The global tungsten alloys market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across aerospace, defense, medical, and energy sectors. According to a 2023 report by Grand View Research, the global tungsten market was valued at USD 5.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by tungsten’s high density, exceptional strength at elevated temperatures, and radiation shielding properties, making it indispensable in high-performance applications. Mordor Intelligence further projects increasing demand from emerging economies and the expanding nuclear energy sector as key drivers over the forecast period. As industries prioritize materials that offer reliability under extreme conditions, tungsten alloys have become a strategic material in advanced manufacturing. This increasing demand has elevated the importance of reliable and innovative manufacturers capable of delivering high-purity, custom-engineered solutions. Here are the top 9 tungsten alloys manufacturers leading the market through technological expertise, global reach, and consistent product quality.
Top 9 Tungsten Alloys Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Expert Manufacturers of Tungsten Alloys
Domain Est. 1998
Website: wolfmet.com
Key Highlights: Wolfmet manufactures tungsten alloy components to the highest specifications and quality standards. Our processes are ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 accredited….
#2 Tungsten Manufacturers
Domain Est. 2007
Website: tungstensuppliers.com
Key Highlights: Quickly locate the top tungsten manufacturers and suppliers who offer high quality tungsten made in the USA and custom quotes with easy online purchasing….
#3 What Are Tungsten Alloys?
Domain Est. 1995
Website: glemco.com
Key Highlights: Tungsten alloys are created to improve the material’s performance in specific applications. Tungsten on its own is a heavy dense metal known for its high ……
#4 Tungsten Alloys
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mttm.com
Key Highlights: Mi-Tech Tungsten Metals manufactures tungsten alloy, tungsten copper, and tungsten silver for industries such as defense, aerospace, and oil & gas….
#5 Midwest Tungsten Service – Custom Parts or Order Online
Domain Est. 1997
Website: tungsten.com
Key Highlights: Midwest Tungsten offers the highest quality TIG Electrodes, Tungsten Bucking Bars, Tungsten Fine Wire, and more! Tungsten products & custom machining….
#6 H.C. Starck Tungsten Powders: High
Domain Est. 1997
Website: hcstarck.com
Key Highlights: For over 100 years, we have developed and produced high-quality powders from the refractory metal tungsten and its compounds for our customers….
#7 Tungsten Products
Domain Est. 2013
Website: samaterials.com
Key Highlights: Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is a trusted global supplier of tungsten alloy solutions, renowned for unmatched reliability and technical expertise in ……
#8 Tungsten Heavy Alloy (WNiFe, WNiCu, WNiCo)
Domain Est. 2018
Website: aemmetal.com
Key Highlights: AEM offers a wide range of tungsten heavy alloys including WNiFe, WNiCo, WNiCu, and more. Discover more about these alloys and request a quote today….
#9 Tungsten Heavy alloy
Website: pollen.am
Key Highlights: Tungsten is a heavy metal alloy, also called hard metal. With density superior to 17.5g/cm 3 it combines the great hardness and strength of tungsten carbide….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tungsten Alloys

H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Tungsten Alloys
The global market for tungsten alloys is anticipated to experience significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, rising demand across defense, aerospace, and industrial sectors, and evolving supply chain dynamics. Tungsten alloys—known for their high density, exceptional strength at elevated temperatures, and radiation shielding capabilities—are poised to benefit from both established applications and emerging use cases.
-
Growth in Defense and Military Applications
By 2026, defense spending—particularly in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific—is expected to remain robust, fueling demand for tungsten alloys as environmentally safer alternatives to depleted uranium in kinetic energy penetrators and armor-piercing ammunition. Regulatory pressure to phase out radioactive materials will accelerate adoption of tungsten-based solutions in munitions and military hardware. -
Aerospace and High-Performance Engineering
The aerospace industry will continue to leverage tungsten alloys for counterweights, balance masses, and vibration damping components in aircraft and satellites. With the expected increase in commercial space missions and next-generation aircraft development, demand for high-density, thermally stable materials like tungsten heavy alloys (WHA) will grow steadily. -
Expansion in Medical and Radiation Shielding Technologies
Tungsten alloys are increasingly favored in medical imaging and radiation therapy equipment due to their superior shielding properties compared to lead. By 2026, the global rise in cancer incidence and investment in advanced radiotherapy systems (e.g., LINACs and proton therapy) will boost demand for tungsten-based shielding components in healthcare infrastructure. -
Electronics and Semiconductor Manufacturing
Miniaturization and performance demands in the electronics sector will drive the use of tungsten alloys in heat sinks, connectors, and semiconductor fabrication tools. Their thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal expansion make them ideal for high-precision applications in 5G infrastructure and electric vehicles (EVs), where power electronics require durable materials. -
Supply Chain and Geopolitical Influences
China dominates global tungsten production, accounting for over 80% of supply. By 2026, export controls, environmental regulations, and strategic stockpiling initiatives by importing nations (e.g., the U.S. and EU) may lead to supply volatility. This could incentivize alternative sourcing, recycling technologies, and investment in non-Chinese mining projects—potentially reshaping global supply chains. -
Sustainability and Recycling Trends
As circular economy principles gain traction, the recycling of tungsten from industrial scrap and end-of-life products will become increasingly important. Advances in recovery technologies and regulatory support for sustainable material use are expected to improve recycling rates, reducing dependency on primary mining. -
Price Volatility and Market Consolidation
Prices for tungsten alloys may experience fluctuations due to supply constraints, energy costs, and geopolitical tensions. Market consolidation among key producers and alloy fabricators is likely, with larger firms investing in vertical integration to secure raw materials and enhance production efficiency.
In summary, by 2026, the tungsten alloys market will be shaped by strong demand from high-tech and defense sectors, supply chain resilience efforts, and sustainability imperatives. Innovation in alloy formulations—such as tungsten-nickel-iron and tungsten-copper composites—will further expand application potential, positioning tungsten alloys as critical materials in advanced industrial ecosystems.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Tungsten Alloys – Quality and Intellectual Property Risks
Sourcing tungsten alloys presents several challenges, particularly concerning quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) protection. These high-performance materials are critical in aerospace, defense, medical, and industrial applications due to their high density, strength, and resistance to extreme environments. However, procurement teams often encounter the following pitfalls:
-
Inconsistent Material Quality and Purity
One of the most common issues is receiving tungsten alloys that do not meet specified compositional or mechanical standards. Substandard alloys may have incorrect ratios of tungsten, nickel, iron, or copper, leading to poor performance or failure in critical applications. Suppliers—especially in regions with less stringent regulatory oversight—may provide materials with undocumented impurities or non-compliance with ASTM, ISO, or MIL specifications. -
Lack of Traceability and Certification
Many suppliers fail to provide full material traceability, including mill test reports (MTRs), certificates of conformance (CoC), or batch-specific data. Without proper documentation, buyers cannot verify the alloy’s origin, heat treatment history, or processing methods, increasing the risk of counterfeit or recycled material being passed off as virgin-grade alloy. -
Counterfeit or Recycled Materials
Due to the high cost of tungsten, some unscrupulous suppliers may substitute genuine alloys with recycled or lower-grade materials. This not only compromises performance but may also introduce unknown variables in manufacturing processes, especially in regulated industries like medical devices or defense systems. -
Intellectual Property (IP) Exposure
When engaging with suppliers—particularly overseas—for custom tungsten alloy formulations or components, there is a significant risk of IP theft. Detailed specifications, proprietary processing techniques, or unique alloy compositions shared during sourcing may be replicated or sold to competitors without adequate legal protection. Jurisdictions with weak IP enforcement exacerbate this risk. -
Inadequate Supply Chain Transparency
Complex, multi-tiered supply chains can obscure the true origin of materials. Intermediaries may lack technical expertise or ethical sourcing practices, increasing exposure to sanctions, conflict minerals, or non-compliant manufacturing processes. This is especially critical given growing regulatory requirements (e.g., U.S. SEC Rule 13p-1, EU Conflict Minerals Regulation). -
Non-Compliance with Export Controls and Regulations
Tungsten alloys are often subject to export controls due to dual-use applications (civilian and military). Sourcing from unauthorized vendors or failing to classify materials correctly under ITAR, EAR, or other regimes can lead to legal penalties and supply chain disruptions.
Mitigation Strategies:
– Conduct rigorous supplier audits and request third-party material testing.
– Require full documentation, including CoC, MTRs, and heat traceability.
– Use non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and limit technical data shared during procurement.
– Partner with suppliers in IP-protected jurisdictions or with proven compliance records.
– Leverage trusted supply chain partners and consider onshoring or nearshoring for critical applications.
In summary, sourcing tungsten alloys demands a proactive approach to quality validation and IP protection. Failure to address these pitfalls can result in product failure, regulatory issues, and long-term competitive disadvantage.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tungsten Alloys
Overview of Tungsten Alloys
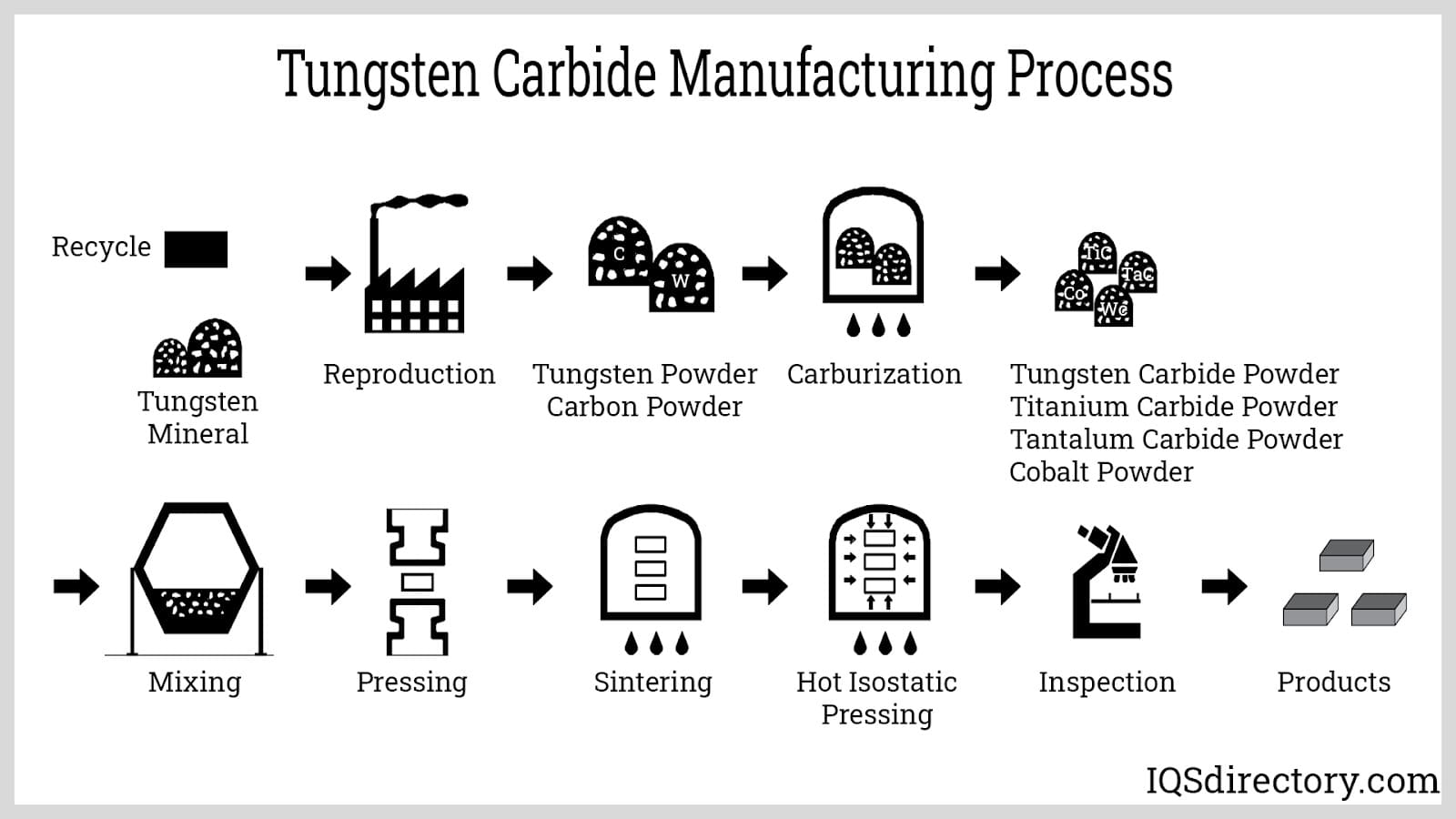
Tungsten alloys are high-density materials composed primarily of tungsten (typically 90–97%) combined with small percentages of nickel, iron, copper, or cobalt. These alloys are widely used in aerospace, defense, medical, and industrial applications due to their exceptional density, strength, and radiation shielding properties. Common forms include rods, bars, sheets, and custom-machined components. Due to their strategic and dual-use nature, the international trade and transport of tungsten alloys are subject to strict regulatory oversight.
Regulatory Classification
Tungsten alloys are subject to multiple regulatory frameworks depending on composition, form, and end-use. Key classification systems include:
– HS (Harmonized System) Codes: Typically fall under 8101.91 (Tungsten Waste and Scrap) or 8101.99 (Other Unwrought Tungsten), though fabricated parts may fall under different codes based on function.
– Export Control Classification Number (ECCN): Under the U.S. Commerce Control List (CCL), tungsten alloys may be classified under ECCN 1C009 (Materials for Chemical or Biological Technologies) or 9A012 (Aerospace and Propulsion), depending on intended use and density.
– ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations): If used in defense articles (e.g., kinetic energy penetrators), tungsten alloys may fall under USML Category XI or XV and require ITAR licensing.
Export Controls and Licensing
Export of tungsten alloys often requires government authorization due to potential dual-use applications. Key considerations include:
– Destination Country: Restrictions apply to sanctioned countries (e.g., Iran, North Korea, Russia). Always consult the latest OFAC and BIS country-specific guidelines.
– End-Use and End-User: Exports require due diligence to prevent diversion to military or nuclear applications. A Validated End-User (VEU) or license may be required.
– Licensing Requirements: Most exports to non-Allied countries require a license from the U.S. Department of Commerce (BIS) or Department of State (DDTC) if ITAR-controlled. Utilize License Exceptions (e.g., LVS, TMP) where applicable.
Transportation and Shipping Requirements
Transport of tungsten alloys must comply with international and carrier-specific regulations:
– Packaging: Secure, non-reactive packaging to prevent damage and contamination. Heavy shielding may be required for radioactive shielding grades.
– Hazard Classification: Generally non-hazardous under IATA/IMDG/ADR unless contaminated or alloyed with regulated materials (e.g., depleted uranium). Always verify material safety data sheets (MSDS/SDS).
– Marking and Labeling: Proper HS codes, net/gross weight, and origin labeling. Include export control markings if applicable (e.g., “Export controlled under ECCN 1C009”).
– Carrier Compliance: Notify freight forwarders of potential export controls. Air and sea carriers may require special documentation.
Customs Documentation
Accurate documentation is essential to avoid delays or penalties:
– Commercial Invoice: Must include detailed description, weight, value, ECCN or HTS code, country of origin, and export license number (if applicable).
– Packing List: Itemized list of contents, weights, and dimensions.
– Certificate of Origin: Required for preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements.
– Export Declaration (e.g., AES in the U.S.): Filed via the Automated Export System for shipments over $2,500 or requiring a license.
Compliance Best Practices
To maintain regulatory compliance:
– Conduct regular internal audits of export practices.
– Maintain records of licenses, end-user statements, and shipping documents for at least 5 years.
– Train staff on EAR, ITAR, and OFAC regulations.
– Screen all parties against denied persons lists (e.g., BIS Denied Persons List, OFAC SDN List).
Sanctions and Restricted Parties
Ensure no dealings with:
– Sanctioned countries, entities, or individuals.
– Military or nuclear end-users without proper authorization.
– Brokers or intermediaries located in embargoed jurisdictions.
Conclusion
The logistics and compliance landscape for tungsten alloys is complex due to their strategic importance and dual-use nature. Companies must implement robust export compliance programs, stay updated on regulatory changes, and work closely with legal and logistics experts to ensure lawful and efficient international trade.
In conclusion, sourcing tungsten alloys requires a strategic approach that balances material quality, supplier reliability, cost-efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Due to their exceptional density, strength, and resistance to high temperatures and wear, tungsten alloys are critical in aerospace, defense, medical, and industrial applications. When selecting suppliers, it is essential to evaluate factors such as certification standards (e.g., ISO, AS9100), manufacturing capabilities, traceability, and ethical sourcing practices—particularly concerning conflict minerals.
Establishing long-term partnerships with reputable suppliers, conducting thorough due diligence, and maintaining diversification in the supply chain can mitigate risks related to supply disruptions and quality inconsistencies. Additionally, staying informed about global market trends, raw material availability, and environmental regulations will support sustainable and resilient procurement strategies. Ultimately, effective sourcing of tungsten alloys is integral to ensuring product performance, compliance, and operational success across high-tech and demanding industries.