The global electric discharge machining (EDM) market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising demand for high-precision components in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. According to Grand View Research, the global EDM market size was valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.4% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by advancements in CNC technology, increasing adoption of small-hole drilling and micro-EDM applications, and the expanding use of hard-to-machine materials like titanium and Inconel. As industries prioritize accuracy and complex geometries, manufacturers are innovating across different EDM modalities—spanning wire, sinker, and hole drilling systems—giving rise to a diverse ecosystem of equipment providers. In this landscape, nine distinct types of EDM manufacturers have emerged, each specializing in unique technological approaches, service models, and industrial applications, shaping the future of precision manufacturing.
Top 9 Types Of Electric Discharge Machining Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
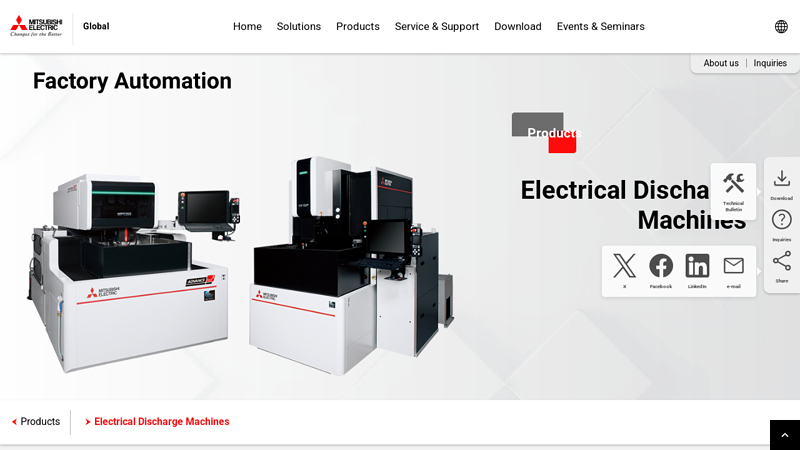
#1 Electrical Discharge Machines
Domain Est. 1996
Website: mitsubishielectric.com
Key Highlights: Product List. Wire-cut Electrical Discharge Machines. Application in wide range from parts manufacturing to ultra-high accurate mold making….
#2 Makino Electrical Discharge Machining
Domain Est. 1996
Website: makino.com
Key Highlights: Types of EDM Machining. Sinker EDMs. Sinker EDMs are ideal for hardened materials and complex part details that are difficult to machine by other methods….
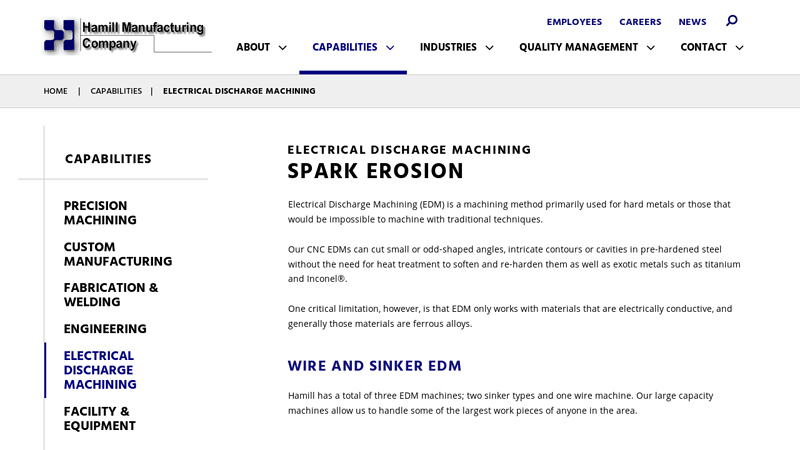
#3 EDM
Domain Est. 1997
Website: hamillmfg.com
Key Highlights: Hamill has a total of three EDM machines; two sinker types and one wire machine. Our large capacity machines allow us to handle some of the largest work pieces ……
#4 Types of EDM Machining and Their Applications
Domain Est. 1998
Website: astromachineworks.com
Key Highlights: There are three different types of EDM machining, which are wire EDM, die sinking EDM, and EDM hole drilling….
#5 UNITED MACHINING
Domain Est. 1999
Website: gfms.com
Key Highlights: The portfolio includes milling, EDM, laser texturing, laser micromachining, and additive manufacturing machines. Our advanced spindles, automation, tooling, and ……
#6 Electrical Discharge Machining Services
Domain Est. 2007
Website: fictiv.com
Key Highlights: There are two main types of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) processes – wire EDM and sinker EDM, which are useful for cutting deep pockets and complex ……
#7 Electrical Discharge Machining Companies
Domain Est. 2004
Website: iqsdirectory.com
Key Highlights: IQS Directory is a top industrial directory listing of leading industrial electrical discharge machining companies and suppliers….
#8 Blog|Taiwan Leading Electrical Discharge Machining …
Domain Est. 2006
Website: oscaredm.com
Key Highlights: This technology mainly includes two types: wire EDM and die- sinker EDM (also known as spark machining). 2024. 06. 13. View more · Electric Discharge Machining ……
#9 10 Best Wire EDM Machine Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2015
Website: xometry.com
Key Highlights: An overview of ten different wire EDM machine manufacturers and which kinds of machines they offer….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Types Of Electric Discharge Machining
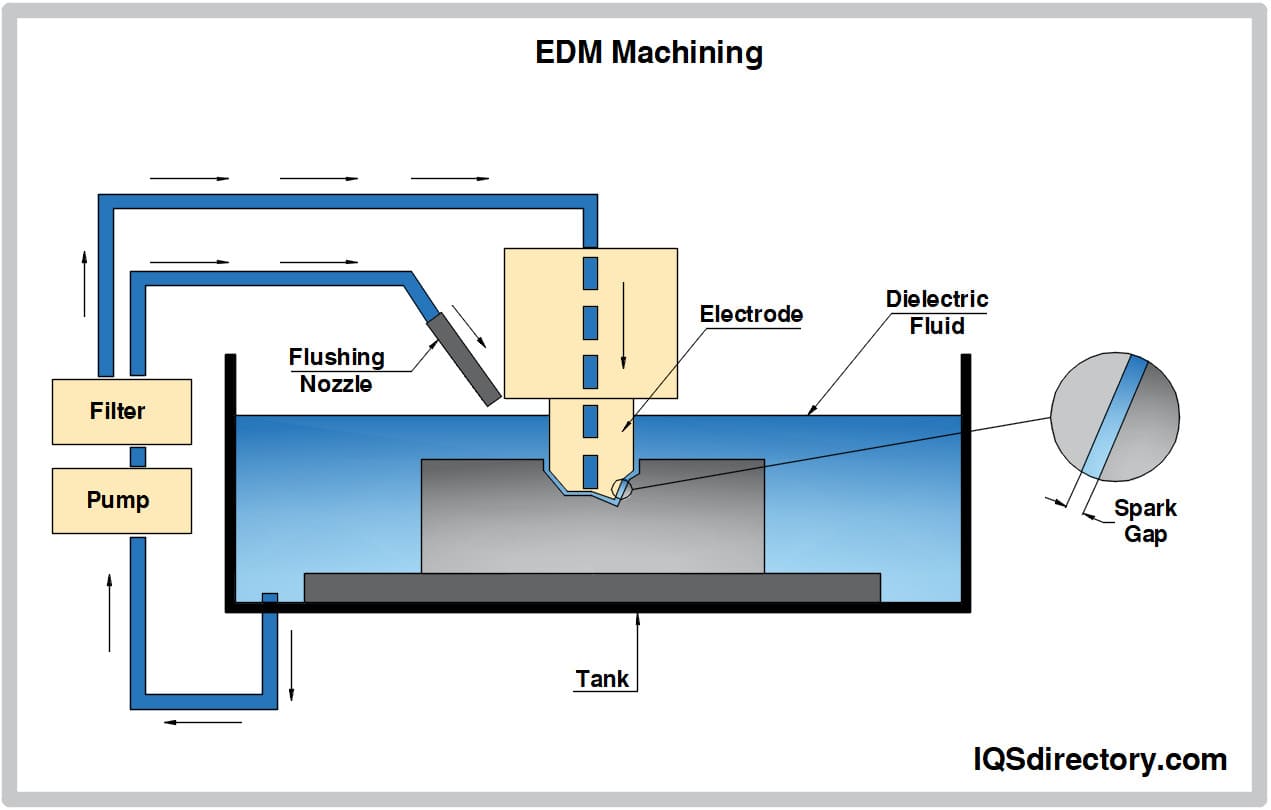
2026 Market Trends for Types of Electric Discharge Machining
Global Demand Surge in Precision Manufacturing
By 2026, the demand for advanced Electric Discharge Machining (EDM) technologies is projected to rise significantly, driven by the growing need for high-precision components in aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and mold-making industries. As manufacturers increasingly focus on complex geometries and hard-to-machine materials such as titanium, Inconel, and hardened steels, EDM remains a critical solution due to its ability to machine conductive materials without direct contact. This shift is particularly influencing the adoption of both Wire EDM and Sinker EDM systems, with market analysts forecasting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 7–9% through 2026.
Advancements in Wire Electric Discharge Machining (Wire EDM)
Wire EDM is expected to dominate the EDM market by 2026 due to continuous technological advancements. Innovations in automated threading, improved dielectric fluid systems, and integration with Industry 4.0 technologies—such as IoT-enabled monitoring and AI-driven process optimization—are enhancing precision, reducing downtime, and improving surface finishes. Multi-wire systems and taper-cutting capabilities are also becoming standard in high-end applications. Additionally, the demand for micro-Wire EDM in the medical and electronics sectors is growing, enabling the production of intricate features in small-scale components.
Growth in Sinker EDM with Enhanced Automation
Sinker EDM (also known as Ram or Conventional EDM) continues to see robust growth, especially in tool and die manufacturing and mold production. By 2026, the integration of automated electrode changers, advanced CNC controls, and adaptive machining strategies is making Sinker EDM more efficient and accessible. The trend toward hybrid machining—combining Sinker EDM with milling or grinding in a single setup—is also gaining momentum, allowing manufacturers to streamline production processes and reduce lead times.
Rising Adoption of Micro-EDM and Small-Hole Drilling EDM
Micro-EDM and small-hole drilling EDM are emerging as high-growth niches within the EDM market. These technologies are critical for producing micro-features in components for aerospace fuel systems, medical implants, and semiconductor equipment. By 2026, increased investment in R&D for miniaturized components and nano-precision machining is expected to boost demand for micro-EDM systems. Moreover, improvements in pulse generators and servo control systems are enabling higher accuracy and faster material removal rates in small-hole drilling applications.
Regional Market Dynamics and Industrial 4.0 Integration
Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and India, is anticipated to lead the global EDM market by 2026, fueled by rapid industrialization and expanding manufacturing sectors. North America and Europe will maintain strong demand, driven by aerospace innovation and high-end medical device production. A key trend across all regions is the integration of EDM machines with digital twins, predictive maintenance platforms, and cloud-based manufacturing execution systems—hallmarks of Industry 4.0—enhancing productivity and enabling smart factory ecosystems.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Initiatives
Environmental considerations are shaping the future of EDM technologies. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to prioritize energy-efficient power supplies, recyclable dielectric fluids, and closed-loop filtration systems to reduce environmental impact. Regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability goals are encouraging the development of greener EDM solutions, further influencing equipment design and operational practices.
In conclusion, the 2026 landscape for Electric Discharge Machining will be defined by innovation, automation, and integration with digital manufacturing ecosystems. Wire EDM, Sinker EDM, and specialized forms like micro-EDM will continue to evolve, meeting the escalating demands of high-precision industries worldwide.
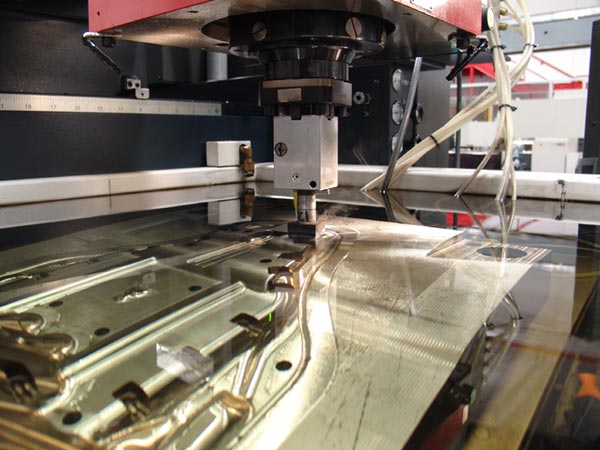

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Types of Electric Discharge Machining (Quality, IP)
Sourcing Electric Discharge Machining (EDM) services—whether Wire EDM, Sinker EDM (also known as Ram EDM), or Hole Drilling EDM—requires careful evaluation to avoid compromising on quality and intellectual property (IP) protection. Below are key pitfalls to watch for in both areas.
Quality-Related Pitfalls
Choosing Low-Capability Machines or Outdated Technology
Not all EDM equipment is created equal. Sourcing from suppliers using outdated or poorly maintained machines can lead to inconsistent tolerances, surface finish issues, and longer lead times. Older machines may lack precision motion control or adaptive spark monitoring, increasing the risk of part defects or rework.
Inadequate Process Control and Documentation
A reliable EDM supplier should employ standardized processes with real-time monitoring and comprehensive documentation (e.g., process logs, inspection reports). Sourcing from vendors without proper quality management systems (like ISO 9001 certification) increases the risk of variability and traceability issues, especially in regulated industries.
Lack of Skilled Operators and Engineers
EDM processes require experienced technicians to set up, monitor, and troubleshoot operations. Sourcing from vendors with insufficiently trained staff can lead to improper parameter selection, electrode wear, or incorrect flushing, resulting in poor dimensional accuracy or damaged workpieces.
Insufficient Post-Processing and Inspection
EDM can leave recast layers or micro-cracks. Failing to source from suppliers who offer proper post-machining treatments (e.g., stress relieving, polishing) and rigorous inspection (e.g., CMM, optical comparators) may result in parts that fail in service despite meeting nominal dimensions.
Intellectual Property (IP) Protection Pitfalls
Weak or Absent NDAs and IP Agreements
Without a legally binding Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) and clear IP ownership clauses in the contract, your designs, tool paths, or proprietary geometries may be exposed. Some suppliers may reuse electrode designs or program logic for other customers, compromising competitive advantage.
Insecure Data Transfer and Storage
Sharing CAD/CAM files without encryption or secure file transfer protocols (e.g., SFTP, secure portals) risks unauthorized access. Vendors with poor cybersecurity practices (e.g., unsecured networks, shared workstations) increase the chance of IP theft or data breaches.
Third-Party Subcontracting Without Oversight
Some EDM providers outsource work to subcontractors without informing the client. This creates a blind spot in IP protection, as your design files may be handled by unvetted parties with no direct contractual obligation to protect your IP.
Lack of Physical and Digital Access Controls
Ensure the supplier limits access to your job files and physical prototypes. Unrestricted access on the shop floor or in design departments—especially in shared facilities—can lead to inadvertent or deliberate IP exposure.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence: verify certifications, audit processes, enforce strong contractual IP terms, and assess both technical capability and data security practices before finalizing a supplier.
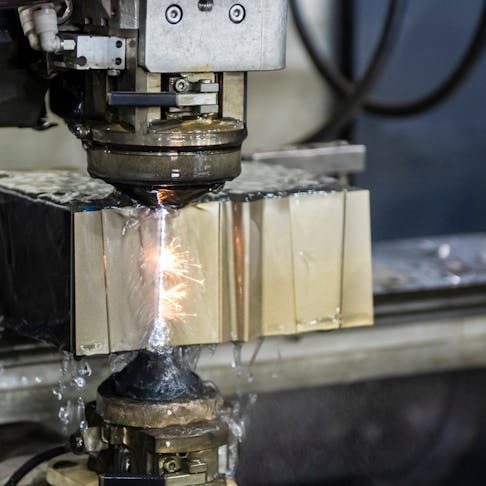

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Types Of Electric Discharge Machining
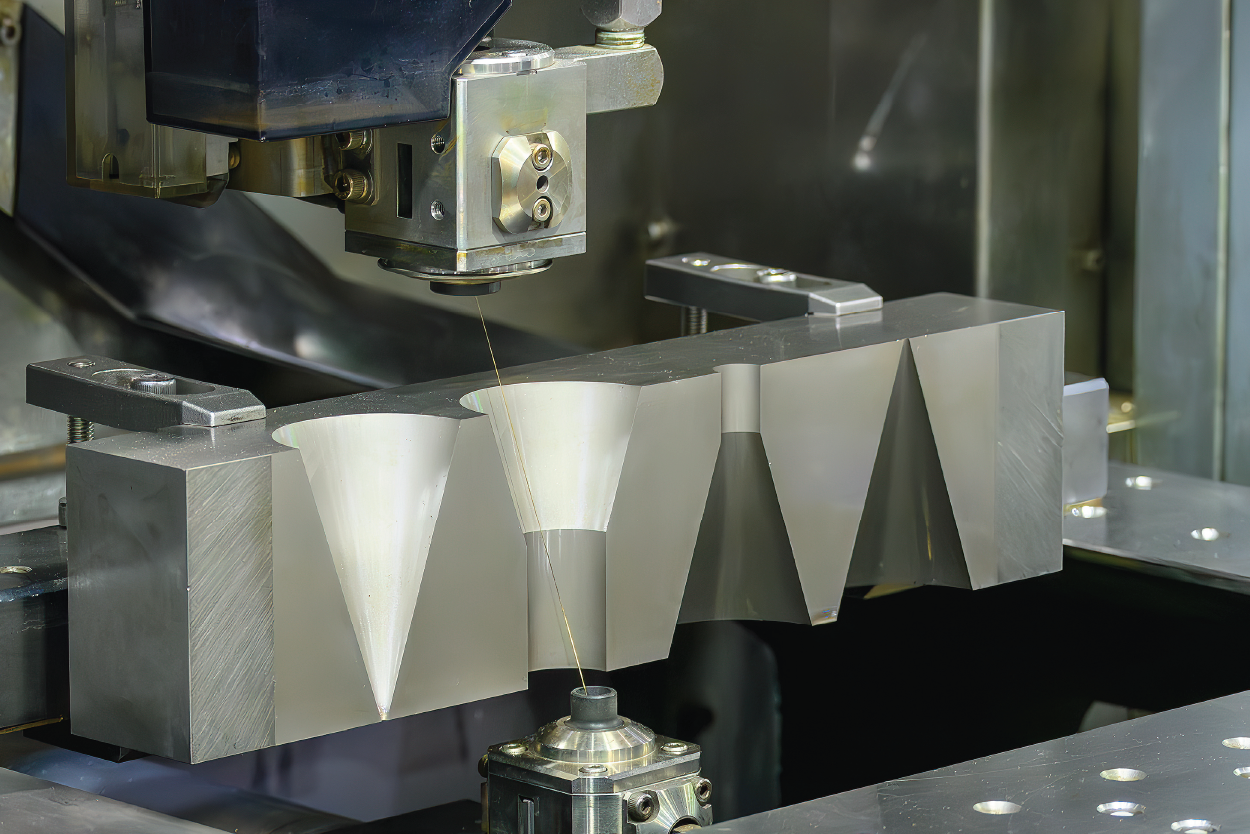
Electric Discharge Machining (EDM) is a precision manufacturing process that uses electrical discharges to shape conductive materials. It is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and tool & die manufacturing. Ensuring efficient logistics and regulatory compliance for EDM operations is essential for safety, environmental responsibility, and operational continuity. This guide outlines key considerations for managing logistics and compliance across the main types of EDM: Wire EDM, Sinker EDM (Ram EDM), and Hole Drilling EDM.
Wire Electric Discharge Machining (Wire EDM)
Wire EDM uses a thin, electrically charged wire to cut intricate shapes through conductive materials. The wire is continuously fed from a spool, allowing for high-precision cutting with minimal material waste.
Logistics Considerations
- Wire Supply and Inventory Management: Ensure a consistent supply of EDM wire (typically brass, zinc-coated, or molybdenum). Monitor usage rates and maintain safety stock to avoid production delays.
- Dielectric Fluid Handling: Deionized water is used as the dielectric medium. Establish a water filtration and recycling system to maintain fluid quality and reduce consumption.
- Waste Management: Collect and properly dispose of used filters, sludge, and spent water. Partner with certified waste disposal vendors to comply with environmental regulations.
- Machine Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance for wire tensioning systems, guides, and power supplies to prevent downtime.
Compliance Requirements
- Environmental Regulations (e.g., EPA, REACH): Monitor wastewater discharge. Ensure compliance with local regulations regarding pH levels, conductivity, and metal content.
- OSHA Standards: Implement safety protocols for high-voltage components and moving parts. Provide operator training on electrical hazards and emergency shutdown procedures.
- RoHS/REACH Compliance: Confirm that wires and consumables do not contain restricted substances, especially when producing parts for EU markets.
Sinker Electric Discharge Machining (Sinker EDM or Ram EDM)
Sinker EDM uses a custom-shaped electrode to erode material from a workpiece submerged in dielectric oil. It is ideal for creating complex cavities and molds.
Logistics Considerations
- Electrode Fabrication and Storage: Electrodes are typically made from graphite or copper. Maintain accurate inventory of electrode blanks and finished tools. Store in dry, temperature-controlled areas to prevent warping.
- Dielectric Oil Management: Use sealed systems to minimize oil evaporation and contamination. Implement oil filtration and reclamation processes to extend fluid life.
- Oil Spill Preparedness: Equip facilities with spill kits and secondary containment systems. Train staff in spill response procedures.
- Part Handling and Fixturing: Ensure secure workpiece clamping and alignment systems to maintain precision and reduce scrap.
Compliance Requirements
- EPA and Local Air Quality Regulations: Control vapor emissions from dielectric oil using fume extraction systems. Monitor volatile organic compound (VOC) levels.
- Fire Safety Standards (NFPA): Dielectric oil is flammable. Comply with NFPA 30 and 70 (electrical code) for storage, handling, and fire suppression systems.
- Hazard Communication (HazCom): Maintain Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for all oils, electrodes, and cleaning agents. Label containers and train workers on chemical hazards.
- Waste Oil Disposal: Used oil is often classified as hazardous waste. Ensure disposal through licensed facilities in accordance with RCRA (Resource Conservation and Recovery Act) guidelines.
Hole Drilling Electric Discharge Machining (EDM Drilling)
EDM drilling uses a rotating tubular electrode to produce deep, small-diameter holes in hard materials, commonly used for cooling channels in turbine blades.
Logistics Considerations
- Electrode Inventory: Stock various diameters and lengths of tubular electrodes. Track usage by job to forecast demand.
- Dielectric Fluid System: Typically uses deionized water under high pressure. Maintain pumps, filters, and reservoirs to ensure consistent flow and pressure.
- Sludge and Debris Removal: Install automated chip and sludge removal systems. Schedule routine cleaning of fluid tanks and nozzles.
- Machine Calibration: Regularly calibrate drilling depth, alignment, and pulse settings to maintain hole accuracy and surface finish.
Compliance Requirements
- Water Discharge Regulations: Treat used water to remove metal particulates before discharge. Comply with Clean Water Act standards.
- Operator Safety Training: Emphasize protection from high-pressure fluid spray and flying debris. Require use of PPE such as face shields and gloves.
- Noise Control: EDM drilling can generate high noise levels. Monitor decibel levels and provide hearing protection as needed under OSHA guidelines.
- Export Controls (ITAR/EAR): If producing components for defense or aerospace applications, ensure compliance with International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) or Export Administration Regulations (EAR) when shipping equipment or parts.
General Compliance and Sustainability Best Practices
Regardless of EDM type, the following best practices support long-term compliance and operational efficiency:
- Energy Efficiency: Use energy-efficient power supplies and variable frequency drives (VFDs) to reduce electricity consumption.
- Documentation and Audits: Maintain logs for maintenance, waste disposal, training, and emissions. Conduct internal audits to prepare for regulatory inspections.
- Supply Chain Due Diligence: Source materials from suppliers that adhere to environmental and ethical standards (e.g., ISO 14001, ISO 45001).
- Digital Monitoring and Traceability: Implement IoT-enabled sensors and ERP/MES systems to track machine performance, material usage, and compliance metrics in real time.
By aligning logistics planning with regulatory requirements, manufacturers can ensure safe, sustainable, and efficient EDM operations across all process types.
In conclusion, the selection of an appropriate sourcing type in electric discharge machining (EDM) plays a critical role in determining the efficiency, accuracy, surface finish, and overall performance of the machining process. Common power sources such as RC circuits, transistor-based pulse generators, and hybrid systems each offer distinct advantages and limitations. RC circuits are simple and cost-effective but provide inconsistent pulse duration and lower machining speed. Transistor-based systems offer precise control over discharge pulses, resulting in improved machining accuracy and higher material removal rates. Hybrid sources combine the benefits of multiple technologies to enhance performance across various applications.
The choice of power source should be guided by specific machining requirements, including material type, desired surface finish, geometric complexity, and production efficiency. Advancements in power supply technology continue to improve the capabilities of EDM, enabling finer control, reduced electrode wear, and faster processing times. Therefore, understanding the characteristics and applications of different sourcing types is essential for optimizing EDM operations and achieving high-quality results in precision manufacturing.