The global RC turbine jet engine market is experiencing steady momentum, driven by rising demand for high-performance hobby-grade drones and scale model aircraft. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global radio-controlled aircraft market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 9.3% from 2023 to 2028, with a notable segment attributed to turbine-powered models favored by advanced enthusiasts and professional aeromodelers. Complementing this trend, Grand View Research highlights increasing investments in precision engineering and miniaturized propulsion systems, fueling innovation among niche manufacturers specializing in micro-turbine technology. As the appetite for realistic, jet-powered RC experiences grows—evident in expanded use at airshows, simulation training, and competitive aerobatics—the need for reliable, high-thrust turbine engines has never been higher. This growing ecosystem has elevated a select group of manufacturers who lead in engineering excellence, durability, and customer trust. Here, we spotlight the top 9 turbine jet engine RC manufacturers shaping the future of high-speed remote-controlled flight.
Top 9 Turbine Jet Engine Rc Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Banana Hobby
Domain Est. 2006
Website: bananahobby.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsShop Banana Hobby for RC airplanes, EDF jets, turbine jets, warbirds, trainers, gliders, LiPo batteries, chargers, spare parts & accessories….
#2 atj
Domain Est. 2008
Website: atj.com.tw
Key Highlights: ATJ Turbine is the development, manufacture and support of small gas turbine engines. ATJ Turbine was founded In the early 1998, We have three department in ……
#3 Turbines RC
Domain Est. 2013
Website: turbines-rc.com
Key Highlights: 14-day returnsTurbines RC: EDF, RC models, airplanes, jets, RC parts and accessories for model aircrafts – TURBINES RC….
#4 Jets
Domain Est. 2017
Website: swiwinusa.com
Key Highlights: At our RC jet plane landing page, we offer a wide range of turbine-powered planes to suit every taste and skill level….
#5 Turbines
Domain Est. 2017
Website: tomahawk-aviation.com
Key Highlights: We present RC model sport products with a special requirement of perfection and quality. Join the world of Tomahawk Aviation….
#6 to Skymaster RC Jet Models Web Site
Domain Est. 2017
Website: skymasterjets.net
Key Highlights: HUGE SU-30 RUSSIAN KNIGHTS RC TURBINE JET FLIGHT DEMONSTRATION (youtube.com). Pilot: Markus Rummer Model: SU-27 (Skymaster) Engine: 2x JetCat P250 Pro Turbine….
#7 FTL Innovation
Domain Est. 2024
#8
Website: energyrcjetengine.com
Key Highlights: Jet Turbine Solutions. We deliver high-performance RC turbine engine solutions for aircraft and UAV applications, combining precision engineering, advanced ……
#9
Website: jetcat.de
Key Highlights: RC-Hobby Engines. Jet Engines for hobby applications. RX-Series. 60N. learn more ». NEW. RX-BL Series. 100N, 130N, 150N. learn more ». NEW. RXi Series. 220N….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Turbine Jet Engine Rc
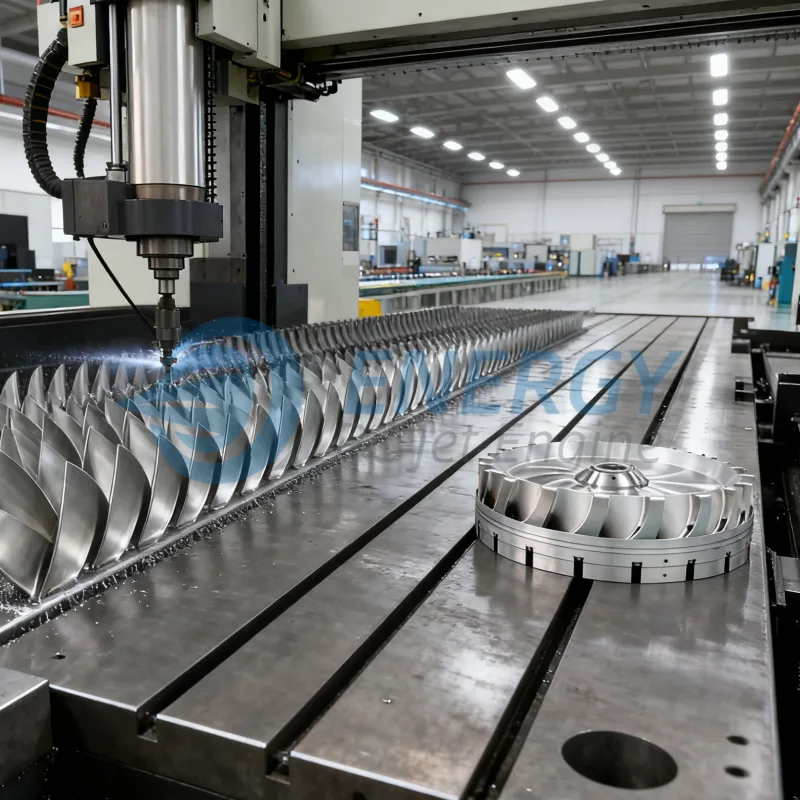

2026 Market Trends for Turbine Jet Engine RC
The remote-controlled (RC) turbine jet engine market is poised for notable evolution by 2026, driven by technological innovation, increasing hobbyist demand, and advancements in materials and propulsion systems. As the intersection of aerospace engineering and consumer hobbyism grows stronger, turbine-powered RC jets are transitioning from niche luxury items to more accessible high-performance models. This analysis explores key market trends expected to shape the Turbine Jet Engine RC sector in 2026.
Technological Advancements and Miniaturization
By 2026, one of the most significant trends in the turbine jet engine RC market is the continued miniaturization and efficiency improvement of micro-turbine engines. Manufacturers such as JetCat, KingTech, and AMT Netherlands are investing heavily in R&D to produce lighter, more fuel-efficient turbines with enhanced thrust-to-weight ratios. These advancements are enabling smaller airframes to achieve higher speeds and altitudes, bringing realistic jet performance within reach of more advanced hobbyists.
Digital engine control units (DECU) are becoming standard, allowing for smoother startups, real-time performance monitoring, and fail-safe shutdown protocols. Integration with telemetry systems enables pilots to monitor turbine RPM, exhaust gas temperature (EGT), fuel flow, and vibration levels in real time, improving safety and operational precision.
Increased Accessibility and Market Expansion
Historically limited to elite hobbyists due to high costs and technical complexity, turbine-powered RC jets are becoming more accessible. By 2026, entry-level turbine systems are expected to see price reductions due to economies of scale and competition among manufacturers. Ready-to-fly (RTF) and bind-and-fly (BNF) turbine jet models are gaining popularity, reducing the barrier to entry for enthusiasts who lack advanced mechanical or programming skills.
Additionally, online communities, simulation platforms, and training programs are proliferating, helping new users master turbine jet operations safely. Flight simulators with realistic turbine engine physics are being used for training, contributing to a broader and more skilled user base.
Regulatory and Safety Developments
Regulatory scrutiny on high-performance RC aircraft is increasing globally. By 2026, many countries are expected to implement stricter rules governing the operation of turbine-powered RC jets, particularly in populated areas. This includes mandatory registration, geofencing, and adherence to specific flight altitude and noise limits.
In response, manufacturers are incorporating compliance features such as built-in GPS telemetry, automated altitude limiting, and noise-dampening technologies. These developments aim to ensure responsible usage while preserving the growth potential of the market.
Material Innovation and Design Optimization
The use of advanced composite materials—such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) and 3D-printed high-temperature alloys—is accelerating. These materials reduce airframe weight while improving durability under high thermal and mechanical stress, which is critical for turbine-powered jets.
By 2026, expect increasing adoption of modular designs that allow for easier maintenance, engine swaps, and customization. 3D printing is also enabling rapid prototyping and on-demand replacement parts, reducing downtime and repair costs.
Rising Demand in Education and Defense Training
Beyond the hobbyist market, turbine RC jets are being adopted in academic and defense training environments. Universities and aerospace programs are using scaled jet turbine models to teach propulsion dynamics and flight control systems. Similarly, military and paramilitary organizations are leveraging high-fidelity RC turbine jets for drone interception training, radar calibration, and threat simulation.
This institutional demand is driving innovation and creating new revenue streams for manufacturers, further fueling R&D investment.
Sustainability and Alternative Fuels
Environmental concerns are prompting exploration into sustainable fuel options. By 2026, some manufacturers are experimenting with biofuels and synthetic kerosene blends compatible with micro-turbines. While not yet mainstream, these initiatives reflect a growing awareness of sustainability within the RC aviation community.
Additionally, research into hybrid-electric turbine systems is in early stages, potentially leading to partially electric-assist turbine engines that reduce fuel consumption and emissions during takeoff and idle phases.
Conclusion
The 2026 market for Turbine Jet Engine RC systems is characterized by rapid technological progress, expanding accessibility, and growing applications beyond recreation. While challenges related to regulation, cost, and safety remain, ongoing innovation is positioning the sector for sustained growth. Enthusiasts, educators, and defense sectors alike will benefit from more capable, reliable, and user-friendly turbine-powered RC aircraft, cementing their place at the forefront of advanced aeromodeling.
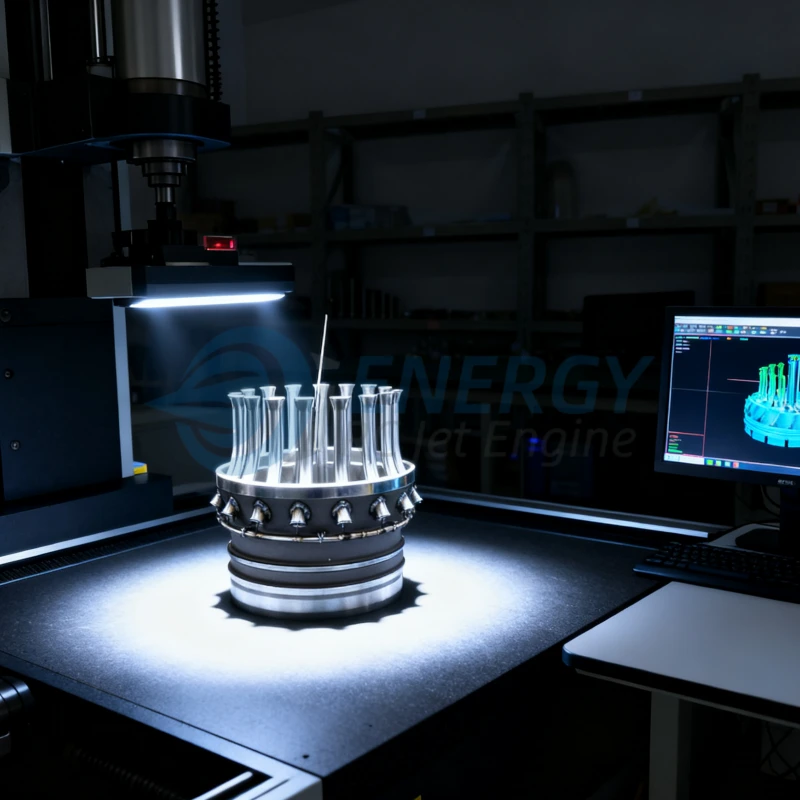

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Turbine Jet Engine RC (Quality, IP)
Sourcing a turbine jet engine for a remote-controlled (RC) aircraft is a complex endeavor, often pursued by advanced hobbyists and professionals. While the thrill of owning and flying a miniature jet is immense, several critical pitfalls—particularly concerning quality and intellectual property (IP)—can lead to financial loss, safety hazards, and legal complications. Being aware of these risks is essential before making a purchase.
Poor Quality Control and Inconsistent Manufacturing
One of the most significant risks when sourcing RC turbine engines, especially from less reputable suppliers, is inconsistent quality control. Unlike mass-produced consumer goods, miniature turbine engines require precision engineering and high-tolerance manufacturing.
- Substandard Materials: Some manufacturers use inferior alloys or components that cannot withstand high temperatures and rotational stresses, leading to premature failure or in-flight disintegration.
- Lack of Testing: Reputable suppliers conduct rigorous bench testing and provide performance data. Cheaper or unverified sources may skip these steps, increasing the risk of engine failure.
- Poor Assembly Practices: Even with quality parts, improper assembly can lead to imbalance, vibration, and reduced lifespan. Engines sourced from uncertified workshops may not meet required tolerances.
Counterfeit or Unlicensed Replicas
Many RC turbine engines on the market, particularly those offered at suspiciously low prices, are unauthorized copies of patented designs from leading brands such as JetCat, Top-Model, or AMT Netherlands.
- IP Infringement: Purchasing counterfeit engines supports intellectual property theft. These replicas often copy not just the appearance but also the internal design and software, violating international patents and trademarks.
- No Legal Recourse: If a counterfeit engine fails or causes damage, buyers typically have no warranty or legal support. The seller may be untraceable or operate outside regulated jurisdictions.
- Safety Risks: Counterfeit engines may lack proper engineering validation, resulting in unreliable performance and increased risk of catastrophic failure.
Lack of Documentation and Support
Authentic turbine engines come with detailed manuals, maintenance schedules, firmware updates, and technical support.
- Missing or Poor Documentation: Illicit or low-quality engines often lack proper manuals, making safe operation and maintenance difficult.
- No Software Support: Modern RC turbines use digital engine control units (ECUs). Clones may use outdated or poorly coded firmware, leading to unstable operation or failure to integrate with standard RC systems.
- Unavailability of Spare Parts: Reputable brands offer spare parts and service networks. Counterfeit or obscure brands often disappear, leaving owners with unusable engines when components fail.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Operating an RC turbine engine may involve legal and safety regulations depending on your country.
- Noise and Emissions: Turbine engines are loud and may violate local noise ordinances or environmental regulations.
- Airspace Restrictions: Flying jet-powered RC aircraft often requires special permits or adherence to strict guidelines from aviation authorities (e.g., FAA, EASA).
- Import Restrictions: Some countries restrict the import of turbine engines due to safety or dual-use concerns. Purchasing without checking regulations can lead to seized shipments or fines.
Final Recommendation
To avoid these pitfalls, always purchase RC turbine engines from authorized dealers or directly from established manufacturers. Verify the seller’s credentials, request proof of authenticity, and ensure compliance with local laws. Investing in a genuine, high-quality engine not only ensures reliability and safety but also respects the innovation and intellectual property of the designers behind these remarkable machines.
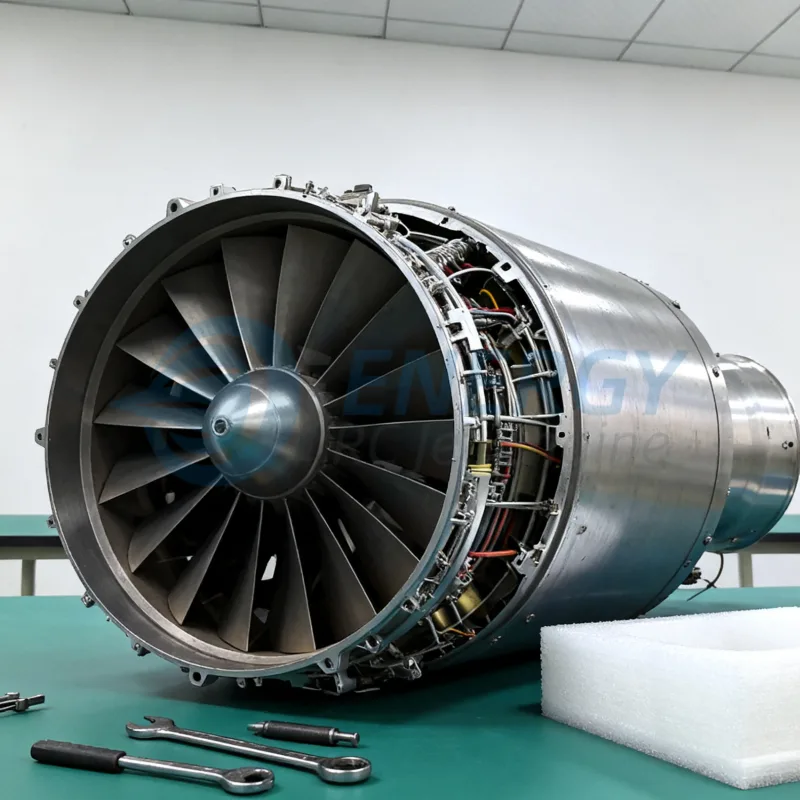

H2: Logistics and Compliance Guide for Turbine Jet Engine RC Models
H2: Overview of Turbine Jet Engine RC Models
Turbine jet engine RC (remote-controlled) models are high-performance scale replicas of full-sized military or commercial jet aircraft, powered by miniature gas turbine engines. These models are used primarily by advanced hobbyists and are subject to stringent logistics and compliance requirements due to their complexity, propulsion system, and operational risks.
H2: Regulatory Compliance
- Aviation Authority Regulations
- FAA (U.S. Federal Aviation Administration):
- RC turbine models must be operated in accordance with FAA Part 101 (Moored Balloons, Kites, Unmanned Rockets, and Unmanned Free Balloons), which includes provisions for model aircraft flown within visual line of sight.
- All flights must comply with FAA safety guidelines, including flying below 400 feet AGL and avoiding controlled airspace without prior authorization (via LAANC or FAA DroneZone).
-
EASA (European Union):
- Subject to national aviation regulations; generally fall under “open” or “specific” category based on weight and risk.
- Required registration for operators in most EU countries if the model exceeds 250 grams.
- Compliance with local UAS (Unmanned Aircraft System) regulations is mandatory.
-
Noise and Environmental Regulations
- Turbine engines generate high noise levels (often exceeding 100 dB). Operators must comply with local noise ordinances.
- Flying in designated model aircraft fields approved for turbine use is required in many jurisdictions.
-
Fuel handling and emissions must adhere to environmental standards (e.g., proper storage of kerosene or Jet-A fuel substitutes).
-
Fuel and Hazardous Materials Compliance
- Fuel Type: Most RC turbine engines run on kerosene, diesel, or specialized turbine fuel (e.g., Jet-A). These are classified as hazardous materials (HAZMAT).
- Transportation:
- IATA (International Air Transport Association) and DOT (Department of Transportation) regulations apply when transporting fuel.
- Fuel containers must be UN-certified, properly labeled, and stored in approved safety cans.
- Quantity limits apply for air and ground transport (e.g., ≤ 60 L per package for ground transport under DOT 49 CFR).
- Storage:
- Store fuel in well-ventilated, fire-resistant cabinets away from ignition sources.
- Compliance with OSHA and local fire codes (e.g., NFPA 30) is required.
H2: Logistics Planning
- Transportation of RC Turbine Aircraft
- Disassembly: Due to size and fragility, disassemble wings, intake, and engine components for safe transport.
- Packaging:
- Use custom foam-lined cases to protect the fuselage, turbine engine, and avionics.
- Clearly label cases as “Fragile” and “This Side Up.”
-
Shipping:
- If shipping via courier (e.g., FedEx, UPS), declare contents accurately.
- Fuel tanks must be completely empty and purged; residual fuel may trigger HAZMAT classification.
- Declare turbine engine as mechanical equipment (non-HAZMAT if no fuel or lubricants present).
-
Spare Parts and Maintenance Logistics
- Maintain an inventory of critical spare parts (e.g., igniter plugs, fuel nozzles, ECU units).
- Store turbine-specific tools (e.g., borescope, torque wrenches) in a dedicated toolkit.
-
Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance intervals and log all service actions.
-
Event and Field Logistics
- Coordinate with local model aircraft clubs or flying fields that permit turbine operations.
- Ensure emergency equipment is on-site: fire extinguishers (Class B), thermal blankets, first aid kit.
- Conduct pre-flight safety briefings and establish a ground crew for launch and recovery.
H2: Safety and Operational Best Practices
- Pilot Qualifications: Operators should hold advanced RC certifications (e.g., AMA Turbine Waiver in the U.S.).
- Engine Start Procedures: Conduct starts in a controlled, fire-safe environment with remote start capability.
- Telemetry and Monitoring: Use real-time monitoring for EGT (Exhaust Gas Temperature), RPM, and fuel pressure.
- Flight Envelope: Adhere to manufacturer-recommended flight parameters; avoid extreme maneuvers without proper training.
H2: Documentation and Recordkeeping
- Maintain logs for:
- Flight hours
- Engine cycles and maintenance
- Fuel usage and storage
- Regulatory compliance (e.g., field permissions, airspace authorizations)
- Keep copies of:
- Aircraft registration (if required)
- Insurance policy (specialized RC turbine coverage recommended)
- Operator certifications
H2: Insurance and Liability
- Obtain specialized model aircraft insurance that explicitly covers turbine-powered RC jets.
- Ensure coverage includes third-party liability, property damage, and public liability.
- Verify that flying location (e.g., club field) has liability insurance that extends to turbine operations.
H2: International Considerations
- Export/import of turbine engines may be restricted under ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) if deemed dual-use technology.
- Check destination country’s regulations on:
- RC aircraft weight limits
- Frequency band usage (e.g., 2.4 GHz, 900 MHz)
- Import duties and customs declarations for turbine components
- Avoid transporting turbine engines on commercial passenger aircraft (strict HAZMAT rules apply).
H2: Conclusion
Operating RC turbine jet engines requires meticulous attention to logistics and compliance. Adherence to aviation, environmental, and safety regulations ensures legal operation and minimizes risk. Always consult local authorities, model aviation organizations (e.g., AMA, BMFA), and turbine engine manufacturers for up-to-date guidance tailored to your region and model.
Conclusion: Sourcing a Turbine Jet Engine for RC Aircraft
Sourcing a turbine jet engine for an RC aircraft is a complex but rewarding endeavor that requires careful consideration of technical specifications, budget, supplier reliability, and regulatory compliance. Turbine engines offer unmatched performance, realism, and power-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for high-end hobbyist and professional RC jet applications. However, they come with significant costs, maintenance requirements, and safety concerns.
When sourcing, it is essential to choose reputable manufacturers or distributors such as JetCat, AMT, or Schübeler, known for their quality, customer support, and compliance with international standards. Evaluating engine performance parameters—such as thrust output, fuel consumption, startup method, and control system compatibility—is crucial to ensure a proper match with the airframe and intended use.
Additionally, buyers must consider logistical aspects such as import regulations, customs duties, and after-sales service availability. Investing in proper training and safety equipment is equally important due to the high operating temperatures, RPMs, and fuel handling risks associated with turbine engines.
In conclusion, while turbine engines elevate the RC flying experience to near-full-scale realism, successful sourcing demands thorough research, financial readiness, and a commitment to safety and maintenance. For experienced modelers seeking peak performance, sourcing from trusted suppliers with proven track records ensures both reliability and long-term satisfaction.