The global precision measurement tools market has witnessed steady expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-accuracy inspection equipment across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global micrometers market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 5.2% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by advancements in manufacturing technologies and stricter quality control standards. This growth is further supported by rising automation and the integration of digital measurement systems in production environments. As one of the most critical tools for internal diameter measurements, tube micrometers have become essential in precision engineering workflows. With this expanding demand, several manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining accuracy, durability, and innovation in their product offerings. The following list highlights the top six tube micrometer manufacturers recognized for their technical excellence, market presence, and contributions to advancing dimensional metrology.
Top 6 Tube Micrometer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
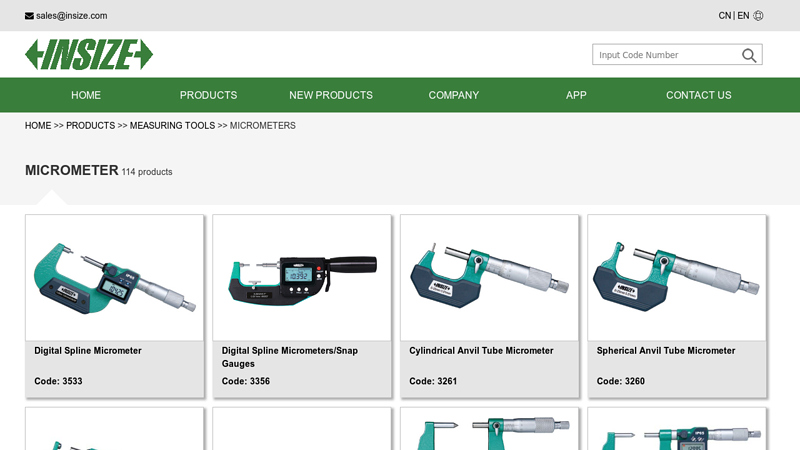
#1 MICROMETER
Domain Est. 2003
Website: insize.com
Key Highlights: Cylindrical Anvil Tube Micrometer Code: 3261 · Spherical Anvil Tube Micrometer Code: 3260 · Digital Spherical Anvil Tube Micrometer Code: 3560 · Digital ……
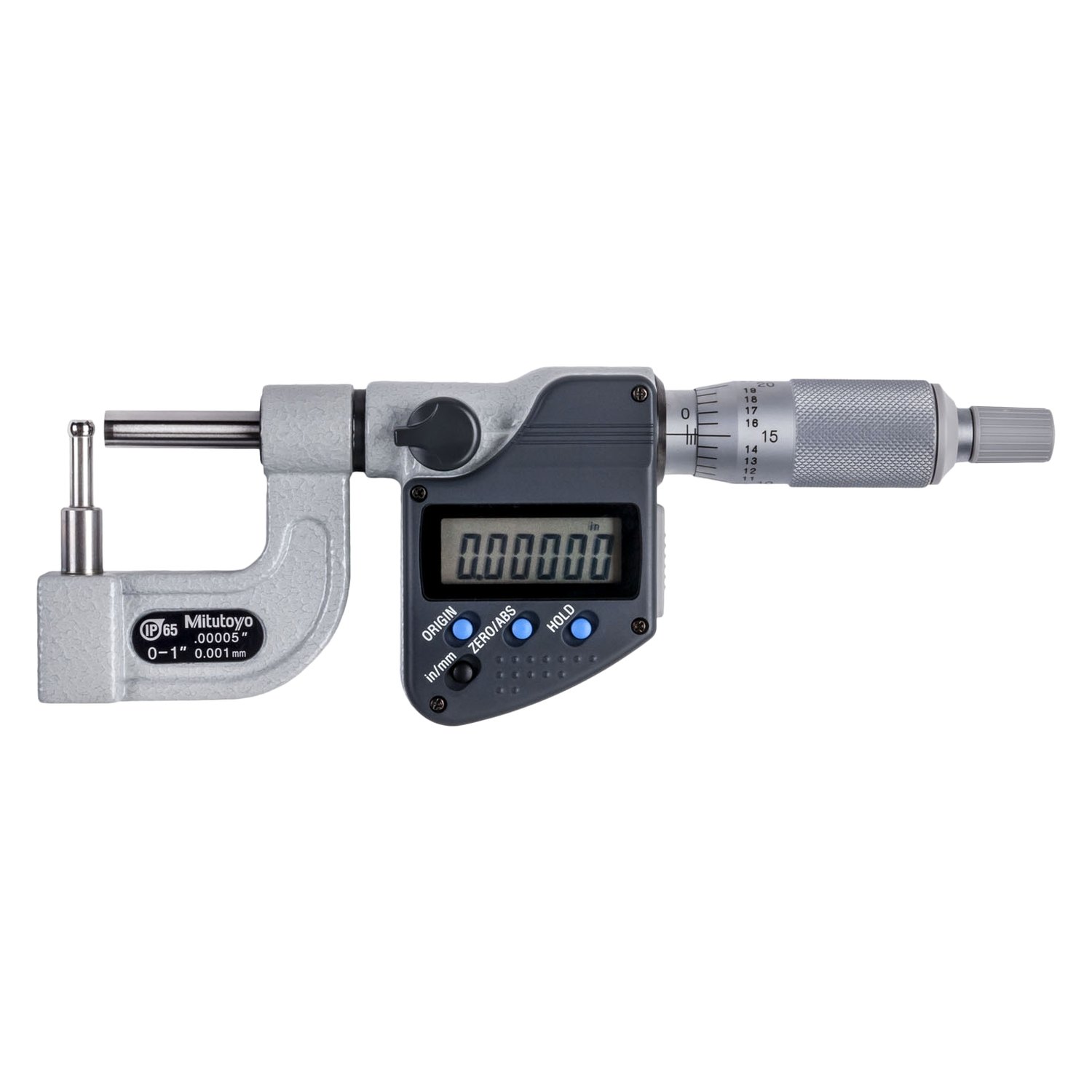
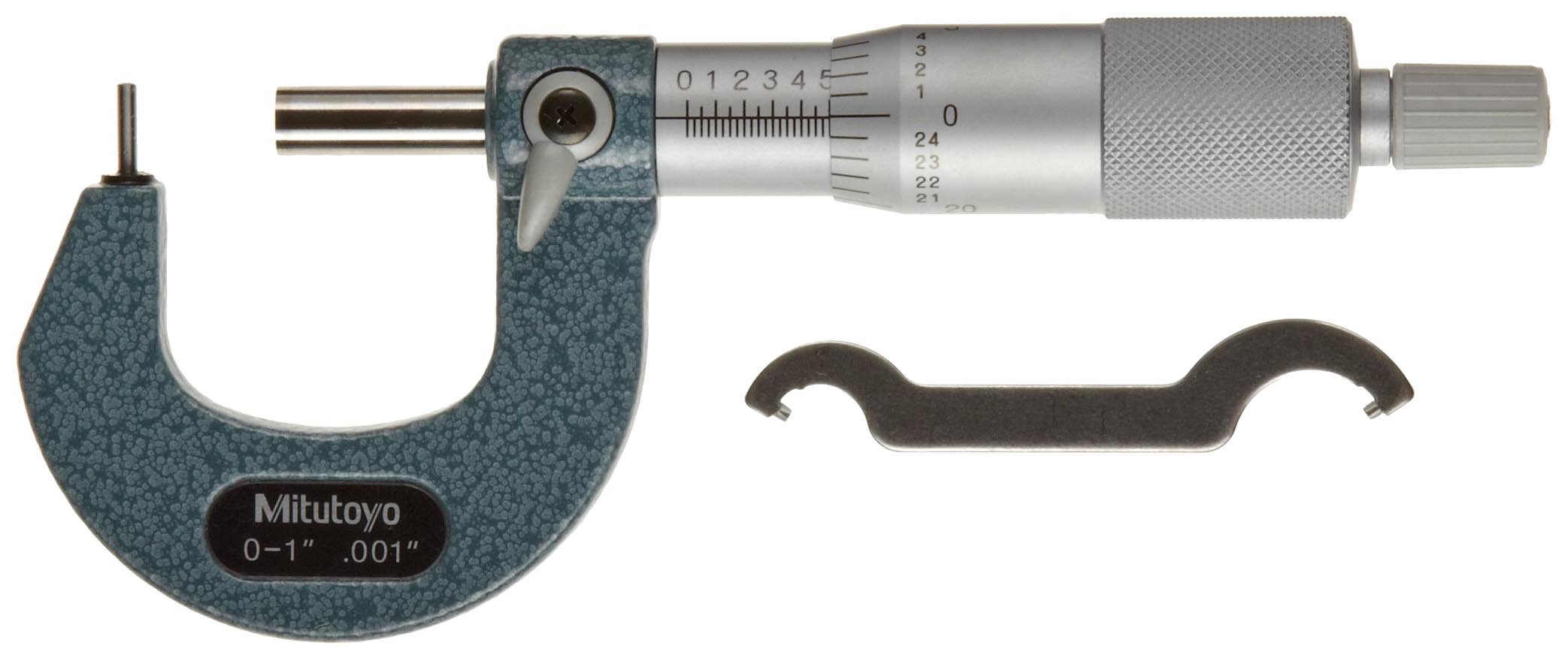
#2 Digital Tube Micrometer, with Cylindrical Anvil, Series 395, Type A
Domain Est. 2007
#3 Mitutoyo 295
Domain Est. 2010
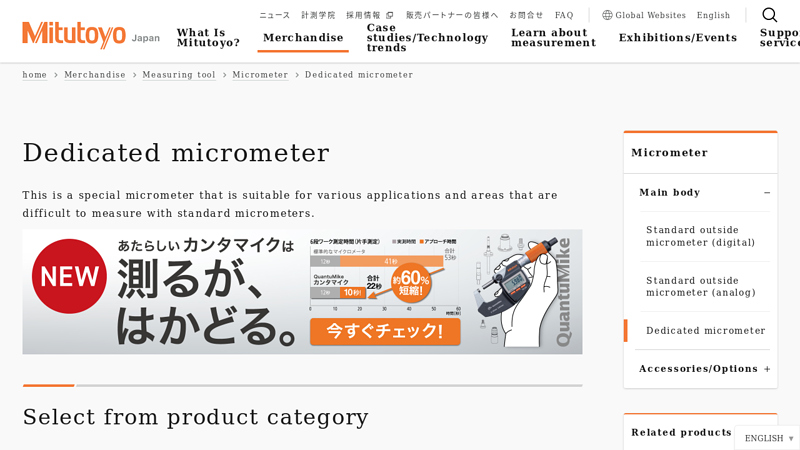
#4 Dedicated micrometer
Domain Est. 2018
Website: en-40020.site-translation.com
Key Highlights: Dedicated micrometer. This is a special micrometer that is suitable for various applications and areas that are difficult to measure with standard micrometers….
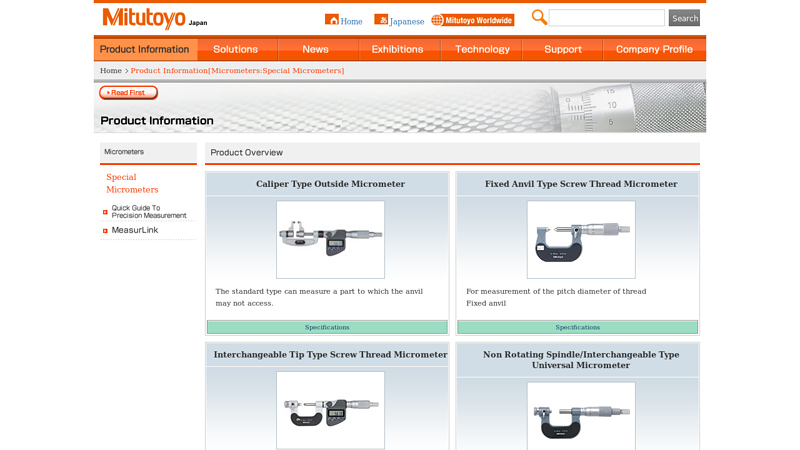
#5 Special Micrometers – MITUTOYO
Website: www2.mitutoyo.co.jp
Key Highlights: Supports measurement of various shapes with 7 types of interchangeable anvils. An anvil dedicated to screw threads is also available….
#6 Discover the Best Tube Micrometers for Precision Measurements
Domain Est. 1998
Website: starrett.com
Key Highlights: 15-day returnsElevate your measurement capabilities with our advanced tube micrometers. Perfect for achieving high-precision results in your projects….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tube Micrometer

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Tube Micrometers
The global tube micrometer market in 2026 is expected to reflect a blend of steady demand driven by enduring industrial needs and subtle shifts influenced by technological advancements and evolving manufacturing practices. While not experiencing explosive growth, the market remains a critical niche within precision measurement, characterized by the following key trends:
-
Stable Demand in Core Industries: Tube micrometers will continue to be indispensable in sectors requiring high-precision measurement of tubular components. Key drivers include:
- Aerospace & Defense: Stringent quality control for hydraulic lines, fuel systems, and structural tubing ensures consistent demand for highly accurate, reliable instruments. Certification requirements favor established, trusted tools like precision micrometers.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Demand persists for measuring brake lines, fuel lines, exhaust components, and structural tubing, particularly in traditional ICE and hybrid vehicle production. Quality standards remain paramount.
- Oil & Gas: Pipeline integrity, downhole tool manufacturing, and refinery piping maintenance necessitate precise tube wall thickness and diameter measurement, supporting steady market demand.
- HVAC & Plumbing: Fabrication and quality control of copper, steel, and composite tubing in commercial and industrial applications rely on accurate micrometers.
-
Gradual Integration of Digitalization (Smart Features): While analog micrometers dominate due to cost and reliability, a noticeable trend towards digital tube micrometers will accelerate by 2026:
- Digital Readouts (DROs): Increased adoption of digital micrometers offering easier reading, data output (USB, Bluetooth), and reduced human error. This is driven by Industry 4.0 initiatives and the need for traceable digital records.
- Data Connectivity: Integration with SPC (Statistical Process Control) software and manufacturing execution systems (MES) becomes more common, allowing real-time monitoring of dimensional data and improved quality assurance.
- Enhanced Features: Digital models may incorporate features like data hold, zero-set at any point, unit switching (mm/inch), and low-battery indicators.
-
Focus on Accuracy, Durability, and Specialization: The market will see continued emphasis on core attributes:
- Higher Precision: Demand for micrometers capable of sub-micron accuracy, especially in aerospace and medical device tubing applications, will push manufacturers to refine manufacturing tolerances and materials.
- Robust Construction: Instruments designed for harsh shop-floor environments (resistant to coolant, oils, dust, and impacts) remain highly valued. Hardened anvils and frames are standard.
- Specialized Variants: Growth in niche applications will fuel demand for specialized tube micrometers, such as those with extended anvils for deep recesses, specific anvil shapes for unique tube ends, or models designed for specific material types (e.g., softer plastics).
-
Competitive Landscape and Cost Pressures:
- Established Players vs. Emerging Manufacturers: The market will remain competitive, with established brands (e.g., Mitutoyo, Starrett, Fowler, Sylvac) competing on reputation, precision, and global support, while Asian manufacturers (particularly from China and India) offer cost-effective alternatives, capturing market share in less critical applications.
- Cost Optimization: Downward pressure on prices, especially for standard models, will persist. This may drive consolidation among smaller players and push all manufacturers towards efficient production and supply chain management.
-
Geographical Shifts:
- Asia-Pacific Growth: The APAC region, driven by manufacturing hubs in China, India, Japan, and South Korea, will likely see the strongest market growth due to expanding industrial production and infrastructure development.
- Mature Markets (North America, Europe): Growth will be more subdued, focused on replacement, upgrades to digital models, and meeting stringent regulatory requirements in key industries. Sustainability and longevity of instruments may gain more emphasis.
-
Sustainability and Longevity: While not a primary driver for tube micrometers specifically, the broader industrial trend towards sustainability may influence:
- Durability: Emphasis on instruments with long service lives and repairability (e.g., replaceable anvils, calibration services) to reduce waste.
- Materials: Potential (though likely minimal by 2026) exploration of more sustainable materials in housings or packaging.
Conclusion for 2026:
The tube micrometer market in 2026 will be characterized by stable, resilient demand anchored in fundamental industrial needs, particularly in aerospace, automotive, and energy sectors. The most significant trend will be the ongoing, though gradual, adoption of digital technology for enhanced usability, data capture, and integration into modern quality systems. Competition will remain intense, balancing the need for high precision and durability against cost pressures, with growth concentrated in the Asia-Pacific region. While core functionality remains unchanged, the integration of digital features and a focus on traceability will define the evolution of this essential precision tool.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a Tube Micrometer (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a tube micrometer—especially for precision measurement in industrial applications—can be fraught with challenges related to both quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure reliable performance and legal compliance.
Poor Quality Control and Inaccurate Calibration
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing tube micrometers is receiving instruments that lack proper calibration or are built with substandard materials. Low-cost suppliers, particularly from regions with less stringent manufacturing standards, may offer devices that appear identical to high-end models but deliver inconsistent or inaccurate measurements. This can lead to defective production outputs and increased operational costs. Always verify that the micrometer comes with a calibration certificate from an accredited body and confirm the presence of quality management certifications such as ISO 9001.
Counterfeit or Replica Instruments
The market includes counterfeit versions of well-known brands that mimic the appearance of genuine tube micrometers. These replicas often compromise on internal mechanisms and durability, leading to premature failure. Moreover, purchasing such products may inadvertently expose buyers to intellectual property violations. Using or distributing counterfeit metrology tools can result in legal liability, especially if they are branded with protected logos or designs.
Lack of IP Compliance in Design and Manufacturing
Some suppliers may produce tube micrometers that infringe on patented technologies, such as unique measurement mechanisms or digital readout systems. Sourcing from manufacturers that do not respect IP rights increases the risk of legal action, shipment seizures, or reputational damage. It is essential to work with suppliers who can demonstrate IP compliance through licensing agreements or original design documentation.
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Reliable sourcing requires full traceability of components and manufacturing processes. Many low-cost suppliers fail to provide detailed technical documentation, material certifications, or proof of design ownership. This lack of transparency not only affects quality assurance but also raises red flags regarding potential IP theft or unauthorized production.
Failure to Verify Supplier Credentials
A common oversight is not conducting due diligence on the supplier’s background. Without verifying a supplier’s history, certifications, and customer reviews, businesses risk engaging with entities involved in IP infringement or poor manufacturing practices. Requesting samples, visiting manufacturing sites, or using third-party inspection services can mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, sourcing a tube micrometer demands careful attention to both product quality and intellectual property considerations. Prioritizing reputable suppliers, demanding verifiable certifications, and ensuring design originality are critical steps to avoid costly mistakes and legal complications.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tube Micrometer
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the safe, efficient, and legally compliant handling, transportation, storage, and use of tube micrometers—precision measuring instruments commonly used in manufacturing, quality control, and engineering applications.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure all activities involving tube micrometers adhere to relevant international, national, and industry-specific regulations.
Measurement Standards
Tube micrometers must conform to recognized metrological standards such as ISO 3611 (Geometrical product specifications – Dimensional measuring instruments) or ANSI B89.1.13. Calibration certificates should be traceable to national standards (e.g., NIST in the U.S., UKAS in the U.K.) to ensure measurement accuracy and compliance with quality management systems like ISO 9001.
Import/Export Regulations
When shipping tube micrometers across borders, verify compliance with customs requirements, including proper Harmonized System (HS) code classification (e.g., 9017.20 for measuring instruments). Some countries may require import licenses or conformity assessments. Ensure all documentation—commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, and calibration certificate—is complete and accurate.
Environmental and Material Compliance
Confirm that the micrometer’s materials (typically hardened steel, carbide, or non-magnetic alloys) comply with environmental directives such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals), especially when shipping to or within the European Union.
Packaging and Handling
Proper packaging and handling are critical to maintaining the precision and longevity of tube micrometers.
Protective Packaging
Use manufacturer-recommended cases or custom-fitted containers with foam or cushioning to prevent shock, vibration, and contamination. Include desiccants to control moisture and prevent corrosion during transit or storage. Clearly label packages as “Fragile” and “Precision Instrument.”
Handling Procedures
Train personnel to handle tube micrometers with clean hands or gloves to avoid oil transfer and corrosion. Never drop or impact the instrument. Always store the micrometer with the measuring faces slightly apart to prevent contact wear and maintain spring tension in the ratchet mechanism.
Transportation Guidelines
Ensure safe and compliant transport across various modes.
Domestic and International Shipping
Use reputable carriers experienced in handling precision instruments. Opt for air or express shipping if time sensitivity is a concern, and insure high-value units. For international shipments, comply with IATA (air), IMDG (sea), or ADR (road) regulations if applicable—note that tube micrometers typically do not contain hazardous materials but still require careful declaration.
Temperature and Humidity Control
Avoid exposing micrometers to extreme temperatures or humidity during transit. Ideal storage and transport conditions are 15–25°C (59–77°F) with relative humidity below 60%. Use climate-controlled transport when necessary.
Storage Requirements
Maintain optimal storage conditions to preserve calibration and functionality.
Environmental Conditions
Store tube micrometers in a clean, dry, temperature-stable environment. Avoid exposure to direct sunlight, dust, and corrosive chemicals. Use sealed storage cabinets with humidity control when possible.
Organization and Inventory
Store micrometers in labeled, dedicated cases to prevent damage and misplacement. Implement an inventory tracking system that includes calibration due dates, usage history, and storage location for compliance audits and quality control.
Calibration and Maintenance
Regular calibration and maintenance are essential for accuracy and regulatory compliance.
Calibration Schedule
Calibrate tube micrometers at regular intervals (e.g., annually or per ISO 17025 standards) by accredited laboratories. Maintain a calibration log with dates, results, and technician details. Adjust frequency based on usage intensity and environmental conditions.
Preventive Maintenance
Clean micrometers after each use with a soft cloth and approved cleaning solution. Inspect for wear, damage, or contamination. Lubricate moving parts only as specified by the manufacturer to avoid measurement errors.
Training and Documentation
Ensure personnel are properly trained and records are maintained.
Operator Training
Provide training on proper use, handling, reading, and care of tube micrometers. Emphasize zeroing procedures, correct measurement technique, and recognition of instrument damage.
Record Keeping
Maintain comprehensive documentation including calibration certificates, maintenance logs, training records, and compliance declarations. These documents support ISO audits, customer requirements, and regulatory inspections.
Disposal and End-of-Life
Handle end-of-life micrometers responsibly.
Recycling and Disposal
Dispose of non-functional micrometers through certified e-waste or metal recycling programs in accordance with local environmental regulations. Do not discard precision instruments in regular waste streams due to metal content and potential contaminants.
Data Security
If the micrometer is part of a digital or connected measurement system, ensure any stored data is securely erased prior to disposal or refurbishment.
Adhering to this logistics and compliance guide ensures the reliability, accuracy, and regulatory conformity of tube micrometer operations across the supply chain.
Conclusion for Sourcing a Tube Micrometer
In conclusion, sourcing a tube micrometer requires careful consideration of application requirements, measurement precision, tube dimensions, and material compatibility. It is essential to select a micrometer that offers the accuracy, durability, and ease of use needed for consistent and reliable tube measurements in industrial, manufacturing, or quality control environments. Evaluating reputable suppliers, comparing features such as digital vs. analog readouts, and ensuring proper calibration and after-sales support are critical steps in the procurement process. By prioritizing quality and suitability, organizations can ensure long-term efficiency, reduce measurement errors, and maintain high standards in tube production and inspection processes.