The global veneer saw manufacturing industry is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for engineered wood products and sustainable timber alternatives in construction, furniture, and interior design. According to Grand View Research, the global wood-based panels market—integral to veneer production—was valued at USD 256.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a CAGR of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. As veneer processing represents a critical stage in panel manufacturing, this growth directly translates into increased demand for high-precision veneer saws. Mordor Intelligence further supports this trajectory, forecasting the woodworking machinery market to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2023 to 2028, citing advancements in automated cutting systems and rising industrialization in Asia-Pacific and Latin America. With efficiency, accuracy, and yield optimization becoming paramount in veneer production, manufacturers are increasingly investing in advanced sawing technology. In this evolving landscape, the following eight companies have emerged as leading veneer saw manufacturers, combining engineering excellence, innovation, and global reach to meet the sector’s growing demands.
Top 8 Veneer Saw Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Kuper FSH Veneer Saw
Domain Est. 1996
Website: stilesmachinery.com
Key Highlights: The Kuper FSH Veneer Saw is your ultimate solution for tear-free, precise parallel cutting for all veneer thicknesses. Engineered for excellence, this machine ……
#2 Veneer Saw HBX
Domain Est. 1997
Website: hultafors.com
Key Highlights: Out of stockProfessional veneer saw for precision cut and flooring. The blade has a radius shaped tip with teeth in order to make a cut in the center of a board….
#3 Veneer Saw
Domain Est. 2000
Website: tchristy.com
Key Highlights: Features. 12″ Veneer Saw; Suitable for Wood, Plastic, and Porous Materials; 12″ Veneer Saw. Product Description. Item # 514602. Veneer Saw – Bahco….
#4 ThinStone® TXS-4000 Series
Domain Est. 2001
Website: parkindustries.com
Key Highlights: Rating 5.0 (5) Our patented ThinStone® TXS-4000 series veneer saws make cutting thinstone veneer flats and 90-degree corners quick, simple, and profitable….
#5 Veneering Tools & Supplies for Your Next Veneer Project
Domain Est. 2003
#6 Thin veneer saws
Domain Est. 2007
Website: gestracz.com
Key Highlights: Thin veneer saws. Gestra CZ has entered into a strategic partnership with Yonani Industries Ltd, a world’s leading company who specializes in manufacturing ……
#7 Thin-Stone Veneer Saws
Domain Est. 2010
Website: poseidonmachinery.com
Key Highlights: Poseidon Industries manufactures world-class thin veneer stone saws that provide high accuracy cutting of thin layers of stone, granite, and marble….
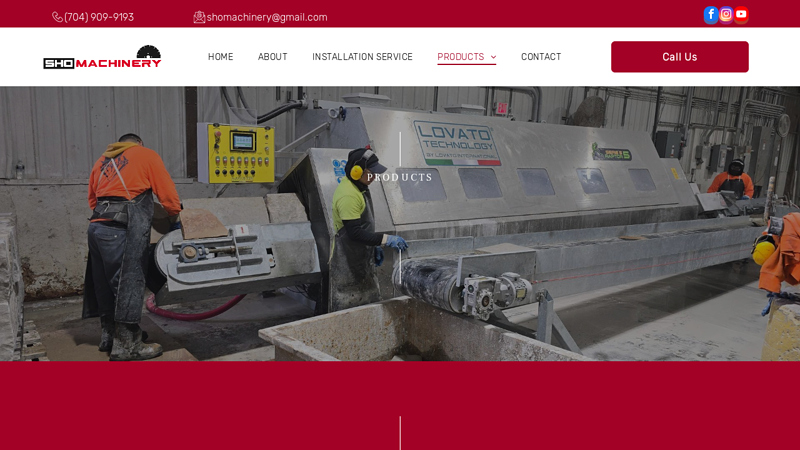
#8 Stone Veneer Machinery for Sale
Domain Est. 2021
Website: shomachinery.com
Key Highlights: SHO Machinery provides a full line of advanced stone veneer machinery, designed for performance, precision, and durability in real-world production ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Veneer Saw

H2 2026 Market Trends for Veneer Saws
The veneer saw market in H2 2026 is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving sustainability demands, and shifting global economic dynamics. Key trends shaping the industry include:
1. Accelerated Adoption of Automation and Smart Technology:
Veneer saws are increasingly integrating AI-driven optimization, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance. Smart saws equipped with IoT sensors enable remote diagnostics and data analytics, improving yield, reducing downtime, and enhancing precision. By H2 2026, fully automated lines with minimal human intervention are expected to become standard in medium-to-large veneer mills, particularly in North America and Europe.
2. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency as Competitive Advantages:
Environmental regulations and corporate ESG goals are pushing manufacturers to develop energy-efficient saws with lower carbon footprints. Demand is rising for machines using recycled materials in construction and optimized power consumption. Additionally, precision cutting reduces wood waste, aligning with circular economy principles—this will be a major selling point in eco-conscious markets.
3. Rising Demand from Emerging Markets:
Growth in construction and furniture industries in Southeast Asia (e.g., Vietnam, Indonesia) and parts of Africa is driving demand for cost-effective, reliable veneer saws. Localized production and tailored machine configurations for smaller operations will be critical for market penetration. Chinese manufacturers are expected to dominate this segment with competitively priced, modular saw systems.
4. Shift Toward Thinner and Specialty Veneers:
The trend toward ultra-thin and engineered wood products (like laminated veneer lumber) requires saws with enhanced precision and reduced kerf loss. High-frequency oscillating saws and laser-guided systems are gaining traction to maintain veneer integrity during slicing. Suppliers investing in R&D for thin-veneer applications will gain a strategic edge.
5. Supply Chain Resilience and Localization:
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and logistics disruptions are prompting veneer producers to shorten supply chains. This favors regional manufacturing of veneer saws and increased after-sales service networks. European and North American OEMs are expanding local support centers to ensure faster maintenance and parts delivery.
6. Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships:
The market is seeing consolidation among equipment suppliers, with larger players acquiring niche technology firms to enhance digital capabilities. Partnerships between saw manufacturers and software providers (e.g., for yield optimization algorithms) are becoming common, offering integrated solutions that improve overall productivity.
Conclusion:
By H2 2026, the veneer saw market will be defined by intelligence, sustainability, and adaptability. Success will depend on manufacturers’ ability to deliver high-precision, energy-efficient, and digitally connected systems that meet the diverse needs of a global and increasingly eco-aware customer base. Companies that innovate rapidly and align with circular economy goals will lead the next phase of industrial evolution in wood processing.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Veneer Saws: Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing veneer saws—especially from international or unfamiliar suppliers—exposes buyers to several critical pitfalls, particularly concerning product quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Avoiding these risks is essential to ensure operational efficiency, legal compliance, and long-term cost savings.
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Performance
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing veneer saws is inconsistent product quality. Suppliers—especially low-cost manufacturers—may use substandard materials, imprecise manufacturing processes, or inadequate testing procedures. This can lead to premature wear, inaccurate cuts, increased downtime, and higher maintenance costs. Buyers might receive units that fail to meet industry standards or perform reliably under continuous operation.
Key Red Flags:
– Lack of documented quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001)
– Inconsistent tolerances or blade alignment across units
– Use of inferior bearings, motors, or blade materials
– Minimal or no post-production performance testing
Misrepresentation of Technical Specifications
Suppliers may exaggerate or misrepresent technical capabilities such as cutting speed, precision, maximum log diameter, or automation features. This misalignment between promised and actual performance can disrupt production planning and reduce yield. For example, a saw advertised for high-speed precision slicing may deliver rough cuts unsuitable for premium veneer applications.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Veneer saw designs—especially advanced models with proprietary automation, blade tensioning systems, or control software—often involve protected intellectual property. Unethical suppliers may produce “clone” machines that infringe on patents, trademarks, or design rights held by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). Purchasing such equipment exposes the buyer to legal liability, shipment seizures, or reputational damage.
Risks Include:
– Importing machines that violate active patents in your country
– Use of counterfeit software or control systems
– Legal action from OEMs for contributory infringement
– Inability to obtain genuine spare parts or firmware updates
Lack of After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Low-cost suppliers may offer attractive upfront pricing but provide little to no after-sales service. When machines break down, sourcing compatible spare parts can become a challenge, especially if components are reverse-engineered or undocumented. This leads to prolonged downtime and increased total cost of ownership.
Inadequate Documentation and Compliance
Sourced machinery may lack essential technical documentation, safety certifications (e.g., CE, UL), or compliance with local environmental and labor regulations. This can result in installation delays, safety hazards, or failure to pass regulatory inspections.
How to Mitigate These Risks
- Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including factory audits and reference checks.
- Require third-party inspection reports and performance testing before shipment.
- Verify IP status through patent searches and legal counsel.
- Insist on clear technical documentation, warranties, and service agreements.
- Work with reputable distributors or OEMs directly when possible.
By proactively addressing quality and IP concerns, buyers can ensure reliable, legal, and cost-effective sourcing of veneer saws.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Veneer Saw
Overview
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the transportation, import/export, and safe handling of Veneer Saws—industrial cutting equipment used in woodworking and veneer production. Adhering to these guidelines ensures regulatory compliance, operational safety, and efficient supply chain management.
Regulatory Compliance
International Trade Regulations
Veneer Saws may be subject to export control regulations depending on their specifications (e.g., automation level, cutting precision). Ensure compliance with:
– Export Administration Regulations (EAR) – Administered by the U.S. Department of Commerce; check Commerce Control List (CCL) for classification (ECCN).
– Customs Tariff Classification (HS Code) – Typically falls under HS Code 8465.95 (Machinery for working wood) depending on design. Verify with local customs authority.
– Import/Export Licenses – Required for certain destinations, especially high-risk or embargoed countries.
Safety and Equipment Standards
Veneer Saws must meet safety and performance standards in the destination market:
– CE Marking (EU) – Compliance with Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, including risk assessments, electrical safety (EN 60204-1), and mechanical safety standards.
– UL/CSA Certification (North America) – Required for electrical components and overall equipment safety.
– ISO Standards – Adherence to ISO 13857 (safety of machinery – distances to prevent hazard zones) and ISO 12100 (risk assessment).
Packaging and Handling
Secure Packaging
- Use wooden crates or reinforced pallets with corner protectors to prevent damage during transit.
- Immobilize moving parts (blades, arms) using locking mechanisms or braces.
- Apply moisture-resistant wrapping to prevent corrosion during sea freight.
Labeling Requirements
- Clearly label packages with:
- “Fragile” and “This Side Up” indicators
- Weight, dimensions, and center of gravity markings
- Handling instructions (e.g., “Do Not Stack”)
- Compliance marks (CE, UL, etc.)
- Serial number and model identification
Transportation Logistics
Mode of Transport
- Sea Freight (FCL/LCL): Most cost-effective for heavy machinery. Use container desiccants to control humidity.
- Air Freight: Suitable for urgent deliveries; ensure weight and size comply with airline restrictions.
- Overland (Truck/Rail): Ideal for regional distribution; use suspension-equipped trailers to minimize vibration.
Freight Documentation
Prepare and verify the following documents:
– Commercial Invoice (with detailed description and value)
– Packing List (itemizing contents per package)
– Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– Export Declaration and Import Permit (if required)
– Equipment Test/Conformity Certificate
Import/Export Clearance
Customs Clearance
- Provide accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes to determine duty rates and restrictions.
- Declare any dual-use components that may trigger additional scrutiny.
- Partner with licensed customs brokers in destination countries to streamline clearance.
Duties and Taxes
- Calculate applicable tariffs, VAT, or GST based on destination country regulations.
- Leverage Free Trade Agreements (e.g., USMCA, CETA) where eligible to reduce duties.
Installation and On-Site Compliance
Pre-Installation Inspection
- Verify equipment was not damaged during transit.
- Confirm all safety guards, emergency stops, and manuals are present and in local language.
Workplace Safety Compliance
- Ensure installation complies with local occupational safety regulations (e.g., OSHA in the U.S., HSE in the UK).
- Conduct operator training on safe use, lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures, and maintenance.
- Implement dust extraction systems to meet air quality standards (e.g., OSHA PEL for wood dust).
Maintenance and Documentation Retention
Record Keeping
- Maintain records of:
- Compliance certifications
- Maintenance logs
- Operator training
- Incident reports
- Retain documentation for minimum of 5–7 years, per regulatory requirements.
Scheduled Maintenance
- Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance to ensure continued compliance and safety.
- Document blade changes, calibration, and safety inspections.
Conclusion
Proper logistics planning and strict adherence to compliance standards are crucial when shipping and operating Veneer Saws globally. By following this guide, businesses can minimize delays, avoid penalties, and ensure safe and efficient deployment of equipment. Always consult local regulators and legal experts for jurisdiction-specific requirements.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, sourcing a veneer saw requires careful consideration of several key factors including precision, blade quality, cutting capacity, automation features, and after-sales support. The right veneer saw should align with the specific production requirements, whether for small-batch artisanal work or large-scale industrial operations. Prioritizing durability, accuracy, and ease of maintenance ensures long-term efficiency and reduces operational downtime. Additionally, partnering with reputable suppliers who offer technical expertise and reliable service support is crucial for optimal performance. By thoroughly evaluating machine specifications, cost-effectiveness, and future scalability, businesses can make a strategic investment that enhances veneer processing quality and overall productivity.