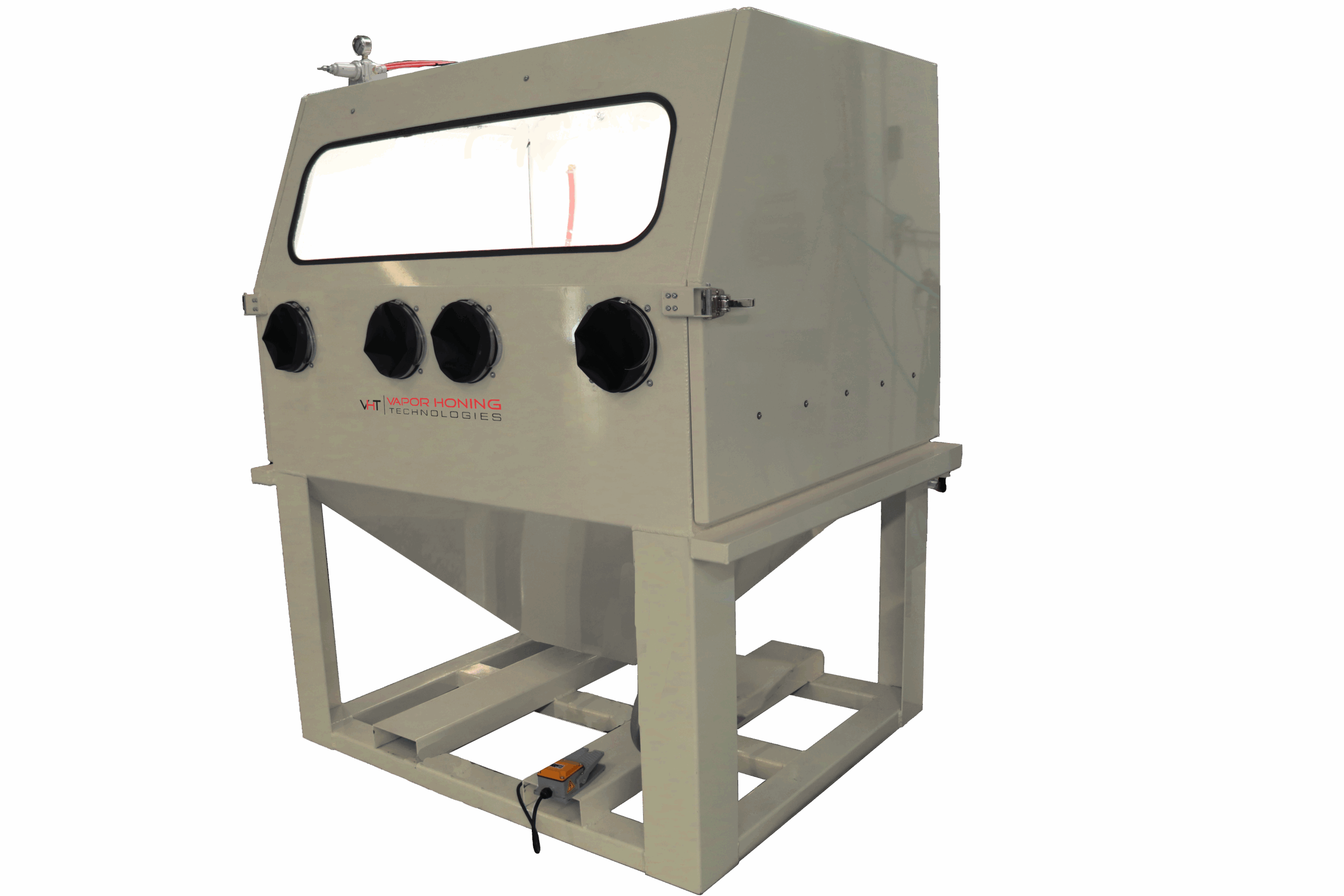
The vapor blasting cabinet market has experienced steady growth driven by increasing demand for precision surface finishing across automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing industries. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global wet blasting equipment market was valued at USD 582 million and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2023 to 2028. This growth is fueled by the rising need for non-destructive cleaning methods that preserve part integrity while removing contaminants. Vapor blasting, known for its eco-friendly process and superior finish compared to traditional sandblasting, is becoming a preferred solution in high-tolerance applications. As industries prioritize sustainable and efficient surface treatment technologies, investment in advanced vapor blast cabinets is on the rise. Based on production capabilities, innovation, market reach, and customer reviews, the following eight manufacturers have emerged as leaders in delivering reliable and high-performance vapor blasting systems.
Top 8 Vapor Blast Cabinet Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 SurfacePrep
Domain Est. 1995
Website: surfaceprep.com
Key Highlights: SurfacePrep is the largest network of distributors of blasting and vibratory media, specialty abrasives, and industrial blasting equipment….
#2 Sand, Abrasive, Wet and Vapor Blaster Cabinets
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mediablast.com
Key Highlights: Media Blast & Abrasive, Inc. provides sandblasting, abrasive blasting, and wet vapor blasting cabinet solutions made in the USA. Shop now!…
#3 Vapor Blasting Systems by Wet Technologies
Domain Est. 1998 | Founded: 1999
Website: wettechnologies.com
Key Highlights: We engineer & manufacture high-quality wet (vapor) slurry blasting & high-pressure water systems. Leading vapor blasting technology & innovation since 1999….
#4 Vapor Blasting Equipment
Domain Est. 1999
Website: bcscompany.com
Key Highlights: A global manufacturer of blast equipment for just about any blasting operation, including stock and custom blast machines, wetblast systems, safety equipment….
#5 Vapor Blast
Domain Est. 2000
Website: vaporblast.net
Key Highlights: Vapor Blast Manufacturing Company is proudly owned and operated by Vapor Honing Technologies, a leading U.S. manufacturer specializing in advanced surface ……
#6 Wet Blast Cabinet RB3630S
Domain Est. 2015
Website: raptorblaster.com
Key Highlights: The RB3630S is a heavy duty, industrial-use wet blast cabinet. Like all our sandblasting cabinets, our vapor blast cabinets are 100% laser cut and hand welded….
#7 Vapor Blast Manufacturing Company
Domain Est. 2000
Website: sandblastequipment.com
Key Highlights: Sandblast cabinets include systems or machinery and components for projecting blast media against a part’s surface to abrade, clean, or modify the surface. Sand ……
#8 Vapor Blasting Equipment for Sale
Domain Est. 2013
Website: vaporhoningtechnologies.com
Key Highlights: We are a US business based in Lincolnton, NC, where we manufacture and sell all of our equipment. We promise to produce quality machines….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Vapor Blast Cabinet
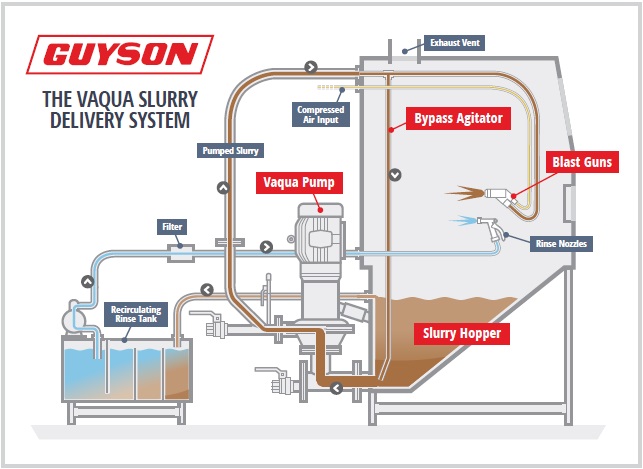
H2: 2026 Market Trends for Vapor Blast Cabinets
The global market for vapor blast cabinets is projected to experience notable growth and transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for eco-friendly surface treatment solutions, and expanding applications across key industries. As manufacturers seek cleaner, more efficient alternatives to traditional abrasive blasting methods, vapor blast cabinets—also known as wet blasting or slurry blasting systems—are emerging as a preferred solution. Below are the key trends shaping the vapor blast cabinet market in 2026:
-
Rising Emphasis on Environmental Sustainability
With stricter environmental regulations and growing corporate sustainability goals, industries are shifting away from dry abrasive blasting, which generates harmful dust and particulate matter. Vapor blast cabinets use a mixture of water, abrasive media, and surfactants, significantly reducing airborne contaminants. This eco-conscious advantage positions vapor blasting as a compliant and responsible choice, particularly in North America and Europe, where environmental standards are stringent. -
Adoption in Automotive and Aerospace Manufacturing
The automotive and aerospace sectors are major drivers of market growth. Vapor blasting is increasingly used to clean, deburr, and surface-finish sensitive components—such as engine parts, turbine blades, and aluminum housings—without causing thermal or mechanical damage. By 2026, OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers are expected to integrate vapor blast cabinets into their production and reconditioning lines to improve part longevity and surface quality. -
Growth in Industrial Maintenance and Restoration
The demand for vapor blast cabinets is rising in industrial maintenance, particularly for restoring molds, dies, and tooling. Unlike dry blasting, vapor blasting minimizes surface erosion and retains dimensional tolerances, making it ideal for precision tool reconditioning. This trend is especially strong in the plastics, die-casting, and injection molding industries. -
Technological Innovations and Automation
By 2026, vapor blast cabinets are expected to incorporate advanced automation, IoT integration, and closed-loop water recycling systems. Manufacturers are introducing robotic arms and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to enable consistent, repeatable surface finishes with minimal operator intervention. These smart systems improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and support Industry 4.0 initiatives. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
While North America and Europe lead in adoption, the Asia-Pacific region—particularly China, India, and South Korea—is witnessing rapid growth in the vapor blast cabinet market. This is fueled by expanding manufacturing sectors, infrastructure development, and rising awareness of surface treatment technologies. Local manufacturers are also beginning to produce cost-effective vapor blasting systems, increasing accessibility. -
Shift Toward Closed-Loop and Water Recycling Systems
Water conservation is becoming a key consideration. Leading vapor blast cabinet models in 2026 are expected to feature integrated water filtration and recycling technologies, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. This trend supports compliance with water discharge regulations and appeals to environmentally responsible enterprises. -
Increased Customization and Modular Designs
End-users are seeking customizable solutions tailored to specific applications, such as high-pressure cleaning for medical devices or gentle finishing for 3D-printed metal parts. Modular vapor blast cabinets that can be scaled or reconfigured for different workflows are gaining popularity, especially among job shops and contract manufacturers.
Conclusion
By 2026, the vapor blast cabinet market is poised for robust growth, underpinned by environmental regulations, technological innovation, and expanding industrial applications. As companies prioritize sustainability, precision, and operational efficiency, vapor blasting is expected to become a standard surface preparation method across multiple sectors. Manufacturers that invest in automation, water recycling, and application-specific designs will likely gain a competitive edge in this evolving landscape.
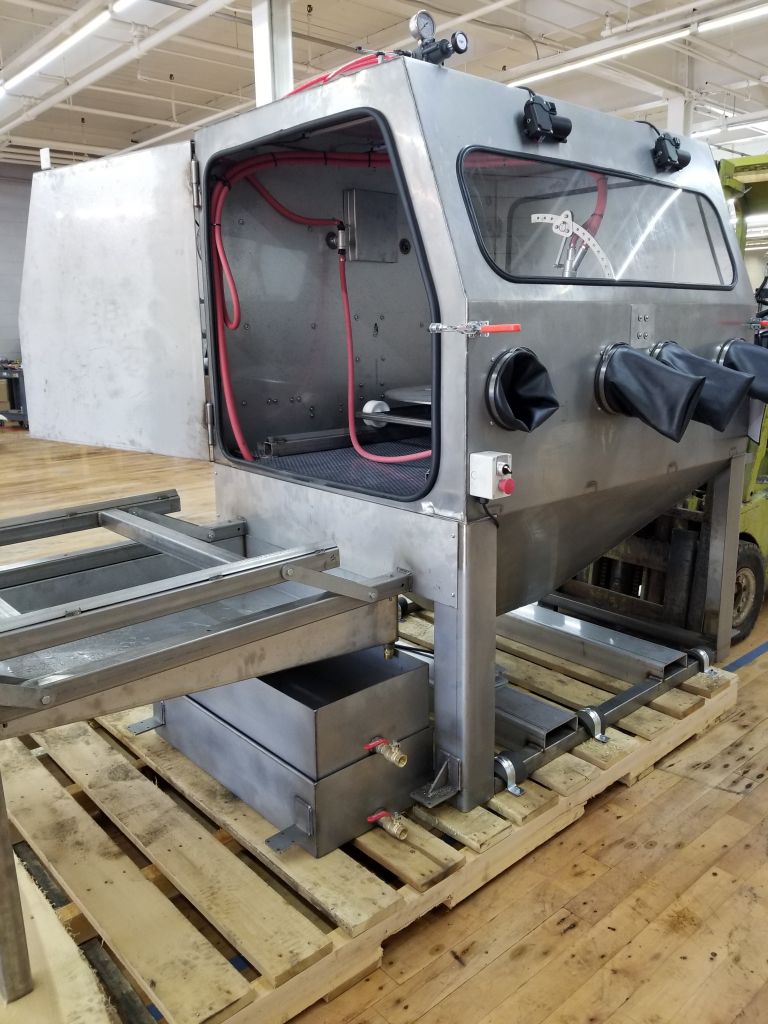

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Vapor Blast Cabinet (Quality & IP)
Sourcing a vapor blast cabinet—also known as wet blasting or slurry blasting equipment—requires careful evaluation to avoid costly mistakes. Buyers often face challenges related to equipment quality, performance consistency, and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these common pitfalls helps ensure you invest in reliable, compliant, and effective equipment.
Poor Build Quality and Material Selection
One of the most frequent issues is receiving a vapor blast cabinet constructed with substandard materials. Cabinets exposed to abrasive slurries and moisture must be made from corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel (typically 304 or 316). Some suppliers cut costs by using mild steel with inadequate coatings, leading to premature rust, leaks, and structural failure. Poor weld quality, thin wall construction, and low-grade seals or viewing windows further compromise durability and operator safety.
Tip: Always verify material specifications and request proof of stainless steel grade. Inspect sample units or existing installations if possible.
Inadequate or Misrepresented Blasting Performance
Many suppliers overstate key performance metrics such as blast pressure, media delivery consistency, or cycle times. Some systems use undersized pumps or poorly designed nozzles that result in inconsistent surface finishes or inefficient processing. Poor agitation systems can cause media settling, leading to clogs and uneven blasting.
Tip: Request third-party performance data or conduct on-site testing. Ask for references from existing customers in your industry.
Lack of Compliance with Safety and Environmental Standards
Low-cost or unverified suppliers may overlook critical safety features such as proper ventilation, dust suppression, emergency stops, or CE/UL certification. Non-compliant cabinets pose health risks from airborne particulates and chemical exposure, and may not meet OSHA or local regulatory requirements.
Tip: Confirm that the cabinet meets relevant safety standards (e.g., CE, UL, ANSI) and includes essential safety systems like interlocks and HEPA filtration.
Limited or No Intellectual Property Protection
When sourcing from manufacturers—especially overseas—there’s a risk of purchasing equipment that infringes on patented technologies. Some suppliers replicate proprietary designs (e.g., closed-loop media recycling systems, specialized nozzle manifolds, or slurry mixing mechanisms) without licensing. If your business uses such equipment, you could face legal exposure, supply chain disruptions, or forced equipment replacement.
Tip: Work with reputable suppliers who can provide IP documentation or proof of licensing. Include IP indemnity clauses in procurement contracts.
Poor After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Even high-quality cabinets require maintenance, but some suppliers—particularly those based overseas—offer limited technical support or long lead times for spare parts. This can result in extended downtime and increased operating costs.
Tip: Evaluate the supplier’s service network, response time, and spare parts inventory before purchase. Prefer vendors with local support or clear service agreements.
Hidden Costs from Incomplete Systems
Some quotes appear competitive but exclude essential components such as media reclamation systems, water filtration units, slurry mixers, or automation controls. These add-ons can significantly increase the total cost of ownership.
Tip: Request a detailed scope of supply and confirm whether installation, training, and commissioning are included.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—focusing on build quality, performance verification, regulatory compliance, IP integrity, and long-term support—you can make a more informed decision and avoid costly issues down the line when sourcing a vapor blast cabinet.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Vapor Blast Cabinet
Proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance are essential for the safe, efficient, and legal transport, installation, operation, and maintenance of a Vapor Blast Cabinet. This guide outlines key considerations to ensure adherence to applicable standards and smooth integration into your facility.
H3: Pre-Shipment & Receiving Logistics
- Site Assessment & Preparation:
- Dimensions & Weight: Verify the cabinet’s dimensions (LxWxH) and shipping weight against your receiving dock, doorways, hallways, and final location. Ensure adequate clearance for maneuvering.
- Floor Requirements: Confirm the floor surface can support the cabinet’s operational weight (cabinet + media + workpieces). A level, stable concrete floor is typically required. Verify load-bearing capacity.
- Utility Access: Ensure proximity to required utilities before delivery:
- Electrical: Confirm voltage (e.g., 208V, 230V, 480V), phase (e.g., 3-phase), amperage, and receptacle type match the cabinet’s specifications. Verify circuit availability and dedicated circuit requirement.
- Compressed Air: Ensure an adequate supply of clean, dry, oil-free compressed air at the required pressure (typically 80-120 psi) and volume (CFM). Verify air line size (e.g., 3/8″ or 1/2″ NPT) and connection location. A dedicated line with proper filtration is recommended.
- Ventilation/Exhaust: Confirm the exhaust ducting path to an external vent or dust collection system. Verify duct size (typically 4″ or 6″ diameter), length, and number of bends meet manufacturer specifications to ensure proper airflow (CFM).
- Drain (if applicable): For cabinets with wash cycles or liquid recovery, ensure a floor drain is accessible and compatible with local wastewater regulations.
- Shipping & Handling:
- Packing: Ensure the cabinet is shipped on a sturdy skid with adequate bracing and protective wrapping. Document any visible external damage upon delivery.
- Receiving: Have appropriate equipment (e.g., forklift rated for the weight, pallet jack) and personnel available for unloading. Follow manufacturer’s lifting points and procedures. Inspect for damage before signing the delivery receipt.
- Storage (if needed): Store indoors, protected from weather, dust, and temperature extremes. Keep upright and on the skid.
H3: Installation & Commissioning
- Qualified Personnel: Installation (especially electrical and compressed air connections) should be performed by qualified technicians familiar with local codes (e.g., NEC in the US, CEC in Canada, IEC standards internationally).
- Electrical: Connect only to a properly grounded, dedicated circuit meeting specifications. Use appropriate conduit and wiring methods. Verify grounding integrity.
- Compressed Air: Connect using correct fittings. Install recommended air filtration (coalescing filter, regulator, lubricator – FRL) close to the cabinet inlet to remove moisture, oil, and particulates.
- Exhaust/Ventilation:
- Connect exhaust duct securely to the cabinet outlet and the external vent or dust collector inlet.
- Ensure duct runs are as short and straight as possible to minimize pressure drop.
- Verify the connected dust collector or exhaust fan provides the required CFM at the cabinet inlet.
- Leveling: Use adjustable leveling feet to ensure the cabinet is perfectly level, especially critical for media recycling systems.
- Initial Setup: Follow the manufacturer’s commissioning checklist: fill media reservoir, add water/detergent (if wet process), test controls, verify door interlocks, conduct initial blast test.
H3: Operational Compliance & Safety
- Regulatory Frameworks:
- OSHA (US): Comply with 29 CFR 1910 Subpart G (General Environmental Controls) – Ventilation (1910.94, 1910.107), Respiratory Protection (1910.134 – if engineering controls are insufficient), Personal Protective Equipment (1910.132), Machine Guarding (1910.212), Hazard Communication (1910.1200 – GHS labeling for media/detergents).
- Workplace Safety (Canada): Comply with provincial regulations (e.g., OHSA in Ontario) covering ventilation, hazardous materials (WHMIS), PPE, machine safety.
- EU: Comply with Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), ATEX Directive (2014/34/EU – if potentially explosive atmosphere), REACH/CLP regulations for chemicals, and relevant national OSH laws.
- Other Regions: Adhere to local occupational health and safety regulations and environmental laws.
- Hazardous Substances (Media & Additives):
- SDS Management: Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS/MSDS) readily accessible for all blasting media, cleaning agents, and additives used. Understand hazards (inhalation, skin/eye contact, flammability, reactivity).
- Substitution: Consider less hazardous media (e.g., plastic, corn cob, soda) where feasible, especially for aluminum or delicate parts.
- Handling & Storage: Store media and chemicals securely, labeled correctly, away from incompatible materials, and according to SDS requirements (e.g., dry, ventilated area).
- Ventilation & Air Quality:
- Engineering Controls: The cabinet’s integrated ventilation and the connected dust collector/exhaust system are the primary controls. This is mandatory. Never operate without functioning ventilation.
- Dust Collector Maintenance: Regularly inspect, clean, and replace filter bags/cartridges according to schedule. Monitor pressure drop. Ensure proper disposal of collected dust (see Waste Compliance).
- Air Monitoring: Conduct initial and periodic air monitoring (e.g., for silica dust if using certain media, general particulate) to verify control effectiveness, especially if media changes or processes are modified. Required if exposure limits might be approached.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Mandatory Minimum: Safety glasses/goggles, hearing protection (earmuffs/plugs), and chemical-resistant gloves (nitrile) when handling media or cleaners.
- Respiratory Protection: Required if engineering controls cannot maintain airborne contaminant levels below Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs/WEELs/OELs). Selection (e.g., N95, half-face APR with P100 filters, PAPR) must be based on air monitoring and an employer’s Respiratory Protection Program (OSHA 1910.134). Fit testing and training are essential.
- Clothing: Wear protective work clothing (coveralls, apron) to minimize skin contact and prevent contamination of personal clothing.
- Machine Safety:
- Interlocks: Never bypass door interlocks, which cut power to the blasting system when the door opens. Ensure they are functional.
- Guarding: Keep all guards in place. Do not operate with damaged viewing windows.
- Training: Provide comprehensive training to all operators on safe operating procedures, emergency shutdown, PPE use, and hazard awareness.
H3: Waste Management & Environmental Compliance
- Spent Media & Sludge:
- Characterization: Determine if spent media/sludge is hazardous waste (e.g., contaminated with oils, heavy metals from blasted parts, lead paint, certain chemical additives). Consult SDS and potentially conduct waste testing (e.g., TCLP).
- Storage: Store waste in labeled, compatible, closed containers in a designated, secondary-contained area.
- Disposal: Dispose of through a licensed hazardous waste disposal contractor if characterized as hazardous. For non-hazardous waste, follow local landfill or recycling regulations. Never dump down drains or in regular trash without verification.
- Wastewater (if applicable):
- Containment: Prevent spills. Use drip trays.
- Treatment & Discharge: Wastewater containing media fines, oils, or detergents likely requires treatment before discharge to sewer. Check local Publicly Owned Treatment Works (POTW) pre-treatment regulations and obtain permits if necessary. On-site filtration or settling may be needed. Never discharge untreated wastewater.
- Used Filters: Handle and dispose of dust collector filters according to the waste characterization of the collected dust.
H3: Maintenance & Record Keeping
- Preventive Maintenance (PM): Follow the manufacturer’s PM schedule rigorously (daily, weekly, monthly, annually). Document all PM activities (lubrication, belt checks, seal inspection, nozzle replacement, filter changes, air pressure checks).
- Calibration & Testing: Regularly test safety interlocks, emergency stops, and alarm systems. Calibrate pressure gauges if required.
- Compliance Records: Maintain clear, accessible records for:
- Equipment manuals, drawings, and certifications.
- SDS for all chemicals/media.
- Air monitoring results.
- Respirator fit testing records and training.
- Hazardous waste manifests and disposal records.
- PM logs and repair history.
- Employee training records (operation, safety, emergency procedures).
- Audits: Conduct periodic internal audits to verify compliance with this guide and all applicable regulations.
Disclaimer: This guide provides general information. Regulations vary significantly by jurisdiction and specific application. Always consult the Vapor Blast Cabinet manufacturer’s documentation, your local environmental, health, and safety authorities, and qualified professionals (industrial hygienists, safety engineers, environmental consultants) to ensure full compliance.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Vapor Blasting Cabinet
After evaluating various suppliers, technical specifications, cost considerations, and long-term operational requirements, sourcing a vapor blasting cabinet represents a strategic investment in improving surface finishing quality, environmental sustainability, and workplace safety. Vapor blasting (also known as wet blasting) offers superior results compared to traditional dry blasting, including reduced media embedment, minimized part warping, and a cleaner, more consistent finish—ideal for precision components in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
By selecting a reputable supplier that offers durable construction, customizable features, efficient recycling of water and media, and reliable technical support, organizations can ensure optimal performance and return on investment. Additionally, the reduced environmental impact and compliance with health and safety regulations further enhance the justification for adopting vapor blasting technology.
In conclusion, procuring a vapor blasting cabinet aligns with goals of operational efficiency, product quality enhancement, and sustainable manufacturing practices. With proper due diligence in supplier selection and attention to specific application needs, the integration of a vapor blast cabinet will provide long-term benefits and a competitive advantage in high-precision cleaning and surface preparation.