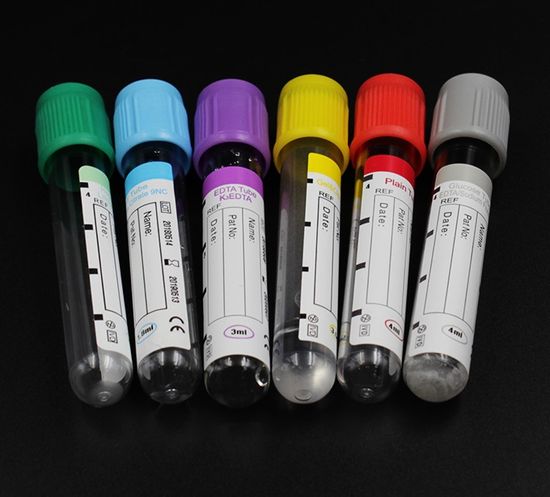
The global vacuum blood collection tube market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for accurate diagnostics, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and increasing prevalence of chronic diseases. According to Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 3.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further fueled by the rising volume of laboratory testing and the adoption of automated blood collection systems in clinical settings. As demand surges, manufacturers are investing in innovation, quality assurance, and scalable production to meet global standards. In this competitive landscape, ten key players have emerged as leaders, combining technological advancement, regulatory compliance, and broad product portfolios to dominate supply chains worldwide. Below is a data-driven overview of the top 10 vacuum blood tube manufacturers shaping the future of diagnostic medicine.
Top 10 Vacuum Blood Tube Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Manufacturer of Lab Disposable Products & Vacuum Blood …
Domain Est. 2003
Website: labtechdispo.com
Key Highlights: Labtech Disposable is one of the largest Manufacturers, Trader and Exporter of Vacuum Blood Collection Tubes, Non Vacuum Blood Collection Tube, Lab Disposable ……
#2 Vacuum blood collection tubes
Domain Est. 2008
Website: sekisuimedical.jp
Key Highlights: We develop, manufacture, and distribute medical devices such as the world’s first commercial plastic vacuum blood collection tubes….
#3 Disposable Vacuum Blood Collection Tube
Domain Est. 2024
Website: beudamed.com
Key Highlights: Medical device information for Disposable Vacuum Blood Collection Tube, manufactured by Henan Tuoren Medical Technology Co.,Ltd., regulated by the EU IVDR ……
#4 BD Vacutainer™ Blood Collection Tubes
Domain Est. 1990
Website: bd.com
Key Highlights: Discover BD Vacutainer™ Blood Collection Tubes, trusted for analytical accuracy, sample quality, and enhanced safety with BD Hemogard™ closures….
#5 Boekel Scientific
Domain Est. 1996
Website: boekelsci.com
Key Highlights: Boekel Scientific manufactures and sells laboratory equipment from blood banking to consumables and more. Shop our full collection of trusted equipment!…
#6 Vacumed® Vacuum Blood Tubes Manufacture
Domain Est. 1999
Website: flmedical.com
Key Highlights: The Vacumed system is one of FL Medical innovations. Even this time we treasured our decennial experience in the field of blood collection tubes….
#7 Vacuum Tube For Blood Collection
Domain Est. 2000
Website: en.kdlchina.com
Key Highlights: Latex-free transparent tubes for easy observation of venous blood draws. Tubes are made of reinforced glass or special plastic, able to withstand 3kg ……
#8 Vacuum blood collection tubes
Domain Est. 2004
Website: sekisuichemical.com
Key Highlights: The world’s first plastic vacuum blood collection tubes with excellent strength, they assist in preventing breakages during examinations….
#9 KBMED Introduces FDA
Domain Est. 2014
Website: kbmed.com
Key Highlights: KBMED offers a comprehensive system for venous blood collection, encompassing both safe and regular blood collection needles, along with various blood ……
#10 Best Vacuum Blood Collection Tube Manufacturer
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ksmedical.com
Key Highlights: KS Medical is one of the main suppliers for Evacuated Blood Collection Tube in the world. Meanwhile, KS Medical offers a large amount of products and services….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Vacuum Blood Tube

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Vacuum Blood Tubes
The global vacuum blood tube market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by technological advancements, rising demand for diagnostic testing, and healthcare system modernization. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Growth in Diagnostic Testing Demand
The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and cancer is fueling the need for routine blood diagnostics. Aging populations in developed regions and expanding healthcare access in emerging economies are contributing to higher volumes of blood collection procedures, directly boosting vacuum blood tube consumption. -
Adoption of Safety-Engineered Devices
Regulatory emphasis on healthcare worker safety is accelerating the shift toward vacuum tubes with integrated safety features—such as needlestick protection and pre-attached holders. By 2026, compliance with standards like the EU Medical Devices Regulation (MDR) and U.S. OSHA guidelines will make safety-centric designs the norm, especially in hospitals and outpatient clinics. -
Expansion of Point-of-Care and Decentralized Testing
The rise of decentralized healthcare models, including home-based testing and mobile clinics, is increasing demand for portable, user-friendly blood collection systems. Vacuum blood tubes compatible with handheld analyzers and designed for minimal training are expected to gain traction, particularly in rural and underserved areas. -
Technological Integration and Smart Tubes
Innovations such as barcoded or RFID-enabled tubes are improving sample tracking, reducing labeling errors, and enhancing laboratory efficiency. By 2026, smart vacuum tubes integrated with digital health platforms are likely to become more common, supporting end-to-end traceability and interoperability with electronic health records (EHRs). -
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Materials
Environmental concerns are prompting manufacturers to explore recyclable materials and reduce plastic waste. By 2026, companies investing in biodegradable tube components or sustainable packaging are likely to gain competitive advantage, especially in environmentally conscious markets like Europe. -
Emerging Markets as Growth Engines
Rapidly improving healthcare infrastructure in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa is creating new opportunities. Countries like India, Brazil, and Nigeria are expected to see strong market growth due to government investments in public health and expanding diagnostic networks. -
Consolidation and Strategic Partnerships
Market consolidation through mergers and acquisitions is anticipated as leading players seek to strengthen distribution networks and R&D capabilities. Collaborations between tube manufacturers and diagnostic companies will likely focus on integrated solutions that streamline pre-analytical workflows.
In conclusion, the 2026 vacuum blood tube market will be characterized by innovation, regulatory compliance, and geographic expansion. Companies that prioritize safety, sustainability, and digital integration are best positioned to capture growth in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Vacuum Blood Tubes (Quality, IP)
Sourcing vacuum blood tubes requires careful attention to both product quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations. Overlooking these aspects can lead to regulatory non-compliance, compromised patient safety, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Non-Compliance
One of the most critical risks in sourcing vacuum blood tubes is receiving products that fail to meet international quality and safety standards. Tubes manufactured under substandard conditions may exhibit inconsistent vacuum levels, incorrect additive concentrations, or poor tube integrity—leading to hemolysis, clotting, or inaccurate test results. Sourcing from suppliers without certifications such as ISO 13485, CE marking, or FDA registration increases the likelihood of receiving non-compliant products. Additionally, inadequate packaging or poor cold-chain management during shipping can compromise tube performance before use.
Inadequate Supply Chain Transparency
Many sourcing pitfalls stem from a lack of visibility into the manufacturing process and supply chain. Suppliers may outsource production to third-party factories without proper oversight, increasing the risk of quality deviations. Without traceability of raw materials—such as silicone coatings, clot activators, or anticoagulants—buyers cannot ensure batch consistency or verify biocompatibility. Conducting on-site audits and requesting documentation (e.g., Certificates of Analysis, manufacturing records) is essential to mitigate this risk.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Vacuum blood tube designs, closure systems, and additive formulations are often protected by patents and trade secrets. Sourcing from suppliers who replicate branded products—such as those mimicking BD Vacutainer® or Terumo systems—can expose the buyer to IP infringement claims, even if unintentional. Using look-alike tubes with similar labeling or packaging may also violate trademark laws. Buyers must verify that the supplier holds appropriate IP rights or licenses and ensure products do not infringe on existing patents, particularly in regulated markets like the U.S. or EU.
Lack of Regulatory Documentation
Suppliers, especially those based in regions with lax regulatory oversight, may fail to provide necessary technical documentation required for market authorization. Missing or incomplete files—such as Design Dossiers, Technical Files, or EU Declaration of Conformity—can delay product registration or lead to import bans. Buyers should confirm that suppliers can supply full regulatory documentation compliant with local requirements (e.g., FDA 510(k), EU MDR).
Insufficient Validation and Compatibility Testing
Vacuum blood tubes must be validated for compatibility with specific analyzers, testing methodologies, and sample types. Sourcing tubes without proper validation data may result in interference with diagnostic assays or instrument errors. Suppliers should provide evidence of performance testing across a range of clinical analyzers and demonstrate adherence to standards like CLSI H1-A7.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: vetting suppliers thoroughly, demanding transparency, verifying regulatory and IP compliance, and conducting pilot testing before full-scale procurement.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Vacuum Blood Tubes
Overview
Vacuum blood tubes are sterile, evacuated glass or plastic tubes used to collect blood samples via venipuncture. Proper logistics and compliance management are critical to ensure sample integrity, patient safety, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency in medical and laboratory settings.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Vacuum blood tubes are classified as in vitro diagnostic (IVD) medical devices in most jurisdictions and must comply with specific regulatory frameworks:
- United States (FDA):
- Must be registered with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under 21 CFR Part 864.
- Subject to Quality System Regulation (QSR) under 21 CFR Part 820.
-
Requires appropriate labeling per 21 CFR Part 801, including intended use, storage conditions, expiration date, and lot number.
-
European Union (EU):
- Must comply with the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) (EU) 2017/746.
- Requires CE marking and technical documentation demonstrating conformity.
-
Designated Notified Body assessment may be required depending on classification.
-
Other Regions:
- Compliance with Health Canada (MDL), Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) in Australia, and other national regulatory bodies as applicable.
- Adherence to ISO 13485 (Quality Management Systems for Medical Devices) is widely recognized and recommended globally.
Labeling and Traceability
Proper labeling ensures compliance and patient safety:
- Each tube must display:
- Product name and intended use
- Manufacturer name and address
- Lot number for traceability
- Expiration date
- Additive type (e.g., K2EDTA, sodium citrate)
- Fill volume
- Storage conditions
-
Unique Device Identifier (UDI), where required (e.g., under FDA or EU IVDR)
-
Barcoding (e.g., GS1 standards) is recommended for inventory management and specimen tracking.
Storage and Handling
Maintaining product integrity during storage and handling is essential:
- Temperature:
- Store at controlled room temperature (typically 2°C to 30°C), unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer.
-
Avoid exposure to extreme heat, cold, or direct sunlight.
-
Humidity:
-
Store in dry conditions to prevent label degradation and packaging compromise.
-
Orientation:
-
Store upright to prevent leakage or damage to the rubber stopper.
-
Shelf Life:
- Monitor expiration dates closely; do not distribute or use expired tubes.
- Implement FIFO (First-In, First-Out) inventory rotation.
Transportation and Distribution
Ensure safe and compliant product movement:
- Packaging:
- Use manufacturer-approved, tamper-evident packaging.
-
Include cushioning to prevent breakage during transit.
-
Shipping Conditions:
- Maintain ambient temperature throughout the supply chain.
-
Use validated cold chain logistics only if specified by the manufacturer.
-
Documentation:
- Include shipping manifests, certificates of conformance, and compliance documentation.
- Maintain transport records for audit and traceability purposes.
Import and Export Regulations
International shipments require adherence to additional requirements:
- Customs Documentation:
- Accurate HS (Harmonized System) code classification (e.g., 3006.50 for diagnostic reagents).
-
Commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading.
-
Regulatory Submissions:
- Import permits or licenses may be required in certain countries.
-
Ensure the product is registered in the destination country.
-
Dangerous Goods:
- Vacuum blood tubes are generally not classified as dangerous goods (non-hazardous), but confirm with IATA/IMDG regulations if in doubt.
Quality Management and Audits
Establish a robust quality system:
- Implement ISO 13485-compliant procedures for procurement, storage, and distribution.
- Conduct regular internal audits and supplier assessments.
- Maintain records of temperature logs, inventory, non-conforming products, and corrective actions.
Disposal and Environmental Compliance
Expired or damaged tubes must be disposed of properly:
- Follow local regulations for medical waste disposal.
- Glass tubes may require special handling due to breakage risk.
- Coordinate with licensed medical waste disposal vendors.
Training and Personnel Competency
Ensure staff are trained in:
- Regulatory requirements for IVDs
- Proper handling, storage, and inventory management
- Emergency response for spills or breakage
- Documentation and traceability procedures
Conclusion
Effective logistics and compliance management for vacuum blood tubes safeguards patient care, ensures regulatory adherence, and supports efficient laboratory operations. By following this guide, organizations can maintain product integrity, meet legal obligations, and enhance overall quality in medical testing processes.
Conclusion for Sourcing Vacuum Blood Collection Tubes:
Sourcing vacuum blood collection tubes requires a strategic approach that balances quality, regulatory compliance, cost-efficiency, and supply chain reliability. These tubes are critical components in diagnostic processes, and their performance directly impacts the accuracy and safety of laboratory testing. Therefore, selecting suppliers that adhere to international standards such as ISO 18113 and ISO 15189, and ensuring products are approved by relevant regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA, CE marking), is paramount.
A successful sourcing strategy involves evaluating multiple factors, including product consistency, material quality (e.g., glass vs. plastic), additive accuracy, shelf life, and packaging integrity. Additionally, building relationships with reputable manufacturers or distributors that offer technical support, scalability, and timely delivery helps mitigate risks associated with supply disruptions.
In an evolving healthcare landscape, considerations such as sustainability (e.g., recyclable materials), innovation (e.g., safety-engineered designs to prevent needlestick injuries), and total cost of ownership—not just unit price—should guide decision-making. Ultimately, effective sourcing of vacuum blood tubes supports reliable diagnostic outcomes, enhances patient safety, and contributes to the overall efficiency of clinical operations.