The global microscope market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand in life sciences, pharmaceuticals, and academic research. According to Mordor Intelligence, the microscope market was valued at approximately USD 3.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7.5% from 2024 to 2029. A significant portion of this growth is attributed to advancements in optical technologies and rising investments in R&D infrastructure, particularly fueling demand for upright microscopes—widely favored for metallurgical analysis, histopathology, and industrial quality control. As the need for high-precision imaging persists, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders in innovation, reliability, and application-specific solutions. Based on market presence, technological capabilities, and customer adoption trends, here are the top seven upright microscope manufacturers shaping the industry landscape.
Top 7 Upright Microscope Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Microscope Products
Domain Est. 1993
Website: microscope.healthcare.nikon.com
Key Highlights: Nikon microscope products, including objective lenses, cameras, confocal, multiphoton, super-resolution, and OEM….
#2 Accu
Domain Est. 1996
Website: accu-scope.com
Key Highlights: We are a leading manufacturer of microscopes and related accessories for life science, clinical, research, education and industrial applications….
#3 Upright Microscopes for Metallographic Sample Preparation
Domain Est. 1995
Website: buehler.com
Key Highlights: Upright Industrial Microscopes are versatile upright microscopes suitable for reflected and/or transmitted light applications. Perfect for high magnification ……
#4 ZEISS Axio Imager 2 for Life Science Research
Domain Est. 1995
Website: zeiss.com
Key Highlights: ZEISS Axio Imager 2. Your Upright Microscope Platform for Life Science Research. Combine the best for life science research in a single upright platform….
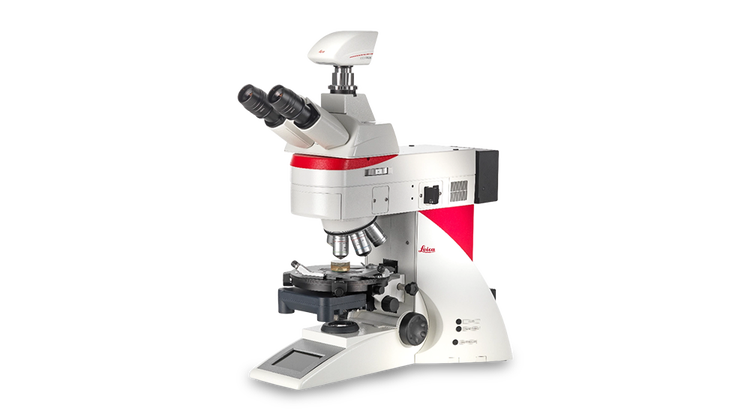
#5 Upright Microscopes
Domain Est. 1997
Website: leica-microsystems.com
Key Highlights: Get the publication-quality imaging and customizable upright microscope solution you need for your Life Science research with Leica Microsystems. These powerful ……
#6 CrestOptics
Domain Est. 2013
Website: crestoptics.com
Key Highlights: CrestOptics S.p.A. is a leading company in the development and manufacturing of advanced systems for fluorescence microscopy. … It is very easy to install and ……
#7 Life Science Microscopes
Domain Est. 2021
Website: evidentscientific.com
Key Highlights: Shop a range of manual and automated upright microscope models ideal for pathology and cytology research, clinical laboratory research, and more. Read more ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Upright Microscope

H2: Projected Market Trends for Upright Microscopes in 2026
The global upright microscope market is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by advancements in imaging technology, rising demand in life sciences and industrial applications, and increasing investments in research and development across academic and commercial sectors. Several key trends are expected to shape the market landscape during this period.
1. Integration of Digital and AI-Driven Imaging
A dominant trend in 2026 will be the integration of digital imaging systems and artificial intelligence (AI) into upright microscopes. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating high-resolution CMOS and CCD cameras, real-time image processing software, and AI-powered analytics to enhance image clarity, automate sample analysis, and reduce human error. These smart microscopes are particularly beneficial in pathology, material science, and drug discovery, where precision and speed are critical.
2. Expansion in Life Sciences and Biomedical Research
Life sciences remain the largest end-use segment for upright microscopes. With ongoing advancements in genomics, cell biology, and neuroscience, research institutions and biotech companies are investing heavily in advanced microscopy tools. The demand for upright models—ideal for observing fixed and stained specimens on slides—will remain strong due to their optical precision and compatibility with fluorescence and phase-contrast techniques.
3. Growth in Emerging Economies
Asia-Pacific, especially countries like China, India, and South Korea, is expected to witness significant market growth by 2026. Expanding educational infrastructure, government funding for scientific research, and the rise of local manufacturing are contributing to increased adoption of upright microscopes. These regions are also becoming hubs for contract research organizations (CROs), further boosting demand.
4. Emphasis on Ergonomics and User Experience
Manufacturers are focusing on improving the ergonomics of upright microscopes to reduce user fatigue during prolonged use. Features such as adjustable viewing heads, motorized stages, and intuitive user interfaces are becoming standard. This trend reflects a broader industry shift toward user-centric design, particularly in clinical and industrial environments where efficiency is paramount.
5. Sustainability and Modular Design
Environmental sustainability is gaining traction in the scientific equipment sector. By 2026, leading vendors are expected to emphasize energy-efficient LED illumination, recyclable materials, and modular designs that allow for easy upgrades rather than full replacements. This reduces electronic waste and appeals to environmentally conscious institutions.
6. Competitive Landscape and Market Consolidation
The upright microscope market will likely see continued consolidation, with major players such as Olympus, Leica Microsystems, Nikon, and Zeiss expanding their portfolios through innovation and strategic partnerships. At the same time, mid-tier and regional manufacturers are gaining ground by offering cost-effective, niche solutions tailored to specific applications.
In conclusion, the 2026 upright microscope market will be characterized by technological innovation, geographic expansion, and a stronger focus on usability and sustainability. These trends will not only enhance research capabilities but also broaden access to advanced microscopy across diverse sectors and regions.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing an Upright Microscope (Quality and IP)
Sourcing an upright microscope requires careful consideration to avoid compromising on performance, longevity, and intellectual property (IP) integrity. Overlooking key factors can lead to substandard equipment, legal exposure, or operational inefficiencies. Below are critical pitfalls to watch for:
Poor Optical Quality and Component Standards
One of the most frequent issues is selecting a microscope with inferior optics or substandard mechanical components. Low-quality objectives, eyepieces, or prisms can result in poor resolution, chromatic aberration, and inconsistent imaging—especially critical in research or diagnostic settings. Buyers may be tempted by lower prices but fail to verify specifications such as Numerical Aperture (NA), anti-reflective coatings, or flat-field correction. Always request optical test reports and evaluate performance under real-use conditions before purchase.
Lack of Traceability and IP Compliance
Sourcing from suppliers that do not provide documentation on component origins or manufacturing processes can pose IP risks. Some manufacturers may integrate patented optical designs or electronic subsystems without proper licensing, exposing the end-user to infringement claims. Ensure the supplier guarantees freedom to operate and can provide evidence of legitimate IP rights for key technologies—especially important in regulated industries or when publishing research.
Inadequate After-Sales Support and Calibration Services
A high-quality microscope requires regular maintenance and calibration. Sourcing from vendors without reliable local service networks or certified technicians can lead to prolonged downtime and degraded performance. Verify whether the supplier offers factory-authorized support, software updates, and access to genuine spare parts. Lack of support also complicates compliance with quality standards (e.g., ISO, GLP).
Hidden Costs from Non-Standard Interfaces or Proprietary Software
Some microscopes use proprietary software or digital interfaces that lock users into a single ecosystem, limiting integration with third-party analysis tools or imaging systems. This can hinder data sharing, automation, and future scalability. Additionally, licensing fees for software upgrades or image analysis packages may not be transparent upfront. Evaluate compatibility with open standards (e.g., DICOM, TIFF export) and inquire about total cost of ownership.
Misrepresentation of Specifications or Performance Claims
Be cautious of exaggerated claims regarding magnification, resolution, or automation capabilities. Some suppliers may cite theoretical maximums under ideal conditions that are unachievable in practice. Always cross-reference specifications with independent reviews or request demo units. Third-party verification (e.g., through microscopy core facilities) can help validate performance claims and prevent procurement of underperforming systems.
By proactively addressing these pitfalls—focusing on verifiable quality metrics and clear IP positioning—organizations can ensure they invest in a reliable, compliant, and future-ready upright microscope.
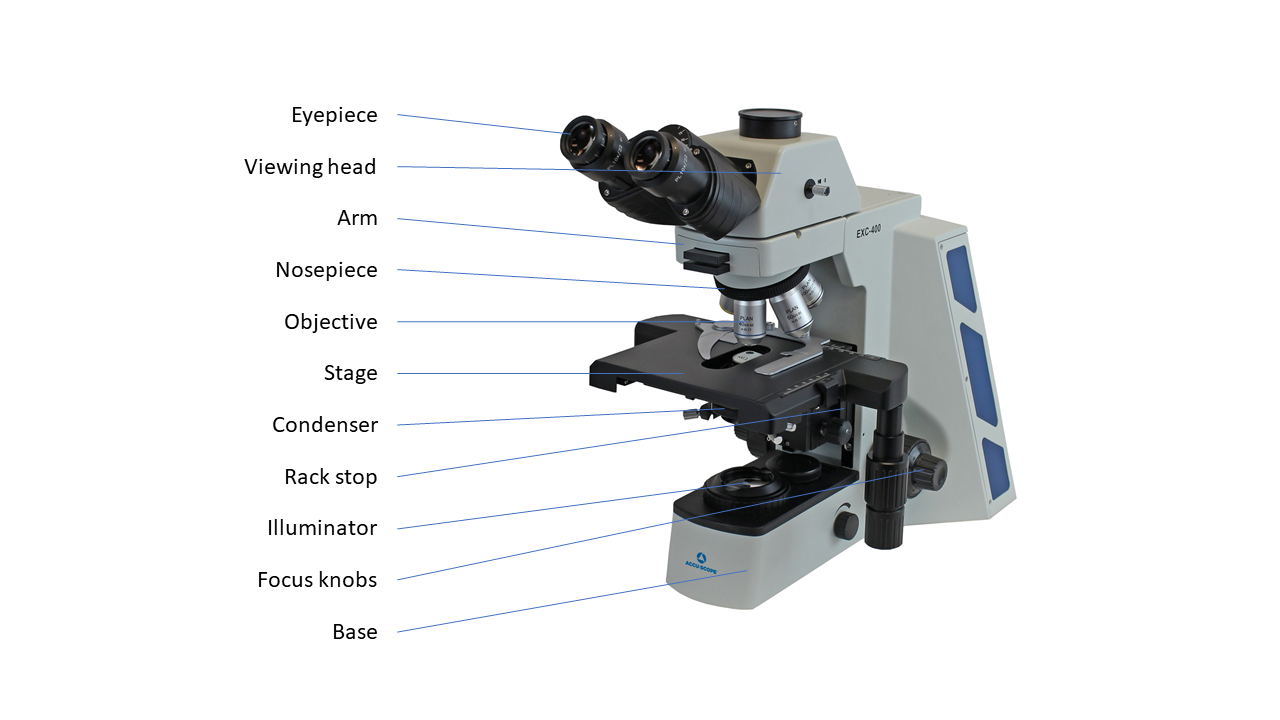
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Upright Microscope
Product Classification and Regulatory Requirements
Upright microscopes are generally classified as non-medical laboratory equipment unless specifically designed and marketed for medical diagnostics. They typically fall under general scientific instrument regulations rather than medical device directives. However, compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 (quality management) and IEC 61010-1 (safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use) is essential. Confirm local regulatory classifications, especially if the microscope includes digital imaging components or software intended for clinical analysis.
Export Controls and Documentation
Ensure compliance with export control regulations, particularly if the microscope contains sensitive components (e.g., high-resolution cameras or laser elements). Most standard upright microscopes are not subject to ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) or EAR (Export Administration Regulations) controls, but verify the ECCN (Export Control Classification Number) before shipment. Required documentation includes a commercial invoice, packing list, and bill of lading/air waybill. Include technical specifications such as voltage rating, weight, and dimensions to support customs clearance.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Package the microscope securely using manufacturer-recommended materials to prevent damage during transit. Use double-walled cardboard boxes with internal foam or molded inserts to immobilize the instrument. Clearly label packages with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” markings. Avoid exposing the microscope to extreme temperatures, humidity, or dust during storage and transport. For international shipments, ensure packaging meets ISPM 15 standards if wooden materials are used.
Import Regulations and Duties
Research destination country import regulations. Some countries may require certification marks (e.g., CE, UKCA, or KC) or local conformity assessments. Low-voltage directive compliance may apply due to electrical components. Import duties and VAT/GST rates vary by region; check the HS (Harmonized System) code—typically 9011.10 or 9011.80—for optical microscopes. Provide accurate valuation on customs forms to avoid delays or penalties.
Transportation and Freight Considerations
Ship via reliable freight carriers experienced in handling precision instruments. Air freight is recommended for urgent deliveries; sea freight may be cost-effective for bulk orders. Use tracked and insured shipping with real-time monitoring. Coordinate with the recipient to ensure availability for customs brokerage and final-mile delivery. For oversized or heavy models, confirm liftgate service or forklift access at delivery points.
Installation and Site Compliance
Verify that the end-user’s facility meets operational requirements: stable power supply (compatible voltage and grounding), vibration-free surface, controlled ambient temperature, and low dust environment. Provide installation guidelines and recommend professional setup for complex configurations. Ensure compliance with local electrical codes and laboratory safety standards (e.g., OSHA or equivalent).
Warranty, Service, and End-of-Life Compliance
Include warranty information compliant with local consumer protection laws (e.g., EU Consumer Rights Directive). Provide accessible service support and spare parts. For end-of-life disposal, comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives in applicable regions. Offer take-back or recycling guidance to ensure environmentally responsible handling of electronic and optical components.
In conclusion, sourcing an upright microscope requires careful consideration of several key factors including optical quality, magnification range, illumination options, durability, and compatibility with digital imaging systems. The intended application—whether for education, research, or industrial use—will heavily influence the specifications and budget. Evaluating reputable suppliers, comparing warranty and after-sales support, and ensuring availability of service and spare parts are crucial steps in making a reliable investment. By aligning technical requirements with cost-effectiveness and long-term usability, organizations can select an upright microscope that delivers consistent performance, enhances productivity, and supports accurate observation and analysis in their respective fields.