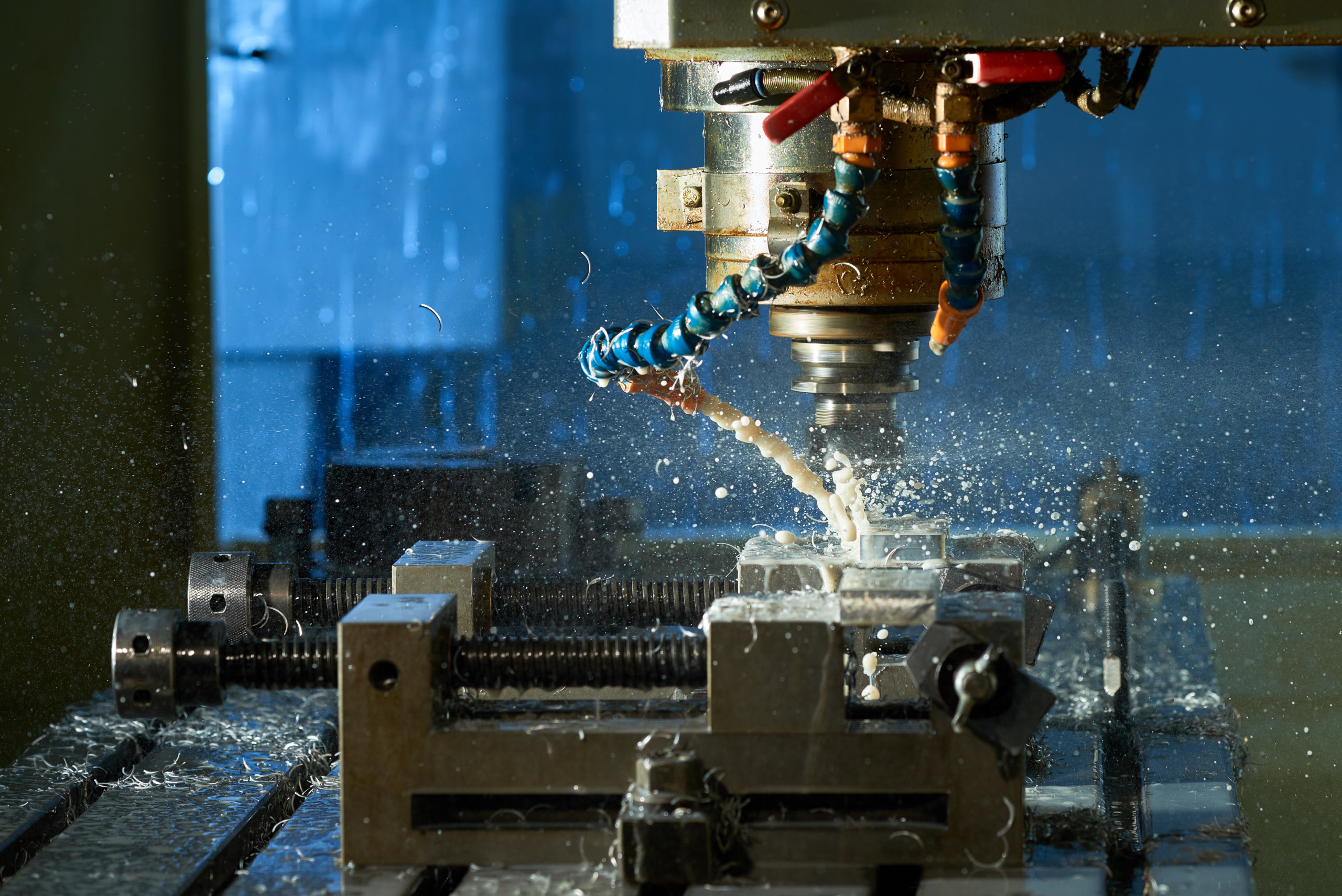

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Vertical Milling Center
This guide outlines essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legally compliant transportation, handling, and operation of a Vertical Milling Center (VMC).
Shipping & Transportation
Ensure the VMC is prepared and shipped correctly to prevent damage during transit. Use a crate or skid designed for heavy machinery, securing the machine with blocking and bracing at multiple anchor points. Confirm that the shipping method (flatbed truck, container, etc.) can handle the machine’s weight and dimensions. Provide clear handling instructions, including center of gravity and lift points, to the carrier. Retain all shipping documentation, including bills of lading and insurance.
Receiving & Inspection
Upon delivery, inspect the packaging for visible damage before accepting the shipment. Document any damage with photos and note it on the delivery receipt. After unpacking, conduct a full visual inspection of the VMC for shipping damage, loose components, or missing parts. Verify that all accessories, tooling, and documentation (manuals, compliance certificates) are included and match the purchase order.
Site Preparation & Installation
Prepare the installation site by ensuring the floor has adequate load-bearing capacity (typically 500–1000 lbs/sq ft) and is level. Provide sufficient space for machine operation, maintenance access, and coolant containment. Ensure proper utility connections are in place: three-phase electrical power with correct voltage and grounding, compressed air supply (if required), and coolant drainage or filtration system. Follow the manufacturer’s installation manual for rigging, leveling, and alignment procedures. Use certified rigging equipment and trained personnel during setup.
Regulatory Compliance
Verify that the VMC complies with relevant regional and international standards. In the U.S., ensure compliance with OSHA regulations and ANSI B11.8 safety standards for milling machines. In the EU, confirm CE marking per the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), including adherence to electrical safety (Low Voltage Directive) and EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive). Retain all compliance documentation, including Declaration of Conformity and risk assessment reports.
Safety & Operational Compliance
Install required safety features such as emergency stop buttons, interlocked guarding, and proper signage. Conduct a risk assessment to identify hazards (e.g., rotating parts, chip ejection, electrical systems) and implement controls. Train all operators and maintenance personnel on safe operating procedures, lockout/tagout (LOTO), and emergency response. Maintain a log of safety inspections and training records to demonstrate compliance during audits.
Environmental & Waste Management
Manage coolant and metal cutting fluid responsibly. Use appropriate filtration and recycling systems to extend fluid life and reduce waste. Dispose of spent coolant and metal chips in accordance with local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA guidelines in the U.S. or national provisions under the EU Waste Framework Directive). Prevent spills with secondary containment measures and maintain spill response kits onsite.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
Maintain a comprehensive compliance file including: machine manuals, electrical schematics, safety certifications, maintenance logs, operator training records, and inspection reports. Keep records of all modifications or repairs that could affect safety or compliance. Update documentation as needed and ensure easy access for auditors or regulatory inspectors.
Import/Export Considerations (if applicable)
For international shipments, classify the VMC under the correct Harmonized System (HS) code (e.g., 8459.11 for numerically controlled milling machines). Prepare required export documentation such as commercial invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin. Verify compliance with import regulations in the destination country, including standards for electrical systems and machine safety. Obtain necessary export licenses if shipping to restricted regions.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Vertical Milling Center
After a comprehensive evaluation of technical requirements, production needs, supplier capabilities, and total cost of ownership, sourcing a vertical milling center represents a strategic investment in enhancing manufacturing precision, efficiency, and capacity. The selected machine meets critical criteria including accuracy, rigidity, spindle performance, automation readiness, and service support. By aligning the procurement decision with long-term operational goals, the chosen vertical milling center will improve part quality, reduce cycle times, and support scalability in response to evolving production demands. Additionally, partnering with a reputable supplier ensures access to technical expertise, training, and reliable after-sales service, minimizing downtime and maximizing return on investment. In conclusion, the acquisition of this vertical milling center strengthens manufacturing capabilities and positions the organization for sustained competitiveness in precision machining.