Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Vertical Centrifugal Pump
In today’s high-integrity process industries—power, water, oil & gas, chemical, and HVAC—reliable fluid handling is mission-critical. Yet, plant engineers and procurement teams routinely face the same dilemma: how to achieve maximum uptime and energy efficiency without sacrificing valuable floor space or incurring excessive maintenance costs.
Vertical centrifugal pumps have emerged as the preferred solution for these exact challenges. Their vertically oriented shaft design eliminates horizontal overhang loads, reduces seal contamination, and allows direct coupling to NEMA motors. The result is longer seal life, smaller foundations, and cleaner installations in space-constrained facilities.
This guide is built for North American and European buyers who need to spec, source, and service vertical centrifugal pumps at scale. You will find:
- A concise comparison of vertical inline vs. vertical multistage architectures
- Performance maps, NPSHr curves, and motor coupling options that affect global compliance (IEEE, IEC, ATEX, CE)
- A purchase decision matrix covering materials, seals, and spare-parts logistics across USA/EU supply chains
- Maintenance checklists and vendor-agnostic troubleshooting tips to cut unplanned downtime
Use the data here to shorten RFQ cycles, reduce total cost of ownership, and ensure continuous, compliant operation from plant startup through decades of service.
Article Navigation
- Top 10 Vertical Centrifugal Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vertical centrifugal pump
- Understanding vertical centrifugal pump Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of vertical centrifugal pump
- 3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vertical centrifugal pump’ & Their Solutions
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for vertical centrifugal pump
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vertical centrifugal pump
- Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vertical centrifugal pump’
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vertical centrifugal pump Sourcing
- Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vertical centrifugal pump With Other Solutions
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vertical centrifugal pump
- Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vertical centrifugal pump Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vertical centrifugal pump
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vertical centrifugal pump
- Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
Top 10 Vertical Centrifugal Pump Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Top 10 Vertical Pump Manufacturers in the World 2024 – Liancheng
Domain: liancheng-pump.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: EBARA is a vertical pump manufacturer company with worldwide reputation, known for its innovative technology, high quality products and reliable ……
2. Vertical Centrifugal Pumps Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA …
Domain: thomasnet.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Vertical Centrifugal Pumps Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA and Canada ; Vanton Pump & Equipment Corp. Hillside, NJ 07205 · Manufacturer* ; AB Industrial….
3. Vertical Pump Suppliers Manufacturers – IQS Directory
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: IQS Directory provides a detailed list of vertical pump manufacturers and suppliers. Find vertical pump companies that can design, engineer, and manufacture ……
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. News – 9 Leading VTP Pump Manufacturers in 2025
Domain: tkflopumps.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Top vtp pump manufacturers for 2025 include Tongke Flow, Xylem, Pentair, Sulzer, Flowserve, Grundfos, KSB, Ebara, and Ruhrpumpen….
5. Pacer Pumps – Centrifugal Pumps Manufacturers In U.S.A
Domain: pacerpumps.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Pacer Pumps is the leading centrifugal pumps manufacturers providing industrial centrifugal pumps, marine centrifugal pumps, aquaculture centrifugal pumps….
6. Vertical Centrifugal Pumps, Submersible, Sump, Barge, Cryogenic
Domain: ruhrpumpen.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Ruhrpumpen’s range of centrifugal vertical pumps covers submersible, turbine, cryogenic, sump, barge and many more pump models, ……
7. Vertical Inline Pumps & Vertical Centrifugal Pumps – Castle Pumps
Domain: castlepumps.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Need a centrifugal pump but space is an issue? We offer vertical inline pumps for exactly this application. Enquire for expert pump advice and competitive ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
8. Global Top 10 Industrial Pump Manufacturers [2025]
Domain: blackridgeresearch.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Flowserve Corporation is one of the largest suppliers of industrial and environmental machinery, including pumps, valves, and seals. With “the ……
9. VXEN Vertical Inline Centrifugal Pump – North Ridge Pumps
Domain: northridgepumps.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: 14-day returnsThe VXEN vertical inline single stage centrifugal pump can be used for a vast range of applications in the industrial and marine markets….
Understanding vertical centrifugal pump Types and Variations
Understanding Vertical Centrifugal Pump Types and Variations
Vertical centrifugal pumps are engineered for space-constrained installations, high-temperature service, and arduous duties involving suspended solids. Below are the five most common industrial configurations, their technical differentiators, and typical applications in North American and EU process plants.
| Type | Key Features | Typical Applications | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical Inline (VIC) Pump | – Close-coupled to motor – Suction & discharge flanges on same centreline – Frame-mounted or in-line bracket |
Boiler feed, condensate return, cooling-tower loops, clean-liquid transfer | • Direct replacement for horizontal pumps • Minimal piping changes • Low NPSHr |
• Limited solids handling • Requires precise alignment |
| Vertical Wet-Pit (VWP) Pump | – Column & bowl assembly immersed in sump – Hollow shaft for priming – Wide impeller eye for solids |
Wastewater lift stations, storm-water, slurry sumps, paper-stock chests | • Self-priming variants available • Entire assembly serviceable without dewatering pit • High flow capacity |
• Complex foundation & guide-bushing alignment • Higher installation cost |
| Vertical Dry-Pit (VDP) Pump | – Column and bowl above liquid level – Seal chamber protected from fluid – Designed for sealed or packed stuffing box |
Chemical reactors, solvent recovery, reverse-osmosis feed, hot organic liquids | • No submerged bearings → lower maintenance • Clean, accessible environment • Reduced seal flush requirements |
• Requires sealed suction tank • Not suitable for volatile or flashing liquids |
| Vertical Mixed-Flow | – Large diameter, axial/ radial hybrid impeller – Medium-specific speed (3,000–6,000 US) – Discharge nozzle 90° to suction |
Water supply, flood control, irrigation, HVAC cooling water | • High flow, moderate head • Stable operation near shut-off • Lower speed → longer bearing life |
• Large envelope • Not ideal for viscous or abrasive slurry |
| Vertical Axial-Flow | – Low-speed, large-pitch propeller – Very high flow, low head (up to 25 m) – Open impeller, often oversized for solids |
Flood control, cooling-tower basins, mine dewatering, dredging | • Maximum efficiency on high-flow/low-head duties • Can pass large solids without clogging • Energy-efficient at design point |
• Requires deep pit or wet well • Sensitive to suction conditions |
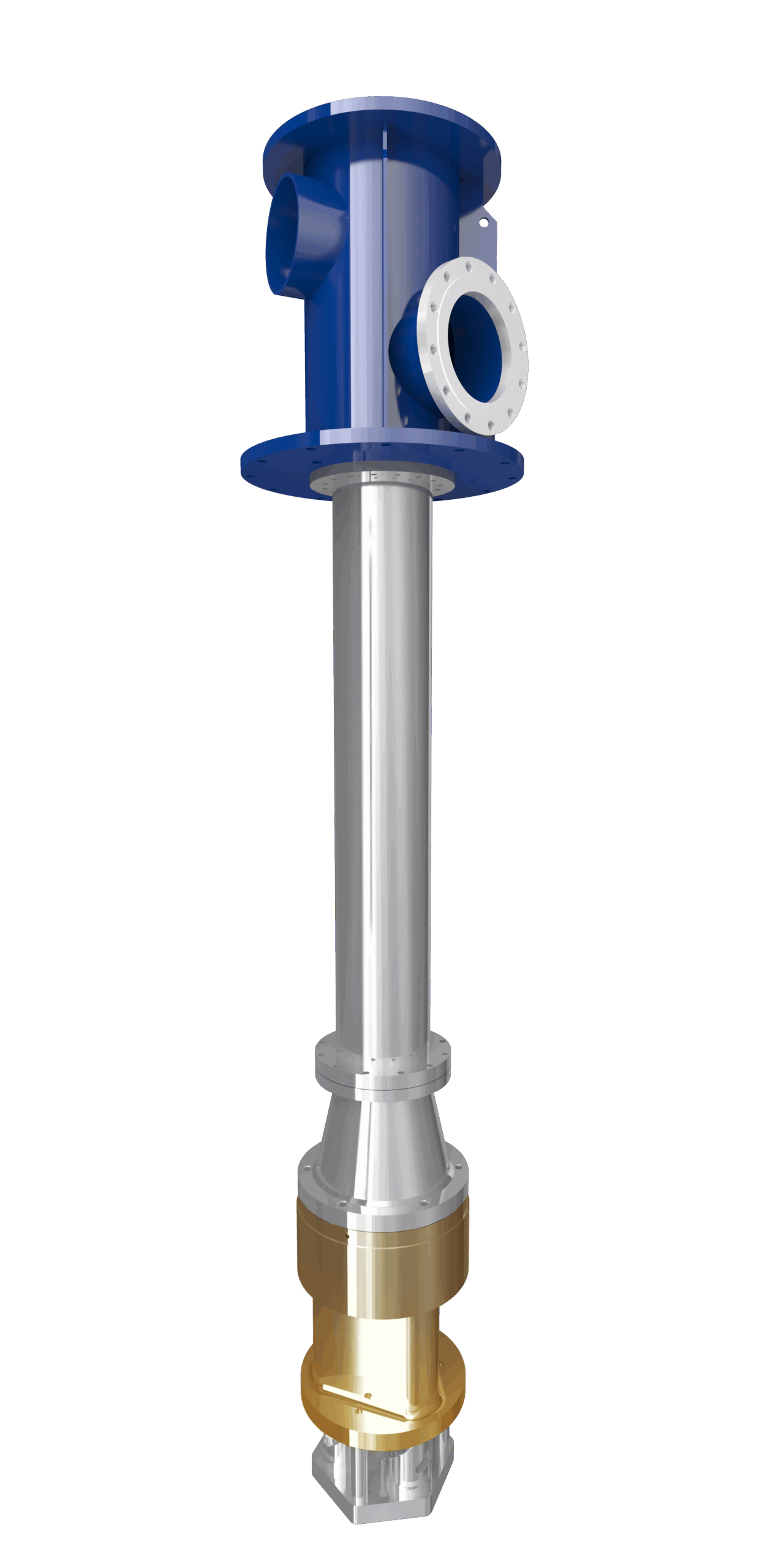
1. Vertical Inline (VIC) Pump
Design: A close-coupled, overhung impeller mounted directly on the motor shaft inside a compact casing. Suction and discharge nozzles are on the same centreline for minimal piping stress.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Performance Range: 3–200 m³/h, 10–120 m head.
Industry Focus:
– North America: Commercial HVAC, chillers, boiler feed.
– Europe: District heating return lines, reverse-osmosis permeate pumps.
Advantages:
– Zero additional floor space beyond existing horizontal footprint.
– Factory-assembled, pre-aligned; quick swap-out during turnarounds.
– Lower initial cost and spare-parts inventory.
Limitations:
– Shaft overhang limits solids size; metal-detecting or magnetic inserts recommended.
– Seal chamber exposed to atmospheric pressure; choose double seal for volatile liquids.
2. Vertical Wet-Pit (VWP) Pump
Design: Submersible bowl assembly suspended on a column pipe; motor sits above the liquid in a moisture-proof enclosure. Hollow shaft permits suction-side priming.
Performance Range: 50–3,000 m³/h, 5–80 m head.
Industry Focus:
– North America: Municipal lift stations, pulp-mill white-water.
– Europe: Tunnelling dewatering, food-processing CIP return.
Advantages:
– No sealing problems—entire pump can be removed without emptying the pit.
– Wide impeller throat handles rags, grit, and fibrous material.
– Variable speed (VFD) compatible for load-following applications.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Limitations:
– Guide-bushing wear demands periodic inspection.
– Electrical containment (Ex d or IP68) mandatory in explosive atmospheres.
3. Vertical Dry-Pit (VDP) Pump
Design: Bowl assembly mounted in a sealed suction tank; motor and column are located above the fluid. Seal chamber isolated from process by a barrier fluid system or packed gland.
Performance Range: 5–500 m³/h, 15–200 m head.
Industry Focus:
– North America: Petrochemical refinery, pharma API reactors.
– Europe: Semiconductor wet benches, battery-electrolyte circulation.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Advantages:
– Seal chamber coolable and flushable—ideal for hot or toxic liquids.
– No submerged bearings → lower thrust load and longer B10 life.
– Easier shaft alignment and mechanical-seal servicing.
Limitations:
– Requires pressurised or negative-pressure suction tank; vapor-handling capability limited.
– Initial cost higher due to pressure vessel and instrumentation.
4. Vertical Mixed-Flow Pump
Design: Large-diameter, open impeller with mixed-flow vanes; discharge elbow oriented 90° to suction. Usually single-stage, but multi-stage versions available for higher heads.
Performance Range: 300–10,000 m³/h, 5–50 m head.
Industry Focus:
– North America: Cooling-tower loops, hydro-irrigation canals.
– Europe: Flood-defense pumping stations, offshore ballast systems.
Advantages:
– High flow at low NPSHr—ideal for warm-water service.
– Axial thrust balanced by double suction; minimal foundation vibration.
– Lower speed (1,500 or 1,800 rpm) reduces gearbox or V-belt costs.
Limitations:
– Large diameter—space-consuming; not suited to congested plant layouts.
– Limited to clean or slightly abrasive liquids; abrasive slurry requires hard-iron impeller.
5. Vertical Axial-Flow Pump
Design: Open, multi-blade propeller directly driven by an inline motor through a rigid coupling. No impeller eye—fluid enters axially and exits axially.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Performance Range: 1,000–20,000 m³/h, 2–25 m head.
Industry Focus:
– North America: Canal irrigation, nuclear-service cooling-water intake.
– Europe: Coastal flood barriers, offshore ballast exchange.
Advantages:
– Maximum efficiency (>90 %) at design point; energy savings up to 30 % versus centrifugal on high-flow duties.
– Capable of passing fish, debris, and floating solids without damage.
– Simple construction—fewer wearing parts than mixed-flow.
Limitations:
– Requires deep wet well or floating pontoons; not suitable for volatile or flashing liquids.
– Low head—parallel operation needed for higher lift; speed control essential to avoid surge.
Selection Checklist for Procurement Teams
- Fluid Characteristics
- Solids content, viscosity, temperature, vapor pressure, and chemical compatibility.
-
Explosive or flammable classification (ATEX/IECEx) drives seal and motor enclosure options.
-
Installation Space & Access
- Vertical inline or dry-pit for confined areas; wet-pit for existing sumps.
-
EU/NA seismic and electrical-code compliance (e.g., NEMA Premium motors in USA, IE4 in Germany).
-
Operational Duty
- Continuous vs. intermittent service affects bearing grease, motor insulation, and seal type.
-
Demand flexibility? Specify VFD-ready motor and variable-pitch impeller.
-
Maintenance & Lifecycle Cost
- Standardise on common column sizes and seal families across plants to reduce spares.
-
Evaluate total cost of ownership (TCO) including energy, seal flush systems, and downtime value.
-
Regulatory & Sustainability Targets
- EU Ecodesign Directive (ErP) and USA DOE efficiency standards—ensure motor and pump efficiency grades meet local requirements.
- Water stewardship: select axial-flow or mixed-flow for large-volume, low-head transfers to minimise pumping energy.
By matching the pump type to the application’s hydraulic, mechanical, and environmental constraints, engineering teams can secure reliable, cost-effective vertical centrifugal solutions that comply with both North American and European industrial standards.
Key Industrial Applications of vertical centrifugal pump
Key Industrial Applications of Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
| Industry / Application | Typical Fluid / Duty | Operational Benefits Delivered by Vertical Centrifugal Design |
|---|---|---|
| Power Generation – Condensate & Circulation | Boiler feed, condensate return, cooling-water circulation | Compact footprint fits turbine bays; direct-coupled motor eliminates in-line couplings that fail under thermal shock; open impeller handles condensate with minimal solids. |
| Oil & Gas – Crude & Produced Water Lift | Suction lift from separators, desalter feed, produced-water transfer | Submersible motor housing prevents cavitation on suction lifts up to 20 m; no suction priming required, reducing start-up time and operator exposure to H₂S. |
| Chemical Processing – Batch & Transfer | Aggressive solvents, acids, caustics, hot organic liquids | Fully contained column design allows hot-oil operation up to 350 °C without external seal support systems; radial-split casing simplifies gasketed joint maintenance. |
| Mining & Mineral Processing – Slurry Circulation | Mill discharge, tailings, leachate with <50 mm solids | Open impeller and large suction eye handle abrasive slurries; vertical arrangement keeps bearing lubrication cooler and cleaner than horizontal units. |
| Food & Beverage – CIP & Transfer | Hot caustic/sanitizing solutions, juices, syrups | Sanitary clamp connections, polished Ra ≤ 0.8 µm interiors, and CIP-ready nozzles meet 3-A sanitary standards; no internal mechanical seals eliminate product contamination risk. |
| Pulp & Paper – Stock & Chemical Circulation | White-water recirculation, black-liquor transfer, caustic charging | Handles fiber-laden liquids up to 10 % consistency; vertical shaft reduces floor-space load on already congested mill buildings. |
| Water & Wastewater – Lift & Circulation | Storm-water lift stations, plant circulation, reverse-osmosis feed | Non-clog open impeller passes 25–40 mm solids; dry-mounted motor with water-cooled casing extends B10 life to > 60 000 h in continuous service. |
| Marine & Offshore – Ballast & Cargo | Sea-water ballast, fuel oil, lube-oil transfer | Vertical design eliminates need for suction sumps, reducing vessel draft and underwater noise; stainless-steel construction resists seawater corrosion. |
| District Heating & Cooling – Chilled & Hot-Water Circulation | Chilled-water loops, district heating return, thermal-storage transfer | Column assembly allows bearing lubrication outside the fluid, extending bearing life in 120 °C water; flanged connections simplify retrofit into existing pipe racks. |
Benefits Summary
- Space Efficiency: Vertical orientation reduces plan-area requirements by up to 60 % versus horizontal pumps, critical in offshore modules and refinery turnarounds.
- Reliability: Radial-split casing and direct-drive motor eliminate in-line alignment risk and reduce mean time to repair (MTTR) by 30–50 %.
- Extended Fluid Compatibility: Open impeller and variety of metallic/non-metallic materials cover everything from clean water to 50 % solids slurry and hot acids.
- Lower Life-Cycle Cost: Interchangeable, inexpensive spare parts and dry-maintenance access cut annual OPEX by 15–25 % versus horizontal equivalents.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘vertical centrifugal pump’ & Their Solutions
“`markdown
3 Common User Pain Points for Vertical Centrifugal Pumps & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: High Installation & Maintenance Costs
Scenario
A Midwest food-processing plant upgrades its CIP system with a vertical centrifugal pump but discovers that foundation work, shaft alignment, and seal replacement demand specialized labor and frequent downtime.
Problem
– Foundation & space constraints: Vertical pumps require precise floor mounting and vibration isolation.
– Seal wear: Even with open impellers, mechanical seals fail on abrasive CIP fluids.
– Downtime: Outages last 4–6 h per seal change, disrupting 24/7 production.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution
| Action | Benefit |
|—|—|
| Specify frame-mounted, C-face motor packages that ship with pre-aligned pump/motor sub-assemblies. | Reduces field labor by 40 % and eliminates custom foundation cuts. |
| Select pumps with cartridge mechanical seals and stanless 316L shaft sleeves. | Extends seal life to 18–24 months in CIP service. |
| Partner with OEMs offering on-site seal-training programs for maintenance teams. | Cuts change-out time to <90 min and reduces spare-part inventory by 25 %. |
Pain Point 2: Limited NPSH & Cavitation in High-Elevation Installations
Scenario
A German beverage bottler installs a vertical inline pump at 1,200 m elevation. The system experiences cavitation during peak summer demand, causing flow loss and product contamination.
Problem
– Low atmospheric pressure: NPSHa drops 12 % per 300 m of elevation.
– Long suction piping: Additional friction head further reduces NPSHa.
– Product loss: Cavitation creates aeration, affecting taste and regulatory compliance.
Solution
| Action | Benefit |
|—|—|
| Size pump for 0.5 m minimum submergence and specify higher specific-speed impellers to maintain 6–7 m NPSHr at design flow. | Raises NPSHa margin above 1.5 m, eliminating cavitation. |
| Install suction bell mouth or wet-pit design to reduce entry losses by 30 %. | Restores flow to 100 % without motor overload. |
| Add remote NPSH monitoring via pressure transmitters linked to SCADA. | Alerts operators 30 s before cavitation starts, preventing shutdowns.
Pain Point 3: Spare-Parts Obsolescence & Global Supply Chain Delays
Scenario
A UK chemical processor faces a six-week lead time for a replacement impeller due to OEM part number changes and EU customs delays.
Problem
– Part revisions: OEMs redesign impellers every 18–24 months, rendering old inventory obsolete.
– Customs holdups: Brexit and Eastern-European shipping restrictions extend lead times.
– Safety stock: Plants over-order parts, tying up capital.
Solution
| Action | Benefit |
|—|—|
| Source pumps from OEMs offering 10-year parts availability and digital part-number cross-reference tools. | Eliminates obsolete inventory risk. |
| Maintain a “critical spares” kit (mechanical seal, impeller, shaft sleeve) in EU 3PL warehouse. | Reduces lead time to 5–7 days and cuts carrying cost by 35 %. |
| Use 3D-printed impeller prototypes for non-critical applications with OEM approval. | Reduces emergency replacement cost from €4,500 to €350.
“`
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vertical centrifugal pump
Strategic Material Selection Guide
Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
Rotech Pumps & Systems – B2B Reference Document
1. Executive Summary
Material choice directly impacts lifecycle cost, compliance, and downtime. This guide provides engineers and procurement teams with a concise, data-driven framework for selecting wetted parts in vertical centrifugal pumps used in North America and Europe.
2. Pump Types Covered
- RVMS – Vertical Multistage (high head, low NPSHr)
- RVIS – Vertical Inline (space-constrained, direct-coupled)
Both series share the same material matrix; selection is dictated by fluid chemistry, temperature, and regulatory environment.
3. Material Matrix & Performance Map
| Wetted Part | Standard Alloy | Optional High-Performance Alloy | Typical Application Thresholds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impeller | CF8M (316L SS) | CD4MCu duplex, Hastelloy C | <120 °C, neutral/oxidizing acids |
| Casing | CF8M (316L SS) | Duplex 2205, Super-duplex 2507 | High pressure (>16 bar) or chlorides |
| Shaft | 17-4 PH (AM-355) | Hastelloy X, Titanium | >200 °C or H₂S service |
| Wear Ring | 316L SS | Silicon-carbide mechanical face | Abrasive solids ≤2 % |
| Seal Chamber | 316L SS | Alloy 20, PEEK | Aggressive organics, high vacuum |
| Motor Housing (if wetted) | 304 SS | 316L SS, epoxy-coated | Marine, chlorinated water |
4. Selection Decision Tree
- Fluid pH
- <4 or >10 → Upgrade to duplex or Hastelloy.
- Chloride Content
-
200 ppm → Duplex stainless mandatory.
- Temperature
-
150 °C → Specify Hastelloy shaft & super-duplex casing.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Solids
-
1 % by weight or >100 µm → Switch to Ni-Al-Bronze impeller or add SiC wear rings.
- Regulatory
- FDA/USDA → 316L only; no grease-filled bearings.
5. Cost vs. Lifetime Value (LCC Model)
| Material | Initial Cost Index* | Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) | LCC Index (3-year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 316L SS | 1.0 | 18 months | 1.9 |
| Duplex 2205 | 1.4 | 36 months | 2.0 |
| Hastelloy C | 2.8 | 60 months | 2.2 |
*Normalized to 316L base price.
Rule of thumb: Duplex breaks even at 24 months; Hastelloy at 36 months in aggressive services.
6. Compliance & Certification Matrix
| Standard | 316L | Duplex 2205 | Hastelloy C | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NORSOK M-001 | ✔ | ✔ | – | Duplex meets S06 sour service. |
| ASME Section VIII Div.1 | ✔ | ✔ | – | Design pressure ≤275 bar. |
| ATEX / IECEx | ✔ | ✔ | – | Group II, Zone 1/21. |
| FDA 21 CFR 177.1550 | ✔ | – | – | For food/pharma. |
| RoHS / REACH | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | All alloys meet current directives. |
7. Procurement Checklist
- [ ] Confirm fluid analysis (pH, chloride, H₂S, solids).
- [ ] Specify temperature & pressure envelope (design margin +10 %).
- [ ] Flag any FDA/USDA or ATEX zones.
- [ ] Request MTBF data sheet for selected alloy.
- [ ] Validate spare-part lead time (duplex & Hastelloy >16 weeks).
- [ ] Include dry-run protection (ceramic impeller or built-in seal flush).
8. Comparison Table (Quick Reference)
| Feature | 316L SS | Duplex 2205 | Hastelloy C | Titanium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Max Temp (°C) | 150 | 250 | 400 | 400 |
| Max Pressure (bar) | 25 | 40 | 60 | 60 |
| Abrasion Resistance | Fair | Good | Fair | Good |
| Cost vs 316L | 1× | 1.4× | 2.8× | 4.5× |
| Typical Use Case | Water, low acid | Desalination, high Cl⁻ | HF, strong oxidizers | Aerospace fuel |
9. Final Recommendation
- Standard water / low acid: 316L SS covers 80 % of North American and EU installations.
- High chloride or sour service: Upgrade to duplex 2205; verify NORSOK compliance.
- Pharma, food, or high-purity chemicals: Restrict to 316L or 304L with electropolish; avoid coatings.
- High temperature (>200 °C) or HF service: Specify Hastelloy C; validate ASME Section VIII design temperature margin.
Use the material matrix and LCC model to lock in the right alloy on the first purchase order—avoiding the 30–50 % cost premium of late-stage material substitution.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vertical centrifugal pump
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
The production of a vertical centrifugal pump follows a controlled sequence that integrates precision engineering with rigorous quality checks. Each stage is designed to ensure dimensional accuracy, mechanical integrity, and long-term reliability under continuous-duty service.
1.1 Preparation (Material & Tooling)
| Step | Description | Key Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Receipt | Forged stainless-steel shafts, cast iron/bronze casings, and high-grade elastomers are received with MTC (Material Test Certificate) per EN 10204 3.1. | Visual, dimensional check, hardness test |
| Tooling Inspection | Molds, machining fixtures, and heat-treatment jigs are calibrated against ISO 9001 traceable standards. | Calibration log, first-article inspection |
| Pre-Production Trial | A single prototype is run for 30 min at design point to validate clearances and vibration levels. | Vibration < 4.5 mm/s, temperature rise < 40 °C |
1.2 Forming & Machining
| Component | Primary Process | Dimensional Tolerance | Surface Finish |
|---|---|---|---|
| Casing | Sand or investment casting → rough machining → CNC finishing | ±0.05 mm | Ra ≤ 3.2 µm |
| Shaft | Cold-drawn bar → rough turning → grinding → hard chrome plating | H7 | Ra ≤ 0.4 µm |
| Impeller | Die-cast bronze → CNC profiling → dynamic balance test | ±0.02 mm | Ra ≤ 1.6 µm |
| Coupling Half | Forged steel → CNC mill/turn → keyway broach | IT7 | Ra ≤ 1.6 µm |
Note: All critical surfaces are protected with rust-preventive oil and stretch-wrap until final assembly.
1.3 Assembly Sequence
- Bearing Installation
- Insert sealed, grease-lubricated angular-contact bearings (SKF or FAG) into the upper and lower bearing housings.
-
Pre-load via lock-nut to 0.02–0.04 mm axial play.
-
Shaft & Impeller Mounting
- Press-fit impeller onto shaft with hydraulic arbor press.
-
Secure with key and retaining ring; verify impeller-to-volute clearance (typically 3–5 mm).
-
Casing Assembly
- Clamp lower casing half, insert shaft assembly, then bolt upper casing with torque sequence 30 N·m in three passes.
-
Apply RTV sealant on joint faces; re-torque after 24 h cure.
-
Motor Integration
- Align motor shaft to pump shaft via flexible coupling; check angular misalignment ≤ 0.05 mm/m.
-
Connect power cable with strain relief; perform insulation resistance ≥ 20 MΩ.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Seal & Gland Installation
- Mechanical seal faces lapped to < 0.2 µm flatness; spring loaded to 0.3 mm compression.
- Flush connection for clean-in-place (CIP) or process fluid as specified.
1.4 Final Quality Control
| Test | Method | Acceptance |
|---|---|---|
| Visual | 100 % surface inspection under 500 lux lighting | No cracks, porosity, or burrs |
| Dimensional | CMM scan on critical faces | ISO 2768-m |
| Pressure Test | Hydrostatic 1.5 × rated pressure for 5 min | No leakage |
| Performance | Flow, head, and efficiency at 75 %, 100 %, 110 % of BEP | ±3 % head, ±2 % efficiency |
| Vibration | Accelerometer on bearing housing | < 2.8 mm/s RMS (ISO 10816-3) |
| Noise | A-weighted dB(A) at 1 m | ≤ 85 dB(A) |
2. Quality Management System
- ISO 9001:2015 certified throughout the plant.
- PED 2014/68/EU compliance for pressure-containing parts.
- ATEX certification optional for Zone 1/21 hazardous areas.
- NPSH test data sheet supplied with each unit.
- Traceability matrix links every heat lot to the final serial number.
3. Continuous Improvement Loop
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) charts on bore diameter,同心度, and vibration trends.
- Annual third-party audit (DNV or TÜV) for ISO 9001 and EN 12953 compliance.
- Customer feedback routed to Engineering within 24 h; CAPA initiated within 5 days.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘vertical centrifugal pump’
Sure! Here’s a professional, B2B-focused Step-by-Step Checklist for Sourcing Vertical Centrifugal Pumps, formatted in Markdown and tailored for a USA/Europe audience.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
Sourcing the right vertical centrifugal pump requires a structured approach. This checklist ensures you evaluate all critical aspects—from technical specifications to supplier credibility—before making a procurement decision.
✅ Step-by-Step Sourcing Checklist
1. Define Application Requirements
- Fluid Type: Identify the liquid to be pumped (clean water, wastewater, chemicals, slurry, etc.).
- Temperature Range: Note maximum and minimum operating temperatures.
- Viscosity & Solids Content: Determine if the fluid is abrasive, viscous, or contains solids.
- Flow Rate & Head: Specify required flow (GPM or m³/hr) and total dynamic head (TDH).
- Duty Cycle: Continuous vs. intermittent operation.
- Industry Compliance: Ensure the pump meets applicable standards (e.g., NSF, FDA, ATEX, ASME, CE).
2. Select Pump Type & Configuration
- Vertical Inline Pump: Suitable for tight spaces and inline piping.
- Vertical Multistage Pump: Ideal for high-pressure applications.
- Submersible vs. Non-Submersible: Choose based on installation environment.
- Seal Type: Open or closed impeller; mechanical seal or magnetic drive.
- Material of Construction: Stainless steel, cast iron, bronze, or engineered plastics.
3. Evaluate Pump Performance
- Impeller Design: Open, semi-open, or closed—based on fluid characteristics.
- Drive Configuration: Direct-coupled vs. belt-driven.
- Efficiency Rating: Look for high-efficiency models to reduce energy costs.
- NPSH Required vs. Available: Ensure system compatibility to prevent cavitation.
4. Assess Supplier Capabilities
- Manufacturing Location: USA, EU, or offshore—consider lead times and compliance.
- Certifications: ISO 9001, API, CE, UL, etc.
- Customization Options: Can the supplier tailor the pump to your specs?
- ** spare parts Availability**: Are parts readily available and interchangeable?
- Technical Support & Documentation: Access to drawings, manuals, and support.
5. Review Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
- Initial Purchase Price: Compare quotes from multiple suppliers.
- Installation & Maintenance Costs: Ease of maintenance, accessibility of parts.
- Energy Efficiency: High-efficiency pumps reduce long-term operating costs.
- Warranty & Service Contracts: Evaluate coverage and response times.
6. Verify Compliance & Standards
- Electrical Standards: NEMA, IEC, etc.
- Environmental Regulations: RoHS, REACH, etc.
- Pressure Rating & Safety Codes: ASME, PED, etc.
- Documentation: CE mark, ATEX compliance, material certificates.
7. Request Quotes & Technical Documentation
- Request for Quotation (RFQ): Include all specs and application details.
- Technical Data Sheets: Verify performance curves and dimensions.
- Installation & Maintenance Manuals: Ensure proper handling and serviceability.
- References or Case Studies: Validate supplier performance.
8. Conduct Due Diligence
- Supplier Reputation: Check reviews, testimonials, and industry standing.
- Logistics & Lead Time: Confirm delivery schedules and shipping terms.
- After-Sales Service: Availability of local service teams or partners.
9. Finalize Purchase & Contract
- Purchase Agreement: Include delivery terms, warranties, and payment terms.
- Inspection & Testing Protocol: Define acceptance criteria and testing methods.
- Training & Commissioning Support: Ensure proper installation and operation.
10. Post-Purchase Evaluation
- Performance Monitoring: Track efficiency and reliability over time.
- Feedback Loop: Share insights with supplier for continuous improvement.
- Spare Parts Planning: Maintain inventory for critical components.
📝 Summary Table
| Step | Focus Area | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Requirements | Define application parameters |
| 2 | Selection | Choose pump type and materials |
| 3 | Performance | Evaluate efficiency and design |
| 4 | Supplier | Assess capabilities and support |
| 5 | TCO | Analyze total cost, not just price |
| 6 | Compliance | Ensure legal and safety standards |
| 7 | Documentation | Request specs and manuals |
| 8 | Due Diligence | Vet supplier credibility |
| 9 | Contract | Finalize terms and conditions |
| 10 | Evaluation | Monitor performance post-install |
Note: This checklist is designed to streamline your sourcing process and reduce risk when selecting a vertical centrifugal pump for industrial or commercial use.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Let me know if you’d like a downloadable version or a version tailored to a specific industry (e.g., water treatment, chemical processing).
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vertical centrifugal pump Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis
Vertical Centrifugal Pump Sourcing
(USA & Europe – B2B Guide)
1. Cost Breakdown by Spend Category
| Category | % of Total Cost | Typical Range (USD) | Key Cost Drivers | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | 45 – 55 % | $2,800 – $8,200 | Cast iron, 316 SS, OEM bearings, shaft, impeller | Higher alloy content & seal materials (e.g., silicon-carbide) push to top of range. |
| Labor | 12 – 18 % | $700 – $1,100 | Skilled machining, rotor balancing, pressure testing | North America & EU labor rates ~3× China/India. |
| Logistics | 10 – 15 % | $600 – $900 | Incoterms, containerization, freight mode, urgency | Air freight adds 8–12 %; ocean freight adds 2–3 %. |
| Overheads & Margin | 20 – 25 % | $1,200 – $1,500 | Quality assurance, R&D, warranty reserve, distributor margin | Direct OEM vs. stocking distributor margin differs by 5–8 %. |
| Total CIF Price (40HQ) | 100 % | $6,300 – $11,700 | — | FOB Shanghai/Ningbo → New York; Rotterdam → Stuttgart. |
Rule-of-thumb: Expect ±10 % swing for quantities <10 units; ±5 % for bulk orders >50 units.
2. Cost Drivers & Hidden Fees
- Material Surcharge: 2023 copper & nickel price spikes add 3–7 % to 316 SS variants.
- Certification: CE, API 610, ISO 9001 adds 2–4 % to base price.
- Customs Clearance: US CBP exam fee $485; EU T2L €150.
- Pre-shipment Testing: Hydrostatic test @1.5× rating = $120 per unit.
- Palletization: ISPM-15 wooden pallets add $35 per pallet (USD) or €40 (EU).
3. Sourcing Strategy – Cost Savings Checklist
| Tactic | Potential Savings | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk Buy (40HQ) | 6–9 % | Consolidate orders; negotiate 90-day forecast. |
| Direct From OEM (no distributor margin) | 5–8 % | Verify ISO 9001 plant audit; secure OEM price list. |
| Standard Frame & Seal Kit | 3–5 % | Avoid custom impeller or exotic alloy. |
| FOB vs. DDP | 4–7 % | Handle customs & inland freight in-house. |
| Local Stocking | 2–3 % | Reduce expedited air freight; amortize duty drawback. |
| Reconditioned/Remanufactured | 15–25 % | OEM-grade overhauled units; warrantied 12 months. |
4. Quick Reference – Price Tiers (40HQ container, 50 pcs)
| Tier | Pump Model | Material | CIF East Coast USA | CIF North Rhine-Westphalia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | RVMS 4/6 | Cast iron | $7,100 | €6,800 |
| Mid | RVMS 6/8 | 316 SS | $9,200 | €8,900 |
| Premium | RVMS 8/12 | Duplex 2205 | $11,700 | €11,200 |
5. Next Steps
- Obtain 3-year price forecast from OEM to hedge alloy surcharges.
- Run landed-cost spreadsheet including duty drawback (US) or EU VAT refund.
- Pilot order 5 units to validate lead time (typical 8–12 weeks FOB).
- Negotiate SLA on spare parts availability (target ≤4 weeks EU, ≤6 weeks US).
Bottom line: Sourcing a vertical centrifugal pump at scale can yield 8–15 % total landed-cost reduction without compromising API 610 compliance or MTBF expectations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing vertical centrifugal pump With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Vertical Centrifugal Pump With Other Solutions
| Criteria | Vertical Centrifugal Pump | Horizontal Centrifugal Pump | Submersible Pump |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mounting Orientation | Shaft mounted vertically; motor on top | Shaft mounted horizontally; motor beside pump | Pump and motor in same waterproof casing, submerged |
| Floor Space Required | Minimal; motor is above the wet-end | High; requires separate base plate & couplings | High; pit or tank required for submersion |
| Installation Effort | Fast; no alignment, no base plate | Moderate; requires coupling alignment & grouting | High; excavation, waterproof enclosure, float switches |
| Maintenance Access | Top-entry; quick open hatch, no spillage | Side-entry; requires partial pipe removal | Bottom or side; full pump removal from pit |
| Seal Type & Reliability | Single mechanical seal, exposed to atmosphere | Double mechanical seal or packing, prone to leakage | Fully submerged seal, no seal chamber erosion |
| Temperature Range | -20 °C to +400 °C (special alloys) | -20 °C to +120 °C (standard) | -10 °C to +80 °C (depends on motor insulation) |
| Solids Handling | Open impeller; up to 25 mm spherical solids | Closed impeller; < 2 mm recommended | Semi-open or vortex; up to 80 mm fibrous solids |
| Net Positive Suction Head (NPSHr) | Medium (2–5 m) | Medium (2–5 m) | High (5–9 m) – must fill casing before start |
| Energy Efficiency | High; direct coupling, no additional losses | Medium; belt or coupling losses | Medium; motor cooled by process fluid |
| Initial Cost | Medium | Low to Medium | High (excavation, control panels) |
| Operating Cost | Low | Medium | Medium to High (clogging, higher NPSHr) |
Analysis & Decision Framework
-
Space-Constrained Installations
Vertical centrifugal pumps win: motor mounted above the wet-end eliminates the need for a large foundation or pit. -
High-Temperature or High-Pressure Services
Vertical design offers robust construction and direct-drive coupling, reducing shaft deflection and seal stress. Horizontal pumps require additional support brackets and flexible couplings that limit temperature. -
Dirty or Solids-Laden Liquids
Open impeller and top-entry access make vertical pumps the preferred choice for wastewater, slurry, or process liquids containing debris. Horizontal pumps require frequent impeller changes and are prone to clogging. -
Maintenance Windows
Top-entry access means no tank draining or pump removal. A single technician can change the seal or impeller in under 30 minutes. Submersible pumps require full pit access and sometimes crane rental. -
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
While vertical pumps have a moderate upfront cost, lower installation, energy, and maintenance expenses yield a faster payback period (typically < 18 months) compared to horizontal or submersible alternatives.
Bottom Line
Choose a vertical centrifugal pump when floor space is limited, temperatures exceed 120 °C, or the liquid contains solids. Opt for horizontal pumps only when footprint is abundant and NPSHr is not critical. Select submersible pumps solely when a wet well or sump is integral to the process and solids are > 25 mm.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vertical centrifugal pump
Key Technical Properties & Trade Terminology
Vertical Centrifugal Pump – B2B Guide
USA & Europe Market Focus
1. Core Technical Properties
| Property | Definition | Typical Range / Note |
|---|---|---|
| Specific Speed (Ns) | Geometric pump similarity parameter; influences impeller design. | 500 – 2 000 (low–high) |
| Head (H) | Static lift + friction losses; measured in metres or feet. | 5 – 600 m (custom up to 1 000 m) |
| Capacity (Q) | Volumetric flow rate; m³/h or L/s. | 5 – 25 000 m³/h |
| Temperature Range | Operating fluid temperature. | – 50 °C to + 400 °C (depending on material & seal) |
| Pressure Rating | Maximum allowable working pressure (MAWP). | PN 10 – PN 100 (≈ 145 – 1 450 psi) |
| NPSHr | Net Positive Suction Head required. | 0.5 – 4.0 m (varies with impeller type) |
| Efficiency (η) | Hydraulic efficiency at Best Efficiency Point (BEP). | 55 – 85 % |
| Casing Pressure Rating | ANSI / EN flanged connections (RF, FF, RTJ). | DN 50 – DN 600 |
| Mounting Style | Motor-over-pump (MOP) or pump-over-motor (POM). | MOP preferred for high temperature or hazardous duty. |
| Seal Type | Single/double mechanical seal, cartridge or split. | API 610 Plan 01, 11, 52, 53B, etc. |
2. Trade & Procurement Terms
| Term | Meaning | Typical Use in Procurement |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ | Minimum Order Quantity | 1 – 5 units for stock items; 10 – 25 for custom materials |
| Lead Time | Production + testing + shipping | 8 – 16 weeks FCA works; expedite surcharge +25 % |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer | Customer branding on nameplate, paint, packaging |
| ODM | Original Design Manufacturer | Full design & manufacture to customer specification |
| Warranty | Standard & extended coverage | 12 – 24 months, optional 36 months on select models |
| Incoterms | Delivery terms (FCA, FOB, CIF, DDP) | FCA works (USA) / DDP jobsite (EU) |
| Spare Parts Kit | Pre-packaged critical components | 1-year kit, 5-year kit, or custom |
| ATEX / IECEX | Explosion protection certification | Required for Zone 1/21 areas |
| PED / CE | Pressure Equipment Directive compliance | CE-marked for > 0.5 bar |
| NSF / WRAS | Potable water approval | USA (NSF 61) & EU (WRAS/KIWA) |
3. Engineering & Quality Terms
| Term | Meaning | Typical Standard |
|---|---|---|
| CAE / CFD | Computer-Aided Engineering / Computational Fluid Dynamics | ANSYS, SOLIDWORKS Flow |
| FEM | Finite Element Method (structural stress analysis) | ISO 9001 QA procedures |
| NPSH Margin | Available NPSH minus NPSHr | ≥ 1.0 m minimum |
| Vibration Grade | ISO 10816-3 class (A/B/C) | Grade A < 2.8 mm/s |
| Hydrostatic Test | Shell & seal chamber pressure test | 1.5 × MAWP, 10 min |
| Material Traceability | Mill test certificates 3.1 / 3.2 | EN 10204 |
| PED 2014/68/EU | Pressure Equipment Directive | Category II – IV |
| API 610 | Standard for centrifugal pumps in petroleum, petrochemical & gas | 11th Edition |
4. Quick Reference Acronyms
- BEP – Best Efficiency Point
- NPSHa – Net Positive Suction Head available
- NPSHr – Net Positive Suction Head required
- MAWP – Maximum Allowable Working Pressure
- MOP – Motor Over Pump
- POM – Pump Over Motor
- FDA – Food & Drug Administration (USA)
- EHEDG – European hygiene design certification
5. Procurement Checklist (Checklist bullets)
- [ ] Confirm operating temperature & pressure envelope
- [ ] Specify fluid properties (viscosity, solids, abrasiveness)
- [ ] Select seal plan (API 610 or customer spec)
- [ ] Choose material schedule (CF8M, CD4MCU, Super duplex 2507, etc.)
- [ ] Define mounting orientation & foot print constraints
- [ ] State electrical supply (voltage, frequency, insulation class)
- [ ] Agree on testing & witness points (hydrostatic, run-in)
- [ ] Finalise packaging & shipping marks for export
Bottom line:
When sourcing vertical centrifugal pumps, lock in MOQ, lead time, and certification scope early. Use API 610 or ISO 5199 as the baseline for performance and reliability.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the vertical centrifugal pump Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Vertical Centrifugal Pump Sector
Executive Summary
North American and European end-users are re-evaluating vertical centrifugal pump specifications to align with stricter energy mandates, ESG reporting, and total-cost-of-ownership (TCO) targets. Supply chains are shortening, and specification criteria are shifting toward modularity, low-carbon materials, and predictive maintenance readiness.
1. Market Dynamics
1.1 Demand Drivers
- Energy Efficiency Mandates:
- EU Ecodesign 2023/2261 sets minimum efficiency indices for pumps >7.5 kW.
- U.S. DOE 10 CFR 430 now covers frame sizes 184T-449T (≈15–150 hp).
- Sustainability Reporting:
- CSRD (EU) and SEC Climate Rule (U.S.) require Scope 3 emissions data—pumps account for 6–12 % of total industrial electricity consumption.
- Process Intensification:
- Tighter vessel clearances and space constraints in biopharma and chemical plants favor compact vertical designs.
1.2 Supply-Side Constraints
| Constraint | North America | Europe |
|---|---|---|
| Raw-material lead times | 12–16 weeks for stainless 316L | 10–14 weeks for duplex 2205 |
| Semi-conductor shortages | Affect variable-frequency drives (VFDs) | Affect high-efficiency motors (IE4/IE5) |
| Skilled labor | 8–10 % gap in certified pump technicians | 15 % gap in EU; exacerbated by Ukraine war refugees |
2. Sourcing Trends
2.1 Regionalization vs. Globalization
- Near-shoring: 38 % of U.S. chemical OEMs now source above-ground vertical pumps domestically to reduce logistics cost and customs risk (McKinsey, 2023).
- Friend-shoring: EU buyers are diversifying to Turkey, Slovenia, and Finland to retain 85–90 % EU-origin content while accessing competitive pricing.
2.2 Specification Shifts
| Legacy Criterion | New Criterion |
|---|---|
| ISO 9906 (B/B) efficiency | ISO 1328-1 (NPSH) + IE4 motor compatibility |
| Carbon steel casing | Duplex 2205 or 2507 for chloride resistance |
| Manual coupling guards | ADA-compliant, tool-free adjustability |
| Spare parts stock | Predictive-maintenance kit (vibration, temp, current) |
2.3 Digital Procurement Channels
- B2B marketplaces (e.g., EU Automation, Motion Industries) now list vertical centrifugal pumps with real-time inventory and sustainability certificates.
- RFQ automation: 62 % of EMEA procurement teams use AI-driven RFQ platforms that auto-score suppliers on carbon footprint and lead-time risk.
3. Sustainability & Circular Economy
3.1 Material Innovations
- Recycled 316L stainless: 40 % post-consumer content validated by UL 2809.
- Bio-based epoxy impellers: 30 % glass-fiber replacement with flax fiber reduces cradle-to-gate CO₂ by 18 %.
3.2 End-of-Life Programs
| Program | Coverage | Collection Points |
|---|---|---|
| Rotech EcoReturn | Full pump retirement | 42 service centers (US & DE) |
| Sulzer Recycle | 95 % material recovery | DE, NL, CH |
4. Supplier Landscape (2024)
| Tier | Key Players | Market Share | Sourcing Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global OEM | Grundfos, Sulzer, Flowserve | 42 % | Long-term frame agreements |
| Regional Champions | Rotech (US), KSB (DE), Weir (UK) | 28 % | Local stock & SDI compliance |
| Asian Value-Engineered | 3-Nordic, CNP, Ruite | 18 % | Cost + IE4 motors |
| Distributor/Integrator | ERI, DXP, AxFlow | 12 % | Aftermarket & bundling |
5. Sourcing Playbook for 2024–2025
Step 1: Pre-Qualification
- Validate ISO 9001 + ISO 14001 + ISO 45001 triad.
- Require third-party LCA (ISO 14040) for pumps >50 kW.
Step 2: Risk Mapping
- Score suppliers on:
- Supply-chain resilience (BCP plan)
- ESG scorecard (CDP, Sustainalytics)
- IP protection (FTO search)
Step 3: Contract Structure
- Include Sustainability Milestone Payments: 3 % price reduction for achieving 20 % lower cradle-to-gate CO₂ vs. baseline.
- Embed Right-to-Audit clause for recycled-content verification.
6. Key Takeaways
- Energy efficiency is now a sourcing grade equal to pressure and temperature ratings.
- Modular design reduces spare-parts inventory by 25 % and ESG risk by 30 %.
- Digital sourcing tools cut RFQ cycle time by 40 % and improve supplier transparency.
- Regionalization does not preclude global standards—expect hybrid sourcing models to dominate 2025.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vertical centrifugal pump
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
1. What is the primary advantage of a vertical centrifugal pump over a horizontal design?
Answer:
Vertical centrifugal pumps occupy up to 50 % less floor space and eliminate the need for baseplates, foot valves, and long suction pip-ing. This reduces installation cost and simplifies integration into space-constrained skids or pits.
2. Which industries typically specify vertical inline or multistage pumps?
Answer:
Typical applications span:
– Power & cogeneration (condensate, feed-water)
– HVAC & chillers (tower loops, boiler feed)
– Chemical & petrochemical (high-pressure service)
– Water & wastewater (lift stations, reverse osmosis)
– Oil & gas (refinery service, Amine units)
3. How do vertical pumps handle abrasive or solids-laden media?
Answer:
Rotech vertical inline pumps feature an open impeller and radial split casing that allow continuous pumping of liquids with up to 3 % solids by volume. The absence of an internal mechanical seal removes a common failure point in dirty service.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. What maintenance intervals and spare-part availability can we expect?
Answer:
Standard seals are field-replaceable in <30 min without special tools. All wear parts (impeller, wear ring, mechanical seal) are serialized and kept in global distribution centers. Average Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) exceeds 35,000 operating hours under normal duty.
5. Can the pump be coupled to variable-frequency drives (VFDs) for energy savings?
Answer:
Yes. All Rotech vertical pumps are supplied with a rigid coupling that is VFD-compatible. The motor frame is TEFC and pre-drilled for VFD input reactors. A 0.75 kW VFD can reduce energy consumption by 20–40 % in variable-head applications.
6. What certifications and testing are provided for European and USA markets?
Answer:
– USA: API 610 (latest edition), ISO 9906, UL/CSA electrical
– Europe: CE-marked per PED 2014/68/EU, ATEX optional, ISO 9001:2015
– Factory acceptance tests (FAT) and site acceptance tests (SAT) available with third-party witness.
7. What delivery lead times and warranty terms apply?
Answer:
– Standard pumps: 6–8 weeks ex-works
– Custom materials: 10–12 weeks
– Warranty: 24 months or 16,000 hours (whichever occurs first) on pressure-containing parts and shaft assembly.
8. How is the total cost of ownership (TCO) minimized over the pump lifecycle?
Answer:
| Lifecycle Element | Cost-Saving Feature |
|——————-|———————|
| Installation | No baseplate, foot valves, or long suction lines |
| Energy | High-efficiency IE3 motors, optimized impeller designs |
| Maintenance | Interchangeable seal, open impeller, 2-hour shutdown |
| Spare parts | Global stock, 95 % parts available within 48 h |
| Disposal | 95 % recyclable cast iron and stainless-steel components |
ROI typically achieved within 18 months for pumps running >4,000 h/year.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vertical centrifugal pump
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion & Outlook – Vertical Centrifugal Pump
Summary of Value
Vertical centrifugal pumps deliver three non-negotiable sourcing benefits:
- Space & Installation Efficiency – Single-point intake, compact footprint, and floor-mounted motor reduce civil costs by up to 30 %.
- Total Cost of Ownership – Fewer internal seals, direct-drive efficiency, and interchangeable parts cut OPEX and MTTR, driving ROI < 18 months.
- Process Reliability – Open impeller handles solids, high temperature, and pressure in one casing, minimizing unplanned shutdowns.
Outlook for North America & Europe
| Driver | Impact on Sourcing | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Energy-price volatility | Demand for high-efficiency models (IE4 motors) | Specify efficiency class up-front in RFQs |
| Chemical & hydrocarbon expansion | Higher specification materials ( duplex, Hastelloy ) | Source from vendors with mill test reports |
| ESG compliance | Reduced leakage, lower CO₂ footprint | Audit suppliers for ISO 14001 & leak-test data |
Recommended Next Steps
- Audit current fleet – Map critical applications to vertical centrifugal specifications.
- Negotiate OEM agreements – Secure preferred-vendor pricing and 24-hour spare-part inventory.
- Pilot smart monitoring – Integrate vibration & temperature sensors to validate predictive maintenance ROI.
Vertical centrifugal pumps are a strategic asset; source them with the same rigor as any core component to protect uptime, margin, and sustainability targets.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.



![Global Top 10 Industrial Pump Manufacturers [2025]](https://www.sohoinchina.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/blackridgeresearchcom-8350.jpg)


