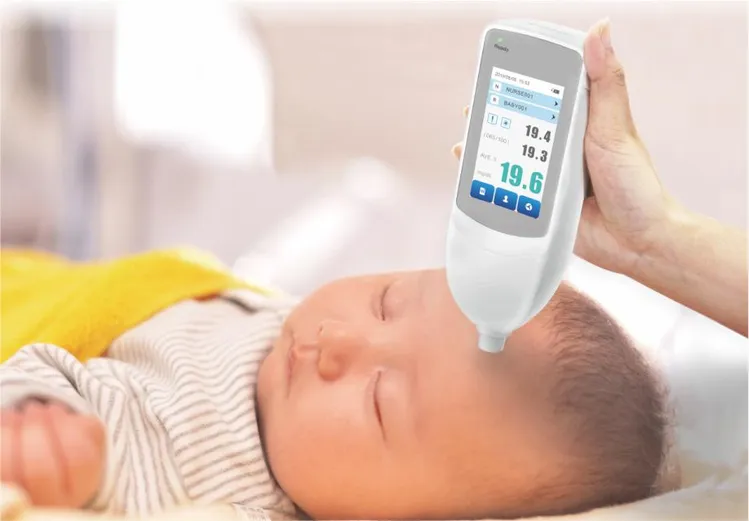
The global transcutaneous bilirubin meter market is witnessing steady expansion, driven by increasing neonatal screenings and the rising prevalence of neonatal jaundice. According to Mordor Intelligence, the market was valued at approximately USD 132 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.5% during the forecast period 2024–2029. This growth is further supported by rising healthcare awareness, technological advancements in non-invasive diagnostic devices, and expanding newborn care infrastructure—especially in emerging economies. As hospitals and birthing centers prioritize early detection and continuous monitoring, demand for reliable, quick, and painless bilirubin measurement tools has intensified, prompting innovation and competition among key players. In this evolving landscape, nine manufacturers have emerged as leaders, combining clinical accuracy, user-centric design, and robust global distribution networks to meet growing market needs.
Top 9 Transcutaneous Bilirubin Meter Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 BiliCare
Domain Est. 1997
Website: mennenmedical.com
Key Highlights: The Transcutaneous Bilirubin Meter. The BiliCare System measures the level of bilirubin using a patented technology to provide accurate results….
#2 Reproducibility of BiliCare™ Transcutaneus Bilirrubin Meter in …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Key Highlights: The BiliCare™ a noninvasive bilirubin meter is a transcutaneous device that uses transmission technology instead of reflection. It adapts with ……
#3 Bilirubin meter,transcutaneous,hand
Domain Est. 1993
Website: supply.unicef.org
Key Highlights: A portable non-invasive transcutaneous bilirubin meter that measures yellowness of subcutaneous tissue to accurately and precisely estimate serum bilirubin ……
#4 Dräger Jaundice Meter JM-105
Domain Est. 1994
Website: draeger.com
Key Highlights: The Dräger Jaundice Meter JM-105 is a non-invasive transcutaneous bilirubinometer that can help identify at-risk infants as young as 35 weeks gestational ……
#5 Transcutaneous bilirubin meter
Domain Est. 1997
Website: medicalexpo.com
Key Highlights: A handhold instrument used in the dynamic clinical examination of neonatal jaundice. It non-invasive and it instantly tests the transcutaneous….
#6 Konica Minolta Contributes to UCSF to Support Clinical Trial for …
Domain Est. 2003
Website: konicaminolta.com
Key Highlights: Konica Minolta launched the world’s first non-invasive Jaundice meter in 1980, which can be measured by flashing light on the chest or forehead ……
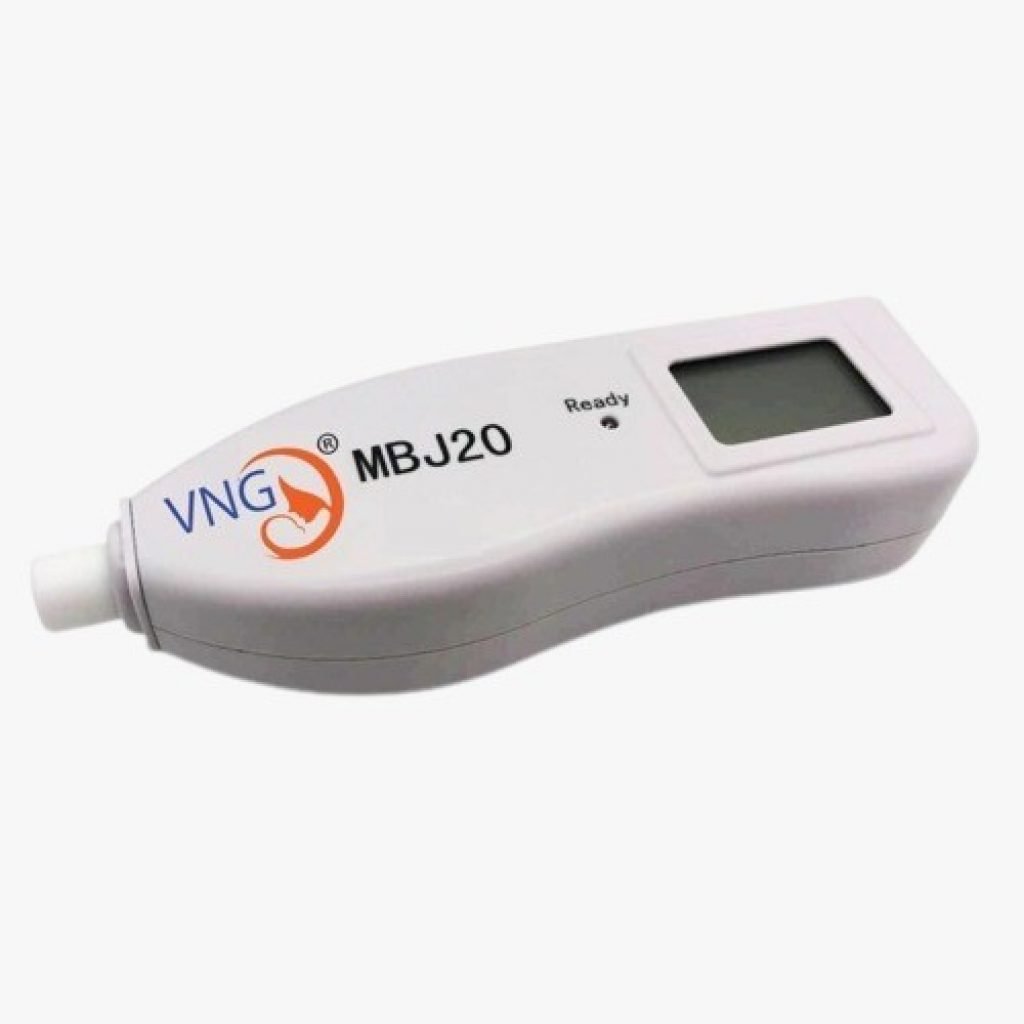
#7 Jaundice Detectors
Domain Est. 2010
Website: hutchisonmedical.com
Key Highlights: The MBJ20 Transcutaneous Jaundice Detector (Transcutaneous Bilirubinometer) is a convenient tool for measuring bilirubin levels. Compact and lightweight, it ……
#8 From Screening to Therapy
Domain Est. 2010
Website: synovaassociates.com
Key Highlights: The Dräger Jaundice Meter JM-105 is designed to accurately identify at-risk infants as young as 35 weeks gestational age using transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) ……
#9 Jaundice Measurement
Domain Est. 2015
Website: deltamedint.com
Key Highlights: The transcutaneous jaundice meter from Delta Medical International offers a reliable, non-invasive method for screening babies for jaundice….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Transcutaneous Bilirubin Meter

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Transcutaneous Bilirubin Meters
The global transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) meter market is projected to experience significant growth and transformation by 2026, driven by technological advancements, rising neonatal care standards, and increasing demand for non-invasive diagnostic tools. Key trends shaping the market include:
-
Increased Adoption in Neonatal Care
By 2026, transcutaneous bilirubin meters are expected to become standard equipment in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) and well-baby nurseries across both developed and emerging economies. Their non-invasive nature reduces the need for frequent blood sampling, enhancing patient comfort and compliance—especially in newborns. -
Technological Innovation and Device Accuracy
Manufacturers are focusing on improving the accuracy and reliability of TcB meters through advanced optical sensors and AI-driven algorithms. Devices are being calibrated for diverse skin tones and gestational ages, addressing previous limitations and expanding usability across global populations. -
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Asia-Pacific and Latin America are anticipated to witness the fastest market growth due to rising healthcare investments, improved neonatal infrastructure, and government initiatives aimed at reducing infant mortality. Countries like India, China, and Brazil are increasing screening programs for neonatal jaundice, fueling demand for TcB meters. -
Integration with Digital Health Platforms
By 2026, many TcB meters are expected to feature Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connectivity, enabling seamless data transfer to electronic health records (EHRs) and mobile health applications. This integration supports remote monitoring, real-time tracking of bilirubin levels, and tele-neonatology services. -
Growing Emphasis on Preventive Care
Public health campaigns promoting early detection of hyperbilirubinemia are boosting the use of point-of-care testing tools like TcB meters. Routine screening at birth and during postnatal check-ups is becoming more common, particularly in primary healthcare settings. -
Competitive Landscape and Product Differentiation
The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with key players such as Dräger, GE Healthcare, and BiliSoft launching next-generation devices with enhanced ergonomics, faster readings, and multi-site measurement capabilities. Strategic partnerships and distribution agreements are also expanding market reach. -
Regulatory Support and Reimbursement Improvements
Regulatory bodies in regions like North America and Europe are streamlining approvals for non-invasive diagnostic devices. Simultaneously, better insurance coverage for neonatal screening procedures is improving access and affordability of TcB meters.
In summary, the 2026 transcutaneous bilirubin meter market will be characterized by innovation, broader accessibility, and integration into digital health ecosystems, ultimately supporting improved outcomes in neonatal jaundice management.

H2: Common Pitfalls in Sourcing Transcutaneous Bilirubin Meters – Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
Sourcing transcutaneous bilirubin meters (TcB meters) for neonatal jaundice screening presents several challenges, particularly regarding product quality and intellectual property (IP) compliance. Organizations and healthcare providers must be vigilant to avoid common pitfalls that can compromise patient safety, regulatory compliance, and long-term supply reliability.
1. Compromised Product Quality
One of the most significant risks when sourcing TcB meters—especially from low-cost manufacturers—is receiving substandard devices. Poor-quality meters may deliver inaccurate bilirubin readings, leading to misdiagnosis, delayed treatment, or unnecessary blood testing. Key quality-related pitfalls include:
- Lack of Clinical Validation: Some devices are not validated against serum bilirubin levels through peer-reviewed, multi-center clinical studies.
- Inconsistent Performance Across Skin Tones: Lower-tier devices may not be calibrated for diverse neonatal populations, resulting in unreliable readings in infants with darker skin pigmentation.
- Absence of Regulatory Approvals: Sourcing from suppliers without certifications such as FDA 510(k), CE marking, or ISO 13485 can indicate non-compliance with safety and performance standards.
2. Intellectual Property Infringement
Many reputable TcB meters, such as the JM-105 by Draeger or BiliCheck by Philips, are protected by patents and trademarks. Sourcing from manufacturers that replicate or reverse-engineer these devices without authorization poses serious IP risks:
- Counterfeit or Clone Devices: Some suppliers offer “compatible” or “equivalent” models that closely mimic branded devices, potentially infringing on design and utility patents.
- Legal and Reputational Risks: Procuring IP-infringing devices can expose healthcare institutions or distributors to legal action, product seizures, or damage to credibility.
- Lack of Technical Support and Updates: Clone devices often lack access to firmware updates, technical support, or calibration services, affecting long-term usability.
3. Inadequate Supplier Due Diligence
Failure to conduct thorough vetting of suppliers increases exposure to both quality and IP risks. Pitfalls include:
- Opaque Manufacturing Origins: Suppliers may obscure the actual manufacturer, making it difficult to verify compliance or traceability.
- Missing Documentation: Absence of clear technical specifications, regulatory certificates, or IP ownership statements is a red flag.
- Unsustainable Support Infrastructure: Low-cost suppliers may lack the capacity for after-sales service, calibration, or spare parts, affecting device longevity.
Conclusion
To mitigate these pitfalls, procurement teams should prioritize suppliers with transparent manufacturing practices, verifiable regulatory approvals, and clear IP legitimacy. Engaging in due diligence—such as requesting clinical validation data, verifying certifications, and consulting legal experts on IP—ensures the acquisition of safe, reliable, and lawful transcutaneous bilirubin meters.
Logistics & Compliance Guide for Transcutaneous Bilirubin Meter
Regulatory Classification and Approval Pathway
Transcutaneous bilirubin meters are classified as medical devices and are subject to regulatory oversight in most jurisdictions. In the United States, the FDA categorizes these devices as Class II medical devices under 21 CFR 870.2150, typically requiring a 510(k) premarket notification to demonstrate substantial equivalence to a predicate device. In the European Union, they fall under the Medical Devices Regulation (MDR) (EU) 2017/745 and generally require conformity assessment by a Notified Body, leading to CE marking. Manufacturers must ensure compliance with essential requirements related to safety, performance, biocompatibility, and electromagnetic compatibility. Technical documentation, including clinical evaluation reports and risk management files per ISO 14971, must be maintained and made available for audit.
Labeling and Instructions for Use (IFU)
Labeling for transcutaneous bilirubin meters must comply with local regulatory requirements and include critical information such as the device name, model number, manufacturer details, intended use, contraindications, warnings, and precautions. The Instructions for Use (IFU) must be provided in the official language(s) of the target market and contain clear, step-by-step guidance on device operation, calibration procedures, measurement techniques, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Special emphasis should be placed on proper skin site selection, device placement, and interpretation of results to avoid clinical misinterpretation. Symbols per ISO 15223-1 must be used on labels and packaging for international consistency.
Import and Export Documentation
Importing and exporting transcutaneous bilirubin meters require adherence to customs and trade regulations. Key documentation includes a Certificate of Free Sale (CFS) issued by the country of origin, a Certificate to Foreign Government (CFG) if required by the destination country, and a Certificate of Conformity (CoC) demonstrating compliance with applicable standards. For export from the U.S., an FDA Export Certificate may be necessary. Accurate commercial invoices, packing lists, and bills of lading are essential for customs clearance. Exporters must verify that the destination country does not require additional pre-approval or special import licenses for medical devices.
Shipping and Storage Conditions
Transcutaneous bilirubin meters are sensitive electronic devices that require careful handling during transportation. They must be shipped in protective packaging that meets ISTA 3A or similar standards to prevent damage from shock, vibration, and moisture. Ambient storage and shipping temperatures should remain within the manufacturer’s specified range (typically 10°C to 40°C), and exposure to extreme temperatures, direct sunlight, or high humidity should be avoided. Devices should be stored in a dry, clean environment prior to distribution. Battery-powered units should be shipped with batteries partially charged or removed, in compliance with IATA/IMDG regulations for lithium batteries, if applicable.
Post-Market Surveillance and Vigilance Reporting
Once on the market, manufacturers are responsible for establishing a post-market surveillance (PMS) system to monitor device performance and detect adverse events. Under EU MDR, a Post-Market Surveillance Plan and Periodic Safety Update Report (PSUR) are required for Class II devices. In the U.S., manufacturers must comply with FDA’s Medical Device Reporting (MDR) regulation (21 CFR Part 803), reporting device malfunctions, injuries, or deaths to the FDA within specified timeframes. Complaint handling procedures must be documented, and trend analysis of field data should inform risk management and potential design improvements.
Training and Clinical Support
Effective logistics includes ensuring end-users receive adequate training. Distributors and healthcare providers should be provided with training materials and access to clinical support to ensure proper use of the device. Manufacturer-led training sessions or online modules can help standardize measurement techniques and improve accuracy. Technical support must be available to address device issues, software updates, or recalibration needs, contributing to sustained compliance and patient safety.
In conclusion, sourcing a transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) meter is a valuable investment for healthcare facilities aiming to improve neonatal care, particularly in the early detection and management of neonatal jaundice. These non-invasive devices offer a safe, quick, and painless alternative to blood sampling, enhancing patient comfort and allowing for frequent monitoring without the risks associated with repeated blood draws. When sourcing a TcB meter, it is essential to evaluate factors such as accuracy, ease of use, device reliability, compatibility with different skin tones, availability of technical support, and cost-effectiveness. Choosing a well-validated and clinically proven device—preferably one approved by regulatory bodies such as the FDA or CE-marked—ensures dependable results and improved clinical outcomes. Ultimately, integrating a high-quality transcutaneous bilirubin meter into routine neonatal assessments supports timely interventions, reduces unnecessary laboratory testing, and contributes to more efficient and patient-centered care.