The global tractor market has experienced steady growth over the past decade, driven by rising agricultural mechanization, increasing demand for precision farming, and government support for modern agricultural technologies. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global tractor market was valued at approximately USD 44.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.2% from 2024 to 2029. A significant contributor to this growth is the rising adoption of enclosed cab tractors, which offer enhanced operator comfort, improved safety, and better performance in extreme weather conditions—making them increasingly popular among commercial and large-scale farmers.
As farm operations become more sophisticated, the demand for high-horsepower tractors equipped with advanced cab features—such as climate control, noise insulation, and ergonomic designs—has surged. Grand View Research reports that the high-horsepower tractor segment (above 75 HP) held a dominant market share in 2023, reflecting the industry’s shift toward more powerful and comfortable machinery. This trend has spurred innovation and competition among manufacturers, positioning cab tractors as a critical segment in agricultural equipment.
In this evolving landscape, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in the design, production, and innovation of tractor cabs—combining engineering excellence with user-centric features. Based on market presence, product range, technological advancements, and global reach, the following list highlights the top 10 tractor cab manufacturers shaping the future of modern agriculture.
Top 10 Tractor Cab Tractors Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
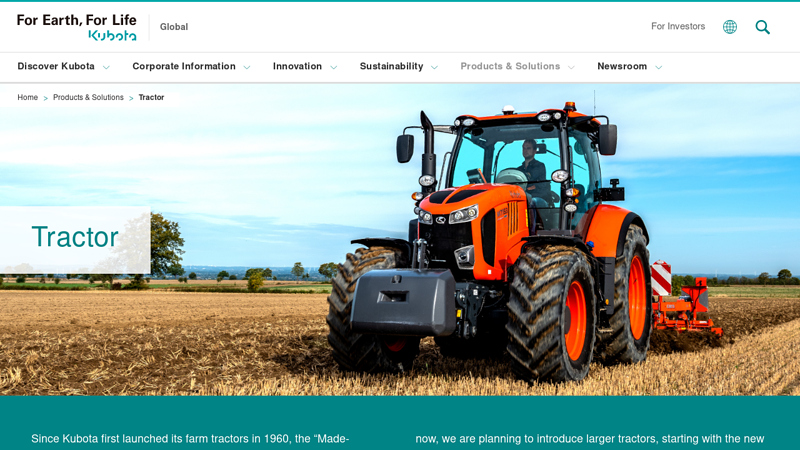
#1 Tractor
Domain Est. 1997
Website: kubota.com
Key Highlights: Kubota offers a full lineup of tractors. Our compact utility tractors, used in domestic, agricultural, and industrial settings, excel in power, performance and ……
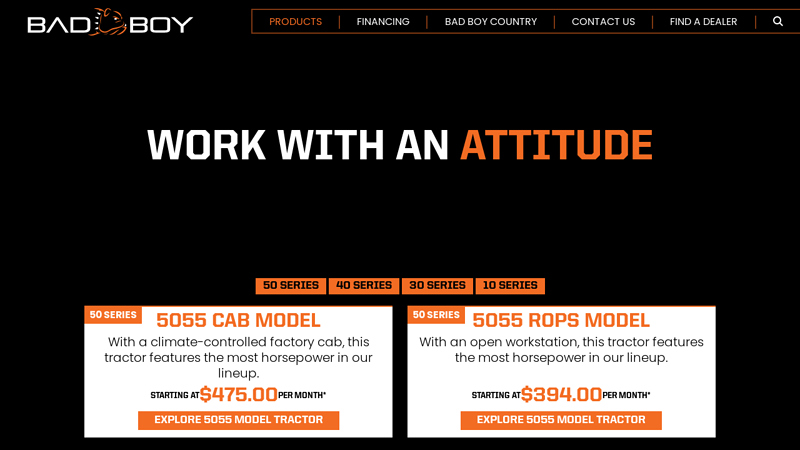
#2 Sub
Domain Est. 2016
Website: badboycountry.com
Key Highlights: The 5045 Cab Tractor takes power, performance, and attitude to the next level with a climate-controlled factory cab. Starting At$448.00Per Month*. Explore 5045 ……
#3 TYM tractors
Website: tym.world
Key Highlights: TYM tractors are made to tackle your unique needs and bring your vision to life. They enhance efficiency with advanced technology and superior quality….
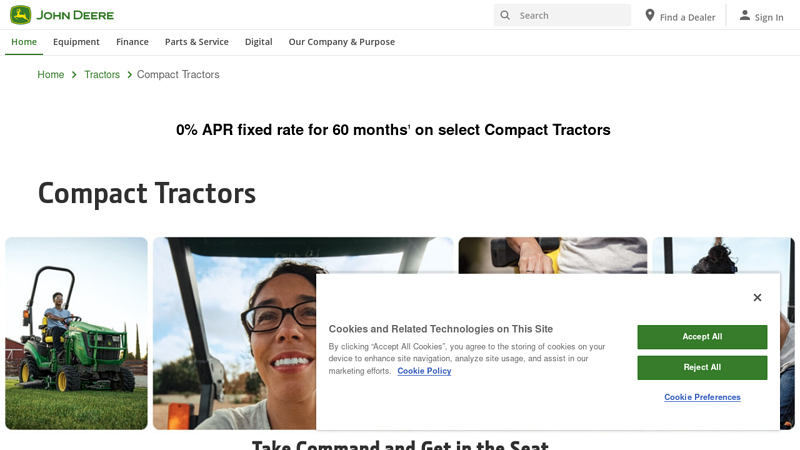
#4 Compact Tractors
Domain Est. 1990
Website: deere.com
Key Highlights: 1-4 Series Compact Utility Tractor. With plenty of raw power and easy-to-use implements, there is no job too ambitious to tackle for these mighty machines….
#5 Tractors
Domain Est. 1995
Website: caseih.com
Key Highlights: Explore Case IH range of tractors, from 25 HP to 725 HP, built for reliability, power, and performance. Perfect for all farming needs, from utility to ……
#6 Massey Ferguson United States
Domain Est. 1996
Website: masseyferguson.com
Key Highlights: Tractors. Massey Ferguson tractors deliver the power, comfort and reliability farmers expect—without the complexity they don’t. From sub-compact to high- ……
#7 Tractors (Compact, Sub
Domain Est. 1997
Website: bobcat.com
Key Highlights: Transform your property with versatility and performance with Bobcat compact, sub-compact, and articulating tractors. Explore models, specs, pricing and ……
#8 Cahaba Tractor Company
Domain Est. 2000
Website: cahabatractor.com
Key Highlights: Cahaba Tractor Company is a full-service dealership offering equipment, parts, service, and more. Visit our site to learn about our current specials and ……
#9 Original Tractor Cabs for All Other Brands
Domain Est. 2000
Website: originalcab.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsHere you will find only the best collection of parts from numerous brands, including but not limited to Ariens, Exmark, Hustler, MTD, Bad Boy, Grasshopper, ……
#10 Sub
Domain Est. 2014
Website: kubotausa.com
Key Highlights: Learn more about the full line of Kubota tractors – Subcompact (BX Series), Compact Tractors, Specialty & Utility Tractors, the M7 Ag Tractor & our TLB Series….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tractor Cab Tractors

H2: 2026 Market Trends for Tractor Cab Tractors
As we approach 2026, the global market for tractor cab tractors is undergoing a transformative shift driven by technological innovation, sustainability demands, and evolving agricultural practices. These shifts are reshaping the design, functionality, and adoption of cab-equipped tractors across developed and emerging markets alike.
1. Rising Demand for Operator Comfort and Safety
One of the most significant trends influencing the 2026 market is the increasing emphasis on operator comfort and safety. Modern farmers are spending longer hours in the field, prompting manufacturers to enhance cab ergonomics with features such as climate control, noise reduction, suspension seats, and intuitive control panels. Advanced safety systems—including rollover protection structures (ROPS), backup cameras, and collision avoidance—are becoming standard, especially in high-horsepower models.
2. Integration of Smart and Connected Technologies
The proliferation of smart agriculture is pushing tractor cab tractors toward full digital integration. By 2026, a majority of new cab tractors are expected to feature telematics, GPS guidance systems, and real-time data analytics displayed through in-cab touchscreens. Connectivity enables remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and seamless integration with farm management software, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
3. Electrification and Alternative Powertrains
Sustainability goals are accelerating the development of electric and hybrid cab tractors. While still a niche segment, battery-powered models from companies like John Deere, AGCO, and startups such as Monarch Tractor are gaining traction, particularly in Europe and North America. By 2026, stricter emissions regulations and government incentives are expected to boost the adoption of low-emission cabs, especially in regulated agricultural zones.
4. Automation and Autonomous Capabilities
Semi-autonomous and fully autonomous tractor systems are moving from prototype to commercial deployment. In 2026, many cab tractors will serve as both manned and remotely operated platforms, with features like auto-steer, implement control, and task sharing with drones or robotic units. The cab evolves into a command center, allowing farmers to oversee multiple operations simultaneously.
5. Regional Market Diversification
While North America and Europe lead in adopting high-tech cab tractors, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific (especially India and China) and Latin America are seeing increased demand for mid-range cabs with balanced cost and functionality. Government subsidies for mechanization and rising farm consolidation are driving this growth, with localized manufacturing helping reduce costs.
6. Focus on Durability and Serviceability
As farms operate under tighter margins, reliability and low maintenance costs are paramount. Manufacturers are designing cabs with modular components, easy access to filters and fluids, and corrosion-resistant materials. Enhanced service networks and over-the-air software updates are also improving long-term value.
Conclusion
By 2026, tractor cab tractors will be at the nexus of agricultural modernization—blending comfort, intelligence, and sustainability. The cab is no longer just a shelter but a high-tech control hub central to precision farming. As digital integration, automation, and green technologies mature, the global market for cab tractors is poised for sustained growth, innovation, and transformation.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing Tractor Cab Tractors (Quality, IP)
Sourcing tractor cab tractors—especially from international or non-OEM suppliers—presents several risks related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) infringement. Being aware of these pitfalls is essential to avoid costly delays, legal issues, and operational failures.
Quality Inconsistencies and Substandard Materials
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing tractor cabs is inconsistent build quality. Suppliers, particularly in low-cost manufacturing regions, may use inferior materials such as subpar steel, non-durable seals, or low-grade paint that chips or rusts prematurely. This compromises operator safety, cab longevity, and overall tractor performance. Additionally, poor welding, misaligned mounting points, or inadequate noise/vibration insulation can lead to premature failure and increased maintenance costs.
Lack of Compliance with Safety and Environmental Standards
Many sourced tractor cabs fail to meet recognized safety standards (e.g., ROPS – Roll-Over Protection Structures, FOPS – Falling Object Protection Structures) or regional emissions and noise regulations. Non-compliant cabs not only endanger operators but can also result in fines, import denials, or liability in the event of an accident. Always verify that the supplier provides certification from accredited testing bodies.
Intellectual Property (IP) Infringement Risks
Sourcing cabs that mimic OEM designs—especially those bearing logos, part numbers, or styling cues protected by trademarks or design patents—can expose buyers to IP litigation. Many third-party manufacturers produce “compatible” cabs that closely replicate proprietary designs from major brands (e.g., John Deere, Case IH, AGCO). Even if not branded, the design itself may be protected, leading to seizure of goods at customs or legal action from IP holders.
Inadequate Documentation and Traceability
Suppliers may fail to provide critical documentation such as material certifications, weld inspection reports, or compliance test results. Without proper traceability, it becomes difficult to ensure quality or defend against liability claims. This lack of transparency also complicates warranty claims and after-sales support.
Poor After-Sales Support and Spare Parts Availability
Tractor cabs often require maintenance or component replacements (e.g., windows, HVAC parts, seals). Sourcing from unreliable suppliers may result in long lead times for spare parts or complete lack of support. This leads to extended equipment downtime and increased total cost of ownership.
Misrepresentation of Compatibility and Fitment
Some suppliers claim universal compatibility or precise OEM fitment without rigorous testing. In reality, dimensional inaccuracies or interface mismatches can make installation difficult or impossible without costly modifications. Always request sample testing or third-party fitment verification before bulk ordering.
Conclusion
To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, require independent quality inspections, verify IP compliance, and insist on full technical documentation. Engaging legal counsel to review contracts and IP clearances is also recommended when sourcing tractor cab tractors.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tractor Cab Tractors
Tractor cab tractors—full-featured agricultural or industrial tractors equipped with enclosed operator cabs—are essential machinery in modern farming and construction. Transporting and operating these vehicles involves specific logistical planning and adherence to regulatory compliance standards. This guide outlines key considerations for safe, legal, and efficient handling of tractor cab tractors.
Transportation Logistics
Proper transportation ensures tractors arrive at their destination undamaged and on schedule. Due to their weight, size, and specialized nature, special handling is required.
Load Securing and Trailering
Use a lowboy or step-deck trailer with adequate weight capacity (typically 10–20+ tons depending on model). Secure the tractor with heavy-duty tie-down straps (minimum four, attached to certified anchor points on the frame). Chock the wheels and ensure stability during loading/unloading via ramps rated for the tractor’s gross vehicle weight.
Route Planning
Plan routes to avoid low bridges, narrow roads, and weight-restricted bridges. Check for overhead utility lines and road conditions. For oversized loads, obtain necessary permits and use escort vehicles if required by local regulations.
Operator and Equipment Preparation
Before transport, lower all hydraulics, disconnect PTO shafts, and engage the parking brake. Remove loose tools or accessories. Ensure lights and reflectors are functional if the tractor is driven on public roads during loading.
Regulatory Compliance
Operating and transporting tractor cab tractors must comply with national and regional regulations to ensure safety and legal adherence.
DOT and FMCSA Regulations (U.S.)
If transported across state lines, compliance with the Department of Transportation (DOT) and Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) is required. This includes commercial driver’s license (CDL) requirements for drivers, hours-of-service rules, vehicle inspection standards, and proper load documentation.
Oversize/Overweight Permits
Tractor cab tractors often exceed standard road dimensions or weight limits. Operators must obtain permits from state transportation departments specifying travel times, routes, and any required signage (e.g., “Oversize Load” banners).
Emissions and Environmental Standards
Ensure the tractor meets current emissions standards such as Tier 4 Final (U.S. EPA) or Stage V (EU). Keep maintenance records to prove compliance, especially for cross-border operations.
Workplace Safety (OSHA/MSHA)
When used on job sites or farms, tractors must comply with OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) or MSHA (Mine Safety and Health Administration) standards. This includes roll-over protective structures (ROPS), seat belts, fire extinguishers, and proper operator training.
Import/Export Requirements
For international movement, additional compliance layers apply.
Customs Documentation
Prepare a bill of lading, commercial invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin. Declare the correct HS code (e.g., 8701.90 for tractors) to determine tariffs and duties.
Certification and Homologation
Verify that the tractor meets destination country standards (e.g., CE marking in Europe, CCC in China). Some regions require type approval or on-site inspections before registration.
Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Measures
Agricultural tractors may be subject to cleaning and inspection to prevent the spread of soil, pests, or plant diseases. Provide proof of decontamination if required.
Maintenance and Recordkeeping
Ongoing compliance depends on proper maintenance and documentation.
Maintenance Logs
Keep detailed records of servicing, repairs, and safety inspections. This supports warranty claims and regulatory audits.
Operator Training Certification
Ensure all operators are trained and certified, especially when using specialized implements or working in hazardous environments.
Registration and Licensing
Keep the tractor registered with the appropriate state or national agency. Agricultural exemptions may apply, but rules vary by jurisdiction.
Conclusion
Efficient logistics and strict compliance are critical when managing tractor cab tractors. By following transportation best practices, adhering to regulatory standards, and maintaining accurate records, businesses can minimize risks, avoid fines, and ensure operational continuity. Always consult local authorities and legal experts when navigating cross-jurisdictional movements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Tractor Cabs and Tractors
Sourcing tractor cabs and tractors requires a strategic approach that balances cost, quality, durability, and long-term operational efficiency. After evaluating suppliers, product specifications, certifications, and market trends, it is evident that selecting the right sourcing partner is critical to ensuring reliable performance, operator safety, and compliance with industry standards.
Investing in high-quality tractor cabs with enhanced ergonomics, climate control, noise reduction, and safety features not only improves operator comfort but also contributes to increased productivity and reduced fatigue during extended use. When sourcing, prioritizing manufacturers or suppliers with proven track records, strong after-sales support, and adherence to international quality standards (such as ISO or CE) ensures long-term value and minimizes downtime.
Additionally, considering total cost of ownership—rather than initial purchase price—helps identify suppliers offering sustainable, fuel-efficient, and technologically advanced models. The integration of digital procurement platforms and global supply chain networks presents opportunities for cost savings and improved delivery timelines.
In conclusion, a well-structured sourcing strategy that emphasizes quality, reliability, supplier credibility, and lifecycle costs will lead to the acquisition of durable tractors and cabs that meet operational demands while supporting long-term agricultural or industrial productivity.