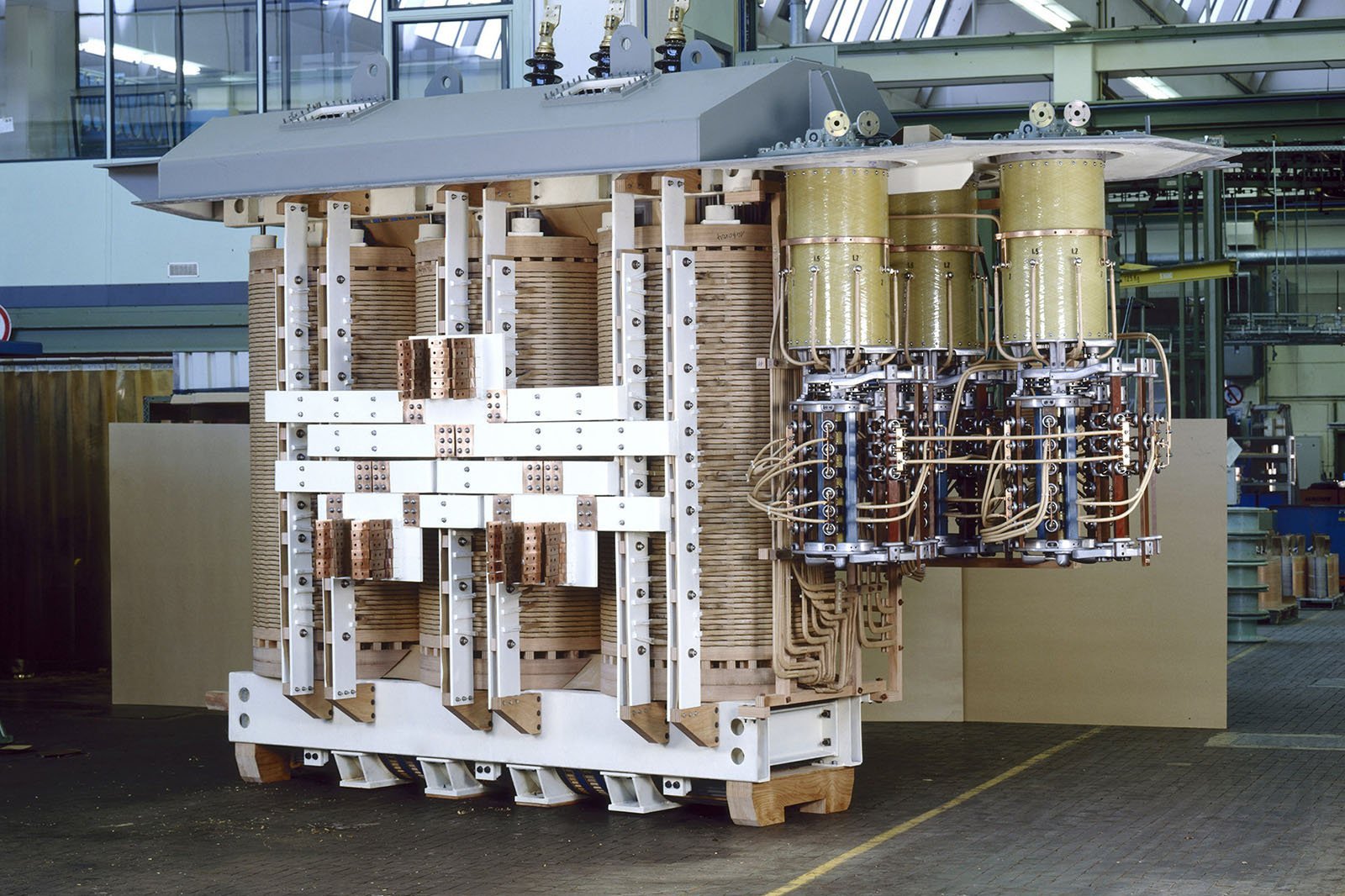
The global transformer market is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising electricity demand, grid modernization initiatives, and the expansion of renewable energy infrastructure. According to Mordor Intelligence, the transformer market was valued at USD 63.78 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 86.11 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 6.15% during the forecast period. Similarly, Grand View Research notes increasing investments in smart grid technologies and high-voltage transmission systems as key drivers, particularly in emerging economies. As power generation capacity expands worldwide—especially in solar, wind, and conventional thermal sectors—the demand for reliable and efficient generator transformers continues to surge. In this evolving landscape, leading manufacturers are leveraging advanced materials, digital monitoring, and eco-efficient designs to meet stringent regulatory and performance standards. Below are the top 9 transformer generator manufacturers shaping the future of global power transmission and distribution.
Top 9 Transformers Generator Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Virginia Transformer Corp
Domain Est. 1997 | Founded: 1971
Website: vatransformer.com
Key Highlights: The largest U.S.-owned custom power transformer manufacturer since 1971, with six advanced facilities across the U.S. and Mexico….
#2 SGB
Domain Est. 2003
Website: sgb-smit.com
Key Highlights: The pure-play transformer specialist from Europe with the highest customer dedication. Wherever electricity is required, generated and distributed….
#3 Transformers I Power and Distribution Transformer Solutions
Domain Est. 2007
Website: siemens-energy.com
Key Highlights: Global manufacturer of high-performance transformers for power systems. Siemens Energy is a globally recognized transformer manufacturer and supplier, offering ……
#4 Transformer Manufacturer
Website: prolec.energy
Key Highlights: Prolec manufactures 1200MVA, 345kV transformers top rated and manufactured to the latest IEEE, ANSI, NEMA & ISO 9001:2015 quality standards….
#5 Alfa Transformer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: alfatransformer.com
Key Highlights: Alfa Transformer offers new, energy efficient, single-phase and three-phase low voltage (600V class) and medium voltage dry type transformers from 0.05 KVA to ……
#6 Basler Electric
Domain Est. 1996
Website: basler.com
Key Highlights: Discover Basler Electric’s innovative power solutions, now amplified by Littelfuse. Explore our products and industry-leading energy technologies….
#7 VanTran Transformers
Domain Est. 1998
Website: vantran.com
Key Highlights: VanTran is a transformer manufacturing company in Waco, TX that offers a wide range of high-quality, distribution transformers….
#8 Reinhausen: MR
Domain Est. 1998
Website: reinhausen.com
Key Highlights: Welcome to MR! THE POWER BEHIND POWER. Our world’s desire for energy knows no bounds, from electrification and digitalization to urbanization….
#9 Generator, Motor & Transformer Coolers
Domain Est. 2018
Website: wabteccorp.com
Key Highlights: Turbine, generator, motor, transformer coolers and pumps for use in large power generation & distribution applications….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Transformers Generator

H2: Analysis of 2026 Market Trends for Transformers and Generators
The global market for transformers and generators is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by technological innovation, rising energy demands, and the global push toward decarbonization. This analysis explores key trends shaping the transformers and generators sector in the H2 (second half) of 2026, focusing on demand dynamics, technological advancements, regional developments, and regulatory influences.
1. Increased Demand from Renewable Energy Integration
By H2 2026, the integration of renewable energy sources—particularly solar and wind—into national grids will continue to be a primary driver of transformer demand. As intermittent power generation requires more robust grid infrastructure, the need for advanced power and distribution transformers will rise. Grid modernization efforts, especially in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific, will prioritize smart transformers capable of handling bidirectional power flow and voltage regulation.
Generators, particularly backup and hybrid models, will see sustained demand in regions with unreliable grid infrastructure or frequent extreme weather events. However, their role is increasingly shifting from primary power sources to transitional or emergency support, especially as battery storage becomes more cost-effective.
2. Adoption of Smart and Digital Transformers
Digitalization will gain momentum in H2 2026, with utilities investing in smart transformers equipped with IoT sensors, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities. These technologies improve grid reliability and reduce downtime. Major manufacturers such as Siemens, ABB, and GE are expected to expand their portfolios of digitally enabled transformers, aligning with smart city and grid resilience initiatives.
The use of digital twins for transformer performance modeling will become more widespread, allowing for better lifecycle management and reduced operational costs.
3. Growth in Modular and Mobile Generators
The demand for modular and mobile generators is projected to grow, particularly in remote areas, disaster recovery zones, and temporary infrastructure projects (e.g., construction sites, mining operations). By H2 2026, manufacturers will focus on lightweight, fuel-efficient, and low-emission generator sets, incorporating hybrid technology (diesel-electric or natural gas-electric) to comply with stricter emissions standards.
Additionally, hydrogen-ready generators are expected to enter pilot phases in several developed markets, setting the stage for future zero-carbon backup power solutions.
4. Impact of Geopolitical and Supply Chain Factors
Supply chain resilience remains a concern in H2 2026. Ongoing geopolitical tensions and raw material price volatility—especially for copper, steel, and rare earth elements—will continue to impact production costs and lead times. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly regionalizing production and investing in local sourcing to mitigate risks.
Trade policies and import regulations, particularly in the U.S. and EU, are expected to favor domestically produced transformers and generators that meet energy efficiency and cybersecurity standards.
5. Regulatory and Sustainability Pressures
Environmental regulations will play a pivotal role in shaping product development. The EU’s Ecodesign Directive and similar policies in other regions will push manufacturers to produce energy-efficient, low-loss transformers. The phase-out of PCB-containing and high-SF6 equipment will accelerate, with increased adoption of eco-friendly insulating materials such as ester-based fluids and dry-type transformers.
For generators, emissions regulations (e.g., U.S. EPA Tier 5 standards) will drive innovation in cleaner combustion technologies and exhaust after-treatment systems.
6. Regional Market Dynamics
-
Asia-Pacific: China and India will remain the largest markets for both transformers and generators, driven by urbanization, industrialization, and rural electrification programs. India’s Green Energy Corridors project will boost demand for high-capacity transformers.
-
North America: The U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act will continue to fund grid upgrades, supporting strong demand for distribution and transmission transformers. Microgrid development will also spur interest in small-scale, intelligent generators.
-
Europe: The Green Deal and REPowerEU initiatives will prioritize grid resilience and renewable integration, favoring smart and modular transformer solutions. Generator demand will be limited to backup applications, with a strong shift toward sustainable alternatives.
-
Africa and Latin America: These regions will see growing demand for diesel and hybrid generators due to grid instability, though investment in solar mini-grids and distribution transformers is expected to rise with international funding.
Conclusion
In H2 2026, the transformers and generators market will be characterized by a strategic shift toward sustainability, digitalization, and resilience. While transformers benefit from long-term grid modernization trends, generators are adapting to a changing energy landscape by embracing hybrid and low-emission technologies. Companies that invest in innovation, supply chain agility, and compliance with environmental standards will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities in this evolving market.

Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Transformers and Generators (Quality, IP)
Sourcing transformers and generators—especially for industrial, energy, or AI infrastructure applications—can be complex. Buyers often face challenges related to quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Control and Substandard Components
One of the most frequent issues in sourcing is receiving equipment that fails to meet performance, safety, or durability standards. This often stems from:
- Use of inferior materials: Suppliers may substitute high-grade copper with aluminum or lower-spec steel in cores, reducing efficiency and lifespan.
- Inadequate testing: Units may not undergo proper load, insulation resistance, or temperature rise testing before shipment.
- Lack of certifications: Absence of internationally recognized certifications (e.g., ISO, IEC, IEEE, UL) increases the risk of non-compliance and field failures.
Tip: Always require test reports (e.g., factory acceptance tests), inspect production facilities, and use third-party quality inspections before shipment.
Counterfeit or Reverse-Engineered Designs (IP Infringement)
Transformers and generators often incorporate proprietary designs and patented technologies. Sourcing from unverified suppliers increases the risk of:
- IP violations: Suppliers may replicate branded products (e.g., Siemens, GE, ABB) without authorization, exposing buyers to legal liability.
- Use of stolen designs: In some regions, manufacturing facilities may use leaked or reverse-engineered technical specifications, infringing on patents or trade secrets.
- Grey market products: Equipment may be diverted from authorized distribution channels, lacking warranty or support.
Tip: Conduct due diligence on suppliers, verify design ownership, and include IP indemnification clauses in procurement contracts.
Inconsistent Performance and Efficiency Claims
Suppliers may exaggerate efficiency ratings (e.g., claiming 99% efficiency without test proof) or misrepresent load capacity and cooling capabilities.
- Transformer losses misrepresented: No-load and load losses may be underreported, impacting long-term operating costs.
- Generator output overstated: Power output, fuel efficiency, and harmonic distortion levels may not match real-world performance.
Tip: Require independent performance validation and insist on standardized testing protocols under real load conditions.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Poor documentation can hinder maintenance, compliance, and warranty claims.
- Missing technical drawings or BOMs: Critical for repairs and spare parts sourcing.
- Incomplete manufacturing records: Serial numbers, batch details, and material certifications may be unavailable.
- No software/firmware logs (for smart generators): Risks cybersecurity and update management.
Tip: Mandate full documentation packages and ensure alignment with regional regulatory requirements (e.g., CE, RoHS, NEBS).
Supply Chain and After-Sales Support Gaps
Even high-quality equipment can fail if support is lacking.
- Long lead times for spare parts: Especially for custom or niche designs.
- No local service network: Delays in maintenance or repairs increase downtime.
- Abandoned IP or obsolete designs: Suppliers may cease operations, leaving buyers without technical support.
Tip: Evaluate supplier longevity, service footprint, and spare parts availability before procurement.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP-related pitfalls, organizations can mitigate risk, ensure reliable performance, and protect themselves from legal and operational setbacks.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Transformers & Generators
This guide provides essential information for the safe, efficient, and compliant transportation, handling, and regulatory management of transformers and generators—critical power equipment used across industrial, commercial, and utility sectors.
Equipment Classification and Regulatory Framework
Transformers and generators are classified as heavy, high-value electrical equipment subject to multiple regulatory bodies depending on jurisdiction. Key regulations include:
– International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards for design and safety (e.g., IEC 60076 for transformers, IEC 60034 for motors/generators).
– National Electrical Code (NEC) and IEEE standards in the United States.
– ATEX/IECEx directives if operating in hazardous environments.
– Environmental regulations such as EPA PCB regulations (for older oil-filled transformers) and RoHS/REACH for material compliance in the EU.
Ensure equipment meets destination country certifications prior to shipment.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging and handling are vital to prevent damage during transit:
– Transformers: Must be securely mounted on skids with lifting lugs clearly marked. Oil-filled units should be sealed and nitrogen-pressurized to prevent moisture ingress. Include breather valves and monitoring gauges where applicable.
– Generators: Should be crated with environmental protection (moisture, dust, impact). Sensitive components (e.g., alternators, control panels) require additional cushioning.
– Use desiccants and humidity indicators inside crates.
– Clearly label with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” weight, center of gravity, and lifting points.
Transportation Logistics
Due to size and weight, special logistics planning is required:
– Mode of Transport:
– Heavy Haul Trucking for regional land transport; requires route surveys for bridge clearances, road weight limits.
– Rail for long-distance, cost-effective transport of large units.
– Sea Freight for international shipments; use flat-rack or open-top containers for oversized units.
– Permits: Oversize/overweight transport permits are often required. Coordinate with local authorities for escort vehicles and travel windows.
– Loading/Unloading: Use certified cranes with appropriate slings; follow OEM lifting instructions. Ensure ground support can bear concentrated loads.
Import/Export Compliance
Cross-border shipments require strict adherence to customs and trade regulations:
– HS Codes: Use correct Harmonized System codes (e.g., 8504.23 for power transformers, 8502.11 for generating sets).
– Documentation: Prepare commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading, certificate of origin, and test/certification reports.
– Duty and Tariff Considerations: Check for trade agreements (e.g., USMCA, GSP) that may reduce tariffs.
– Export Controls: Verify if equipment contains dual-use technologies subject to ITAR or EAR regulations.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Environmental protection and workplace safety are paramount:
– PCB Management: For transformers manufactured before 1979, test for PCBs. If present, comply with EPA disposal and handling rules (40 CFR Part 761).
– Oil Spill Prevention: Transport oil-filled units upright. Have spill containment kits and response plans for transport and installation sites.
– On-Site Safety: Follow OSHA (or local equivalent) standards for rigging, electrical safety (lockout/tagout), and confined space entry during installation.
Installation and Site Readiness
Ensure the destination site complies with operational requirements:
– Foundation: Must meet OEM specifications for load-bearing, vibration dampening, and alignment.
– Clearances: Maintain safe distances per NEC or IEC for ventilation, fire safety, and maintenance access.
– Grounding and Bonding: Install per electrical codes to prevent shock hazards and ensure system stability.
Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain comprehensive records for compliance audits:
– Factory test reports (type and routine tests)
– Shipping and handling logs
– Customs documentation
– Installation and commissioning records
– Maintenance and inspection history
Retention period: Minimum 10 years, or per local regulatory requirement.
Emergency Response and Contingency Planning
Prepare for potential incidents:
– Develop a spill response plan for insulating oil or coolant leaks.
– Train personnel on fire suppression methods (e.g., Class C extinguishers for electrical fires; avoid water on energized equipment).
– Have emergency contact lists for OEM support, hazmat teams, and regulatory agencies.
Note: Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and local regulatory authorities to ensure full compliance. Regulations vary by country and application; site-specific risk assessments are recommended prior to transport and installation.
Conclusion for Sourcing Transformers and Generators:
In conclusion, the successful sourcing of transformers and generators requires a strategic approach that balances technical specifications, reliability, cost-efficiency, and long-term operational needs. These critical power infrastructure components must be selected based on rigorous evaluation of quality, compliance with international standards, supplier reputation, and after-sales support. Conducting thorough market research, engaging with pre-qualified vendors, and performing detailed technical and financial assessments are essential to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Moreover, considering factors such as energy efficiency, scalability, lead times, and logistical requirements plays a crucial role in minimizing downtime and supporting future expansion. By adopting a comprehensive sourcing strategy, organizations can secure reliable power solutions that enhance operational resilience, reduce lifecycle costs, and align with sustainability goals. Ultimately, informed decision-making in the procurement of transformers and generators lays the foundation for a stable, efficient, and future-ready power system.