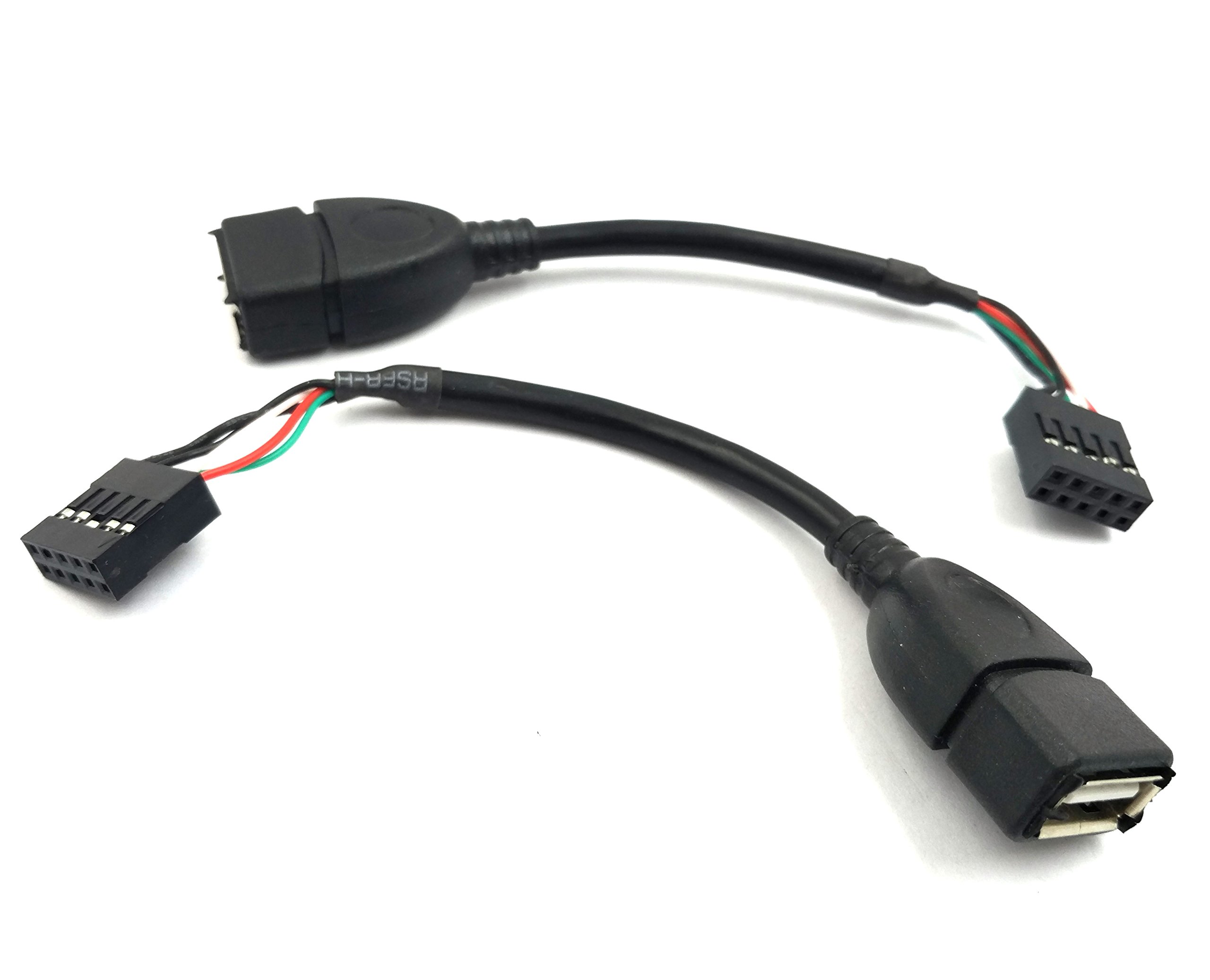
The global USB market continues to expand, driven by rising demand for high-speed data transfer and versatile connectivity solutions across consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications. According to Grand View Research, the global USB market size was valued at USD 63.8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7% from 2023 to 2030. While USB 3.0 and newer standards gain traction, USB 2.0 headers remain a critical component in many systems due to their cost-efficiency, wide compatibility, and sufficient performance for peripherals such as case fans, LED strips, and internal hubs. This sustained relevance has fostered a competitive manufacturing landscape, with key players investing in reliable, high-volume production to meet OEM and aftermarket demands. As design integration and port density evolve, particularly in gaming PCs and compact form factor builds, the role of USB 2.0 headers persists as a foundational connectivity solution. The following list highlights the top 8 manufacturers leading innovation, quality, and market presence in the USB header 2.0 space.
Top 8 Usb Header 2.0 Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 FTDI
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ftdichip.com
Key Highlights: USB High Speed device fully supports the latest USB Type-C and Power Delivery (PD) 3.0 controller standards enabling support for power negotiation….
#2 GCT
Domain Est. 2010
Website: gct.co
Key Highlights: GCT is a leading manufacturer of Standard and Custom PCB Connectors and Cable Assemblies. Browse our innovative product ranges for solutions to your ……
#3 Product Search
Domain Est. 1996
Website: usb.org
Key Highlights: This product search is limited to only those products that are certified to bear the USB-IF logo. Although the listing is maintained by each member company ……
#4 USB 2.0 Compatible Automotive Connector MX45M Series
Domain Est. 1996
Website: jae.com
Key Highlights: The MX45M Series enables access to data stored in personal electronic devices through a USB 2.0 connection….
#5 2m USB 2.0 A to A Cable
Domain Est. 1998
Website: startech.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery 30-day returnsConnect USB 2.0 devices to a USB hub or to your computer · Supports USB 2.0 data transfer rates up to 480 Mbps · Backward compatible with USB 1.1 · High…
#6 Adding a USB header
Domain Est. 2008
Website: forums.raspberrypi.com
Key Highlights: You could try something like this. USB A plug to USB A socket. Just extend it a little and you could add a 4 pin header between the plug and socket….
#7 USB header pinout, connecting a poorly marked cable
Domain Est. 2009
Website: electronics.stackexchange.com
Key Highlights: The motherboard USB header you posted, is a typical 2 port header. Either one will work. While cable color does not always match what it should be, Red is 5v, ……
#8 USB Types and Connectors Guide
Domain Est. 1996
Website: newnex.com
Key Highlights: Here at Newnex, we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-performance USB … Explore Newnex’s USB 2.0 to Header Cables. Newnex USB 2.0 Panel Mount Cable ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Usb Header 2.0
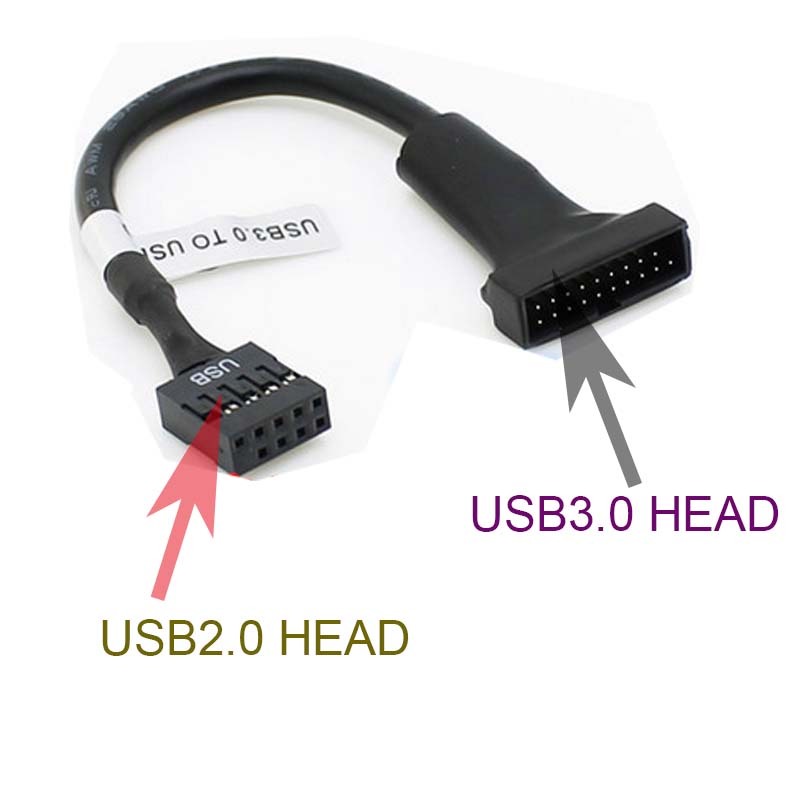

USB Header 2.0 Market Trends in 2026
As of 2026, the market for USB 2.0 headers—commonly found on motherboards to support front-panel or internal USB connectivity—reflects a landscape shaped by technological evolution, cost efficiency, and niche demand. While overshadowed by newer USB standards, USB 2.0 headers retain relevance in specific segments, driven by legacy compatibility, cost constraints, and functional adequacy for certain peripherals.
Declining Relevance Amid Advancing Technologies
By 2026, USB 2.0 headers are increasingly viewed as legacy components in consumer and high-performance computing. The widespread adoption of USB 3.2, USB4, and Thunderbolt 4 across new desktops and laptops has shifted focus toward higher bandwidth and faster data transfer rates. As a result, motherboard manufacturers are prioritizing USB 3.x and USB-C headers, often reducing the number of onboard USB 2.0 header connectors. This trend is particularly evident in premium and gaming motherboards, where space and I/O flexibility are optimized for modern devices such as external SSDs, high-resolution webcams, and VR equipment—applications that benefit significantly from higher speeds.
Sustained Demand in Budget and Industrial Applications
Despite their declining prominence, USB 2.0 headers maintain strong demand in budget PCs, embedded systems, and industrial automation. In cost-sensitive markets—such as education, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and small office/home office (SOHO) environments—USB 2.0 remains sufficient for keyboards, mice, barcode scanners, and basic printers. The low implementation cost and proven reliability of USB 2.0 technology ensure its inclusion in entry-level motherboards and specialized industrial motherboards where longevity and compatibility are prioritized over speed.
Niche Use in DIY and Retro Computing
The enthusiast and DIY PC building community continues to support USB 2.0 headers, particularly for custom PC cases and retro builds. Enthusiasts often use USB 2.0 headers to connect internal hubs for multiple low-bandwidth devices or to maintain compatibility with older case designs. Additionally, retro computing and homelab projects frequently rely on older motherboards or adapters that include USB 2.0 headers, preserving accessibility for vintage peripherals and legacy software environments.
Supply Chain and Component Availability
Component manufacturers have streamlined production around newer USB standards, leading to reduced availability of standalone USB 2.0 header cables and daughterboards. However, major electronics suppliers still stock these parts due to ongoing demand from repair markets and OEMs serving legacy systems. In 2026, most new motherboards include at least one USB 2.0 header as a fallback option, ensuring backward compatibility and supporting essential low-speed functions.
Conclusion
In 2026, the USB 2.0 header market is characterized by contraction in mainstream computing but resilience in cost-driven, industrial, and enthusiast applications. While no longer at the forefront of innovation, USB 2.0 headers persist as a practical solution for non-bandwidth-intensive tasks. Their gradual phase-out from high-end platforms is balanced by enduring utility in environments where simplicity, compatibility, and cost-efficiency remain paramount.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing USB 2.0 Headers – Quality and IP Considerations
Sourcing USB 2.0 headers may appear straightforward, but several critical pitfalls related to quality and intellectual property (IP) can impact product reliability, compliance, and long-term viability. Being aware of these issues helps mitigate risks during component selection and integration.
1. Substandard Build Quality
Many low-cost USB 2.0 headers on the market use inferior materials such as thin plating, low-grade plastics, or weak retention mechanisms. This can lead to poor electrical contact, intermittent connections, or mechanical failure during repeated insertions. Always verify compliance with USB-IF specifications and prioritize vendors with proven manufacturing standards.
2. Lack of Compliance Certification
Some suppliers offer USB 2.0 headers without proper USB-IF (USB Implementers Forum) certification. Using non-compliant components can result in interoperability issues, signal integrity problems, and failure to pass regulatory testing. Ensure components are listed in the official USB-IF vendor directory.
3. Counterfeit or Gray-Market Components
Unauthorized distributors may offer counterfeit or recycled USB headers that mimic reputable brands. These parts often fail prematurely and lack traceability. Source only from franchised distributors or directly from authorized manufacturers to avoid IP and quality risks.
4. Intellectual Property Infringement Risks
Certain USB connector designs are protected by patents or trademarks. Using clones that replicate proprietary mechanical or electrical designs (e.g., specific latch mechanisms or pin configurations) may expose your product to legal challenges. Conduct due diligence on design IP, especially when using non-standard or enhanced versions of USB 2.0 headers.
5. Inadequate Documentation and Support
Poorly documented headers may lack detailed mechanical drawings, insertion force specifications, or lifecycle data. This complicates design integration and long-term supply planning. Choose suppliers that provide comprehensive technical documentation and responsive engineering support.
6. Obsolescence and Supply Chain Instability
USB 2.0 technology, while mature, still faces component lifecycle changes. Some manufacturers may discontinue specific headers without notice. Assess supplier longevity, product lifecycle status, and second-source availability to ensure supply chain resilience.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively—prioritizing certified, high-quality components from reputable sources and verifying IP compliance—designers and procurement teams can ensure reliable, legally sound integration of USB 2.0 headers in their products.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for USB Header 2.0
Overview
USB Header 2.0 refers to a software or firmware component used in embedded systems, IoT devices, or custom hardware to manage USB 2.0 communication protocols via a header file (typically in C/C++ development). While not a physical product, ensuring proper logistics and compliance during its integration, distribution, or deployment—especially in commercial or regulated environments—is essential.
Regulatory & Industry Standards
Ensure the use and integration of USB Header 2.0 align with relevant standards and regulations:
– USB-IF Compliance: Adhere to specifications from the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), especially regarding USB 2.0 signaling, power management, and device enumeration.
– IEC 62368-1: For end-products involving audio/video and IT equipment, ensure hardware using the header complies with safety standards for energy sources and user access.
– FCC Part 15 (USA): If the final product emits radio frequencies, compliance with electromagnetic interference (EMI) standards is required. USB communication may contribute to EMI.
– CE Marking (EU): For products sold in the European Union, ensure conformity with EMC, RoHS, and RED directives as applicable.
– UL/CSA Certification: Required for commercial deployment in North America when part of safety-critical systems.
Note: While the header file itself is software, the end-product must comply with hardware and electromagnetic regulations.
Software Licensing & Intellectual Property
- License Type: Confirm the licensing model of the USB Header 2.0 (e.g., MIT, GPL, proprietary). Open-source headers may impose obligations on derivative works.
- Attribution Requirements: If using open-source code, ensure proper attribution in documentation or source files.
- Patent Risks: Verify that implementation does not infringe on USB-related patents, particularly those held by USB-IF members.
Development & Integration Logistics
- Version Control: Use Git or similar tools to track versions of the header file and manage updates.
- Dependency Management: Document any dependencies (e.g., HAL libraries, RTOS) required for the header to function.
- Build & Compilation: Ensure compatibility with target toolchains (e.g., GCC, Keil, IAR). Include build scripts or Makefiles if distributing.
- Cross-Platform Support: Validate header compatibility across architectures (ARM, x86, RISC-V) if applicable.
Supply Chain & Distribution
- Secure Distribution Channels: Distribute the header file via authenticated and encrypted platforms (e.g., GitHub with signed commits, private repositories).
- Integrity Verification: Provide checksums (SHA-256) or digital signatures to ensure file integrity.
- Export Controls: If distributing internationally, assess compliance with export regulations (e.g., EAR in the U.S.) for software with cryptographic or dual-use potential.
- Third-Party Audits: For regulated industries (medical, automotive), conduct code audits and security reviews before deployment.
Quality Assurance & Testing
- Unit Testing: Validate USB descriptor parsing, endpoint configuration, and control transfers.
- Interoperability Testing: Test with various USB hosts and devices to ensure compliance with USB 2.0 specifications.
- Static Code Analysis: Use tools like SonarQube or Coverity to detect vulnerabilities or non-compliant code patterns.
- Fuzz Testing: Apply malformed USB packets to test robustness.
Documentation & Traceability
- Technical Documentation: Include datasheets, API references, and integration guides with the header.
- Compliance Documentation: Maintain records of testing, certifications, and risk assessments.
- Change Logs: Track modifications, bug fixes, and version history for audit purposes.
- Bill of Materials (BOM): If part of a hardware-software system, include the header in the software BOM for traceability.
End-of-Life & Updates
- Deprecation Policy: Clearly communicate support timelines and end-of-life plans.
- Patch Management: Provide security patches and updates through secure, version-controlled channels.
- Migration Path: Offer guidance for upgrading to USB 3.0 or USB-C headers when necessary.
Summary
While USB Header 2.0 is a software component, its integration into physical products demands rigorous attention to logistics, regulatory compliance, and security. Adhering to industry standards, maintaining clear documentation, and ensuring secure distribution are critical for legal and operational success. Always assess the final product’s compliance—not just the software component.
Conclusion for Sourcing USB 2.0 Headers:
After thorough evaluation of suppliers, product specifications, pricing, and lead times, sourcing USB 2.0 headers from qualified and reliable manufacturers ensures compatibility, cost-efficiency, and supply chain stability for electronic device manufacturing. Key suppliers such as Molex, TE Connectivity, and Amphenol offer high-quality, standardized solutions that meet industry requirements for durability and performance. By prioritizing vendors with strong quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001), consistent production capabilities, and responsive technical support, companies can mitigate risks related to component shortages or non-compliance.
Furthermore, considering factors like mating cycles, pin configuration, and surface-mount vs. through-hole options allows for optimal integration into PCB designs. Bulk purchasing and long-term agreements with preferred suppliers can lead to favorable pricing and inventory reliability, especially given fluctuating market demands.
In summary, a strategic sourcing approach focused on quality, reliability, and scalability ensures that USB 2.0 headers support efficient product development and manufacturing without compromising performance or compliance. As USB 2.0 remains widely used in legacy and new designs alike, maintaining a robust supply of these components is essential for seamless operations.