The global demand for reliable electrical connectivity solutions continues to surge, driven by expanding infrastructure, rising consumer electronics adoption, and the proliferation of electric vehicles. According to Grand View Research, the global plug and socket market was valued at USD 25.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% from 2023 to 2030. With Type B plugs—commonly used in North America and parts of Central and South America—remaining a dominant standard in residential and commercial applications, manufacturers are responding with innovations in safety, durability, and energy efficiency. As regulatory standards tighten and smart building technologies advance, the competitive landscape among Type B plug producers is intensifying. Based on market presence, product certification, production scale, and technological investment, the following nine manufacturers stand out as industry leaders shaping the future of electrical connectivity.
Top 9 Type B Plug Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
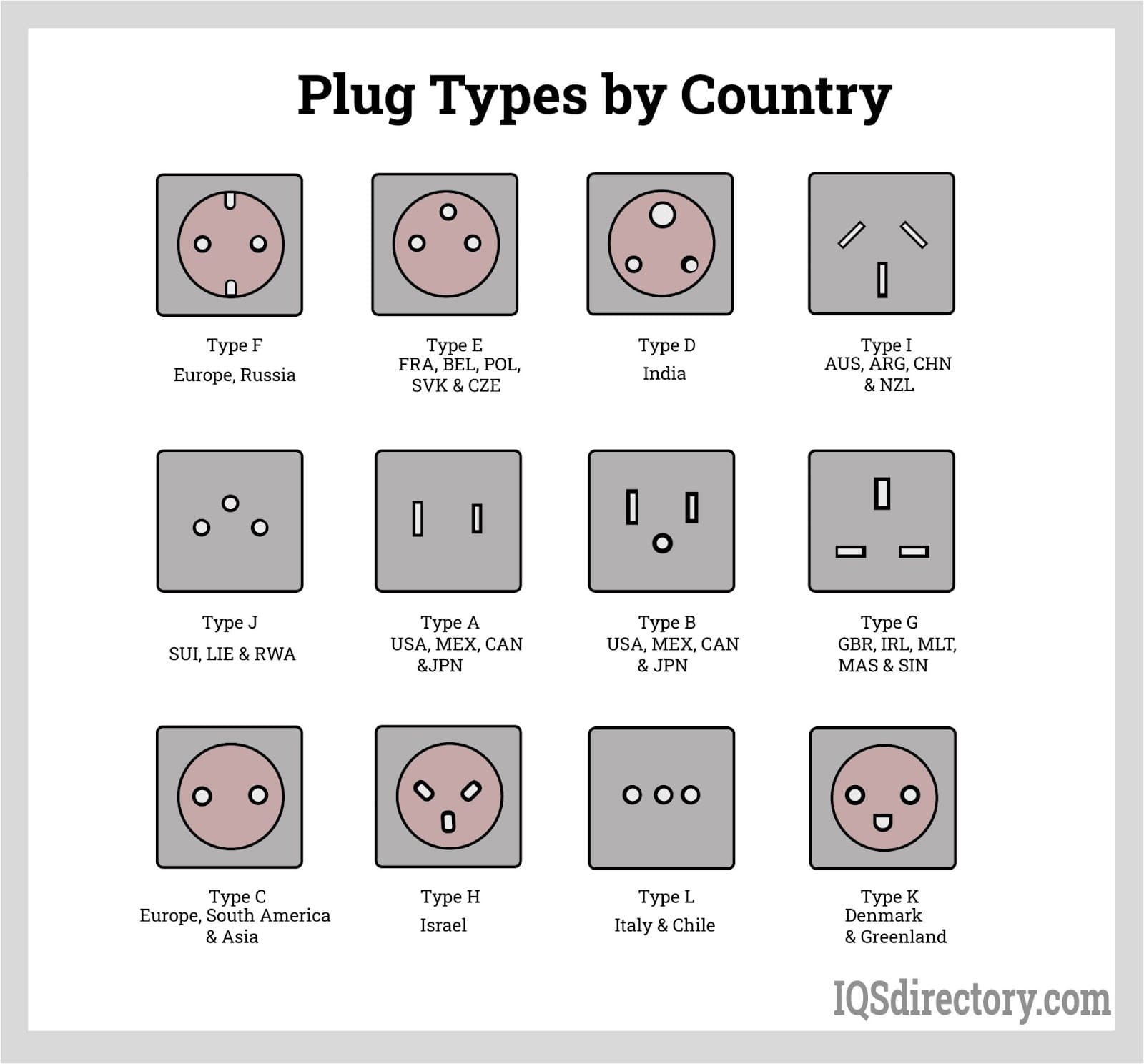
#1 Plugs Types (A, B, C, D, E, F, F/G, G, H, I, J, K, L, N)
Domain Est. 1993
Website: volex.com
Key Highlights: Volex is a leading global manufacturer and supplier of electrical plugs and power cords with plugs types A, B, C, D, E, F, F/G, G, H, I, J, K, L, N….
#2 Power Cord Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2019
Website: powercordmanufacturers.com
Key Highlights: Type A plugs have two prongs, while Type B plugs have three, with the third prong providing additional electrical flow and grounding. A snug fit between the ……
#3 Connectors
Domain Est. 1994
Website: molex.com
Key Highlights: Molex offers a wide variety of Board-to-Board Connectors for microminiature, high-speed, high-density, and high-power applications….
#4 Type 2507
Domain Est. 1995
Website: burkert.com
Key Highlights: Cable plug Type 2507 from Bürkert ➤ Form B (industry standard) ✓ Degree of protection IP 65 ✓ Numerous variants ✓ Buy online now!…
#5
Domain Est. 1995
Website: hubbell.com
Key Highlights: Burndy manufactures connectors for splicing, tapping, terminating, conducting or grounding, and provides certification and testing of tool and connector ……
#6 Power Cords and Adapters
Domain Est. 1996
Website: tripplite.eaton.com
Key Highlights: We offer AC power cords, extension cords, splitters and adapters for computers, servers and PDUs. Our cords have innovative features like coiled cords and ……
#7 Type B (NEMA 5
Domain Est. 2012
Website: netio-products.com
Key Highlights: The Type B electrical socket (American standard NEMA 5-15) has two flat parallel pins and a round earth pin. The earth pin is longer than the flat pins….
#8 Amphenol Connectors
Domain Est. 2021
Website: amphenol-cs.com
Key Highlights: Amphenol Communications Solutions (ACS), a division of Amphenol Corporation, is a world leader in interconnect solutions for Communications, Mobile, RF, ……
#9 World plugs
Website: iec.ch
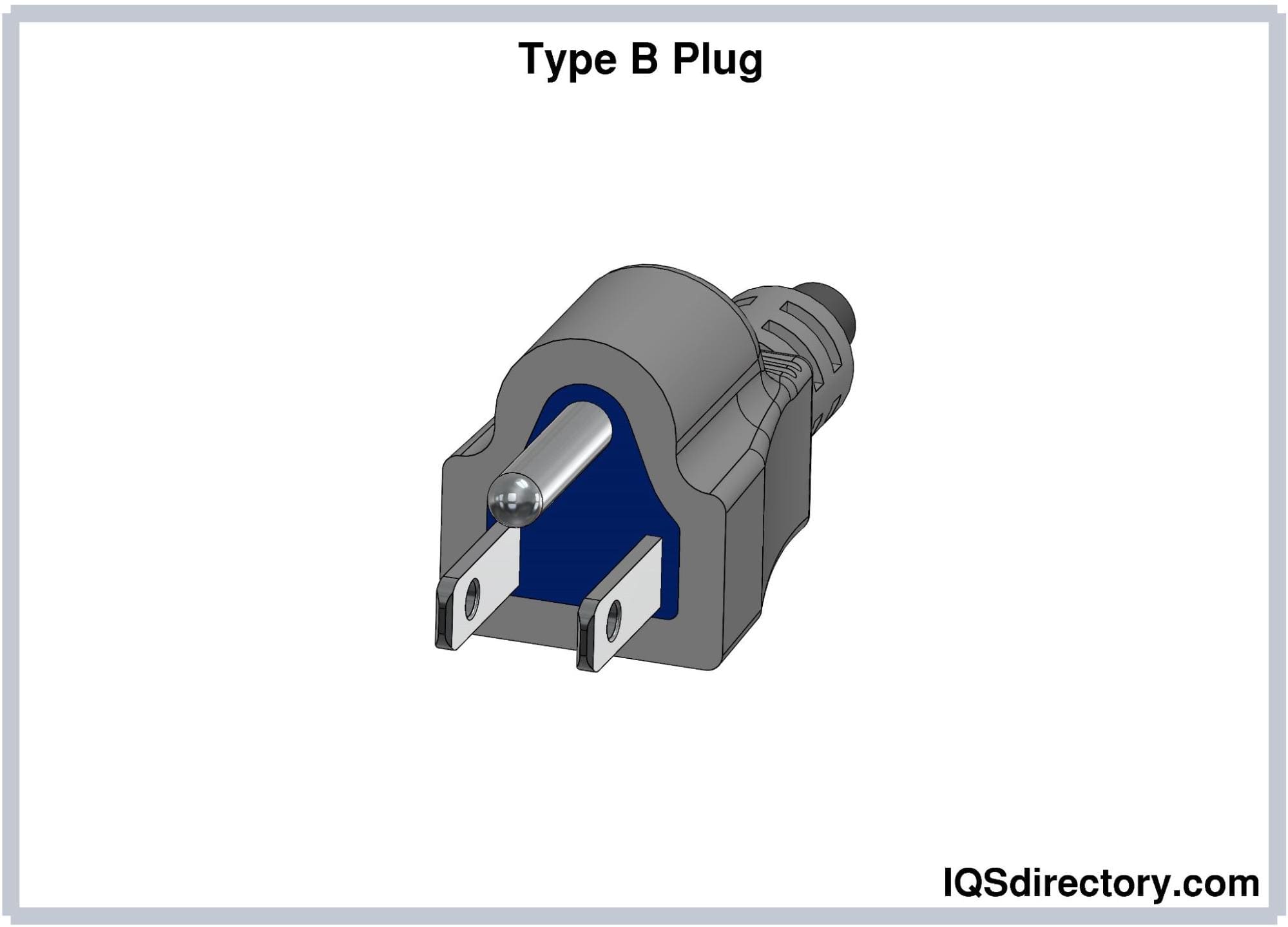
Key Highlights: Plug Type B. Used in: North and Central America, Japan The Type B electrical plug has two flat parallel pins and a round grounding (or earth) pin. The earth ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Type B Plug

H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Type B Plugs
As the global demand for reliable and standardized electrical infrastructure continues to evolve, the market for Type B plugs—commonly known as NEMA 5-15P in North America—is expected to experience several transformative trends by 2026. These trends are being driven by advancements in technology, regulatory changes, sustainability mandates, and shifting consumer behaviors. Below is a comprehensive analysis of the key market dynamics shaping the Type B plug landscape in 2026.
1. Increased Demand from Smart Home and IoT Ecosystems
The proliferation of smart home devices—ranging from smart thermostats and lighting systems to voice-assisted appliances—is significantly boosting the need for standardized, safe, and efficient power connectivity. Type B plugs remain the dominant AC power interface in residential North America, and their integration into smart power strips, energy-monitoring outlets, and IoT-enabled wall receptacles is accelerating. By 2026, a growing share of Type B plug-in devices will feature embedded intelligence, supporting real-time energy tracking and remote control via mobile applications.
2. Regulatory Push for Energy Efficiency and Safety
Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) are tightening energy efficiency standards for consumer electronics and appliances. This includes requirements for low standby power consumption and enhanced electrical safety. As a result, manufacturers are redesigning Type B plug-connected products with improved insulation, overload protection, and arc-fault detection. The 2026 market will likely see a rise in certified “smart” Type B receptacles that comply with updated National Electrical Code (NEC) standards, particularly in new residential constructions.
3. Rise of Electric Vehicles and Charging Infrastructure
While EVs primarily use specialized connectors (e.g., J1772, CCS), the auxiliary systems in EVs and home charging stations often rely on Type B plugs for Level 1 charging (120V). With EV adoption projected to grow steadily through 2026, especially in North America, there will be increased demand for durable, weather-resistant Type B outlets in garages and outdoor settings. Retrofit kits and smart charging stations with Type B compatibility are expected to gain market share, particularly in suburban and rural areas where 240V installations are cost-prohibitive.
4. Sustainability and Circular Economy Initiatives
Environmental concerns are driving innovation in materials and lifecycle management. By 2026, leading manufacturers are expected to phase in recyclable or bio-based plastics for Type B plug housings and adopt modular designs that allow for easy repair and component replacement. Additionally, e-waste regulations may require labeling or take-back programs for electrical accessories, impacting how Type B plugs are distributed and disposed of.
5. Competitive Pressure from Universal and USB-C Integration
The growing prevalence of USB-C as a universal charging standard poses a long-term challenge to traditional AC plug reliance. Many consumer electronics now ship with USB-C power adapters that plug into Type B outlets. This trend is pushing manufacturers to develop hybrid outlets combining Type B receptacles with built-in USB-C ports. By 2026, dual-format wall outlets are expected to dominate new installations, reducing the need for external adapters and improving user convenience.
6. Supply Chain and Regional Market Dynamics
North America remains the primary market for Type B plugs, with the U.S. and Canada accounting for over 90% of global demand. However, geopolitical factors and supply chain diversification efforts are prompting a shift toward regional manufacturing. Companies are investing in domestic production facilities to mitigate risks from trade disruptions, which could lead to price stabilization or slight reductions by 2026.
Conclusion
By 2026, the Type B plug market will be characterized by technological integration, regulatory compliance, and sustainability. While the fundamental design is unlikely to change due to entrenched infrastructure, its application will evolve through smart features, energy efficiency, and hybrid functionality. Stakeholders—including manufacturers, regulators, and consumers—must adapt to these trends to ensure safe, efficient, and future-ready electrical connectivity in residential and light commercial environments.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Type B Plug (Quality, IP)
When sourcing Type B plugs—commonly used in North America and parts of Central and South America—several critical pitfalls can compromise product quality, safety, and intellectual property (IP) protection. Being aware of these issues helps mitigate risks during procurement, especially when sourcing from overseas manufacturers.
Poor Quality Control Standards
One of the most frequent issues is inconsistent or substandard manufacturing processes. Many suppliers, particularly in low-cost regions, may not adhere to rigorous quality control protocols. This can result in plugs that fail safety certifications (such as UL or CSA), have loose wiring connections, or use subpar materials like flammable plastics or undersized conductors. These defects increase the risk of electrical fires, short circuits, or equipment damage.
Inadequate Material Specifications
Some manufacturers cut costs by using inferior materials, such as non-compliant thermoplastics or copper-clad aluminum instead of pure copper conductors. These materials degrade faster, reduce conductivity, and may not meet National Electrical Code (NEC) or International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards. Without thorough material verification, buyers risk receiving products that fail under normal operating conditions.
Misrepresentation of Certification Compliance
Suppliers may falsely claim that their Type B plugs are UL-listed, CSA-certified, or compliant with RoHS/REACH regulations. Without independent verification—such as requesting test reports or conducting third-party audits—buyers may unknowingly import non-compliant products, leading to regulatory penalties, product recalls, or liability in case of accidents.
Intellectual Property Risks
When custom designs or proprietary plug configurations are involved, there’s a significant risk of IP theft. Suppliers may duplicate designs for other clients or sell them on the grey market. Lack of robust legal agreements (e.g., NDAs, IP assignment clauses) and insufficient oversight can expose companies to counterfeit products and loss of competitive advantage.
Inconsistent IP (Ingress Protection) Ratings
Although Type B plugs are not typically rated for high moisture or dust resistance, some applications require enhanced durability. Suppliers may falsely advertise an IP rating (e.g., IP54) without proper testing or sealing mechanisms. Misleading IP claims can lead to equipment failure in demanding environments, especially in industrial or outdoor applications.
Supply Chain Transparency Issues
Limited visibility into subcontractors or secondary suppliers increases the risk of component substitution and quality drift. Without clear traceability, it becomes difficult to ensure consistent quality or respond effectively to failures in the field.
Lack of Long-Term Supplier Reliability
Some suppliers offer attractive initial pricing but lack the infrastructure for long-term production stability. Factors such as high turnover, financial instability, or limited production capacity can disrupt supply and affect scalability.
To avoid these pitfalls, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence, enforce strict quality agreements, perform regular audits, and secure IP through legal and technical safeguards. Engaging with reputable manufacturers and using third-party inspection services can significantly reduce risks associated with sourcing Type B plugs.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Type B Plug
Overview of Type B Plug
The Type B plug, also known as the NEMA 5-15P or NEMA 5-20P, is the standard electrical plug used in North America and several other countries. It features two flat parallel pins (one neutral, one hot) and a round grounding pin. This plug is rated for 120V and typically supports 15A (NEMA 5-15P) or 20A (NEMA 5-20P) circuits. Ensuring compliance and efficient logistics for products using Type B plugs is essential for market access and safety.
Regulatory & Safety Compliance
1. Certification Requirements
– UL Certification (USA): Mandatory for electrical safety under OSHA regulations. Products must be tested and certified by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) such as UL, Intertek (ETL), or CSA.
– CSA Certification (Canada): Required for sale in Canada; often harmonized with UL standards (e.g., UL 498, CSA C22.2 No. 42).
– FCC Compliance: Required if the product includes electronic components that may emit radio frequency interference (Part 15 regulations).
2. Electrical Standards
– Adherence to ANSI/NEMA WD-6 specifications for dimensional accuracy and safety.
– Comply with National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 406 for proper plug and receptacle installation and use.
– Ensure grounding continuity and insulation resistance meet minimum thresholds (typically >10MΩ).
3. Labeling & Documentation
– Clearly label plug with:
– Voltage (120V)
– Current rating (15A or 20A)
– Manufacturer name or trademark
– Certification marks (e.g., UL, CSA)
– Include user instructions in English (and French in Canada) covering proper use, warnings, and maintenance.
Import & Customs Regulations
1. United States (CBP & FDA)
– Declare under appropriate HTSUS code (e.g., 8536.69.80 for plugs and sockets).
– No FDA registration unless part of a medical device; if applicable, comply with 21 CFR.
– Ensure compliance with the Lacey Act if wooden packaging materials are used in shipping.
2. Canada (CBSA)
– Use HS code 8536.69.00 for import classification.
– Must meet Canadian Electrical Code (CEC) requirements enforced by local authorities.
– English and French bilingual labeling required on packaging and product.
3. Other Markets
– While Type B is used in countries like Japan, Taiwan, and parts of Central/South America, verify local certification needs (e.g., PSE in Japan, NOM in Mexico).
Packaging & Logistics
1. Packaging Standards
– Use anti-static and moisture-resistant packaging if shipped in humid environments.
– Secure plugs to prevent movement; use clamshells or blister packs for retail.
– Include compliance labels and user manuals inside retail packaging.
2. Shipping & Handling
– Comply with ISTA 3A or ASTM D4169 for package durability testing.
– Avoid sharp bending of cables; use coiled or figure-eight winding for corded plugs.
– Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments (typically 10°C to 30°C).
3. Marking for Transport
– Use standard shipping marks: country of origin, weight, handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up”).
– Include UN numbers if batteries are included (though not typical for standalone plugs).
Environmental & Sustainability Compliance
1. RoHS (USA & Canada)
– Comply with substance restrictions (e.g., lead, cadmium, mercury) per state (e.g., California RoHS) and Canadian Environmental Protection Act (CEPA).
2. WEEE & Recycling
– Although not federally mandated in the U.S., retailers may require take-back programs.
– In Canada, adhere to provincial e-waste regulations (e.g., Ontario’s Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment program).
3. REACH (if exported to EU)
– Even if not sold in the EU, components may be subject to REACH if sourced from EU suppliers. Ensure SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) declarations are available.
Final Quality Assurance & Market Surveillance
1. Pre-Shipment Inspection
– Conduct batch testing for:
– Dimensional accuracy
– Insertion/extraction force (per UL 498)
– Dielectric strength (1,200V for 1 minute)
– Verify correct certification marks and labeling.
2. Post-Market Compliance
– Monitor recalls via CPSC (U.S.) and Health Canada.
– Maintain records of compliance for at least 5 years.
– Respond promptly to consumer complaints or safety incidents.
Summary of Key Actions
- Obtain UL/CSA certification before market entry.
- Label clearly in required languages and include safety warnings.
- Use compliant packaging and follow robust logistics protocols.
- Stay updated on regional regulatory changes (e.g., energy efficiency standards).
By adhering to this guide, manufacturers and importers can ensure safe, compliant, and efficient distribution of Type B plug-equipped products across North America and compatible markets.
In conclusion, sourcing Type B plugs requires careful consideration of safety standards, regulatory compliance, and supplier reliability. Ensuring that the plugs meet recognized international standards such as UL (USA), CSA (Canada), or other locally applicable certifications is essential for product safety and market acceptance. It is also important to evaluate suppliers based on quality control processes, manufacturing capabilities, and ethical practices. By partnering with reputable manufacturers and conducting thorough due diligence, businesses can secure reliable, safe, and cost-effective Type B plug supplies that meet both technical requirements and regulatory demands. Ultimately, a strategic sourcing approach enhances product quality, reduces risk, and supports long-term supply chain sustainability.