The global turbocharger market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by increasing demand for fuel-efficient and low-emission internal combustion engines across automotive, industrial, and power generation sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global turbocharger market size was valued at USD 23.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is further amplified by stringent emission regulations and the rising adoption of downsized, turbocharged engines, particularly in passenger and commercial vehicles. As the demand for high-performance turbocharger blowers continues to rise, manufacturers are investing heavily in innovation and scalability to meet evolving industry requirements. In this context, nine leading companies have emerged as key players, combining technical expertise, global reach, and advanced manufacturing capabilities to dominate the competitive landscape.
Top 9 Turbocharger Blower Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 HST™ turbocompressors with magnetic bearings deliver …
Domain Est. 1996
Website: sulzer.com
Key Highlights: The unique technology of our HST turbocompressors enables optimal operating efficiency with minimized energy consumption….
#2 Turbo blowers, Turbo compressors, Vacuum pumps, Side channel …
Domain Est. 2000
Website: dutair.com
Key Highlights: Official manufacturer website for Dutair turbo blowers, side channel blowers and centrifugal fans. Premium compressors and vacuum pumps for air and gases….
#3 Blowers, Compressors & Turbos – Made by AERZEN
Domain Est. 2001
Website: aerzen.com
Key Highlights: High Speed Turbo Blowers. AERZEN oilfree turbo blowers are known for their high energy efficiency & highly developed technology. Read more ……
#4 Howden products
Domain Est. 2001
Website: chartindustries.com
Key Highlights: Our range of turbo blowers encompasses industrial type blowers used in the power, mining and water industries. We also have turbo compressors that are suited ……
#5 Napier Turbochargers
Domain Est. 2007
Website: napier-turbochargers.com
Key Highlights: Napier Turbochargers design, manufacture, market and support high efficiency Industrial Turbochargers for Marine Propulsion, Rail Traction and Power ……
#6 High Speed Turbo Blower
Domain Est. 2012
Website: turboblower.com
Key Highlights: Our gearless (high speed) turbo blower represents the most successful and largest installed base in the world of this technology….
#7 Garrett Turbo ()
Domain Est. 1995
Website: holley.com
Key Highlights: Holley is an official distributor for Garrett turbochargers and components. Garrett technologies and innovations have been used by nearly every major global ……
#8 Turbo Blowers
Domain Est. 2006
Website: apg-neuros.com
Key Highlights: Our Turbo Blowers are energy efficient, reliable, high quality products that are easy to install and require minimal maintenance….
#9 Next Turbo Technologies
Domain Est. 2014
Website: next-turbo.com
Key Highlights: Next Turbo designs and produces robust and high efficient Integrally geared, single stage, centrifugal turbocompressors with variable diffuser vanes and/or ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for Turbocharger Blower

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Turbocharger Blowers
The turbocharger blower market in 2026 is poised for significant evolution, driven by a confluence of regulatory pressures, technological innovation, and shifting global energy dynamics. While “turbocharger blower” can sometimes refer to auxiliary blowers in specific industrial contexts, the dominant market driver is the automotive and heavy-duty engine sector. Here’s an analysis of the key trends shaping this market in 2026:
-
Stringent Emissions & Fuel Efficiency Regulations as Primary Drivers:
- Global Standardization: Regulations like Euro 7 (Europe), Bharat Stage VII (India), China 6b/7 (China), and increasingly stringent US EPA standards will remain the paramount force. These mandates demand drastic reductions in CO2, NOx, and particulate matter (PM).
- Downsizing & Downspeeding: Turbocharger blowers are essential for enabling engine downsizing (smaller displacement) and downspeeding (lower operating RPM) without sacrificing power. This trend will accelerate in 2026 as manufacturers strive to meet fleet-wide CO2 targets, making advanced turbocharging non-negotiable for internal combustion engines (ICEs).
-
Dominance of Advanced Turbocharging Technologies:
- Electric Turbochargers (e-Turbos) Moving Mainstream: While still commanding a premium, e-Turbos (featuring an electric motor integrated with the turbo) will see significant adoption growth in 2026, particularly in premium passenger vehicles, performance segments, and heavy-duty trucks. They effectively eliminate turbo lag, provide instant boost, and enable advanced energy recovery systems, crucial for meeting emissions and performance demands.
- Variable Geometry Turbochargers (VGTs/VNTs) Proliferation: VGTs, which adjust vane angles to optimize boost across the engine speed range, will become standard on a wider range of diesel and gasoline engines, especially in trucks, SUVs, and performance cars, due to their superior low-end torque and efficiency.
- Twin-Turbo & Multi-Stage Systems: Complex systems (e.g., sequential, parallel, or compound turbos) will remain prevalent in high-performance and large-displacement engines (especially diesels in trucks and marine applications) to manage wide power bands and minimize lag.
-
Electrification’s Impact: A Nuanced Reality:
- ICE Hybridization as the Bridge: While pure electric vehicle (EV) adoption grows, the transition is gradual. The widespread deployment of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) creates a new demand for turbochargers. Downsized, highly efficient turbocharged engines are the core of most hybrid powertrains in 2026.
- ICE Resilience in Key Segments: Turbochargers remain critical for commercial vehicles (trucks, buses), off-highway machinery (construction, agriculture), marine, and aviation auxiliary power units (APUs) where full electrification faces significant hurdles (range, payload, infrastructure, cost). This segment provides a stable and growing market base.
- Focus on Efficiency, Not Just Power: Turbocharger development shifts further towards maximizing thermal efficiency and minimizing parasitic losses, directly contributing to lower fuel consumption and emissions in hybrid and conventional ICEs.
-
Material & Manufacturing Innovation:
- High-Temperature Materials: Demand for materials capable of withstanding extreme exhaust gas temperatures (driven by higher boost pressures and EGR rates) will increase. This includes advanced nickel-based superalloys, ceramics, and specialized coatings.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Adoption will grow for prototyping and producing complex, lightweight components (e.g., turbine housings, compressor wheels) with optimized internal geometries impossible with traditional methods, improving efficiency and reducing weight.
-
Regional Market Dynamics:
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) Dominance: China, India, Japan, and South Korea will remain the largest production and consumption hubs, driven by massive automotive industries, stringent local regulations, and growth in commercial vehicle fleets. Local suppliers will gain strength.
- Europe: Focus on premium technology (e-Turbos, advanced VGTs) and stringent regulations will drive high-value market growth, with significant R&D activity.
- North America: Strong demand from the heavy-duty trucking sector (driven by EPA regulations) and the performance vehicle market will sustain the market, with increasing adoption of e-Turbos.
- Emerging Markets: Growth in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa will be linked to economic development and the expansion of commercial vehicle and off-road equipment fleets, often utilizing established turbo technologies.
-
Supply Chain & Cost Pressures:
- Integration & Consolidation: Tier 1 suppliers will increasingly offer integrated turbocharger modules or even complete air management systems to simplify integration for OEMs.
- Cost Optimization: Intense price pressure from OEMs, especially in high-volume passenger segments, will drive continuous efforts in design optimization, manufacturing efficiency, and material cost reduction, even for advanced technologies.
Conclusion for 2026:
The turbocharger blower market in 2026 will be characterized by technological sophistication driven by regulatory necessity. While electrification reshapes the broader automotive landscape, turbochargers are not becoming obsolete; instead, they are becoming more essential and more advanced. The market will see:
* Growth fueled by ICE hybridization and resilience in non-passenger vehicle segments.
* Technology Shift towards e-Turbos, advanced VGTs, and complex multi-stage systems.
* Material & Design Innovation to handle higher thermal and mechanical stresses.
* Regional Strength concentrated in APAC and Europe, with steady demand in North America.
Success in 2026 will depend on suppliers’ ability to deliver high-efficiency, reliable, and increasingly electrified turbocharging solutions that enable OEMs to navigate the complex transition towards lower emissions while meeting performance and cost targets.
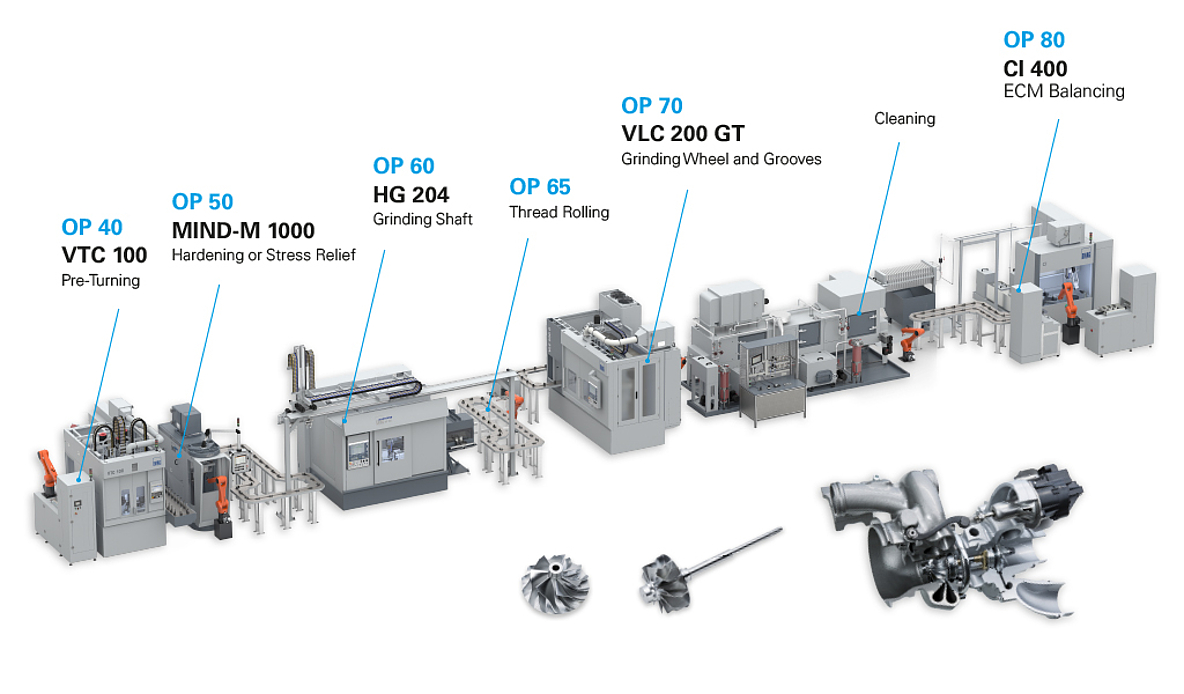
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Turbocharger Blowers (Quality & IP)
Sourcing turbocharger blowers—especially for critical applications such as power generation, industrial processes, or aerospace—requires careful attention to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. Overlooking these aspects can lead to operational failures, legal disputes, and significant financial losses. Below are the most common pitfalls to avoid.
1. Prioritizing Cost Over Proven Quality
One of the most frequent mistakes is selecting suppliers based solely on low pricing. Inexpensive turbocharger blowers may use substandard materials, poor manufacturing tolerances, or lack rigorous testing, leading to:
- Premature mechanical failure (e.g., bearing wear, rotor imbalance)
- Reduced efficiency and higher energy consumption
- Increased downtime and maintenance costs
Best Practice: Evaluate total cost of ownership (TCO), including reliability, service life, and energy efficiency. Request documented quality certifications (ISO 9001, AS9100 for aerospace) and performance test reports (e.g., API 617 compliance).
2. Inadequate Supplier Vetting and Traceability
Many buyers fail to conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, particularly those from emerging markets. This increases the risk of:
- Counterfeit or reconditioned components misrepresented as new
- Lack of material traceability (e.g., no mill test reports for alloys)
- Unverified manufacturing capabilities or outdated production methods
Best Practice: Perform on-site audits or third-party inspections. Require full traceability documentation for critical components (e.g., compressor wheels, shafts) and verify supply chain transparency.
3. Overlooking Compliance with Industry Standards
Turbocharger blowers must meet specific international standards (e.g., API 617, ISO 10439, ASME) depending on the application. Ignoring compliance can result in:
- Safety hazards and non-compliance penalties
- Incompatibility with existing systems
- Voided warranties or insurance claims
Best Practice: Clearly specify required standards in procurement contracts. Demand certification test data and third-party validation where applicable.
4. Insufficient Attention to Intellectual Property Rights
When sourcing turbocharger blowers—especially OEM-equivalent or aftermarket units—IP infringement is a significant risk. Pitfalls include:
- Purchasing blowers that copy patented designs, impeller geometries, or control systems
- Unlicensed use of proprietary software or firmware in integrated controls
- Exposure to legal action from original equipment manufacturers (OEMs)
Best Practice: Require suppliers to provide IP indemnification clauses in contracts. Conduct patent landscape reviews for critical components and ensure designs are either licensed or independently developed.
5. Poor Documentation and Lack of Technical Support
Many suppliers, especially smaller or offshore manufacturers, provide inadequate technical documentation, such as:
- Missing or low-quality CAD drawings, assembly manuals, or maintenance guides
- No access to performance curves or surge margin data
- Limited post-sale engineering support
This leads to difficulties in installation, commissioning, and troubleshooting.
Best Practice: Make comprehensive documentation a contractual requirement. Confirm availability of technical support and spare parts before finalizing the purchase.
6. Assuming Interchangeability Without Verification
Buyers often assume that aftermarket or “compatible” turbocharger blowers are direct replacements. However, minor dimensional, aerodynamic, or control differences can cause:
- Performance degradation
- Vibration or resonance issues
- System integration failures
Best Practice: Conduct dimensional and performance benchmarking before procurement. Whenever possible, test units under real operating conditions before full-scale deployment.
Conclusion
To mitigate risks when sourcing turbocharger blowers, organizations must balance cost considerations with rigorous quality validation and IP due diligence. Establishing clear technical specifications, conducting supplier audits, and securing legal protections are essential steps in ensuring long-term reliability and compliance.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for Turbocharger Blowers
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legal shipment of Turbocharger Blowers globally. Adherence to these guidelines ensures product integrity, regulatory compliance, and timely delivery.
H2: 1. Packaging & Handling
- Robust Protection: Use heavy-duty, shock-resistant packaging (e.g., double-walled corrugated cardboard, wooden crates) to withstand vibration, impact, and stacking pressure during transit. Internal cushioning (foam inserts, molded pulp, air bags) must immobilize the blower and protect critical surfaces (shafts, housings, ports).
- Moisture Prevention: Include desiccant packs within sealed packaging or vapor corrosion inhibitor (VCI) paper to prevent rust and corrosion, especially for sea freight or humid environments. Ensure breathable seals if using VCI.
- Secure Sealing: Seal packages with high-tensile strapping or banding and moisture-resistant tape. Clearly mark “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Do Not Stack” using standardized labels.
- Weight & Dimensions: Accurately measure and document gross weight and external dimensions. Ensure packaging is suitable for the weight and facilitates safe manual or mechanical handling (e.g., pallets with forklift entry points).
- Palletization: Securely strap/blotch blowers to standard pallets (e.g., EUR/EPAL, GMA). Use corner boards for added stability. Ensure overhang is minimized.
H2: 2. Transportation Modes & Requirements
- Air Freight:
- Priority: Fastest option for urgent shipments or high-value components.
- Compliance: Strict adherence to IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR) is CRITICAL. While most blowers are non-hazardous, confirm:
- Lubricants: Residual oil/grease? If > specific thresholds (e.g., > 20ml in porous materials), may be Class 9 (Miscellaneous) or Class 3 (Flammable Liquid). Declare accurately.
- Batteries: Any integrated sensors with batteries? Must meet IATA DGR for Lithium batteries (UN 3480, 3481).
- Documentation: Air Waybill (AWB) with precise commodity description, weight, dimensions, and hazard classification (if applicable). Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (DGD) required if hazardous.
- Cost: Highest cost; optimize packaging for volumetric weight.
- Sea Freight (FCL/LCL):
- Priority: Most cost-effective for large volumes or heavy shipments over long distances.
- Compliance: Follow IMDG Code for hazardous materials (similar checks as IATA for lubricants/batteries). Ensure packaging withstands humidity and salt spray. Use moisture barriers on pallets.
- Documentation: Bill of Lading (B/L) with detailed cargo description, HS codes, and weight/volume. Packing List essential.
- Containers: Secure blowers within containers using dunnage and blocking/bracing to prevent shifting. Consider container desiccant.
- Road Freight:
- Priority: Primary mode for regional/continental transport (e.g., EU, NAFTA).
- Compliance: ADR regulations (Europe) or equivalent (e.g., 49 CFR in USA) for hazardous materials (lubricants, batteries). Ensure vehicle suitability and secure load.
- Documentation: CMR Waybill (International), Bill of Lading (Domestic), Packing List.
- Rail Freight: Similar requirements to Road freight, often used in conjunction.
H2: 3. Regulatory Compliance & Documentation
- Accurate Classification:
- HS Codes: Determine correct Harmonized System (HS) code for import/export (e.g., 8414.59 for air blowers, specific sub-codes may apply). This dictates tariffs and regulations. Consult customs broker.
- ECCN/USML: For US exports, determine if the blower falls under Export Administration Regulations (EAR) ECCN (e.g., 9A151 for certain high-performance turbomachinery) or International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) USML. Non-compliance carries severe penalties.
- Core Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice: Detailed description, value, currency, Incoterms® (e.g., FOB, EXW, DDP), buyer/seller details, country of origin.
- Packing List: Itemizes contents per package, weights, dimensions, marks & numbers.
- Certificate of Origin (C/O): Required for tariff preferences (e.g., free trade agreements). May need Chamber of Commerce certification.
- Bill of Lading (B/L) / Air Waybill (AWB): Contract of carriage and title document (for negotiable B/L).
- Specialized Documentation (If Applicable):
- Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods (DGD): Mandatory for hazardous shipments (IATA/IMDG/ADR).
- Export/Import Licenses: Required for controlled items (determined by ECCN/USML, destination country).
- Phytosanitary Certificate: If using wooden packaging (ISPM 15 compliant).
- Test/Inspection Certificates: Buyer or customs may require proof of quality/performance.
- Incoterms® 2020: Clearly define responsibilities (costs, risks, documentation) between buyer and seller (e.g., EXW, FCA, DAP, DDP). Crucial for compliance allocation.
H2: 4. Country-Specific Requirements (Examples)
- USA: FDA may regulate materials if blower contacts food/medical products (unlikely for standard industrial, but verify). FCC compliance if electronic controls emit RF. CBP entry filing.
- EU: CE Marking may be required if the blower is part of a machine falling under the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC). RoHS compliance for restricted substances. REACH compliance for chemicals. EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility) fees possible.
- China: CCC Marking unlikely for standalone blowers, but check. CIQ (Customs Inspection and Quarantine) may inspect. Strict packaging waste regulations.
- Brazil: ANVISA (health) or INMETRO (technical standards) certification possible. Complex customs procedures.
- Always verify requirements with a local customs broker or freight forwarder for the destination country.
H2: 5. Key Recommendations
- Partner with Experts: Utilize experienced freight forwarders and customs brokers familiar with machinery and your trade lanes.
- Verify Hazard Status: Rigorously assess lubricants, batteries, and materials against IATA DGR, IMDG Code, and ADR.
- Precise Documentation: Ensure 100% accuracy in HS codes, descriptions, weights, and values on all documents. Inconsistencies cause delays and penalties.
- Robust Packaging: Invest in packaging that exceeds minimum requirements to prevent damage.
- Clear Communication: Define Incoterms® upfront and maintain clear communication with all parties (shipper, carrier, receiver, broker).
- Stay Updated: Regulations (export controls, environmental, customs) change frequently. Monitor updates from government agencies (e.g., BIS, CBP, DG MOVE).
Disclaimer: This guide provides general information. Specific requirements depend on the exact product configuration, materials, destination, and trade regulations. Always consult with legal counsel, compliance specialists, and logistics professionals for your specific shipments.
Conclusion on Sourcing a Turbocharger Blower
Sourcing a turbocharger blower requires careful consideration of technical specifications, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and long-term support. After evaluating various suppliers and options, it is evident that selecting a high-quality turbocharger blower from a reputable manufacturer ensures optimal performance, durability, and fuel efficiency in the intended application. Critical factors such as compatibility with existing systems, maintenance requirements, warranty terms, and availability of spare parts must be prioritized during the procurement process.
Additionally, establishing strong relationships with trusted suppliers—preferably those offering technical support and global service networks—can significantly reduce downtime and operational risks. Whether opting for OEM components or qualified aftermarket alternatives, due diligence in supplier vetting and product validation is essential.
In conclusion, a strategic sourcing approach that balances performance, cost, and support will lead to a reliable and efficient turbocharger blower solution, ultimately contributing to improved system performance and operational sustainability.