The global market for data transmission and network cabling solutions has seen steady expansion, driven by rising digital infrastructure demands across enterprise and residential sectors. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) and FTP (Foiled Twisted Pair) cables market was valued at approximately USD 12.8 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.4% through 2029. This growth is fueled by increasing adoption of high-speed networks, smart building systems, and the expansion of data centers—especially across Asia-Pacific and North America. As demand for reliable, cost-effective cabling solutions intensifies, differentiation among manufacturers in terms of performance, shielding efficiency, and compliance with Category 6A/8 standards has become critical. With UTP dominating in cost-sensitive, high-volume deployments and FTP gaining traction in electromagnetically noisy environments, evaluating the top manufacturers in this space requires a data-backed assessment of market share, product innovation, and global reach. The following analysis identifies the top 10 UTP vs FTP manufacturers shaping the future of structured cabling.
Top 10 Utp Vs Ftp Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Category 6 Cables
Domain Est. 1994
Website: commscope.com
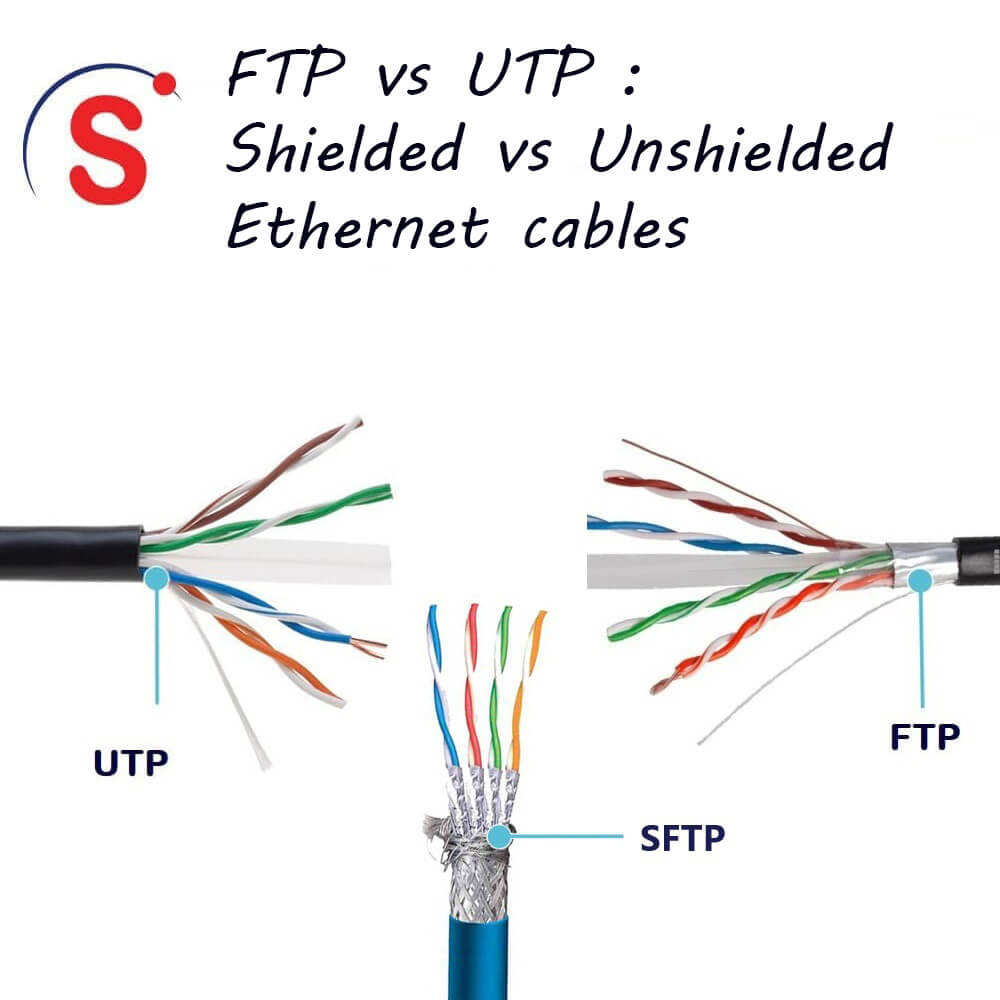
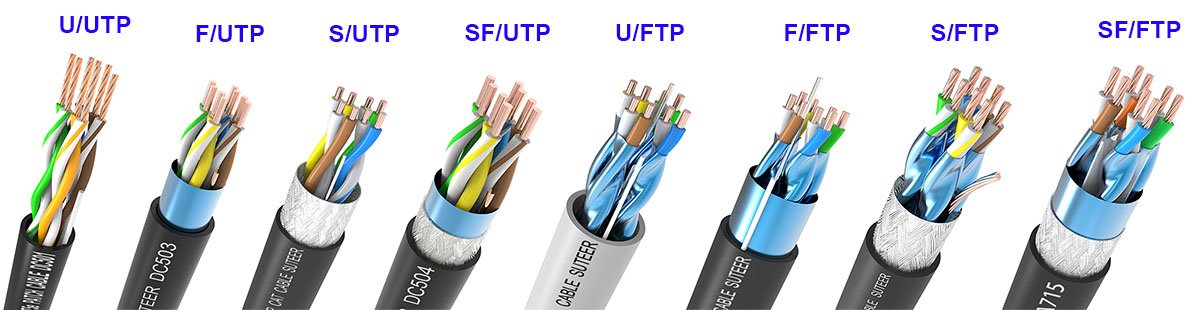
Key Highlights: Variety of Types: Whether you need F/FTP (Foiled/Foiled Twisted Pair), F/UTP (Foiled/Unshielded Twisted Pair), or U/UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) ……
#2 Ethernet Cables Explained
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tripplite.eaton.com
Key Highlights: U/UTP, UTP or TPP, None, None. F/UTP, FTP or STP, Foil, None. S/UTP, STP, Braiding, None. SF/UTP, SFTP or STP, Braiding & Foil, None. U/FTP, STP, None, Foil. F/ ……
#3 STP, UTP, FTP Cable & More
Domain Est. 1997
Website: belden.com
Key Highlights: Use SF/UTP cable when you need protection from low- and high-frequency noise interference. It supports easy connectorization and is moderately flexible….
#4 What does UTP, S/UTP, FTP, STP and SFTP mean?
Domain Est. 2001
Website: universalnetworks.co.uk
Key Highlights: U/UTP: UNSHIELDED TWISTED PAIRS. Also known as UTP, this is currently the most common and basic method of cable construction, consisting of pairs of wires ……
#5 The Difference Between UTP, FTP, STP, and S/FTP Cabling
Domain Est. 2002
Website: store.cablesplususa.com
Key Highlights: UTP cables are technically U/UTP per industry standards, indicating no shielding around all pairs and no shielding on individual pairs….
#6 UTP vs FTP Ethernet Cables
Domain Est. 2021
Website: monkcables.com
Key Highlights: The Most Common Differences Between UTP and FTP Cables · 1. Installation Hassle. The FTP (Foiled Twisted Pairs) cables have a thick outer jacket as they have an ……
#7 UTP vs FTP: unshielded or shielded network cable?
Website: netwerkkabel.eu
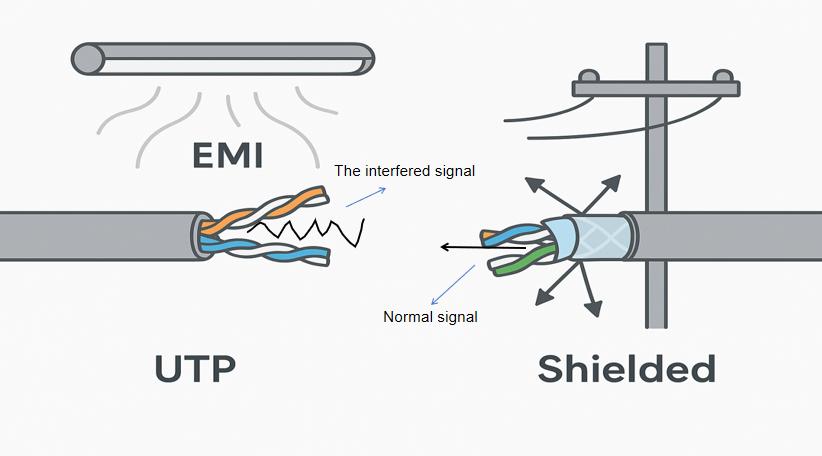
Key Highlights: UTP stands for Unshielded T wisted P air . Unshielded means unshielded. This means that interference can easily occur. Pretty simple, right?…
#8 FTP vs UTP vs STP
Domain Est. 2016
Website: infinity-cable-products.com
Key Highlights: UTP: UTP cables are cost-effective and widely available, making them a popular choice for home networks. · FTP: FTP cables are slightly more ……
#9 FTP vs. UTP vs. STP: A Comprehensive Guide
Domain Est. 2018
Website: tscables.com
Key Highlights: UTP is the easiest to find. Another important thing to note is that FTP or UTP both come in various jacket ratings, including plenum and riser. ……
#10 Are FTP Cables Always Better Than UTP Cables?
Domain Est. 2022
Website: cat6acabling.com
Key Highlights: In low-interference environments (like home networks or standard office spaces), UTP performs just as well as FTP. FTP cables require grounding; ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Utp Vs Ftp

H2: Market Trends in UTP vs FTP Cabling for 2026
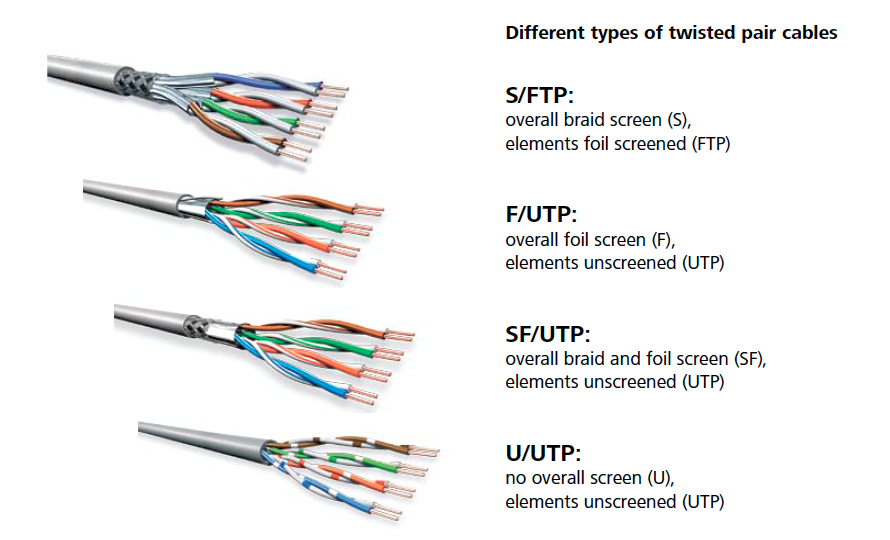
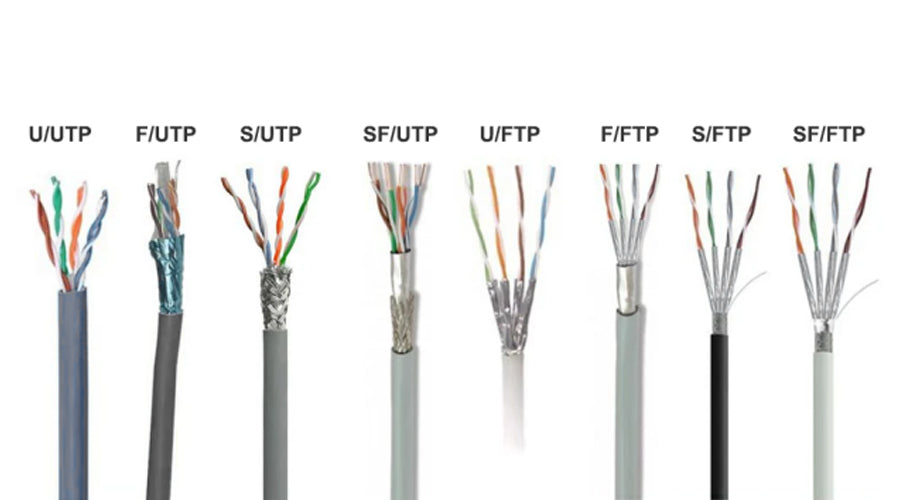
As global digital infrastructure evolves rapidly, the choice between Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Foiled/Foiled Twisted Pair (FTP) cabling remains a critical consideration for enterprise networks, data centers, and smart buildings. In 2026, several converging technological, economic, and environmental trends are shaping the competitive landscape between UTP and FTP solutions.
1. Increased Demand for High-Speed Connectivity
The widespread rollout of 5G, Wi-Fi 6E/7, and the proliferation of IoT devices are driving demand for higher bandwidth and lower latency. While Category 6A and Category 8 UTP cables support up to 10 Gbps and 40 Gbps respectively over short distances, FTP cables—particularly shielded Cat 6A and Cat 7/8 variants—offer superior electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection, making them increasingly favored in high-noise industrial and dense urban environments. By 2026, FTP adoption is expected to grow in data centers and enterprise backbones where signal integrity is paramount.
2. Expansion of Industrial and Smart Building Applications
With the rise of Industry 4.0 and smart infrastructure, environments with high EMI (e.g., manufacturing plants, hospitals, and transportation hubs) are prioritizing FTP for its shielding capabilities. FTP cables, with their overall foil shield (typically labeled as F/UTP or S/FTP), reduce crosstalk and external interference. This makes them ideal for mission-critical applications. In contrast, UTP remains dominant in office environments and residential deployments due to lower cost and easier installation. However, in 2026, hybrid cabling strategies are emerging, with UTP used for horizontal runs and FTP for backbone and high-interference zones.
3. Cost and Installation Considerations
UTP continues to hold a significant cost advantage in both materials and labor. It requires simpler termination processes and does not mandate grounding, which reduces installation complexity. In budget-sensitive markets—particularly in developing regions—UTP is expected to maintain a larger market share. However, as labor costs rise and automation in cabling (e.g., pre-terminated systems) becomes more common, the installation gap between UTP and FTP is narrowing, boosting FTP’s appeal in premium installations.
4. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Trends
Sustainability is a growing priority. FTP cables, while more material-intensive due to shielding, can contribute to network efficiency by reducing retransmissions caused by interference, thus lowering power consumption over time. Additionally, recyclable shielding materials and improved manufacturing processes are making FTP more environmentally viable. In 2026, green building certifications like LEED and BREEAM are increasingly factoring in cabling performance, indirectly promoting FTP in high-performance buildings.
5. Standardization and Future-Proofing
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and TIA continue to update cabling standards (e.g., ISO/IEC 11801-1:2022, TIA-568.2-D), emphasizing performance consistency and support for future technologies like 800G Ethernet and beyond. FTP cables align better with these future-proofing goals due to their lower noise susceptibility. Enterprises planning long-term infrastructure investments are more likely to opt for FTP to extend cabling lifecycle and avoid early obsolescence.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
In North America and parts of Asia-Pacific, UTP remains the default choice for most commercial installations due to legacy infrastructure and contractor familiarity. However, in Europe—where stricter EMC regulations (e.g., EU EMC Directive) are enforced—FTP adoption is significantly higher. By 2026, regulatory harmonization and global best practices are expected to drive FTP adoption in other regions, particularly in government, healthcare, and finance sectors.
Conclusion
In 2026, while UTP continues to dominate in cost-sensitive and low-interference environments, FTP is gaining ground in high-performance, high-reliability applications. The market is trending toward a segmented adoption model: UTP for general-purpose use and FTP for specialized, interference-prone, or future-focused deployments. As network demands escalate and shielding technologies become more cost-effective, FTP is poised for sustained growth, narrowing the historical gap with UTP in key verticals.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing UTP vs FTP Cables: Quality and IP Considerations
When selecting between Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Foiled/Foiled Twisted Pair (FTP) cables for network installations, buyers often encounter pitfalls related to quality and IP (Ingress Protection) ratings. Understanding these issues is critical to ensuring long-term performance, reliability, and compliance with environmental demands.
Misunderstanding Shielding Requirements
One of the most common mistakes is assuming that FTP cables are always superior due to their shielding. While FTP cables offer better protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI), they are not always necessary. In low-interference environments (e.g., standard office spaces), UTP cables (e.g., Cat6 or Cat6a) are often sufficient and more cost-effective. Over-specifying FTP can lead to unnecessary expense and installation complexity.
Poor Quality Control in Shielded Cables
FTP cables require proper grounding to be effective. A frequent quality pitfall is sourcing low-grade FTP cables with inconsistent foil shielding, poorly bonded drain wires, or inadequate termination components. If the shield is discontinuous or improperly grounded, it can act as an antenna, increasing interference rather than reducing it. Buyers may unknowingly purchase substandard FTP cables that fail to deliver promised performance.
Overlooking Installation Expertise
Installing FTP cables demands greater skill and attention to detail than UTP. Incorrect termination, such as damaging the foil during termination or failing to maintain shield continuity, compromises performance. Without trained technicians, the benefits of FTP are lost, leading to network issues that may be misdiagnosed as equipment failure.
Assuming IP Ratings Apply to All Cables
A critical misconception is expecting standard UTP or FTP cables to have high IP (Ingress Protection) ratings. Most indoor network cables (both UTP and FTP) are not rated for dust or water resistance. Buyers often overlook this when deploying cables in harsh environments (e.g., outdoor, industrial, or high-moisture areas), leading to premature cable degradation. For such environments, cables must be specifically designed with IP-rated jackets (e.g., IP66, IP67) and proper sealing, regardless of whether they are UTP or FTP.
Confusing Cable Shielding with Environmental Protection
Shielding (UTP vs FTP) addresses EMI, not physical or environmental protection. A common pitfall is selecting FTP under the mistaken belief that it offers better durability or weather resistance. In reality, environmental resilience depends on the jacket material, UV resistance, and IP rating—not the presence of foil shielding. Using standard FTP cables outdoors without proper outer protection results in rapid deterioration.
Cost vs. Performance Trade-Offs
Sourcing decisions are often driven by upfront cost, leading to the selection of cheaper UTP cables in environments where FTP is warranted, or vice versa. Low-quality UTP may suffer from crosstalk and signal loss in high-noise areas, while over-deploying high-cost FTP where unnecessary inflates project budgets without benefit. A balanced assessment of the environment and interference risks is essential.
Lack of Compliance Verification
Buyers may fail to verify that cables meet relevant standards (e.g., ISO/IEC 11801, TIA/EIA-568) for shielding effectiveness and transmission performance. Counterfeit or non-compliant cables—especially in FTP variants—may appear identical but deliver poor signal integrity. Always request test reports and certification from reputable manufacturers.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, assess the actual EMI environment, required durability, and installation conditions before choosing between UTP and FTP. Prioritize certified, high-quality cables and ensure proper installation practices. For outdoor or harsh environments, specify cables with appropriate IP ratings and robust jacketing, independent of shielding type.

Logistics & Compliance Guide: UTP vs FTP
Understanding the differences between Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Foiled Twisted Pair (FTP) cables is critical for ensuring proper logistics planning and regulatory compliance in networking infrastructure deployments. This guide outlines key considerations for handling, transporting, installing, and certifying both cable types.
Cable Construction & Handling Requirements
UTP cables consist of twisted copper pairs without any metallic shielding, making them lightweight and flexible. They are less sensitive to physical bending and kinking, simplifying handling during shipping and installation. In contrast, FTP cables include an overall foil shield around the twisted pairs, which provides improved electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection but requires careful handling to avoid damaging the delicate foil layer. During logistics, FTP cables must be coiled properly and protected from crushing or sharp bends that could compromise the shield integrity.
Storage & Environmental Conditions
Both UTP and FTP cables should be stored in dry, temperature-controlled environments to prevent moisture ingress and jacket degradation. However, FTP cables are more susceptible to environmental stress due to their metallic components. Prolonged exposure to humidity can lead to corrosion of the foil shield, affecting performance and compliance. Ensure storage areas are free from high EMI sources (e.g., heavy machinery) especially for FTP, as improper storage may pre-compromise shielding effectiveness.
Transportation & Packaging
UTP cables are typically shipped on reels or in boxes with minimal protective packaging due to their durability. Standard freight handling procedures are generally sufficient. FTP cables, however, require reinforced packaging to prevent deformation of the foil shield. Use crush-resistant reels and moisture barriers during transit. Label packages clearly as “Foil Shielded – Handle with Care” to alert logistics personnel. Avoid stacking heavy items on FTP shipments to maintain cable integrity.
Installation Best Practices
UTP installation is straightforward, allowing for faster deployment with fewer tools. Grounding is not required. FTP cables must be installed with attention to grounding protocols—the foil shield must be properly terminated to ground at one end (typically the patch panel) to prevent ground loops and ensure EMI protection. Use shielded connectors and compatible jacks. Improper grounding can render the shielding ineffective and may violate safety codes.
Regulatory & Compliance Standards
Both UTP and FTP cables must comply with industry standards such as ISO/IEC 11801, TIA/EIA-568, and local electrical codes. FTP installations often fall under stricter electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations, especially in industrial, medical, or data center environments. Ensure that FTP systems are tested and certified for EMC compliance (e.g., EN 55032, FCC Part 15). UTP cables may be sufficient for general office environments where EMI is minimal, simplifying compliance requirements.
Testing & Certification
Post-installation testing is essential for both cable types. UTP links are validated using standard continuity, length, and crosstalk tests (e.g., with Fluke DSX testers). FTP cables require additional verification of shield continuity and grounding. A failed shield test can indicate compliance issues with EMC standards. Document all test results to support compliance audits and warranty claims.
Disposal & Environmental Regulations
Dispose of both UTP and FTP cables in accordance with local e-waste and environmental regulations (e.g., RoHS, WEEE). FTP cables contain metallic shielding, classifying them as mixed-material waste, which may require specialized recycling procedures compared to UTP. Maintain disposal records to demonstrate compliance with sustainability standards.
Summary: Choosing Based on Logistics & Compliance
- UTP: Best for cost-effective, high-volume logistics; easier handling, simpler compliance in low-EMI environments.
- FTP: Required in high-interference zones; demands careful handling, proper grounding, and stricter compliance documentation.
Selecting the appropriate cable type involves balancing performance needs with logistical capabilities and regulatory obligations. Always verify local codes and project specifications before deployment.
Conclusion: Sourcing UTP vs. FTP Cables
When sourcing UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) versus FTP (Foiled Twisted Pair) cables, the decision should be driven by the specific requirements of the installation environment, performance needs, budget, and future scalability.
UTP cables are generally more cost-effective, easier to install, and sufficient for most standard office and residential environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is minimal. Their flexibility and widespread compatibility make them ideal for general networking applications, especially in environments with low to moderate data traffic and limited sources of interference.
In contrast, FTP cables offer enhanced protection against electromagnetic interference due to their overall foil shielding. This makes them better suited for industrial environments, data centers, or areas with high EMI from machinery, fluorescent lighting, or other electronic devices. While FTP cables are slightly more expensive and require proper grounding for optimal performance, they provide greater signal integrity and reliability in challenging conditions.
Ultimately, sourcing decisions should balance performance requirements with practical considerations. For standard IT environments, UTP remains the preferred and economical choice. However, in high-interference or mission-critical applications, investing in FTP cables can ensure long-term network stability and reduce the risk of signal degradation. Proper assessment of the deployment environment will guide the optimal selection between UTP and FTP.