The global insecticide market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising agricultural productivity demands and increasing pest resistance to conventional chemicals. According to Mordor Intelligence, the insecticide market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by expanding farmland and the urgent need for crop protection solutions. Within this expanding sector, venom-based insecticides—leveraging bioactive peptides derived from natural venoms—have gained attention for their targeted pest control mechanisms and lower environmental impact. Innovations in biotechnology and peptide synthesis are accelerating the commercialization of these next-generation solutions. As the demand for sustainable yet effective pest management rises, a select group of manufacturers are emerging at the forefront of venom-inspired insecticide development. Below are the top nine companies leading this niche but rapidly evolving segment.
Top 9 Venom Insecticide Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Valent BioSciences Venom Insecticide
Domain Est. 2000
Website: morr.com
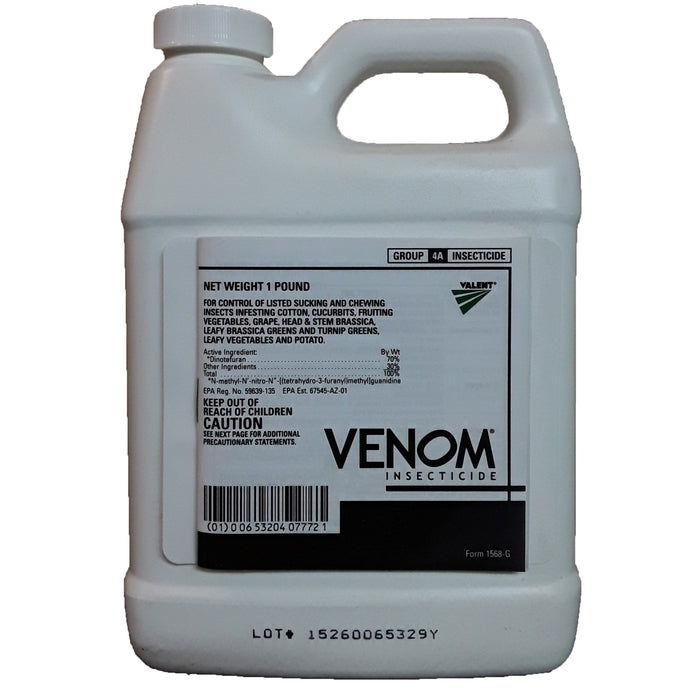
Key Highlights: Venom Insecticide is a highly concentrated, systemic insecticide containing 70% dinotefuran, a Group 4A (neonicotinoid) active ingredient….
#2 Vestaron
Domain Est. 2009
Website: vestaron.com
Key Highlights: Vestaron is leading a revolution in crop protection with new peptide technology. Our insecticides deliver powerful new modes of action to rival traditional ……
#3 Venom® Insecticide
Domain Est. 1995
Website: valent.com
Key Highlights: Venom is super-systemic, so it strikes fast to take out even the toughest pests, and it provides reliable, long-lasting control….
#4 Venom Insecticide
Domain Est. 1997
Website: greenbook.net
Key Highlights: View the product label for Venom Insecticide from Valent U.S.A. LLC Agricultural Products. See active ingredients, product application, restrictions, ……
#5 VENOM® Insecticide
Domain Est. 1998
Website: adama.com
Key Highlights: VENOM is your powerful, broad spectrum insecticide for controlling pests in kiwifruit, tomatoes, buttercup squash, pumpkins and vegetable brassicas….
#6 Venom Insecticide
Domain Est. 2002
Website: chemicalwarehouse.com
Key Highlights: In stock Free deliveryVenom is super-systemic, so it strikes fast to take out even the toughest pests and it provides long-lasting control….
#7 [PDF] venom_label.pdf
Domain Est. 2014
Website: domyown.com
Key Highlights: If using Venom Insecticide in a tank mixture, observe all directions for use, crops/sites, use rates, dilution ratios, precautions and limitations which appear ……
#8 Atticus LLC
Domain Est. 2015
Website: atticusllc.com
Key Highlights: Atticus offers a crop protection portfolio of branded-generic fungicides, herbicides and insecticides for the row crop and specialty crop agricultural ……
#9 VENOM
Domain Est. 2017
Expert Sourcing Insights for Venom Insecticide

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Venom Insecticide
The global market for insecticides is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by evolving regulatory standards, increasing demand for sustainable agriculture, and technological advancements in pest management. Within this context, Venom Insecticide—a product known for its active ingredient, dinotefuran, a neonicotinoid-class compound—faces both opportunities and challenges that will shape its market trajectory.
1. Regulatory and Environmental Pressures
By 2026, regulatory scrutiny on neonicotinoids remains a dominant factor influencing Venom’s market performance. Due to concerns over pollinator health—particularly bee populations—several regions, including the European Union and parts of North America, continue to restrict or ban certain neonicotinoid applications. This regulatory environment limits Venom’s usage in foliar sprays on flowering crops, constraining its adoption in key agricultural sectors like orchards and oilseed production. However, targeted uses such as soil drenching, seed treatments, and non-agricultural pest control (e.g., in turf and ornamental plants) offer compliant avenues for continued market presence.
2. Demand in Specialty Crops and Urban Pest Control
Venom Insecticide is projected to maintain strong demand in niche markets. Its efficacy against sap-feeding insects such as aphids, whiteflies, and thrips makes it valuable in high-value specialty crops, including vegetables, fruits, and greenhouse-grown plants. Additionally, urban and residential pest control applications—where integrated pest management (IPM) practices incorporate selective chemical controls—support steady demand. By 2026, urbanization and increased focus on landscape maintenance in emerging economies are expected to expand these markets.
3. Shift Toward Sustainable and Precision Agriculture
The agriculture sector is increasingly adopting precision application technologies and sustainable practices. Venom’s systemic mode of action allows for lower application rates and reduced environmental runoff when applied correctly. As farmers seek effective yet environmentally responsible tools, Venom may benefit from integration into IPM programs, especially when used in rotation with biopesticides or non-chemical controls to delay resistance development.
4. Competition and Market Differentiation
Venom faces stiff competition from newer chemistries, bio-based insecticides, and generic alternatives to neonicotinoids. By 2026, its market position will depend on strategic differentiation—such as formulation improvements, combination products, and technical support for responsible use. Manufacturers may emphasize Venom’s rapid uptake and translaminar movement to highlight performance advantages over alternatives.
5. Regional Market Dynamics
In Asia-Pacific and Latin America, where regulatory frameworks are less restrictive and demand for crop protection solutions is growing, Venom is likely to see expanded use—particularly in countries with large vegetable and cotton industries. Conversely, in North America and Europe, market growth will be constrained unless new data emerges supporting its safe use under specific conditions or new formulations reduce off-target exposure.
Conclusion
By 2026, Venom Insecticide is expected to occupy a specialized but stable segment of the global insecticide market. While regulatory and environmental challenges limit broad-scale use, its effectiveness in controlled applications ensures continued relevance in high-value agriculture and urban pest management. Success will depend on responsible marketing, compliance with evolving regulations, and integration into sustainable pest control strategies.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Venom Insecticide (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing Venom Insecticide—whether for agricultural use, pest control distribution, or resale—can present several challenges, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) rights. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure compliance, efficacy, and legal safety.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Counterfeit or Substandard Products
One of the most common risks when sourcing Venom Insecticide is encountering counterfeit or diluted formulations. Unscrupulous suppliers may offer products that mimic the branding and packaging of legitimate versions but contain incorrect active ingredient concentrations or inert, ineffective substitutes. This compromises pest control effectiveness and may lead to crop damage or resistance development.
2. Lack of Third-Party Testing and Certifications
Reputable insecticides undergo rigorous quality control and are backed by certifications from regulatory bodies (e.g., EPA in the U.S., PMRA in Canada, or equivalent agencies). Sourcing from suppliers who cannot provide certificates of analysis (COA), safety data sheets (SDS), or registration documents increases the risk of receiving low-quality or non-compliant products.
3. Inconsistent Batch Quality
Even when sourcing from legitimate manufacturers, inconsistent manufacturing practices can result in batch-to-batch variability in potency and performance. This is especially prevalent with overseas suppliers lacking stringent quality management systems (e.g., ISO certification).
4. Improper Storage and Handling During Transit
Venom Insecticide may degrade if exposed to extreme temperatures, moisture, or sunlight during shipping. Sourcing through unreliable logistics channels without temperature-controlled transport can compromise product integrity before it reaches the end user.
Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
1. Trademark and Brand Infringement
“Venom Insecticide” may be a registered trademark owned by a specific agrochemical company. Sourcing generic versions that use identical or confusingly similar branding, logos, or product names can lead to legal action for trademark infringement, even if the chemical composition is similar.
2. Patent Infringement on Formulation or Method of Use
The active ingredient(s) in Venom Insecticide may be protected by composition-of-matter patents, or its specific formulation, delivery system, or method of application may be patented. Producing or importing a chemically identical product before patent expiry can result in costly litigation.
3. Unauthorized Manufacturing or Distribution Rights
Only authorized distributors or licensees may legally sell or distribute branded insecticides in many jurisdictions. Sourcing Venom Insecticide from unauthorized resellers—even if the product is genuine—can violate distribution agreements and expose the buyer to liability, especially if the product is diverted from its intended market.
4. Grey Market Imports and IP Violations
Purchasing Venom Insecticide from international grey markets may appear cost-effective but often breaches territorial IP rights. Many manufacturers enforce regional exclusivity, and importing branded products without permission can constitute parallel importation, leading to seizure by customs or legal consequences.
Best Practices to Avoid Pitfalls
– Verify supplier credentials and regulatory compliance.
– Request full product documentation, including COAs and registration proofs.
– Conduct due diligence on IP status (trademarks, patents) in your target market.
– Source only through authorized distributors or under proper licensing.
– Use legal counsel to review supply agreements for IP and quality assurance clauses.
By addressing both quality and IP concerns proactively, businesses can mitigate risks and ensure they are sourcing effective, legal, and reliable pest control solutions.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Venom Insecticide
Product: Venom Insecticide (Active Ingredient: Dinotefuran)
Formulation: Water-dispersible granules (WDG)
EPA Registration Number: [Insert EPA Reg. No. – e.g., 66568-78]
Manufacturer: [Insert Manufacturer Name – e.g., Valent USA Corporation]
Primary Use: Systemic insecticide controlling sucking insects (aphids, whiteflies, thrips, etc.) on various crops.
H2: Storage & Handling Requirements
-
Storage Conditions:
- Temperature: Store in a cool, dry place between 40°F (4°C) and 100°F (38°C). Avoid freezing and prolonged exposure to excessive heat.
- Environment: Store in original, tightly closed container in a well-ventilated, secure area (e.g., locked pesticide storage cabinet/shed) separate from food, feed, fertilizers, seeds, and other incompatible chemicals.
- Humidity: Protect from moisture. Keep containers dry to prevent caking and degradation.
- Light: Store away from direct sunlight.
-
Handling Procedures:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear chemical-resistant gloves, long-sleeved shirt, long pants, and shoes plus socks when handling the concentrated product. Wear protective eyewear if splashing is possible (e.g., during mixing). Refer to the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and product label for specific PPE requirements.
- Hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling, before eating, drinking, chewing gum, or using the toilet. Remove contaminated clothing and wash it separately before reuse.
- Contamination Prevention: Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing. Do not breathe dust or mist. Do not eat, drink, or smoke while handling.
- Spills: Contain spills immediately. Use absorbent material (e.g., vermiculite, sand, kitty litter) to soak up liquid. Collect contaminated material and place in a suitable, labeled container for disposal according to local regulations. Clean the area thoroughly with water and detergent. Report significant spills as required by law.
H2: Transportation Regulations (US Focus – Consult Local/International Rules)
- Classification: Venom Insecticide (WDG) is generally classified as a Pesticide – Technical or Pesticide – Formulation for transport. It is typically NOT classified as a Hazardous Material (HazMat) under US DOT 49 CFR when transported in its original, unopened retail packaging meeting specific criteria (e.g., inner packaging < 1 oz / 30g for solids, outer packaging < 119 fl oz / 3.5L for liquids – VERIFY against specific product packaging and current regulations). ALWAYS CONFIRM THE EXACT CLASSIFICATION AND EXEMPTION STATUS FOR THE SPECIFIC PRODUCT AND PACKAGING SIZE BEING TRANSPORTED.
- Packaging: Must be transported in the original, unopened manufacturer’s container. Ensure containers are securely closed. Outer packaging (e.g., box) must be strong enough to prevent breakage and leakage under normal transport conditions. Package must be clearly labeled with the product name, EPA Reg. No., and net contents.
- Documentation:
- Bill of Lading (BOL): Clearly identify the product by name (Venom Insecticide) and EPA Reg. No. Include shipper/consignee details.
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Must be readily available to transport personnel during transit (e.g., in the cab of the vehicle). Provide a copy to the receiver upon delivery.
- Segregation: Do not transport with food, feed, fertilizers, or incompatible chemicals (e.g., strong oxidizers, strong acids/bases). Segregate according to carrier and regulatory requirements.
- Vehicle Requirements: Ensure vehicles are clean, dry, and in good condition. Secure loads to prevent shifting, damage, or leakage. Protect from weather. Avoid transporting in passenger compartments.
- Driver Requirements: Drivers must be trained in basic hazardous materials awareness (if applicable) and emergency response procedures. They must know the location and use of the SDS.
- International/Other Regions: For transport outside the US, comply with relevant international regulations (e.g., IMDG Code for sea, IATA DGR for air, ADR for Europe). Classification and requirements may differ significantly. Consult with the carrier and regulatory authorities well in advance.
H2: Regulatory Compliance
-
Label Compliance:
- Primary Rule: THE LABEL IS THE LAW. Strictly follow all use instructions, application rates, target pests, crops/sites, pre-harvest intervals (PHI), restricted entry intervals (REI), and precautions on the current, approved product label.
- EPA Registration: Ensure the product is registered for use in the state/country of application. Registration status can change.
- Label Updates: Regularly check the manufacturer’s website or contact them for updated labels. Use only the most current label.
-
Recordkeeping:
- Maintain detailed pesticide application records as required by federal (e.g., FIFRA) and state/provincial laws. Records typically must include:
- Product name and EPA Reg. No.
- Date and time of application.
- Location (field, block, site).
- Crop/site treated.
- Target pest(s).
- Application rate and total amount used.
- Method of application (e.g., ground spray, aerial, soil drench).
- Weather conditions.
- Applicator’s name, license number (if required), and signature.
- REI observed.
- Retain records for the duration specified by law (often 2-3 years minimum).
- Maintain detailed pesticide application records as required by federal (e.g., FIFRA) and state/provincial laws. Records typically must include:
-
Applicator Certification:
- Certified Applicators: In the US, applying restricted-use pesticides (RUPs) requires certification. VERIFY IF VENOM INSECTICIDE IS CLASSIFIED AS AN RUP IN THE TARGET JURISDICTION. Even if classified as General Use, commercial applicators often need state licensing.
- Training: Ensure all personnel handling or applying the product are trained on the label, SDS, PPE, application techniques, and emergency procedures.
-
Environmental Protection:
- Pollution Prevention: Prevent runoff, drift, and spills into water bodies (streams, ponds, lakes, ditches, storm drains), wetlands, or non-target areas. Follow label buffer zones.
- Endangered Species: Comply with any Endangered Species Act (ESA) consultation requirements or use limitations (e.g., Bulletins Live! Two) specific to the application area. Check the EPA website.
- Pollinator Protection: Follow all label precautions regarding pollinators (bees, butterflies). Avoid application during bloom, when bees are actively foraging, or on windy days. Consider using buffer zones.
-
Waste Disposal:
- Triple Rinse: Triple rinse empty containers according to label instructions. Add rinsate to the spray tank. Puncture or crush rinsed containers to prevent reuse.
- Disposal: Dispose of empty, properly rinsed containers and any unused product or rinse water according to label directions and all applicable federal, state, and local regulations. NEVER pour pesticides or rinsate down drains, toilets, or onto the ground. Contact local waste management authorities for household hazardous waste (HHW) disposal programs or agricultural chemical collection events.
-
Reporting:
- Report any adverse effects (e.g., crop injury, environmental contamination, human/animal incidents) to the manufacturer and relevant regulatory agency (e.g., State Lead Agency, EPA) as required.
H2: Emergency Procedures
- Spills: See “Handling Procedures” above. Evacuate area if large spill creates dust cloud. Call emergency services if necessary.
- Fire: Use water spray, alcohol-resistant foam, dry chemical, or carbon dioxide to extinguish. Fire produces irritating vapors. Wear full protective gear (including SCBA) during firefighting.
- First Aid:
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. Seek medical attention immediately.
- Skin Contact: Wash immediately with plenty of soap and water. Remove contaminated clothing. Seek medical attention.
- Eye Contact: Flush immediately with clean water for at least 15 minutes, lifting upper and lower eyelids occasionally. Seek immediate medical attention.
- Ingestion: Do NOT induce vomiting unless directed by medical personnel. Call a poison control center or doctor immediately. Have the product container or label available.
- Emergency Contacts:
- Manufacturer/Emergency Hotline: [Insert Manufacturer Emergency Phone Number – e.g., Valent: 1-800-628-3285]
- National Poison Control Center (US): 1-800-222-1222
- Local Emergency Services: 911 (or local equivalent)
Disclaimer: This guide provides general information based on typical regulations and product characteristics. ALWAYS CONSULT THE MOST CURRENT PRODUCT LABEL, SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS), AND APPLICABLE FEDERAL, STATE, PROVINCIAL, AND LOCAL REGULATIONS FOR THE SPECIFIC JURISDICTION AND SITUATION. Regulations and product formulations can change. The manufacturer and distributor are the primary sources for authoritative information.
Conclusion for Sourcing Venom Insecticide:
Sourcing Venom insecticide requires a careful evaluation of quality, supplier reliability, regulatory compliance, and cost-effectiveness. Venom, known for its potent active ingredients and effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pests, is a valuable tool in integrated pest management programs. Ensuring that the product is sourced from authorized and reputable suppliers guarantees authenticity, proper formulation, and adherence to safety and environmental standards. Additionally, verifying certifications, checking shelf life, and confirming logistical capabilities are essential steps to maintain supply chain integrity. Ultimately, strategic sourcing of Venom insecticide not only supports effective pest control but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices and long-term crop protection.


![[PDF] venom_label.pdf](https://www.sohoinchina.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/pdf-venom-labelpdf-798.jpg)