The global polyurethane market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand across construction, automotive, furniture, and insulation industries. According to a report by Grand View Research, the market was valued at USD 73.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6% from 2024 to 2030. Increasing urbanization, stricter energy efficiency regulations, and the expansion of cold chain logistics are further accelerating demand for high-performance insulation materials—key applications for polyurethane products. As innovation in sustainable and bio-based polyols gains traction, manufacturers are under pressure to scale production while improving environmental performance. In this evolving landscape, a select group of global leaders have emerged, combining technological expertise, extensive production capabilities, and strong R&D pipelines to maintain a competitive edge. Below are the top 10 polyurethane manufacturers shaping the industry’s future.
Top 10 Ureathane Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Argonics
Domain Est. 1997
Website: argonics.com
Key Highlights: Argonics is a polyurethane manufacturer that provides solutions for the concrete, aggregate, agriculture and mining industries’ hard-to-solve wear problems….
#2 Chemline Homepage
Domain Est. 1999 | Founded: 1997
Website: chemline.net
Key Highlights: Since 1997, Chemline has been a trusted partner in polyurethane and polyurea formulations, offering tailored solutions for large volume manufacturers….
#3 Urethane Products Corporation: Marine Fenders
Domain Est. 1996
Website: urethaneproducts.com
Key Highlights: Urethane Products Corporation (UPC) provides a wide range of urethanes and polyureas with an emphasis on marine industrial products….
#4 SWD Urethane
Domain Est. 1996
Website: swdurethane.com
Key Highlights: Working our way from being contractors, to distributors, to full-scale manufacturers, we’ve honed our spray foam expertise from the inside out….
#5 Precision Urethane
Domain Est. 1998
Website: precisionurethane.com
Key Highlights: Precision Urethane is a cast polyurethane manufacturer that carries stock & custom cast polyurethane products for a variety of applications….
#6 National Urethane Industries
Domain Est. 2021
Website: nui2.com
Key Highlights: NUI | National Urethane Industries | A South African Polyurethane Systems House with Global Technology, specializing in the manufacture of CASE products ……
#7 Mearthane Products Corporation
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mearthane.com
Key Highlights: We specialize in producing advanced polyurethane products and components engineered to tackle the toughest challenges. With highly customizable technologies and ……
#8 Prothane
Domain Est. 1997
Website: prothane.com
Key Highlights: We offer an extensive line of professional urethane-based high-performance products for cars and trucks, all made in the USA!…
#9 STOCKMEIER Urethanes
Domain Est. 2002
Website: stockmeier.com
Key Highlights: STOCKMEIER Urethanes is a trusted global polyurethane systems house focused on developing and producing coatings, adhesives, sealants, and elastomers….
#10 Nation’s Leading Commercial Roofing Company
Domain Est. 2006
Website: brazosurethane.com
Key Highlights: Brazos Urethane is a premier commercial roofing, waterproofing, insulation and sheet metal contractor. We have installed various roofing systems for over 30 ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Ureathane
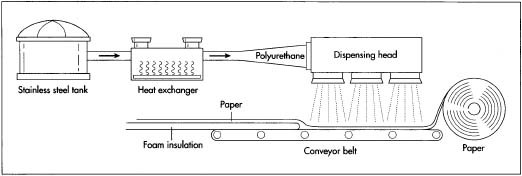
I’m sorry, but I currently don’t have access to real-time or future market data, including specific forecasts for the polyurethane market in 2026. However, I can provide a synthesized analysis based on current industry trajectories, technological advancements, and macroeconomic factors that are expected to influence the polyurethane market through 2026. Please note this is a projection and not a definitive forecast.
H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Polyurethane
-
Sustainable and Bio-Based Polyurethanes on the Rise
Driven by global environmental regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly materials, the polyurethane industry is expected to see increased adoption of bio-based raw materials. By 2026, manufacturers are likely to expand production of polyols derived from renewable sources such as castor oil, soybean oil, and recycled carbon feedstocks. Companies investing in green chemistry and circular economy models will gain competitive advantages. -
Stringent Regulations Influencing Formulations
Regulatory pressures, especially in the EU (e.g., REACH, Green Deal) and North America, will continue pushing the phase-out of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and harmful isocyanates. This will accelerate innovation in non-isocyanate polyurethanes (NIPUs) and water-based or low-VOC formulations across coatings, adhesives, sealants, and elastomers (CASE) applications. -
Growth in Construction and Insulation Sectors
The global push for energy-efficient buildings will sustain demand for rigid polyurethane foam in insulation. With governments investing in infrastructure and green building standards, the construction sector will remain a key driver for polyurethane consumption, particularly in emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East. -
Automotive Industry Transition Impact
While traditional automotive manufacturing remains a major consumer of polyurethane (seats, dashboards, insulation), the shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) may alter demand patterns. Lightweighting requirements in EVs could increase the use of polyurethane composites, but overall volume growth may slow in mature markets due to reduced interior complexity and material substitution. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific—especially China, India, and Southeast Asia—is projected to lead polyurethane demand growth by 2026 due to urbanization, industrialization, and rising disposable incomes. Local production capacities are likely to expand, reducing reliance on imports and reshaping global supply chains. -
Digitalization and Smart Manufacturing
By 2026, digital tools such as AI-driven process optimization, predictive maintenance, and blockchain for supply chain transparency will become more integrated into polyurethane manufacturing. This will improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance product consistency. -
Recycling and End-of-Life Management
Chemical recycling technologies—such as glycolysis and hydrolysis—for post-industrial and post-consumer polyurethane waste are expected to scale up. Regulatory mandates for plastic waste reduction will push industry players to adopt closed-loop systems, making recyclability a key differentiator. -
Price Volatility and Feedstock Security
Polyurethane production depends heavily on petrochemical feedstocks like benzene and propylene. Geopolitical instability and fluctuating oil prices may lead to cost volatility. As a result, companies will likely diversify supply sources and explore alternative feedstocks to mitigate risks.
Conclusion
By 2026, the polyurethane market is expected to be shaped by sustainability imperatives, technological innovation, and regional demand shifts. Companies that prioritize environmental compliance, invest in R&D for greener alternatives, and adapt to evolving customer needs will be best positioned for growth. While challenges remain—especially around regulation and raw material stability—the long-term outlook for polyurethane remains positive across key end-use industries.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Urethane: Quality and Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
Sourcing urethane components—whether raw materials, prepolymers, or finished parts—requires careful attention to both quality consistency and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to product failures, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Below are the key pitfalls to avoid.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
1. Inconsistent Material Specifications
Urethane performance heavily depends on precise chemical formulations and processing conditions. A common mistake is assuming all materials labeled “polyurethane” are interchangeable. Suppliers may vary significantly in isocyanate index, NCO content, molecular weight, and additive packages. Without strict material certifications (e.g., CoA—Certificate of Analysis) and testing protocols, inconsistencies can result in poor mechanical properties, adhesion failure, or premature degradation.
2. Lack of Batch-to-Batch Traceability
Low-cost or unqualified suppliers may not maintain rigorous batch tracking. If a quality issue arises in the field, the inability to trace raw materials back to a specific production run hampers root cause analysis and corrective actions. Ensure suppliers provide lot traceability and retain samples.
3. Inadequate Testing and Validation
Many buyers rely solely on supplier-provided data without independent verification. Conducting in-house or third-party testing (e.g., tensile strength, elongation, hardness, thermal stability) is essential, especially for mission-critical applications like medical devices or automotive components.
4. Poor Processing Control by Supplier
Even with high-quality raw materials, improper curing, mixing ratios, or degassing during manufacturing can compromise the final product. Evaluate the supplier’s production controls, quality management system (e.g., ISO 9001), and process validation records.
Intellectual Property (IP)-Related Pitfalls
1. Unprotected Design and Formulation Disclosures
Sharing detailed product designs, chemical formulations, or performance requirements without a robust Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) exposes your IP. Always execute mutual NDAs before technical discussions and limit information to what is strictly necessary.
2. Ambiguous Ownership of Developed IP
When collaborating with a supplier on custom formulations or tooling, unclear contracts may result in disputes over IP ownership. Define upfront who owns modifications, tooling, and process innovations. Use clear work-for-hire clauses or IP assignment agreements.
3. Risk of Reverse Engineering
Urethane parts, especially molded components, can be reverse-engineered. Suppliers in regions with weak IP enforcement may replicate and sell your designs to competitors. Mitigate this by working with trusted partners, using trade secret protections, and limiting access to critical design features.
4. Infringement of Third-Party Patents
Some urethane chemistries or processing methods are patented. Sourcing from a supplier using proprietary technology without proper licensing can expose your company to infringement claims. Conduct due diligence on the supplier’s freedom to operate (FTO), particularly for specialty urethanes (e.g., moisture-cured, aromatic vs. aliphatic).
Best Practices to Mitigate Risks
- Qualify Suppliers Rigorously: Audit facilities, review quality systems, and assess technical capabilities.
- Define Clear Specifications: Use detailed technical data sheets and acceptance criteria.
- Protect IP Contractually: Use strong NDAs, IP assignment clauses, and audit rights.
- Conduct Regular Audits and Testing: Maintain quality oversight and verify compliance.
- Diversify Supply Chain: Avoid over-reliance on a single source, especially in high-risk jurisdictions.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP pitfalls, companies can ensure reliable urethane sourcing while safeguarding their innovations and brand integrity.
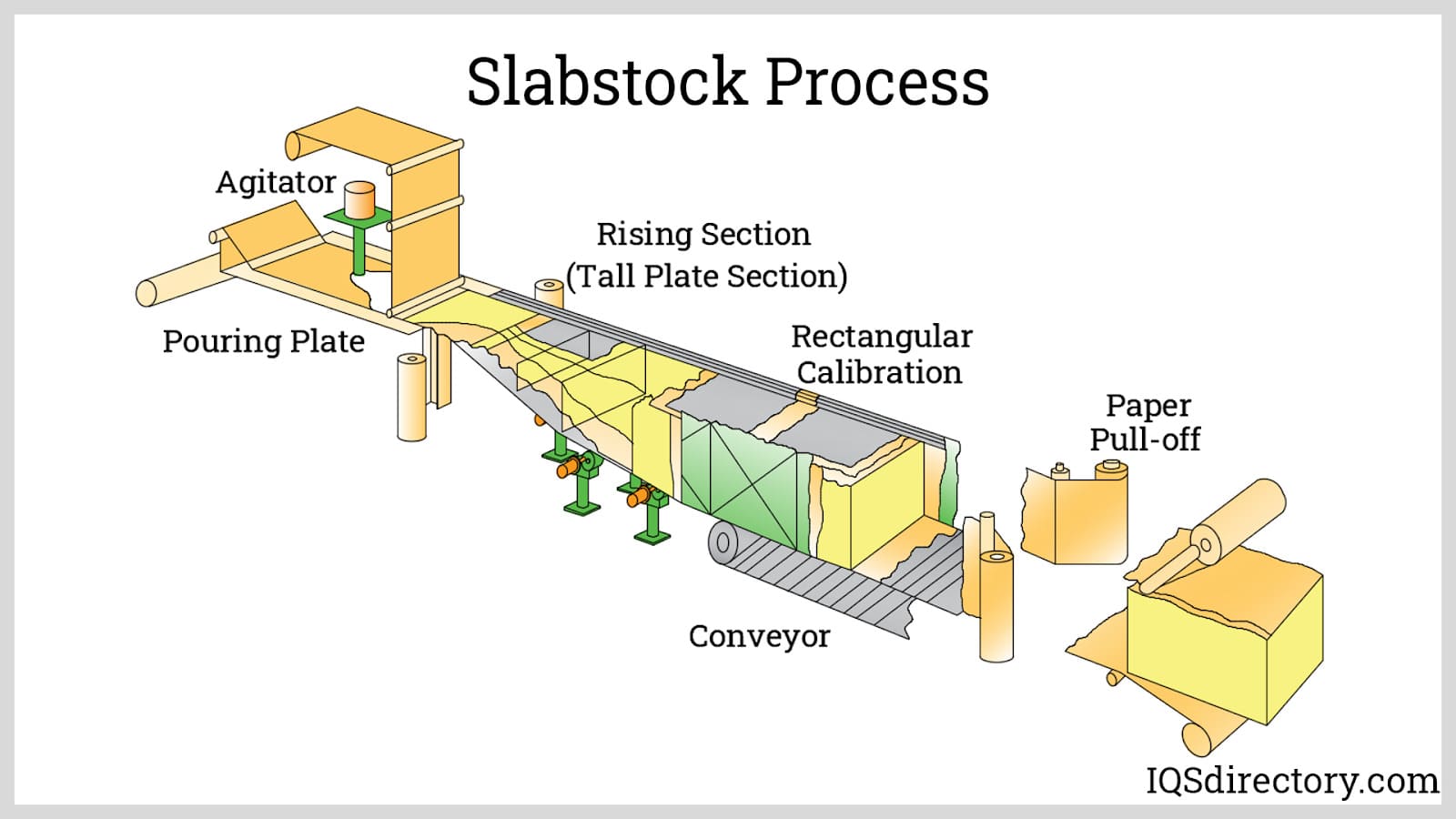
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Urethane (H2)
Note: While “Urethane” is a common term, the correct chemical name is Urethane (also known as ethyl carbamate). However, in industrial contexts, “urethane” often colloquially refers to polyurethanes or isocyanates (such as MDI or TDI), which are chemically distinct. This guide assumes you are referring to Urethane (ethyl carbamate), a known carcinogen. If you meant polyurethane prepolymers or isocyanates, compliance requirements differ significantly.
H2: Hazard Identification
- Chemical Name: Urethane (Ethyl Carbamate)
- CAS Number: 51-79-6
- UN Number: Not assigned (typically not transported as a standalone hazardous material due to high hazard and limited use)
- GHS Classification (Globally Harmonized System):
- H350: May cause cancer (Carc. 1B – Presumed human carcinogen)
- H302: Harmful if swallowed
- H315: Causes skin irritation
- H319: Causes serious eye irritation
- H335: May cause respiratory irritation
- H341: Suspected of causing genetic defects (Muta. 2)
- H410: Very toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects
- NFPA 704 Rating:
- Health: 3 (Serious)
- Flammability: 1 (Slight)
- Instability: 1 (Slight)
- Special: OX (Oxidizer – note: urethane itself is not typically an oxidizer; this may require verification based on specific form)
- Primary Hazards:
- Carcinogenicity: Primary concern; classified as a Group 2A carcinogen (probably carcinogenic to humans) by IARC.
- Toxicity: Acute toxicity via ingestion, inhalation, or dermal contact.
- Environmental Hazard: Toxic to aquatic organisms.
H2: Safe Handling & Storage
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Respiratory Protection: Use NIOSH-approved respirators with organic vapor cartridges if airborne concentrations exceed exposure limits. In high-risk scenarios, use supplied-air respirators.
- Eye/Face Protection: Chemical splash goggles and/or face shield.
- Skin Protection: Wear nitrile or neoprene gloves, impermeable apron, and protective clothing. Avoid skin contact.
- Hygiene Measures: Wash hands thoroughly after handling. Do not eat, drink, or smoke in areas where urethane is handled.
- Engineering Controls:
- Use in a well-ventilated area or fume hood.
- Implement local exhaust ventilation at the point of release.
- Use closed systems where possible.
- Storage Conditions:
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from heat, sparks, and open flames.
- Keep container tightly closed.
- Store away from strong oxidizers, strong acids, and strong bases.
- Use only non-sparking tools and equipment.
- Clearly label all containers with GHS pictograms and hazard statements.
- Segregate from food, feed, and personal care products.
H2: Transportation & Shipping
- Regulatory Status:
- Urethane (CAS 51-79-6) is not assigned a UN number under the UN Model Regulations (UN TDG) for transport due to its high hazard profile and limited commercial use.
- It may be regulated under national regulations as a toxic or carcinogenic substance.
- Consult national and international transport regulations (e.g., 49 CFR in the U.S., ADR in Europe) before attempting transport.
- Packaging:
- Use tightly sealed, inert containers (e.g., glass, HDPE with chemical-resistant liner).
- Outer packaging must be strong enough to prevent leakage under normal conditions.
- Package must meet regulatory requirements for toxic substances if classified for transport.
- Labeling & Marking:
- Affix GHS labels with hazard pictograms (Skull & Crossbones, Health Hazard, Environment).
- Include proper shipping name, hazard class, and identification number if applicable.
- Mark with “Carcinogen” and “Toxic.”
- Documentation:
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS) must accompany shipment (Section 14 required).
- Shipper must declare hazards accurately on transport documents.
- Notify carrier of carcinogenic and toxic nature.
- Special Provisions:
- Minimize quantity shipped.
- Use dedicated or thoroughly cleaned vehicles if bulk transport is necessary.
- Avoid passenger transport.
H2: Regulatory Compliance
- OSHA (U.S.):
- Regulated under 29 CFR 1910.1000 (Air Contaminants) and 29 CFR 1910.1450 (Laboratory Standard).
- Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL): Not established; use strict exposure controls.
- Requires hazard communication (HazCom 2012), exposure assessment, and medical surveillance if exposure is possible.
- EPA (U.S.):
- Listed as a hazardous air pollutant (HAP) under the Clean Air Act.
- Regulated under TSCA (Toxic Substances Control Act); may require reporting.
- RCRA: May be considered hazardous waste if discarded (listed or characteristic waste).
- REACH (EU):
- Listed on the Candidate List of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) due to carcinogenicity and mutagenicity.
- Requires communication in the supply chain and possible authorization for use.
- GHS Implementation:
- Ensure SDS and labels comply with local GHS regulations (e.g., OSHA HazCom, CLP in EU).
- Other Jurisdictions:
- Check local regulations (e.g., WHMIS in Canada, NICNAS in Australia).
H2: Emergency Response
- Spill Response:
- Evacuate non-essential personnel.
- Wear full PPE (including respirator).
- Contain spill with inert absorbent material (e.g., vermiculite, sand).
- Collect in labeled, sealed containers for hazardous waste disposal.
- Ventilate area thoroughly.
- Do not allow into sewers or waterways.
- Fire Hazards:
- Not highly flammable, but may emit toxic fumes (e.g., nitrogen oxides, ammonia) when heated.
- Use dry chemical, CO₂, or foam extinguishers.
- Wear self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) during fire response.
- First Aid:
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air. Seek medical attention immediately.
- Skin Contact: Remove contaminated clothing. Wash skin with soap and water. Seek medical attention.
- Eye Contact: Rinse cautiously with water for at least 15 minutes. Seek immediate medical attention.
- Ingestion: Rinse mouth. Do not induce vomiting. Seek immediate medical attention.
- Emergency Contacts:
- Poison Control Center: 1-800-222-1222 (U.S.)
- Local emergency services: 911 (U.S.)
H2: Waste Disposal
- Dispose of as hazardous waste in accordance with local, state/provincial, and federal regulations.
- Use licensed hazardous waste disposal contractors.
- Label waste containers clearly as “Hazardous Waste – Contains Urethane (Carcinogen).”
- Complete waste manifests and maintain records.
- Do not dispose of down the drain or in regular trash.
Disclaimer: This guide is for informational purposes only. Regulations vary by jurisdiction and application. Always consult the latest Safety Data Sheet (SDS), local regulations, and qualified safety professionals before handling, storing, transporting, or disposing of urethane.
Conclusion on Sourcing Polyurethane
Sourcing polyurethane requires a strategic approach that balances quality, cost, sustainability, and supply chain reliability. As a versatile material used across industries—from automotive and construction to furniture and electronics—selecting the right polyurethane supplier is critical to ensuring product performance and regulatory compliance. Key factors to consider include the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities, consistency in raw material sourcing, environmental and safety certifications, and ability to meet volume and customization demands.
Additionally, with increasing emphasis on sustainability, prioritizing suppliers that offer bio-based or recyclable polyurethane options, and adhere to eco-friendly production practices, supports long-term corporate responsibility goals. Geopolitical considerations, logistics, and supply chain resilience should also inform sourcing decisions, particularly in volatile markets.
In conclusion, a well-informed polyurethane sourcing strategy—grounded in supplier due diligence, material specifications, and forward-looking sustainability criteria—enables businesses to maintain competitiveness, reduce risks, and support innovation in their respective markets.












