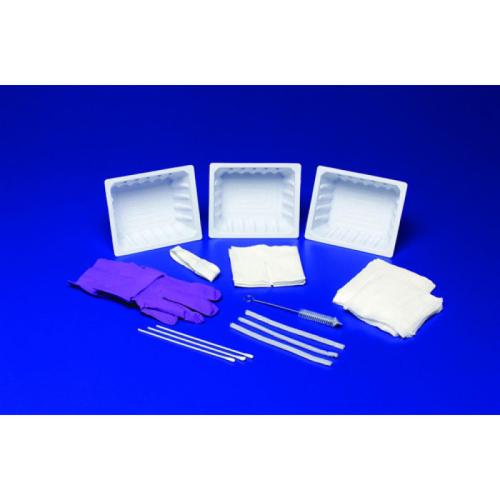
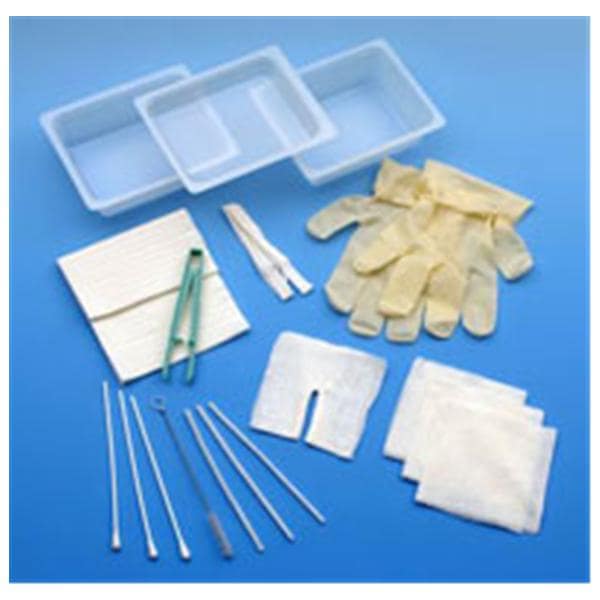
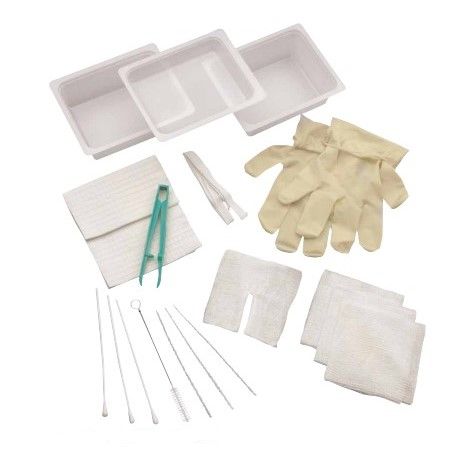
The global tracheostomy devices market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising incidences of respiratory disorders, increasing ICU admissions, and a growing demand for minimally invasive airway management solutions. According to Mordor Intelligence, the tracheostomy devices market was valued at USD 520 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. This expansion is further supported by advancements in tracheostomy tray designs, heightened focus on infection control, and the rising geriatric population requiring prolonged ventilatory support. As hospitals and ambulatory care centers prioritize efficiency and sterility, the demand for comprehensive, ready-to-use tracheostomy trays has intensified. In this evolving landscape, several manufacturers have emerged as key players, combining innovation, regulatory compliance, and clinical reliability. Based on market presence, product quality, and technological advancement, the following eight companies represent leading tracheostomy tray manufacturers shaping the standard of care worldwide.
Top 8 Tracheostomy Tray Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Kendall Healthcare Tracheostomy Care Tray, Standard, Sterile
Domain Est. 1995
Website: edgepark.com
Key Highlights: Kendall Healthcare Tracheostomy Care Tray, Standard, Sterile | Edgepark ; Item #6847835 ; Manufacturer: CARDINAL HEALTH-PR ; General Support; 1-800-321-0591 ……
#2 Argyle™ Tracheostomy Care Trays
Domain Est. 1996
Website: cardinalhealth.com
Key Highlights: Argyle™ tracheostomy trays provide exactly what is required for efficient and quick tracheostomy care procedures….
#3 Tracheostomy
Domain Est. 1997
Website: icumed.com
Key Highlights: Enhance tracheostomy care with ICU Medical’s comprehensive range. Trust in our expertise for improved patient outcomes….
#4 Tracheostomy Clean and Care Trays
Domain Est. 1997
Website: amsino.com
Key Highlights: AMSure Tracheostomy Clean and Care Trays feature the necessary components to perform cleaning in and around the stoma….
#5 TC7470 Tracheostomy Tray
Domain Est. 2005
Website: henryscheindental.com
Key Highlights: Shop Henry Schein Medical for TC7470 Tracheostomy Tray. Browse our full selection of products and order online….
#6 BOENMED® Tracheostomy Care Tray
Domain Est. 2006
Website: boenmedical.com
Key Highlights: Tracheostomy Care Tray Components: 1 Three Compartment Tray, 1 Trach Brush, 1 Trach Gauze 4″ x 4″, 3 Pipe Cleaners, 1 Trach Tie, 4 Gauze Sponge 4″ x 4″….
#7 Trach Care
Domain Est. 2008
Website: lslhealthcare.com
Key Highlights: Trach Care And Clean Set. The lidded Trach Care and Clean Set is an essential, sterile kit designed to simplify tracheostomy care….
#8 Tracheostomy care kit with Simulated Tray
Domain Est. 2013
Website: pristine-medical.com
Key Highlights: In stock 4–10 day deliveryTracheostomy care kit designed for medical training. Includes gloves, forceps, gauze, a simulated tracheostomy tray, and more for hands-on practice….
Expert Sourcing Insights for Tracheostomy Tray
H2: Projected 2026 Market Trends for Tracheostomy Trays
The global tracheostomy tray market is poised for steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand for critical care interventions, rising incidence of respiratory diseases, and advancements in surgical and emergency care. Key trends shaping the market include technological innovation, expansion of healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies, and the growing prevalence of conditions requiring airway management, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), sleep apnea, and trauma-related injuries.
One significant trend is the integration of single-use, sterile, and pre-packaged tracheostomy trays in hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers. These disposable kits reduce the risk of infection, ensure procedural consistency, and align with global infection control protocols—especially in the post-pandemic healthcare landscape. Manufacturers are focusing on ergonomic designs, improved instrument quality, and sterilization standards to meet stringent regulatory requirements in North America and Europe.
Additionally, the shift toward minimally invasive percutaneous tracheostomy techniques is fueling demand for specialized trays compatible with bronchoscopic and ultrasound-guided procedures. This trend is supported by growing adoption in intensive care units (ICUs), where bedside tracheostomies reduce patient transfer risks and hospital stays.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the highest growth rate by 2026 due to expanding healthcare access, rising medical tourism, and increasing government investments in emergency medical services. Meanwhile, North America will maintain a dominant market share, bolstered by advanced critical care facilities and high healthcare expenditure.
Finally, market consolidation and strategic partnerships among medical device manufacturers are anticipated to enhance product portfolios and distribution networks. Companies are also investing in training modules and clinical support to promote proper use of tracheostomy trays, further driving adoption.
In summary, the 2026 tracheostomy tray market will be characterized by innovation in design, increased demand in emerging markets, and a strong focus on safety and efficiency in airway management procedures.
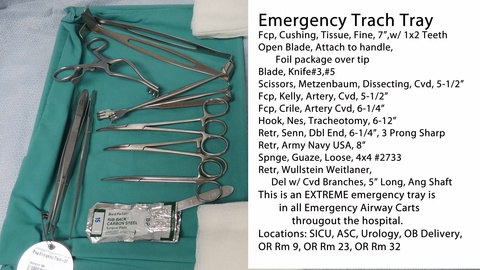
Common Pitfalls Sourcing Tracheostomy Trays: Quality and Intellectual Property Concerns
When sourcing tracheostomy trays—medical device kits used in emergency and surgical airway management—organizations must navigate several critical risks, particularly related to product quality and intellectual property (IP) violations. Failure to address these pitfalls can result in regulatory non-compliance, patient safety issues, and legal liabilities.
Poor Quality Control and Non-Compliance
One of the most significant risks in sourcing tracheostomy trays is receiving substandard products that do not meet medical-grade standards. Many suppliers, especially in low-cost manufacturing regions, may cut corners in material selection, sterilization processes, or manufacturing precision. Tracheostomy trays include critical components such as dilators, obturators, and tracheostomy tubes, where dimensional accuracy and biocompatibility are essential. Poor quality can lead to device failure, infection risks, or complications during insertion.
Additionally, sourced trays may not comply with regulatory requirements such as FDA 510(k) clearance, CE marking, or ISO 13485 certification. Using non-compliant devices exposes healthcare providers and distributors to regulatory enforcement actions, recalls, and liability in the event of patient harm.
Intellectual Property Infringement
Another major pitfall involves sourcing tracheostomy trays that infringe on existing intellectual property rights. Some third-party or “compatibility” kits are designed to mimic patented designs from established medical device manufacturers. While marketed as cost-effective alternatives, these products may violate design patents, utility patents, or trade dress protections.
Purchasing or distributing such IP-infringing devices can expose buyers and importers to legal action, including cease-and-desist orders, financial damages, and seizure of goods by customs authorities. Even if the infringement is unintentional, ignorance is typically not a legal defense in IP matters. This is especially relevant when sourcing from regions with weaker IP enforcement, where counterfeit or cloned medical devices are more prevalent.
Lack of Traceability and Documentation
Sourcing from unreliable suppliers often results in inadequate documentation, including missing or falsified certificates of conformity, sterilization reports, or material traceability records. This lack of transparency makes it difficult to verify product authenticity, validate quality management systems, or conduct effective vendor audits.
Without proper documentation, healthcare institutions and distributors cannot ensure compliance with medical device regulations or defend against liability claims. It also complicates incident investigations and recall management if a device-related adverse event occurs.
Mitigation Strategies
To avoid these pitfalls, organizations should:
– Conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers, including on-site audits and verification of regulatory certifications.
– Require full traceability documentation and batch-specific quality records.
– Consult legal counsel to assess IP risks when sourcing compatible or alternative tracheostomy kits.
– Prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in medical device manufacturing and compliance.
By addressing quality and IP concerns proactively, stakeholders can ensure the safe, legal, and reliable sourcing of tracheostomy trays.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for Tracheostomy Tray
Product Overview
A Tracheostomy Tray is a sterile, pre-packaged medical device kit containing essential instruments and components used during tracheostomy procedures—surgical or percutaneous—performed to establish an airway through the trachea. These trays are typically single-use and designed for immediate availability in emergency or operating room settings. Components commonly include a tracheostomy tube (with obturator and inner cannula), dilators, scalpel, forceps, suction catheters, gauze, and other ancillary items.
Regulatory Classification
Tracheostomy Trays are classified as medical devices under major regulatory frameworks:
– United States (FDA): Classified as Class II medical devices under 21 CFR 878.4700 (Tracheostomy Device). They require 510(k) premarket notification unless exempt.
– European Union (EU MDR): Classified as Class IIb under Regulation (EU) 2017/745. Requires conformity assessment by a Notified Body.
– Canada (Health Canada): Classified as Class II under the Medical Devices Regulations (SOR/98-282), requiring a Medical Device License (MDL).
– Other Regions: Local regulatory requirements apply (e.g., TGA in Australia, PMDA in Japan, ANVISA in Brazil).
Sterility and Packaging Requirements
- All Tracheostomy Trays must be terminally sterilized, typically using ethylene oxide (EtO) or gamma irradiation.
- Packaging must maintain sterility until point of use, utilizing ISO 11607-compliant materials (e.g., medical-grade pouches or rigid containers).
- Each tray must display:
- Sterile barrier system integrity indicators.
- Expiration date.
- Lot number.
- Sterilization method.
- Single-use label.
Labeling and Instructions for Use (IFU)
- Labeling must comply with relevant regulatory standards (e.g., FDA UDI requirements, EU MDR labeling rules).
- Each tray must include:
- Unique Device Identifier (UDI) in human- and machine-readable format.
- Clear instructions for use (IFU), including contraindications, warnings, precautions, and step-by-step procedural guidance.
- Manufacturer name, address, and contact information.
- Symbols per ISO 15223-1 (e.g., sterile, single-use, do not reuse).
- Language requirements: Local language(s) for target markets (e.g., EN/FR in Canada, DE in Germany).
Storage and Handling
- Store in a clean, dry environment with controlled temperature (typically 15–30°C) and low humidity.
- Avoid direct sunlight, heat sources, and physical compression.
- Do not store near volatile chemicals or sterilizing agents.
- Rotate inventory using FIFO (First In, First Out) method to prevent expiration.
- Inspect packaging for damage or breaches prior to use.
Transportation and Distribution
- Ship in temperature-controlled conditions if specified by the manufacturer.
- Use validated packaging to prevent physical damage during transit.
- Comply with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations if shipping sterilized devices treated with EtO (residual gas considerations).
- Maintain documentation for chain of custody and temperature monitoring where applicable.
- Distributors must be authorized and comply with local medical device distribution laws.
Import/Export Compliance
- Ensure all necessary regulatory approvals are in place before importing/exporting:
- FDA registration and listing (for U.S. import).
- CE Certificate of Conformity (for EU).
- Import licenses from local health authorities (e.g., Health Canada, TGA).
- Accompany shipments with accurate Harmonized System (HS) codes and commercial invoices.
- Declare devices properly to avoid customs delays; tracheostomy trays typically fall under HS Code 9018.90 (Other medical instruments).
- Maintain records of export documentation for audit purposes.
Post-Market Surveillance and Vigilance Reporting
- Implement a post-market surveillance (PMS) system per FDA 21 CFR Part 803 (MDR reporting) and EU MDR Article 83–86.
- Report adverse events, device malfunctions, or suspected product defects to relevant authorities within required timelines:
- FDA: Within 30 calendar days (initial report).
- EU: Within 15 days for serious incidents.
- Maintain a U.S. Agent if marketing in the U.S. as a foreign manufacturer.
- Conduct periodic safety update reports (PSURs) for EU Class IIb devices.
Quality Management System (QMS)
- Manufacturers must maintain a QMS compliant with:
- ISO 13485:2016 (Medical devices – Quality management systems).
- FDA Quality System Regulation (21 CFR Part 820).
- QMS must cover design controls, risk management (per ISO 14971), supplier controls, and corrective and preventive actions (CAPA).
- Regular audits and management reviews are required.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
- Tracheostomy Trays are single-use and must be disposed of as medical waste after use.
- Follow local biohazard waste regulations (e.g., EPA, OSHA in the U.S., EU directives on waste).
- Do not incinerate PVC-containing components unless using controlled medical waste incinerators.
- Unused expired devices should be returned to the manufacturer or disposed of per medical device take-back programs.
Training and Clinical Support
- Provide healthcare professionals with training materials or in-service sessions on proper tray use.
- Offer clinical support hotlines for technical or procedural inquiries.
- Ensure IFUs are accessible in digital and printed formats.
Key Compliance Contacts
- Regulatory Affairs: Responsible for submissions, approvals, and ongoing compliance.
- Quality Assurance: Manages audits, non-conformances, and CAPA.
- Customer Support: Handles complaints and field safety notices.
- Distribution Partner: Ensures logistics and local regulatory adherence.
This guide ensures safe, compliant handling of Tracheostomy Trays across the supply chain—from manufacturing to clinical use. Always consult specific regulatory authorities and internal SOPs for updated requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing Tracheostomy Tray
In conclusion, the sourcing of tracheostomy trays requires a comprehensive approach that balances clinical efficacy, patient safety, regulatory compliance, and cost-efficiency. It is essential to partner with reputable suppliers who adhere to medical device standards such as ISO 13485 and FDA/CE regulations to ensure product quality and sterility. Key considerations include tray completeness (containing all necessary instruments and components), material quality (stainless steel or single-use disposables), compatibility with clinical protocols, and timely availability to support emergency and routine procedures.
Additionally, input from interdisciplinary clinical teams—such as ICU staff, ENT specialists, and respiratory therapists—should inform procurement decisions to meet real-world use-case demands. Establishing strong supply chain resilience, including backup vendors and inventory management systems, minimizes disruptions in patient care. Ultimately, a well-sourced tracheostomy tray contributes significantly to improved procedural outcomes, reduced complication rates, and enhanced patient safety across healthcare settings.