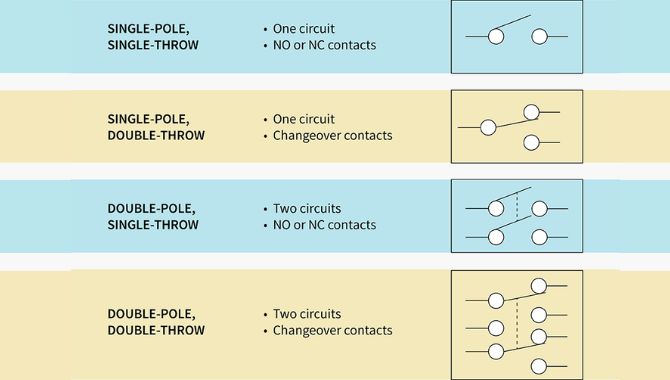
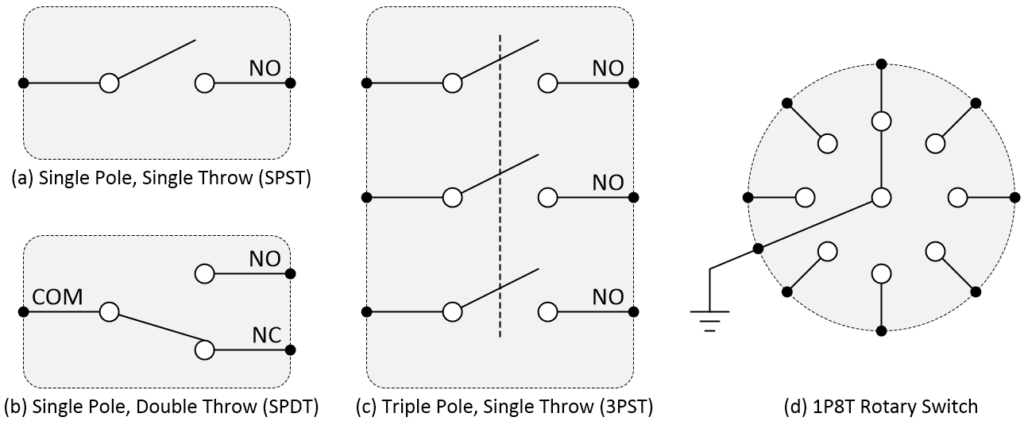
The global market for electromechanical switches, including triple pole single throw (TPST) configurations, is witnessing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industrial automation, telecommunications, and consumer electronics sectors. According to a 2023 report by Mordor Intelligence, the global electrical switches market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.2% from 2023 to 2028, fueled by infrastructure modernization and increased adoption of smart manufacturing technologies. TPST switches, known for their ability to simultaneously control three independent circuits with a single input, are becoming increasingly critical in complex control systems where reliability and space efficiency are paramount. As industrial and commercial applications grow more sophisticated, the need for high-quality, durable switching solutions has intensified, positioning leading manufacturers to innovate in materials, durability, and miniaturization. In this competitive landscape, eight manufacturers have emerged as key players, combining technological expertise, global reach, and robust product portfolios to meet evolving industry standards.
Top 8 Triple Pole Single Throw Switch Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 George Risk Industries, Inc.
Domain Est. 1997
Website: grisk.com
Key Highlights: George Risk Industries, Inc. is your choice when reliability matters. Find magnetic reed switches, security products, installation solutions, and more!…
#2 Swtich Poles and Switch Throws
Domain Est. 1992
Website: te.com
Key Highlights: TE manufactures a variety of switches to meet customer requirements. Learn about the differences in switch pole and switch throw attributes as well as other ……
#3 Qorvo QPC1006 Single
Domain Est. 1995
Website: mouser.com
Key Highlights: $4.99 delivery 30-day returnsOperating from 0.15 to 2.8GHz, the QPC1006 typically supports 50W input power handling at control voltages of 0/−40V for CW and pulsed RF operations….
#4 Electric switch
Domain Est. 1996
Website: eaton.com
Key Highlights: A 3-way switch is larger than a single pole switch and has three screw terminals for wiring connections, plus a ground….
#5 D325NR
Domain Est. 1998
Website: granitecityelectric.com
Key Highlights: This Single Throw Safety Switch which has a rated current of 400A with a NEMA 3R degree of protection. This fusible disconnect switch comes with a neutral ( ……
#6 H-Series 3 Pole Toggle Switch
Domain Est. 2000
Website: carlingtech.com
Key Highlights: The H-Series three pole toggle switches are heavy duty, high voltage AC rated switches. They feature a slow-make, slow-break contact mechanism….
#7 Three & Four Pole Toggle Switches
Domain Est. 2001
Website: spemco.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $993 & 4 Pole ; 1201-Q/16 Four Pole On-Off-On Toggle Switch, Spade terminals. $12.25 ; HK271-73 Carling Three Pole On-Off Toggle Switch 17 Amps, Spade Terminals….
#8 Relays & Coax Switches
Domain Est. 2024
Website: teledyne-ade.com
Key Highlights: Teledyne Relays provides rugged, high-reliability relays for aerospace and defense, ensuring mission-critical performance in extreme conditions….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Triple Pole Single Throw Switch

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Triple Pole Single Throw (TPST) Switch
The global market for Triple Pole Single Throw (TPST) switches is poised for steady growth and transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in industrial automation, rising demand for energy-efficient systems, and increased integration in commercial and residential infrastructure. As a fundamental electromechanical component used to control three separate circuits simultaneously with a single actuator, TPST switches are critical in applications ranging from industrial machinery and HVAC systems to power distribution units and control panels.
One of the primary drivers shaping the 2026 market landscape is the expansion of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 initiatives. Factories are increasingly adopting modular control systems where TPST switches provide reliable and cost-effective circuit control. Their ability to isolate multiple power lines simultaneously enhances safety and simplifies maintenance procedures, aligning with stricter industrial safety standards globally.
Additionally, the growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainable infrastructure is influencing TPST switch design and deployment. Manufacturers are focusing on developing switches with lower contact resistance, higher current ratings, and improved durability to support green energy applications such as solar inverters and electric vehicle (EV) charging stations. These applications often require robust, multi-pole switching solutions to manage high-voltage and high-current loads safely.
Another significant trend is the regional shift in manufacturing and demand. Asia-Pacific—particularly China, India, and Southeast Asia—is emerging as a key market and production hub due to rapid urbanization, government investments in smart cities, and the expansion of electrical infrastructure. This regional growth is prompting global suppliers to localize production and tailor product specifications to meet regional regulatory standards such as CCC (China Compulsory Certification) and BIS (Bureau of Indian Standards).
Technological innovation is also evident in the integration of digital diagnostics and IoT-readiness in industrial switches. While traditional TPST switches remain mechanical, some advanced variants now include auxiliary contacts or sensors to provide feedback to control systems, enabling predictive maintenance and remote monitoring—features increasingly demanded in modern industrial environments.
Market competition is intensifying, with key players such as ABB, Schneider Electric, Siemens, and Eaton enhancing product portfolios through miniaturization, improved materials (e.g., flame-retardant thermoplastics), and compliance with international standards like IEC 60947 and UL 508. Price pressures and supply chain resilience remain challenges, particularly in the wake of geopolitical tensions and semiconductor shortages, prompting companies to diversify sourcing and invest in automation to maintain margins.
In summary, by 2026, the TPST switch market will be characterized by steady demand in traditional industrial sectors, growing adoption in renewable energy and smart infrastructure, and innovation focused on reliability, safety, and digital integration. While the core function of TPST switches remains unchanged, their role within intelligent systems is expanding, ensuring continued relevance in a rapidly evolving electrical ecosystem.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing Triple Pole Single Throw (TPST) Switches
Sourcing a reliable and compliant Triple Pole Single Throw (TPST) switch requires careful attention to both quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings. Overlooking key details can lead to system failures, safety risks, or non-compliance. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Components and Materials
One of the most frequent issues is selecting TPST switches made from substandard materials or with inconsistent manufacturing. Low-cost switches may feature brittle plastic housings, weak internal contacts, or inadequate spring mechanisms, leading to premature failure under normal use. Poorly manufactured switches can exhibit inconsistent actuation, contact bounce, or increased resistance, which compromises circuit reliability. Always verify certifications (such as UL, CE, or IEC) and opt for reputable manufacturers with proven track records in industrial or commercial applications.
Misunderstanding or Misrepresenting IP Ratings
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating is critical for switches used in harsh environments. A common mistake is assuming a generic “industrial” label implies dust or water resistance. For example, an IP65-rated switch is dust-tight and protected against low-pressure water jets, while IP40 only protects against solid objects larger than 1mm with no water protection. Sourcing a switch with an insufficient IP rating for the application—such as using an IP20 switch in an outdoor or washdown environment—can lead to corrosion, short circuits, or mechanical failure. Always match the IP rating to the environmental demands, and verify test documentation from the supplier.
Inadequate Electrical Ratings for the Application
Another pitfall is selecting a TPST switch based solely on physical form factor without considering electrical specifications. TPST switches vary widely in current and voltage ratings (e.g., 10A at 250VAC vs. 30A at 600V). Using an underrated switch in high-load applications causes overheating, contact welding, or fire hazards. Always cross-check the switch’s rated load with the actual circuit requirements, including inrush currents and duty cycles.
Lack of Mechanical Durability and Lifespan Verification
Switches in industrial settings undergo frequent operation. A common oversight is failing to verify mechanical lifespan—often expressed in operating cycles (e.g., 50,000 cycles). Low-quality switches may degrade quickly with repeated use, leading to inconsistent contact performance or actuator failure. Ensure the specified mechanical endurance meets or exceeds expected usage, especially in automated or high-traffic environments.
Inconsistent Terminal Types and Mounting Options
Mismatched terminal types (screw, quick-connect, PCB) or mounting configurations (panel, flange, snap-in) can complicate installation and maintenance. Sourcing a switch that doesn’t align with existing panel cutouts or wiring practices leads to delays and added costs. Confirm dimensional drawings, terminal compatibility, and mounting requirements before procurement.
Avoiding these pitfalls requires thorough due diligence: request samples, validate specifications with test reports, and partner with trusted suppliers who provide full technical documentation.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Triple Pole Single Throw (TPST) Switch
This guide outlines key logistics considerations and compliance requirements for the import, export, distribution, and use of Triple Pole Single Throw (TPST) switches. Adhering to these guidelines ensures legal operation, safety, and smooth supply chain management.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure TPST switches meet all applicable international, national, and regional standards. Key certifications include:
- UL/CSA (North America): Certified to UL 61058-1 or UL 60947 standards for switch safety and performance.
- CE Marking (European Union): Compliance with Low Voltage Directive (LVD 2014/35/EU), Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive (2014/30/EU), and RoHS (2011/65/EU) for restricted hazardous substances.
- UKCA (United Kingdom): Equivalent to CE marking for products placed on the UK market post-Brexit.
- CCC (China): Required for electrical switches sold in China under the China Compulsory Certification program.
- KC Mark (South Korea): Compliance with South Korean electrical safety standards.
Maintain up-to-date technical documentation, Declaration of Conformity (DoC), and test reports from accredited laboratories.
Product Classification & HS Code
Accurately classify TPST switches for customs purposes using the Harmonized System (HS) code. Typical classifications may fall under:
- HS Code 8536.50: Electrical apparatus for switching or protecting electrical circuits (e.g., switches for voltage ≤ 1,000 V).
Confirm the exact code with local customs authorities, as subcategories may vary by region and application (industrial vs. consumer use).
Packaging & Labeling Requirements
- Packaging: Use anti-static, shock-resistant packaging to prevent damage during transit. Include desiccants if shipping to high-humidity environments.
- Labeling: Each unit and shipping container must display:
- Manufacturer name and part number
- Voltage and current ratings
- Certifications (e.g., UL, CE)
- RoHS/WEEE compliance symbols
- Country of origin
Ensure multilingual labeling where required (e.g., EU, Canada).
Import/Export Documentation
Prepare essential documentation for cross-border shipments:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading or Air Waybill
- Certificate of Origin
- Test Reports and Certificates of Conformity
- Import/Export Licenses (if required by destination country)
Verify Incoterms (e.g., FOB, DDP) to define responsibility for logistics and compliance.
Environmental & Safety Regulations
- RoHS Compliance: Confirm switches are free from lead, mercury, cadmium, and other restricted substances.
- REACH (EU): Ensure no use of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHCs) above threshold levels.
- WEEE (EU): Provide information on proper end-of-life disposal and recycling.
- Conflict Minerals: Comply with U.S. Dodd-Frank Act Section 1502 if applicable; disclose use of tin, tantalum, tungsten, or gold from conflict-affected regions.
Transportation & Handling
- Mode of Transport: Choose appropriate method (air, sea, ground) based on urgency, volume, and destination.
- Hazard Classification: TPST switches are generally non-hazardous but verify with Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) if applicable.
- Storage Conditions: Store in dry, temperature-controlled environments (typically 5°C to 40°C) away from corrosive agents.
Quality Assurance & Traceability
- Implement lot or batch numbering for full traceability.
- Conduct incoming and outgoing quality inspections per ISO 9001 standards.
- Maintain records of supplier qualifications and component sourcing.
End-of-Life & Recycling
Provide customers with WEEE disposal instructions. Partner with certified e-waste recyclers to support responsible end-of-life management, especially in regulated markets.
Adhering to this guide ensures global market access, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency throughout the TPST switch supply chain.
In conclusion, sourcing a Triple Pole Single Throw (3PST) switch requires careful consideration of technical specifications, application requirements, and supplier reliability. It is essential to verify the switch’s current and voltage ratings, pole configuration, actuation method, mounting style, and environmental durability to ensure compatibility with the intended system. Additionally, evaluating suppliers based on product quality, certifications, lead times, and cost-effectiveness will help secure a reliable and efficient component for both prototyping and large-scale production. By following a structured sourcing approach, organizations can ensure operational safety, long-term performance, and compliance with industry standards.